Abstract
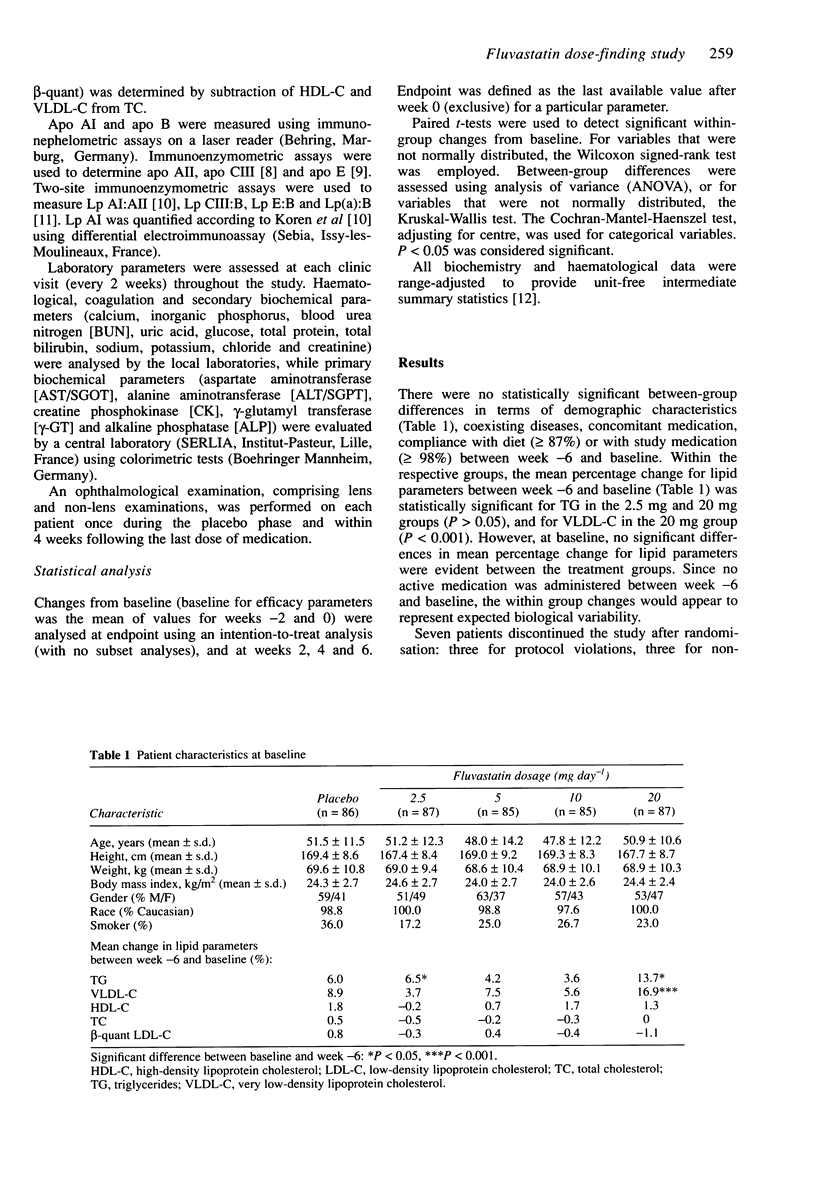
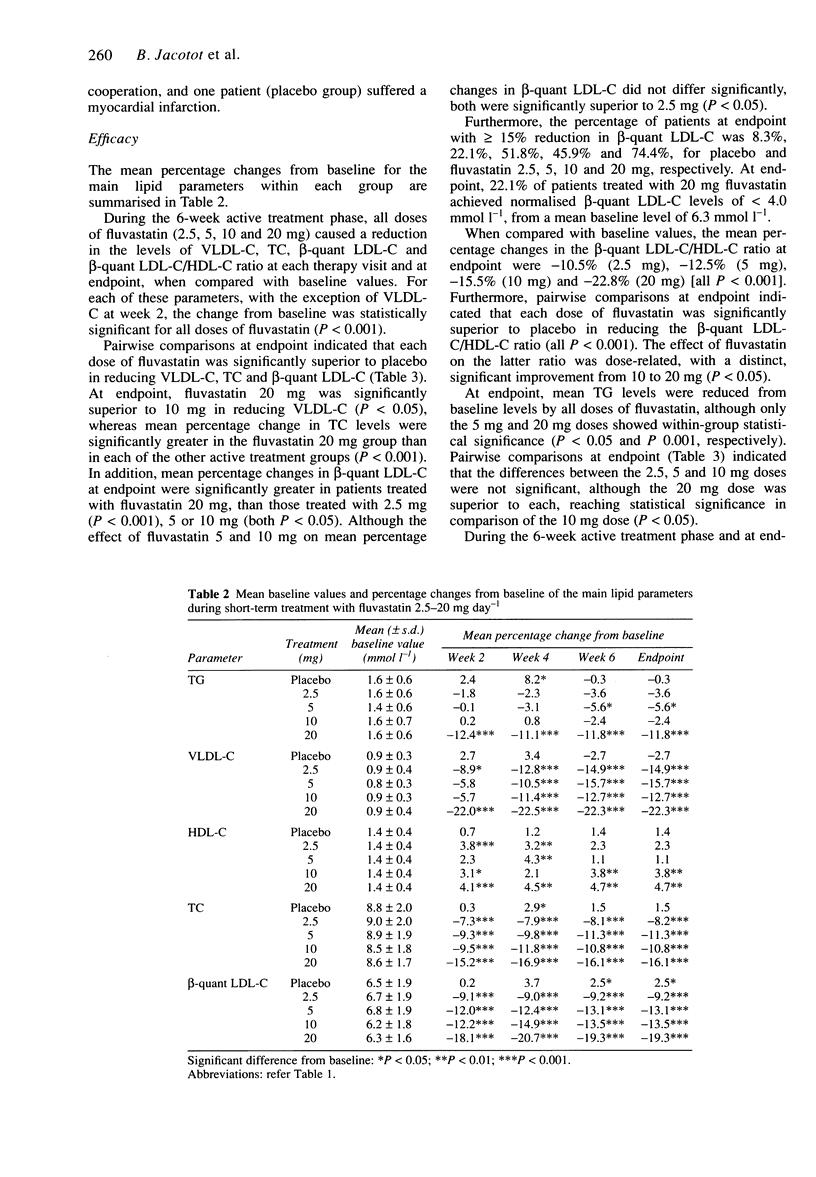
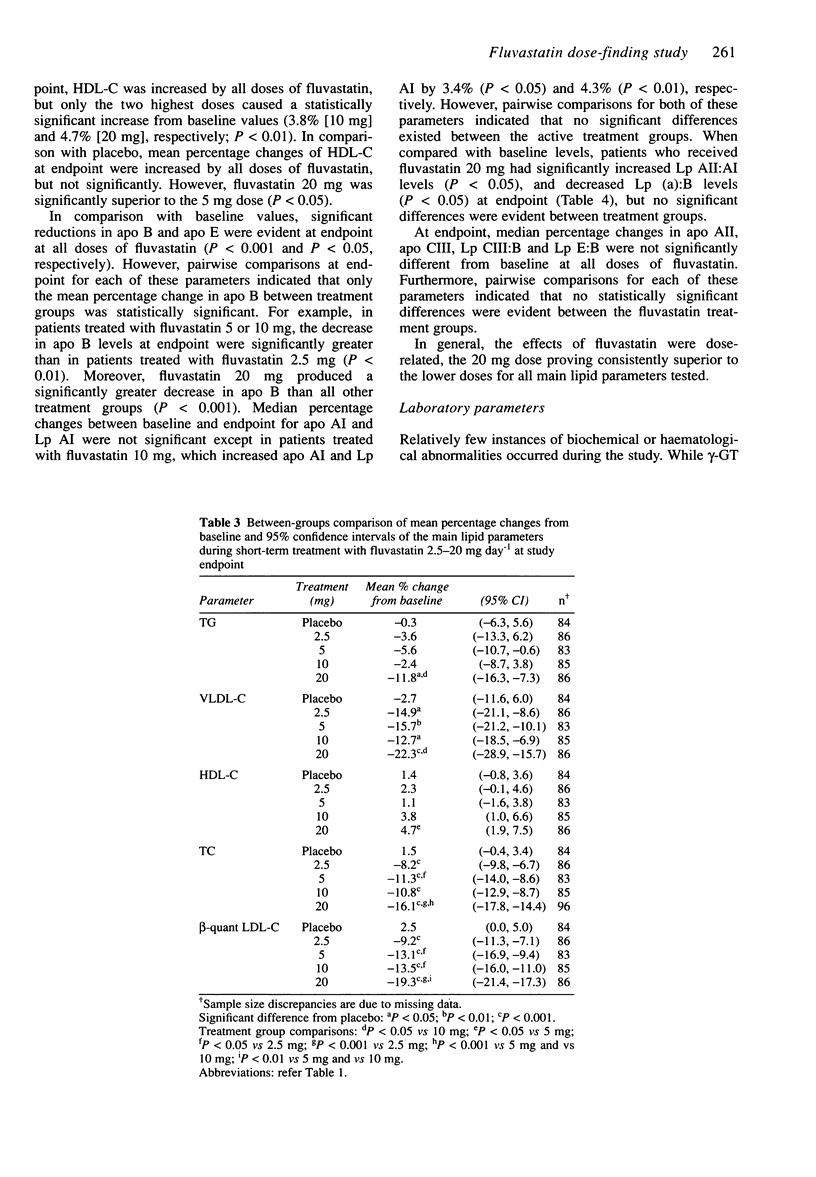
1. In this randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, the efficacy of four dosages of fluvastatin (2.5, 5, 10 and 20 mg day-1) were assessed in 431 patients with primary hypercholesterolaemia recruited in 17 centres. 2. Following an 8-week dietary stabilisation phase and a 6-week placebo phase, the patients were randomised to receive placebo or fluvastatin 2.5, 5, 10 or 20 mg once daily at night for a period of 6 weeks. 3. Total cholesterol, beta-quant LDL-C, and the beta-quant LDL-C/HDL-C ratio were significantly reduced by all doses of fluvastatin, and HDL-C was significantly increased by the 10 mg and 20 mg doses. Fluvastatin 20 mg day-1 also significantly decreased TG and Lp(a):B levels. 4. Fluvastatin was well tolerated during the study, and relatively few biochemical or haematological abnormalities occurred. 5. Of the dosages tested, 20 mg fluvastatin day-1 is the optimal hypolipidaemic dose.