Abstract
In the rabbit, recent investigations have provided evidence that gene conversion leads to the generation of diversity of heavy chain rearranged VH-DH-JH genes. No data have been published on a similar mechanism for rabbit light chains. In our laboratory, we initially infected rabbits with Trypanosoma brucei, which stimulates B-cell hyperplasia and hypergammaglobulinaemia. The heterozygous rabbits exhibited the Ckappa1 b4 and b9 kappa light chain allotypes. After reverse transcription of mRNA, and cloning and sequencing of cDNA, the Vkappa-Jkappa-Ckappa genes provided evidence for both somatic hypermutation and gene conversion. We saw that in each of the b4 and b9 kappa light chain cDNA, CDR1 and CDR3 carried both point mutation and provisional gene conversion traits. In the CDR2 region, point mutation and gene conversion inserts were observed in the b4 genes, with only gene conversion in two b9 genes. In the CDR regions, although some genes exhibited only somatic hypermutation or gene conversion, others showed linkage of both somatic hypermutation and gene conversion in the same sequence. This also marks the first time that somatic hypermutation and gene conversion in the same cloned CDR region has been observed in Vkappa1 genes; however, it has been seen earlier in rabbit heavy chain VH sequences. Furthermore, the addition of several codons to the CDR3 segment by gene conversion may have provided a mechanism for length variation. In addition, we demonstrated that Jkappa and framework region segments contained examples of somatic hypermutation. Confirmation of gene conversion necessitates that donor sequences be identified as providing the templated inserts. Thus after cloning two pseudogenes we found putative CDR3 donor segments for two CDR3 rearranged genes. The results offer additional mechanisms for the generation of diversity among rearranged rabbit kappa light chain genes. Whether there is a relationship or influence of gene conversion upon somatic hypermutation or vice versa is not discernable at present.
Full text
PDF

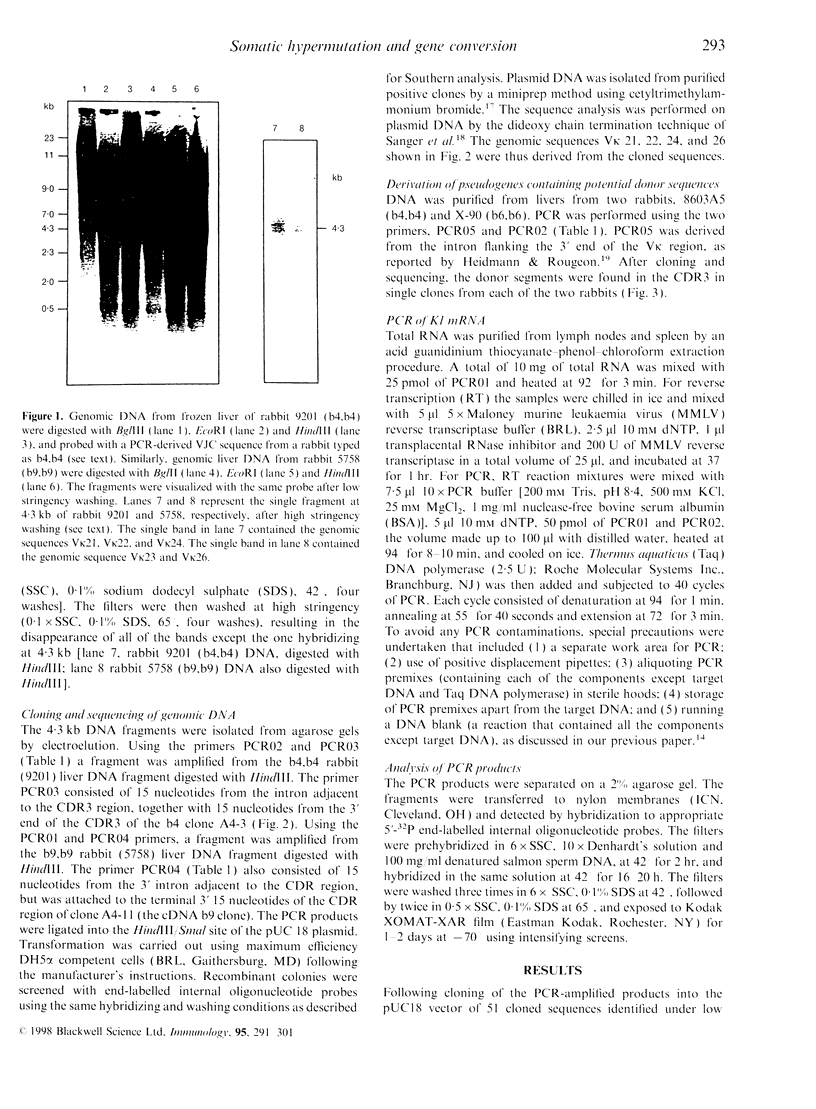
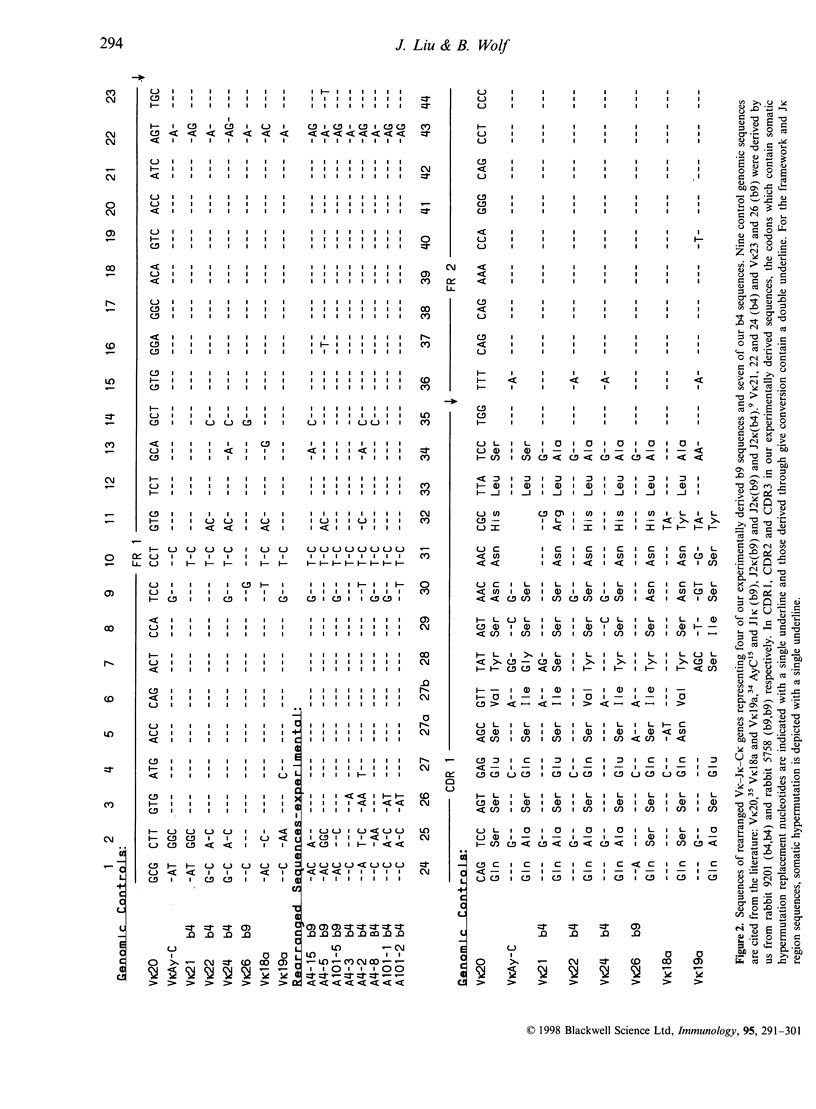


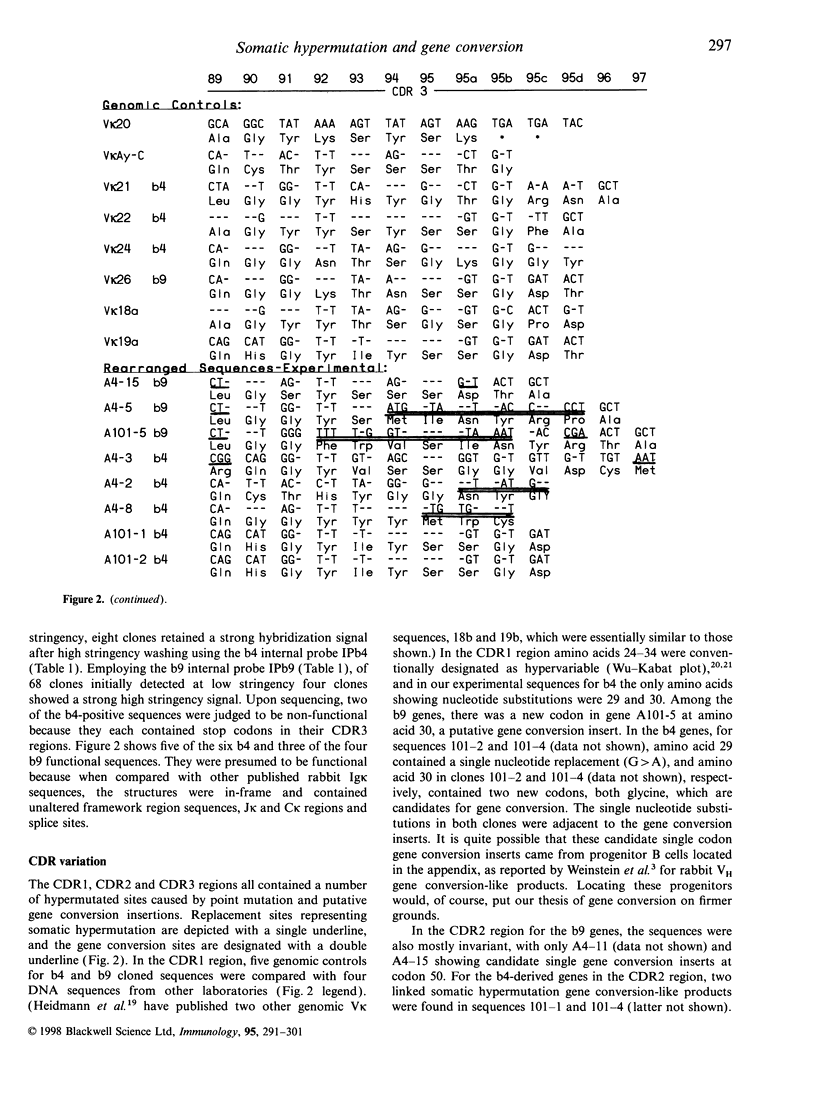
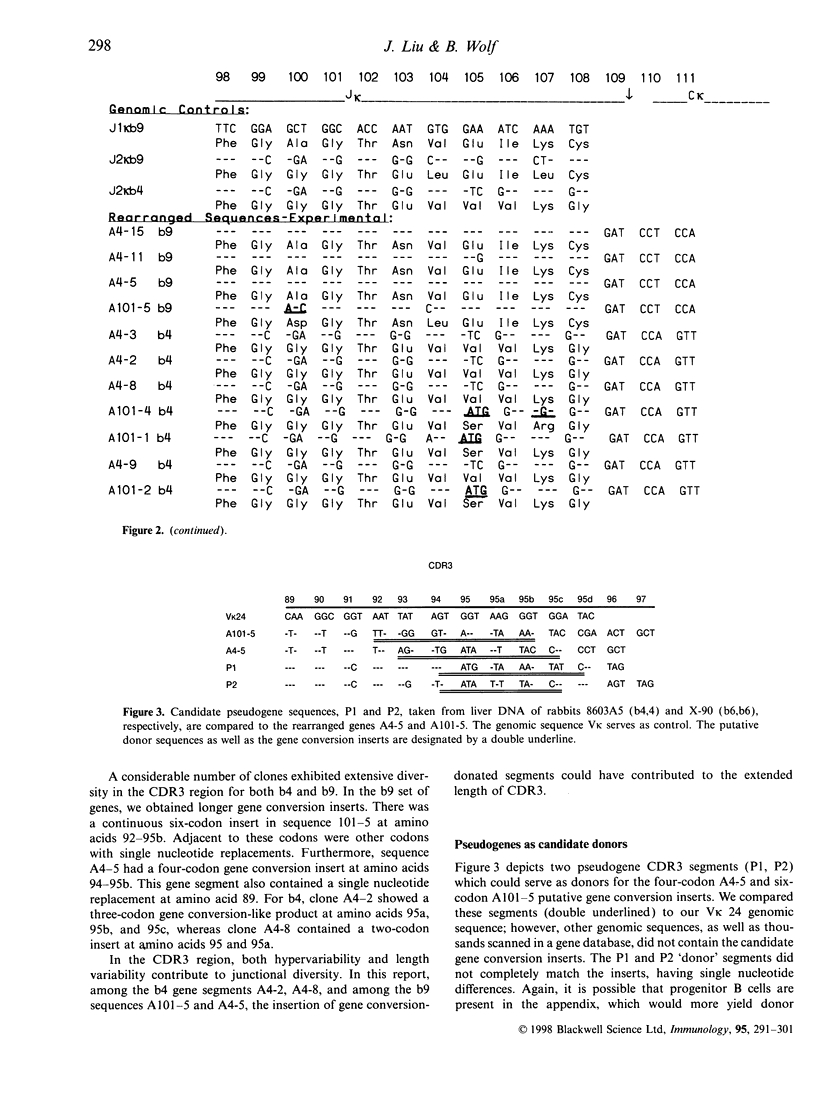



