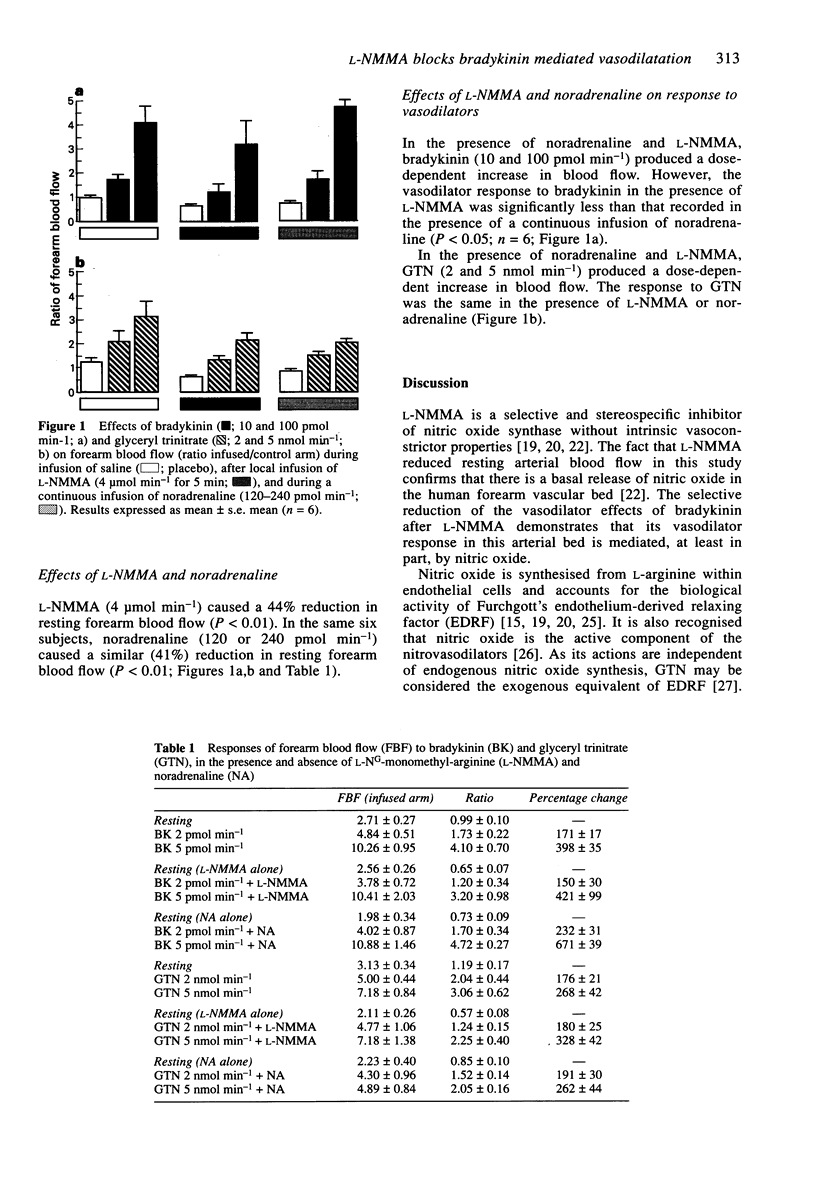
Abstract
1. Studies in animals indicate that bradykinin relaxes blood vessels directly through an action on smooth muscle and indirectly through the release of endothelium-derived mediators. Its precise mechanism of action in the human arterial circulation is not yet known. 2. In this study the effects of a specific inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, L-NG-monomethyl-arginine (L-NMMA) and noradrenaline on the vasodilator responses to bradykinin were examined in the forearm arterial bed of healthy volunteers. Noradrenaline was used as a control for vasoconstriction by L-NMMA; glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) as a control vasodilator acting independently of the NO synthase enzyme. 3. L-NMMA (4 mumol min-1; 5 min) alone reduced resting forearm blood flow by 44% (P < 0.01; n = 6) confirming that nitric oxide plays an important role in regulating vascular tone. 4. Bradykinin (10 and 100 pmol min-1; 3 min each dose) and GTN (2 and 5 nmol min-1; 3 min each dose) increased forearm blood flow in a dose-dependent manner (percentage changes 171 +/- 17% and 398 +/- 35%, and 176 +/- 21% and 268 +/- 42%, respectively; n = 6). 5. The response to bradykinin, but not that to GTN, was attenuated by L-NMMA compared with noradrenaline (P < 0.05; n = 6), suggesting that bradykinin-induced vasodilatation in the forearm is mediated, at least in part, by stimulating release of nitric oxide.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedarida G. V., Kim D., Blaschke T. F., Hoffman B. B. Characterization of an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase in human-hand veins. Horm Metab Res. 1994 Feb;26(2):109–112. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1000784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin N., Cockcroft J. R., Collier J. G., Dollery C. T., Ritter J. M., Webb D. J. Local inhibition of converting enzyme and vascular responses to angiotensin and bradykinin in the human forearm. J Physiol. 1989 May;412:543–555. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxton I. L., Cheek D. J., Eckman D., Westfall D. P., Sanders K. M., Keef K. D. NG-nitro L-arginine methyl ester and other alkyl esters of arginine are muscarinic receptor antagonists. Circ Res. 1993 Feb;72(2):387–395. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carretero O. A., Miyazaki S., Scicli A. G. Role of kinins in the acute antihypertensive effect of the converting enzyme inhibitor, captopril. Hypertension. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):18–22. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry P. D., Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V., Jothianandan D. Role of endothelial cells in relaxation of isolated arteries by bradykinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2106–2110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costello A. H., Hargreaves K. M. Suppression of carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia, hyperthermia and edema by a bradykinin antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 21;171(2-3):259–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dachman W. D., Ford G. A., Blaschke T. F., Hoffman B. B. Mechanism of bradykinin-induced venodilation in humans. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;21(2):241–248. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199302000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT D. F., HORTON E. W., LEWIS G. P. Actions of pure bradykinin. J Physiol. 1960 Oct;153:473–480. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERREIRA S. H. A BRADYKININ-POTENTIATING FACTOR (BPF) PRESENT IN THE VENOM OF BOTHROPS JARARCA. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1965 Feb;24:163–169. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1965.tb02091.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOX R. H., GOLDSMITH R., KIDD D. J., LEWIS G. P. Bradykinin as a vasodilator in man. J Physiol. 1961 Aug;157:589–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feelisch M., Noack E. A. Correlation between nitric oxide formation during degradation of organic nitrates and activation of guanylate cyclase. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 2;139(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90493-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Zawadzki J. V. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980 Nov 27;288(5789):373–376. doi: 10.1038/288373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENFIELD A. D., PATTERSON G. C. Reactions of the blood vessels of the human forearm to increases in transmural pressure. J Physiol. 1954 Sep 28;125(3):508–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavras I., Gavras H. Role of bradykinin in hypertension and the antihypertensive effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Am J Med Sci. 1988 Apr;295(4):305–307. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198804000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. E., Wood K. S., Byrns R. E., Fukuto J., Ignarro L. J. NG-methyl-L-arginine causes endothelium-dependent contraction and inhibition of cyclic GMP formation in artery and vein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4430–4434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes W. G., Noon J. P., Walker B. R., Webb D. J. L-NMMA increases blood pressure in man. Lancet. 1993 Oct 9;342(8876):931–932. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(93)91981-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L. Effect of bradykinin and thrombin on prostacyclin synthesis in endothelial cells from calf and pig aorta and human umbilical cord vein. Thromb Res. 1980 Jun 15;18(6):787–795. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högström H., Claeson G., Larsson-Backström C., Lundberg D., Wenngren E., Haglund U. Septic shock in the rat: activation of plasma proteolytic systems and effects of a kallikrein inhibitor/bradykinin antagonist (S-2441). Acta Chir Scand. 1987 Mar;153(3):161–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Buga G. M., Byrns R. E., Wood K. S., Chaudhuri G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor and nitric oxide possess identical pharmacologic properties as relaxants of bovine arterial and venous smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jul;246(1):218–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. The discovery of nitric oxide as the endogenous nitrovasodilator. Hypertension. 1988 Oct;12(4):365–372. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.12.4.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., al-Swayeh O. A., Chong N. W., Evans R. A., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro arginine (L-NOARG), a novel, L-arginine-reversible inhibitor of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):408–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Key S. L., Denny S. E., Isakson P. C., Marshall G. R. Mechanism and modification of bradykinin-induced coronary vasodilation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2060–2063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Rees D. D., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1251–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richard V., Tanner F. C., Tschudi M., Lüscher T. F. Different activation of L-arginine pathway by bradykinin, serotonin, and clonidine in coronary arteries. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 2):H1433–H1439. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.5.H1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritter J. M., Doktor H. S., Cragoe E. J., Jr Actions of bradykinin and related peptides on rabbit coeliac artery rings. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;96(1):23–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAAMELI K., ESKES T. K. Bradykinin and cardiovascular system: estimation of half-life. Am J Physiol. 1962 Aug;203:261–265. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.203.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance P., Collier J., Moncada S. Effects of endothelium-derived nitric oxide on peripheral arteriolar tone in man. Lancet. 1989 Oct 28;2(8670):997–1000. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallance P., Collier J., Moncada S. Nitric oxide synthesised from L-arginine mediates endothelium dependent dilatation in human veins in vivo. Cardiovasc Res. 1989 Dec;23(12):1053–1057. doi: 10.1093/cvr/23.12.1053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanhoutte P. M., Auch-Schwelk W., Biondi M. L., Lorenz R. R., Schini V. B., Vidal M. J. Why are converting enzyme inhibitors vasodilators? Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;28 (Suppl 2):95S–104S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03585.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITNEY R. J. The measurement of volume changes in human limbs. J Physiol. 1953 Jul;121(1):1–27. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weipert J., Hoffmann H., Siebeck M., Whalley E. T. Attenuation of arterial blood pressure fall in endotoxin shock in the rat using the competitive bradykinin antagonist Lys-Lys-[Hyp2, Thi5,8, DPhe7]-Bk (B4148). Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):282–284. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittle B. J., Lopez-Belmonte J., Rees D. D. Modulation of the vasodepressor actions of acetylcholine, bradykinin, substance P and endothelin in the rat by a specific inhibitor of nitric oxide formation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):646–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12639.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


