Abstract
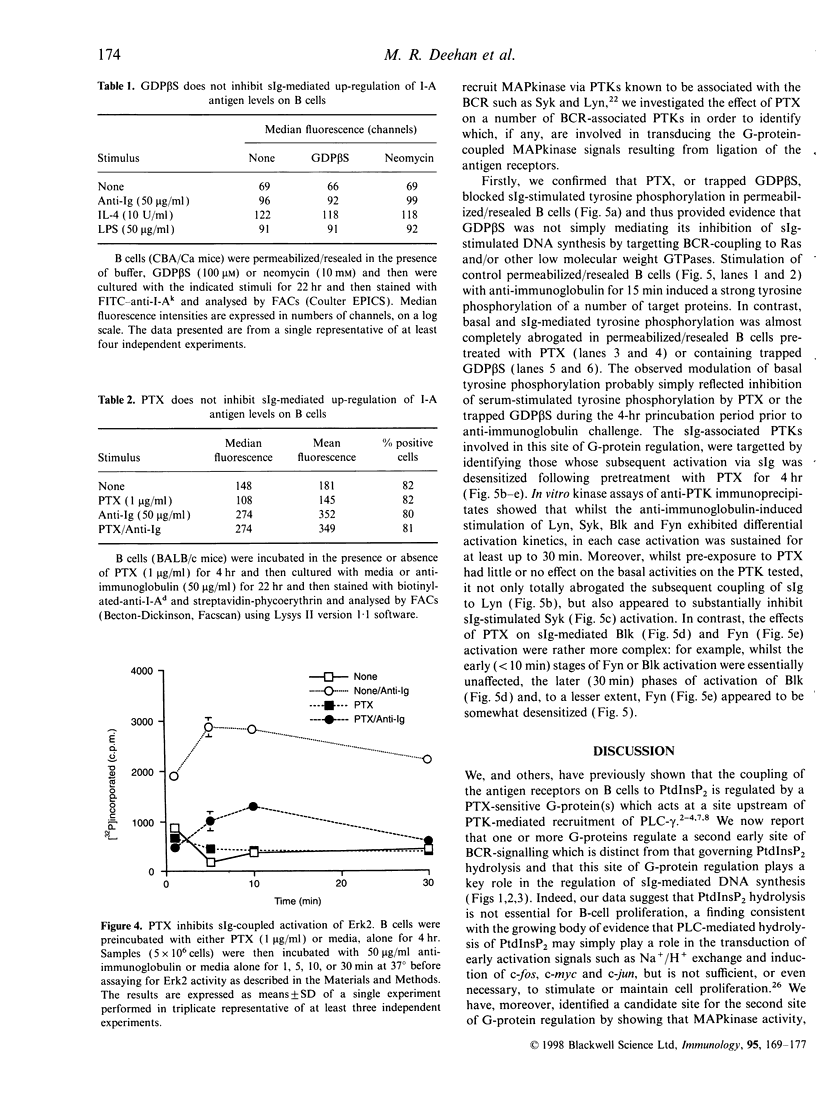
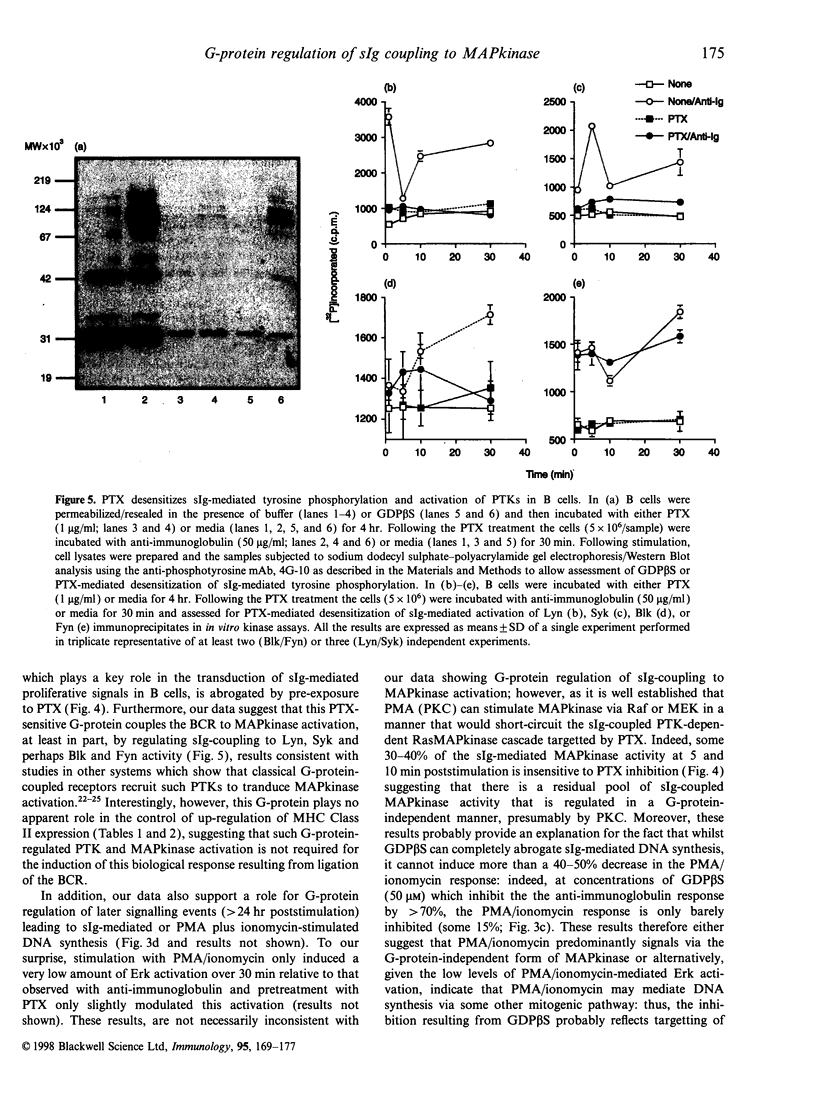
Ligation of the antigen receptors on B cells transduces transmembrane signals leading to the induction of DNA synthesis. We now show that a pertussis toxin-sensitive heterotrimeric G-protein(s) of the Gi class plays a key role in the regulation of surface immunoglobulin (sIg)-mediated DNA synthesis in B cells. This site of G-protein regulation is distinct from that we have previously reported to govern the coupling of the antigen receptors on B cells to the phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate. We have, moreover, identified a candidate target for this new G-protein regulation by showing that mitogen-activating protein kinase (MAPkinase) activity, which plays a key role in the transduction of sIg-mediated proliferative signals in B cells, is abrogated by pre-exposure to pertussis toxin that covalently modifies and inactivates heterotrimeric G-proteins of the Gi class. Furthermore, our data suggest that this pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein couples the antigen receptors to MAPkinase activation, at least in part, by regulating sIg-coupling to Lyn, Syk and perhaps Blk and Fyn activity, results consistent with studies in other systems which show that classical G-protein-coupled receptors recruit such protein tyrosine kinases to tranduce MAPkinase activation. Interestingly, however, this G-protein plays no apparent role in the control of up-regulation of major histocompatibility complex class II expression on B cells, suggesting that such G-protein-regulated-tyrosine kinase and MAPkinase activation is not required for the induction of this biological response following antigen receptor ligation.
Full text
PDF

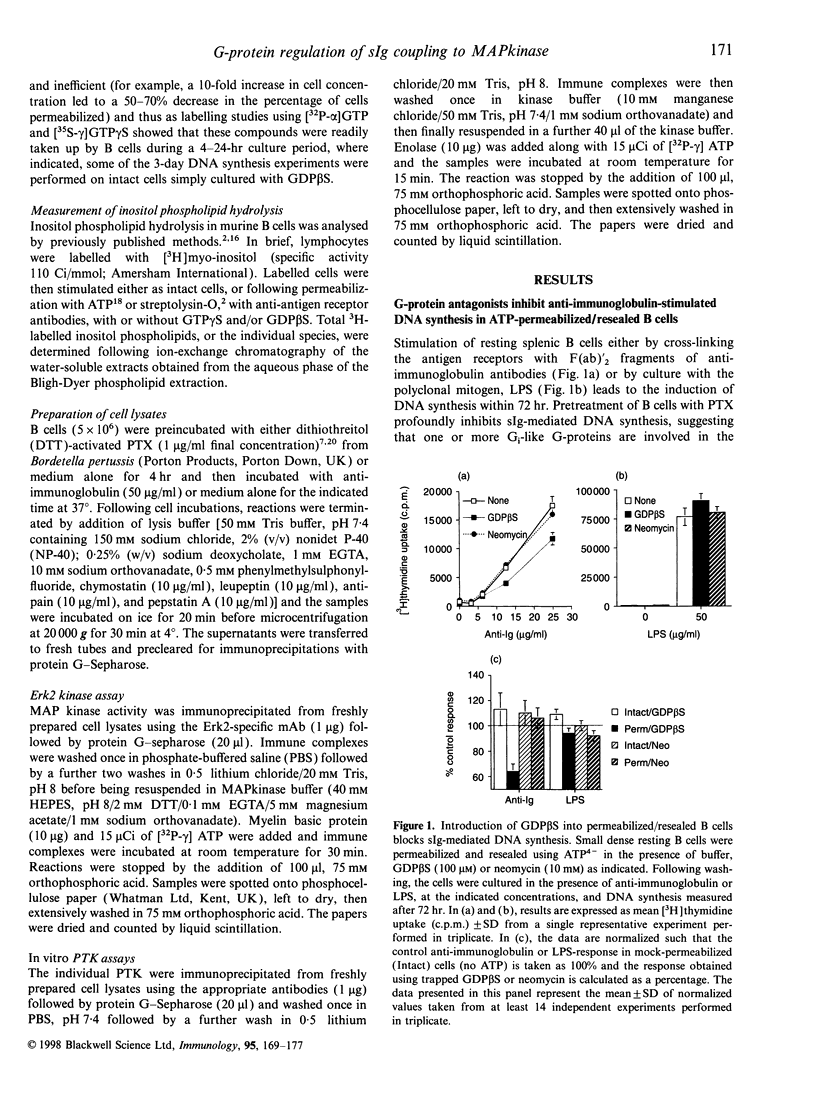
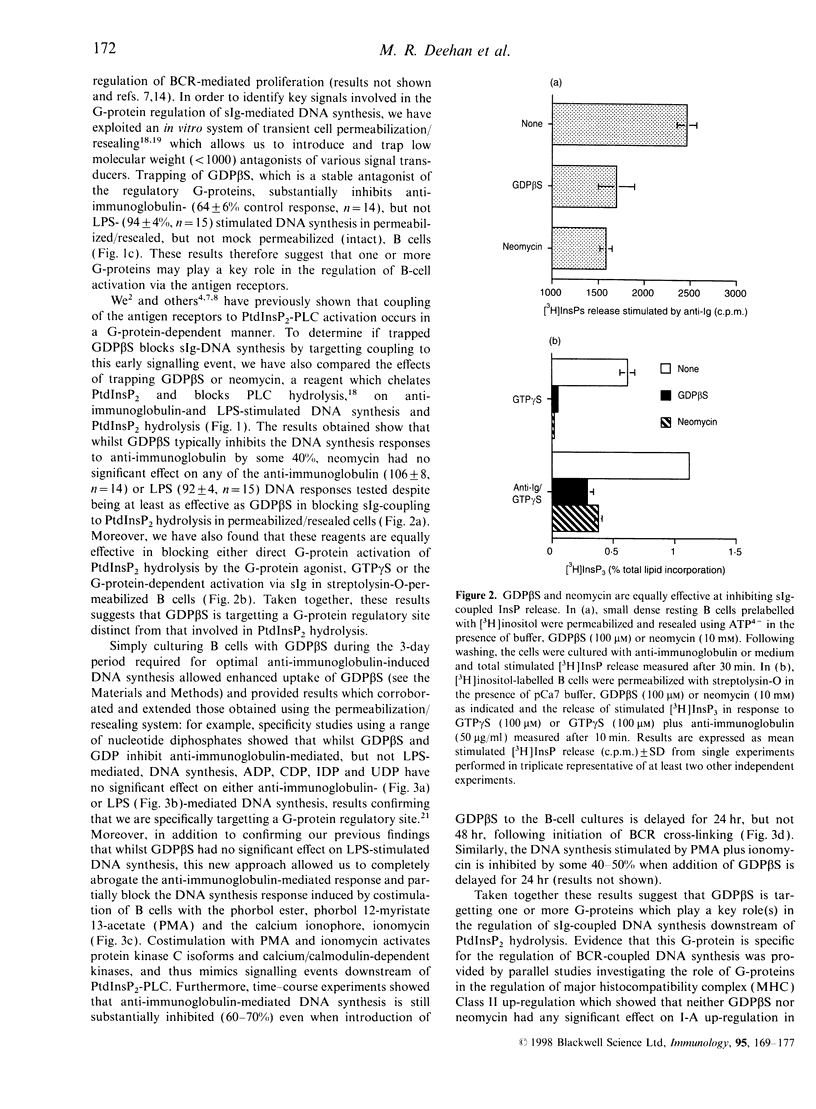
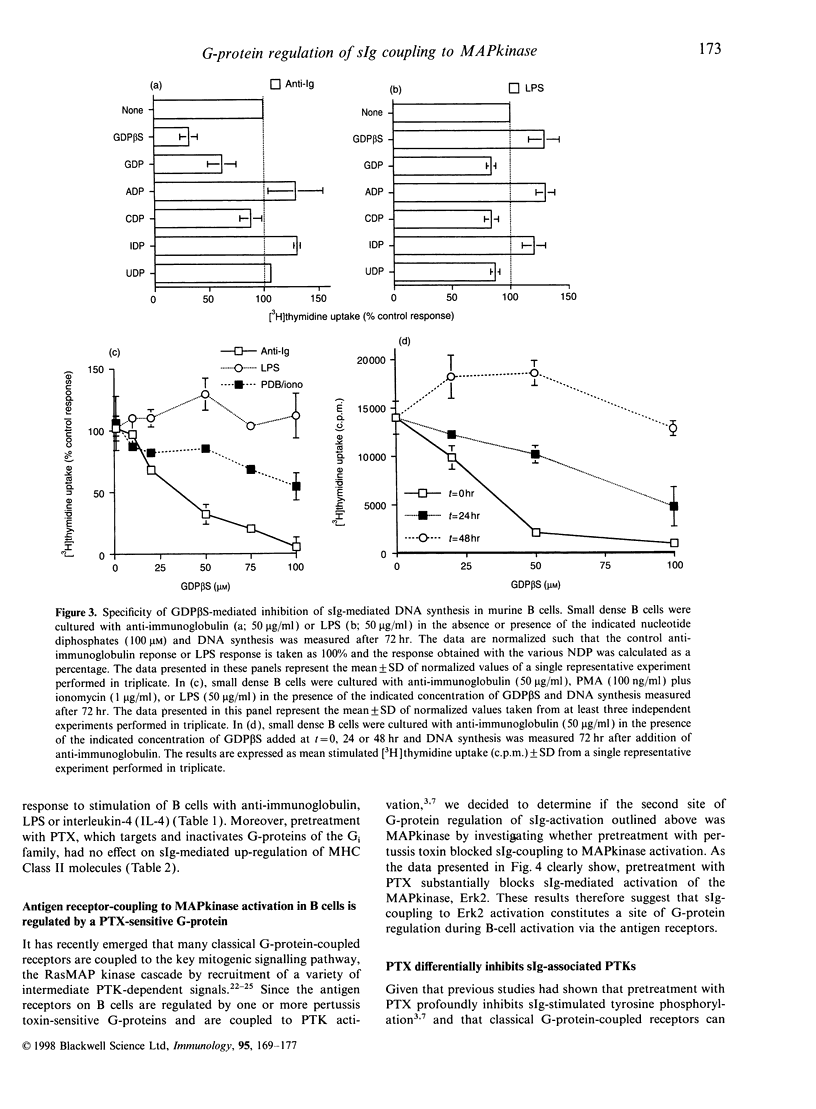


