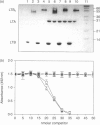
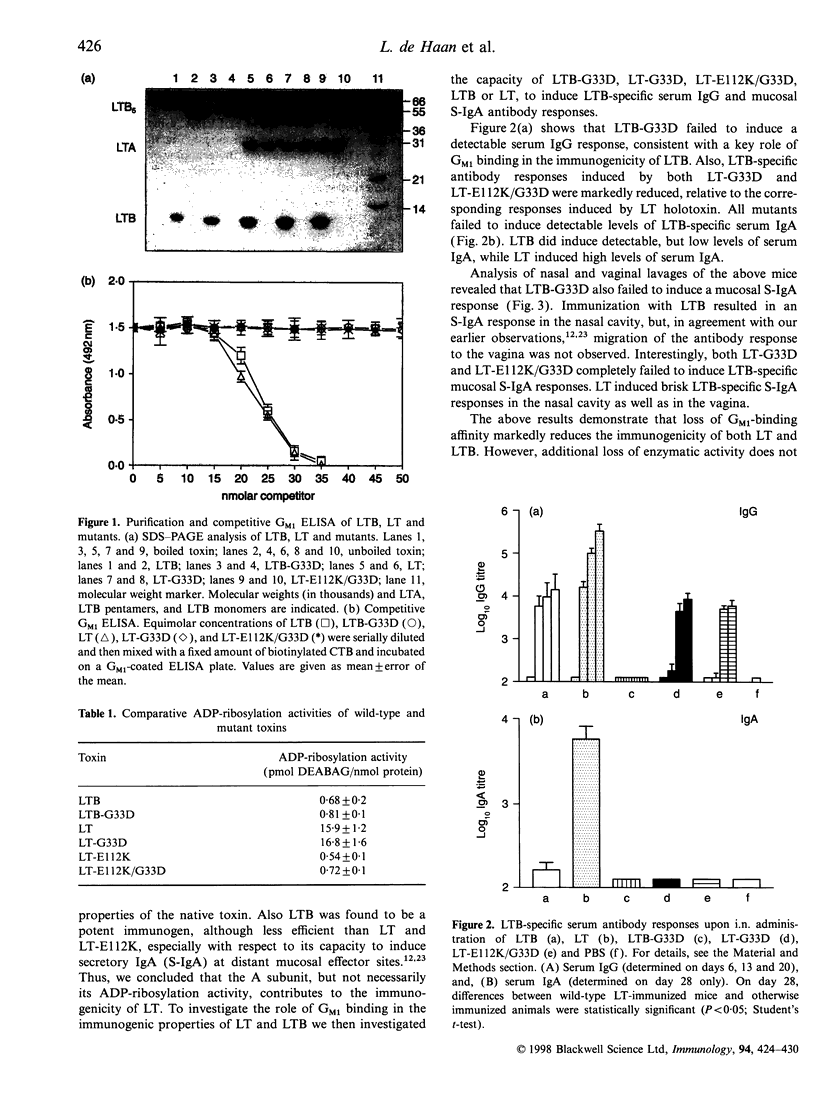
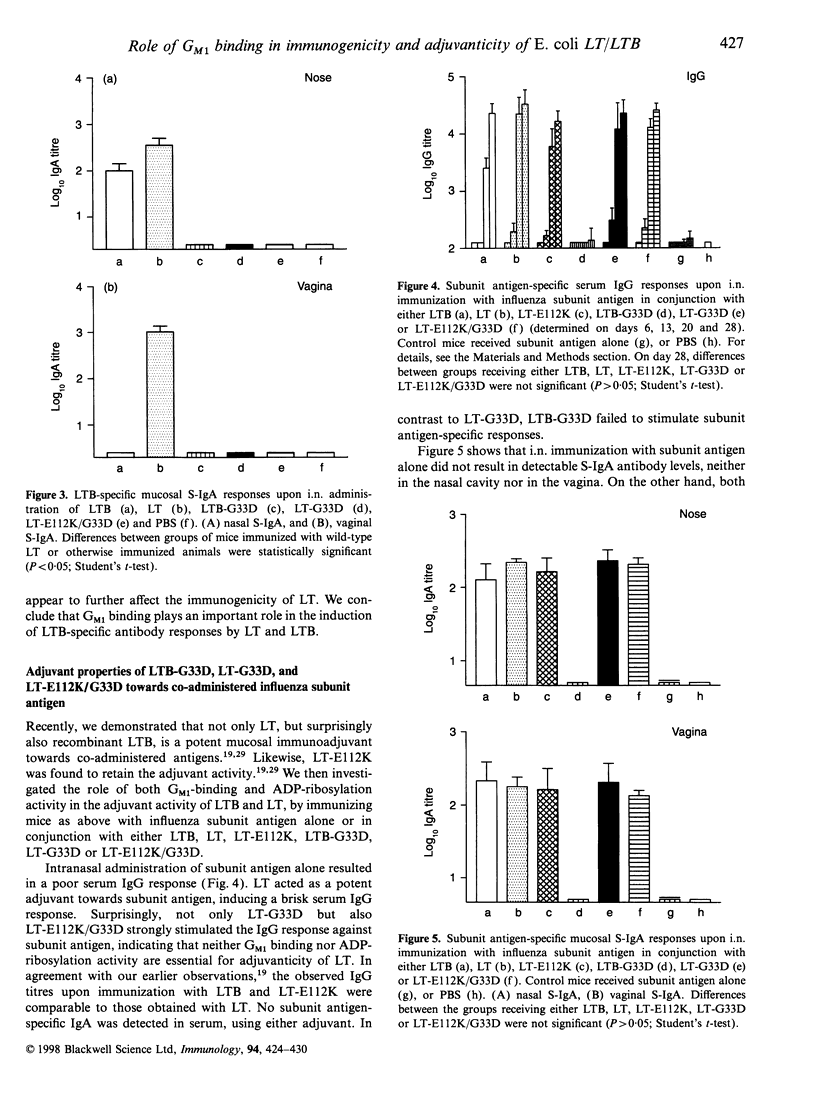
Abstract
Escherichia coli (E. coli) heat-labile toxin (LT) is a potent mucosal immunogen and immunoadjuvant towards co-administered antigens. LT is composed of one copy of the A subunit, which has ADP-ribosylation activity, and a homopentamer of B subunits, which has affinity for the toxin receptor, the ganglioside GM1. Both the ADP-ribosylation activity of LTA and GM1 binding of LTB have been proposed to be involved in immune stimulation. We investigated the roles of these activities in the immunogenicity of recombinant LT or LTB upon intranasal immunization of mice using LT/LTB mutants, lacking either ADP-ribosylation activity, GM1-binding affinity, or both. Likewise, the adjuvant properties of these LT/LTB variants towards influenza virus subunit antigen were investigated. With respect to the immunogenicity of LT and LTB, we found that GM1-binding activity is essential for effective induction of anti-LTB antibodies. On the other hand, an LT mutant lacking ADP-ribosylation activity retained the immunogenic properties of the native toxin, indicating that ADP ribosylation is not critically involved. Whereas adjuvanticity of LTB was found to be directly related to GM1-binding activity, adjuvanticity of LT was found to be independent of GM1-binding affinity. Moreover, a mutant lacking both GM1-binding and ADP-ribosylation activity, also retained adjuvanticity. These results demonstrate that neither ADP-ribosylation activity nor GM1 binding are essential for adjuvanticity of LT, and suggest an ADP-ribosylation-independent adjuvant effect of the A subunit.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clements J. D., Hartzog N. M., Lyon F. L. Adjuvant activity of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and effect on the induction of oral tolerance in mice to unrelated protein antigens. Vaccine. 1988 Jun;6(3):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(88)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dertzbaugh M. T., Elson C. O. Reduction in oral immunogenicity of cholera toxin B subunit by N-terminal peptide addition. Infect Immun. 1993 Feb;61(2):384–390. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.2.384-390.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Tommaso A., Saletti G., Pizza M., Rappuoli R., Dougan G., Abrignani S., Douce G., De Magistris M. T. Induction of antigen-specific antibodies in vaginal secretions by using a nontoxic mutant of heat-labile enterotoxin as a mucosal adjuvant. Infect Immun. 1996 Mar;64(3):974–979. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.3.974-979.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson B. L., Clements J. D. Dissociation of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin adjuvanticity from ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Infect Immun. 1995 May;63(5):1617–1623. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.5.1617-1623.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douce G., Turcotte C., Cropley I., Roberts M., Pizza M., Domenghini M., Rappuoli R., Dougan G. Mutants of Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin lacking ADP-ribosyltransferase activity act as nontoxic, mucosal adjuvants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1644–1648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Cholera toxin feeding did not induce oral tolerance in mice and abrogated oral tolerance to an unrelated protein antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):2892–2897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elson C. O., Ealding W. Generalized systemic and mucosal immunity in mice after mucosal stimulation with cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2736–2741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feil I. K., Reddy R., de Haan L., Merritt E. A., van den Akker F., Storm D. R., Hol W. G. Protein engineering studies of A-chain loop 47-56 of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin point to a prominent role of this loop for cytotoxicity. Mol Microbiol. 