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Koffigan M., Kora I., Clavey V., Bard J. M., Chapman J., Fruchart J. C. Quantification of human apolipoprotein E in plasma and lipoprotein subfractions by a non-competitive enzyme immunoassay. Clin Chim Acta. 1987 Mar 30;163(3):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(87)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koren E., Puchois P., Alaupovic P., Fesmire J., Kandoussi A., Fruchart J. C. Quantification of two different types of apolipoprotein A-I containing lipoprotein particles in plasma by enzyme-linked differential-antibody immunosorbent assay. Clin Chem. 1987 Jan;33(1):38–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G. M., Gavish D., Leopold B., Bolzano K., Weintraub M. S., Breslow J. L. HMG CoA reductase inhibitors lower LDL cholesterol without reducing Lp(a) levels. Circulation. 1989 Nov;80(5):1313–1319. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.5.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsy D., Clavey V., Fievet C., Kora I., Duriez P., Fruchart J. C. Quantification of apolipoprotein C-III in serum by a noncompetitive immunoenzymometric assay. Clin Chem. 1985 Oct;31(10):1632–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmell P. S., Gorder D. D., Hall Y., Tillotson J. L. Assessing dietary adherence in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial (MRFIT). I. Use of a dietary monitoring tool. J Am Diet Assoc. 1980 Apr;76(4):351–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A., Weisser B., Vetter W. A comparative review of the adverse effects of treatments for hyperlipidaemia. Drug Saf. 1991 Mar-Apr;6(2):118–130. doi: 10.2165/00002018-199106020-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J., Armstrong V. W., Schleef J., Creutzfeldt C., Creutzfeldt W., Seidel D. Serum lipoprotein Lp(a) concentrations are not influenced by an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor. Klin Wochenschr. 1988 May 16;66(10):462–463. doi: 10.1007/BF01745519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse F. L., Jaffe J. M., Troendle A. Pharmacokinetics of fluvastatin after single and multiple doses in normal volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;32(7):630–638. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1992.tb05773.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu Dac N., Mezdour H., Parra H. J., Luc G., Luyeye I., Fruchart J. C. A selective bi-site immunoenzymatic procedure for human Lp[a] lipoprotein quantification using monoclonal antibodies against apo[a] and apoB. J Lipid Res. 1989 Sep;30(9):1437–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