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimenko M. A., Mariamé B., Rougeon F. Evolution of the immunoglobulin kappa light chain locus in the rabbit: evidence for differential gene conversion events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5180–5183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allegrucci M., Young-Cooper G. O., Alexander C. B., Newman B. A., Mage R. G. Preferrential rearrangement in normal rabbits of the 3' VHa allotype gene that is deleted in Alicia mutants; somatic hypermutation/conversion may play a major role in generating the heterogeneity of rabbit heavy chain variable region sequences. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):411–417. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Gene conversion: some implications for immunoglobulin genes. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):592–594. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker R. S., Knight K. L. Somatic diversification of immunoglobulin heavy chain VDJ genes: evidence for somatic gene conversion in rabbits. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Rabbitts T. H. Evolution of immunoglobulin V genes: evidence indicating that recently duplicated human V kappa sequences have diverged by gene conversion. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90508-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berek C., Ziegner M. The maturation of the immune response. Immunol Today. 1993 Aug;14(8):400–404. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. M., McCormack W. T., Postema C. E., Humphries E. H., Thompson C. B. Templated insertions in the rearranged chicken IgL V gene segment arise by intrachromosomal gene conversion. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):536–547. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou C. T., Cinader B., Dubiski S. Unequal expression of allelic allotypic specificities in circulating immunoglobulins, experimentally-elicited antibodies, and receptor-carrying cells. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 30;11(1-3):304–313. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90029-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David V., Folk N. L., Maizels N. Germ line variable regions that match hypermutated sequences in genes encoding murine anti-hapten antibodies. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):799–811. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emorine L., Dreher K., Kindt T. J., Max E. E. Rabbit immunoglobulin kappa genes: structure of a germline b4 allotype J-C locus and evidence for several b4-related sequences in the rabbit genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5709–5713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esworthy S., Max E. E. The rabbit kappa 1 b5 immunoglobulin gene: another J region gene cluster with only one functional J gene segment? J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):1107–1111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S., Dono M., Wakai M., Allen S. L., Lichtman S. M., Schulman P., Vinciguerra V. P., Ferrarini M., Silver J., Chiorazzi N. Somatic diversification and selection of immunoglobulin heavy and light chain variable region genes in IgG+ CD5+ chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. J Exp Med. 1995 Apr 1;181(4):1507–1517. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.4.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann O., Rougeon F. Immunoglobulin kappa light-chain diversity in rabbit is based on the 3' length heterogeneity of germ-line variable genes. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):74–76. doi: 10.1038/311074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Wakiya M., Kawano-Nishi Y., Yi J., Sanokawa R., Taki S., Shimamura T., Kishimoto T., Tsurui H., Nishimura H. Somatic diversification and affinity maturation of IgM and IgG anti-DNA antibodies in murine lupus. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Nov;23(11):2813–2820. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishaq M., Wolf B., Dreher K. cDNA sequences encoding rabbit latent kappa 1 b5 and b6 Ig L chains. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3463–3467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishaq M., Wolf B., Ritter C. Large-scale isolation of plasmid DNA using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Biotechniques. 