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrams C. S., Zhao W., Brass L. F. A site of interaction between pleckstrin's PH domains and G beta gamma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996 Dec 12;1314(3):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4889(96)00109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowman M. M., Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Differential control of azurophilic and specific granule exocytosis in Sendai-virus-permeabilized rabbit neutrophils. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:115–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blank J. A., Clark G. C., Wiegand G., Luster M. I. Pertussis toxin inhibition of anti-immunoglobulin-stimulated proliferation and inositol phosphate formation. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;106(2):278–286. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(90)90247-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Walker G., Huang H. S. Interactions between a lymphoma membrane-associated guanosine 5'-triphosphate-binding protein and the cytoskeleton during receptor patching and capping. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2242–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Pleiman C. M., Clark M. R. Signal transduction by the B cell antigen receptor and its coreceptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:457–486. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. Signal-transducing protein phosphorylation cascades mediated by Ras/Rho proteins in the mammalian cell: the potential for multiplex signalling. Biochem J. 1996 Sep 15;318(Pt 3):729–747. doi: 10.1042/bj3180729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikic I., Tokiwa G., Lev S., Courtneidge S. A., Schlessinger J. A role for Pyk2 and Src in linking G-protein-coupled receptors with MAP kinase activation. Nature. 1996 Oct 10;383(6600):547–550. doi: 10.1038/383547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Jakway J. P., DeFranco A. L. Involvement of a guanine-nucleotide-binding component in membrane IgM-stimulated phosphoinositide breakdown. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3604–3613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant K. R., Harnett W., Milligan G., Harnett M. M. Differential G-protein expression during B- and T-cell development. Immunology. 1997 Apr;90(4):564–571. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1997.00196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett M. M. Analysis of G-proteins regulating signal transduction pathways. Methods Mol Biol. 1994;27:199–211. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-250-7:199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett M. M., Klaus G. G. G protein coupling of antigen receptor-stimulated polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis in B cells. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):3135–3139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett M., Rigley K. The role of G-proteins versus protein tyrosine kinases in the regulation of lymphocyte activation. Immunol Today. 1992 Dec;13(12):482–486. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90022-Y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnett W., Harnett M. M. Inhibition of murine B cell proliferation and down-regulation of protein kinase C levels by a phosphorylcholine-containing filarial excretory-secretory product. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 1;151(9):4829–4837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Gilman A. G. G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90005-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hivroz C., Gény B., Brouet J. C., Grillot-Courvalin C. Altered signal transduction secondary to surface IgM cross-linking on B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Differential activation of the phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 15;144(6):2351–2358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justement L. B., Campbell K. S., Chien N. C., Cambier J. C. Regulation of B cell antigen receptor signal transduction and phosphorylation by CD45. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1839–1842. doi: 10.1126/science.1648262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., O'Garra A., Bijsterbosch M. K., Holman M. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. VIII. Induction of DNA synthesis in B cells by a combination of calcium ionophores and phorbol myristate acetate. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Jan;16(1):92–97. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langhans-Rajasekaran S. A., Wan Y., Huang X. Y. Activation of Tsk and Btk tyrosine kinases by G protein beta gamma subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 12;92(19):8601–8605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.19.8601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus A. H., Kawauchi K., Rapoport M. J., Delovitch T. L. Antigen-induced B lymphocyte activation involves the p21ras and ras.GAP signaling pathway. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1765–1769. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang M. N., Garrison J. C. The epidermal growth factor receptor is coupled to a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide regulatory protein in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13342–13349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon S. B., Monroe J. G. Activation of the p21ras pathway couples antigen receptor stimulation to induction of the primary response gene egr-1 in B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):417–422. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamed I., Wang G., Roifman C. M. Antigen receptor-mediated protein tyrosine kinase activity is regulated by a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):169–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. G., Haldar S. Involvement of a specific guanine nucleotide binding protein in receptor immunoglobulin stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Oct 9;1013(3):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Wieland D., White M. F., Behnke B., Gebhardt A., Neumann S., Krone W., Kahn C. R. Pertussis toxin inhibits autophosphorylation and activation of the insulin receptor kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1479–1485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92106-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Takata M., Yamamura H., Kurosaki T. Tyrosine phosphorylation of Shc is mediated through Lyn and Syk in B cell receptor signaling. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 24;270(12):6824–6829. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.12.6824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T., Katada T., Murayama Y., Ui M., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. A simple structure encodes G protein-activating function of the IGF-II/mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):709–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90116-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pleiman C. M., Clark M. R., Gauen L. K., Winitz S., Coggeshall K. M., Johnson G. L., Shaw A. S., Cambier J. C. Mapping of sites on the Src family protein tyrosine kinases p55blk, p59fyn, and p56lyn which interact with the effector molecules phospholipase C-gamma 2, microtubule-associated protein kinase, GTPase-activating protein, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5877–5887. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Viciana P., Warne P. H., Dhand R., Vanhaesebroeck B., Gout I., Fry M. J., Waterfield M. D., Downward J. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase as a direct target of Ras. Nature. 1994 Aug 18;370(6490):527–532. doi: 10.1038/370527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. I., Strathmann M. P., Gautam N. Diversity of G proteins in signal transduction. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):802–808. doi: 10.1126/science.1902986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata M., Kurosaki T. A role for Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cell antigen receptor-mediated activation of phospholipase C-gamma 2. J Exp Med. 1996 Jul 1;184(1):31–40. doi: 10.1084/jem.184.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tordai A., Franklin R. A., Patel H., Gardner A. M., Johnson G. L., Gelfand E. W. Cross-linking of surface IgM stimulates the Ras/Raf-1/MEK/MAPK cascade in human B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7538–7543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada S., Simon M. I., Witte O. N., Katz A. Binding of beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins to the PH domain of Bruton tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11256–11260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]