1996 May;20(4):823–832. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02520.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidry J. J., Cárdenas L., Cheng E., Clements J. D. Role of receptor binding in toxicity, immunogenicity, and adjuvanticity of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1997 Dec;65(12):4943–4950. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.12.4943-4950.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazama M., Mayumi-Aono A., Miyazaki T., Hinuma S., Fujisawa Y. Intranasal immunization against herpes simplex virus infection by using a recombinant glycoprotein D fused with immunomodulating proteins, the B subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and interleukin-2. Immunology. 1993 Apr;78(4):643–649. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Fredman P., Lindblad M., Svennerholm A. M., Svennerholm L. Rabbit intestinal glycoprotein receptor for Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin lacking affinity for cholera toxin. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):424–433. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.424-433.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobling M. G., Holmes R. K. Analysis of structure and function of the B subunit of cholera toxin by the use of site-directed mutagenesis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1755–1767. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Holmgren J. Strong adjuvant properties of cholera toxin on gut mucosal immune responses to orally presented antigens. Immunology. 1986 Oct;59(2):301–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke N., Tsuji T., Holmgren J. The adjuvant effect of Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxins is linked to their ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Sep;22(9):2277–2281. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nashar T. O., Webb H. M., Eaglestone S., Williams N. A., Hirst T. R. Potent immunogenicity of the B subunits of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin: receptor binding is essential and induces differential modulation of lymphocyte subsets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jan 9;93(1):226–230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Fontana M. R., Giuliani M. M., Domenighini M., Magagnoli C., Giannelli V., Nucci D., Hol W., Manetti R., Rappuoli R. A genetically detoxified derivative of heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin induces neutralizing antibodies against the A subunit. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2147–2153. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears C. L., Kaper J. B. Enteric bacterial toxins: mechanisms of action and linkage to intestinal secretion. Microbiol Rev. 1996 Mar;60(1):167–215. doi: 10.1128/mr.60.1.167-215.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider D. P. The mucosal adjuvant activities of ADP-ribosylating bacterial enterotoxins. Crit Rev Immunol. 1995;15(3-4):317–348. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v15.i3-4.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman G., Narayanan J., Martin B. L., Graves D. J. Use of substituted (benzylidineamino)guanidines in the study of guanidino group specific ADP-ribosyltransferase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 15;25(14):4113–4119. doi: 10.1021/bi00362a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spangler B. D. Structure and function of cholera toxin and the related Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):622–647. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.622-647.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Asanuma H., Tomita T., Komase K., Kawahara K., Danbara H., Hattori N., Watanabe K., Suzuki Y., Nagamine T. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunits supplemented with a trace amount of the holotoxin as an adjuvant for nasal influenza vaccine. Vaccine. 1994 Sep;12(12):1083–1089. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(94)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Yamanaka A., Shimohara M., Tomita T., Komase K., Tsuda Y., Suzuki Y., Nagamine T., Kawahara K., Danbara H. Synergistic action of cholera toxin B subunit (and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin B subunit) and a trace amount of cholera whole toxin as an adjuvant for nasal influenza vaccine. Vaccine. 1994 Apr;12(5):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(94)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teneberg S., Hirst T. R., Angström J., Karlsson K. A. Comparison of the glycolipid-binding specificities of cholera toxin and porcine Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin: identification of a receptor-active non-ganglioside glycolipid for the heat-labile toxin in infant rabbit small intestine. Glycoconj J. 1994 Dec;11(6):533–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00731304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tochikubo K., Isaka M., Yasuda Y., Kozuka S., Matano K., Miura Y., Taniguchi T. Recombinant cholera toxin B subunit acts as an adjuvant for the mucosal and systemic responses of mice to mucosally co-administered bovine serum albumin. Vaccine. 1998 Jan-Feb;16(2-3):150–155. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(97)00194-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uesaka Y., Otsuka Y., Lin Z., Yamasaki S., Yamaoka J., Kurazono H., Takeda Y. Simple method of purification of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and cholera toxin using immobilized galactose. Microb Pathog. 1994 Jan;16(1):71–76. doi: 10.1006/mpat.1994.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadolas J., Davies J. K., Wright P. J., Strugnell R. A. Intranasal immunization with liposomes induces strong mucosal immune responses in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Apr;25(4):969–975. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Y., Russell M. W. Induction of mucosal and systemic immune responses by intranasal immunization using recombinant cholera toxin B subunit as an adjuvant. Vaccine. 1998 Jan-Feb;16(2-3):286–292. doi: 10.1016/s0264-410x(97)00168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Kiyono H., Yamamoto M., Imaoka K., Fujihashi K., Van Ginkel F. W., Noda M., Takeda Y., McGhee J. R. A nontoxic mutant of cholera toxin elicits Th2-type responses for enhanced mucosal immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 May 13;94(10):5267–5272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.10.5267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Takeda Y., Yamamoto M., Kurazono H., Imaoka K., Yamamoto M., Fujihashi K., Noda M., Kiyono H., McGhee J. R. Mutants in the ADP-ribosyltransferase cleft of cholera toxin lack diarrheagenicity but retain adjuvanticity. J Exp Med. 1997 Apr 7;185(7):1203–1210. doi: 10.1084/jem.185.7.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haan L., Holtrop M., Verweij W. R., Agsteribbe E., Wilschut J. Mucosal immunogenicity of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin: role of the A subunit. Vaccine. 1996 Mar;14(4):260–266. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(95)00235-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Haan L., Verweij W. R., Feil I. K., Lijnema T. H., Hol W. G., Agsteribbe E., Wilschut J. Mutants of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin with reduced ADP-ribosylation activity or no activity retain the immunogenic properties of the native holotoxin. Infect Immun. 1996 Dec;64(12):5413–5416. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.12.5413-5416.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]