1990 Jul;9(1):19-20, 22, 24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., Becker R. S. Molecular basis of the allelic inheritance of rabbit immunoglobulin VH allotypes: implications for the generation of antibody diversity. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):963–970. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90344-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman R., Emorine L., Max E. E. Structure of a germline rabbit immunoglobulin V kappa-region gene: implications for rabbit V kappa-J kappa recombination. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2753–2756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage R. G., Pincus J. H., Alexander C., Freedman M. H. Studies of hyperimmune restricted and partially restricted anti-pneumococcal polysaccharide antibodies from allotype-defined pedigreed rabbits. II. Allotypes and idiotypes in sera and electrofocused fractions. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Aug;4(8):560–564. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830040808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels N. Somatic hypermutation: how many mechanisms diversify V region sequences? Cell. 1995 Oct 6;83(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90227-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila P., Korpela J., Tenkanen T., Pitkänen K. Fidelity of DNA synthesis by the Thermococcus litoralis DNA polymerase--an extremely heat stable enzyme with proofreading activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4967–4973. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack W. T., Tjoelker L. W., Barth C. F., Carlson L. M., Petryniak B., Humphries E. H., Thompson C. B. Selection for B cells with productive IgL gene rearrangements occurs in the bursa of Fabricius during chicken embryonic development. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):838–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J. T., Lewis S. M. P nucleotides in V(D)J recombination: a fine-structure analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1078–1092. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. A., Dykes D. D., Polesky H. F. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1215–1215. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parng C. L., Hansal S., Goldsby R. A., Osborne B. A. Gene conversion contributes to Ig light chain diversity in cattle. J Immunol. 1996 Dec 15;157(12):5478–5486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Anquez V., Grimal H., Weill J. C. A hyperconversion mechanism generates the chicken light chain preimmune repertoire. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock E. P., Sibbald P. R., Davis M. M., Chien Y. H. CDR3 length in antigen-specific immune receptors. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):323–328. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogerson B. J. Somatic hypermutation of VHS107 genes is not associated with gene conversion among family members. Int Immunol. 1995 Aug;7(8):1225–1235. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.8.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A., Melchers F. Molecular and cellular origins of B lymphocyte diversity. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1081–1094. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90032-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor K. D., Capra J. D. An apparently common mechanism of generating antibody diversity: length variation of the VL-JL junction. Mol Immunol. 1994 Jan;31(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. S., Berry J., Manser T., Claflin J. L. Position of the rearranged V kappa and its 5' flanking sequences determines the location of somatic mutations in the J kappa locus. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3652–3655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein P. D., Anderson A. O., Mage R. G. Rabbit IgH sequences in appendix germinal centers: VH diversification by gene conversion-like and hypermutation mechanisms. Immunity. 1994 Nov;1(8):647–659. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler C. J., Maloney D., Fogel S., Goodenow R. S. Microconversion between murine H-2 genes integrated into yeast. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):192–194. doi: 10.1038/347192a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Gefter M. L. Gene conversion and the generation of antibody diversity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:509–531. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


