Abstract
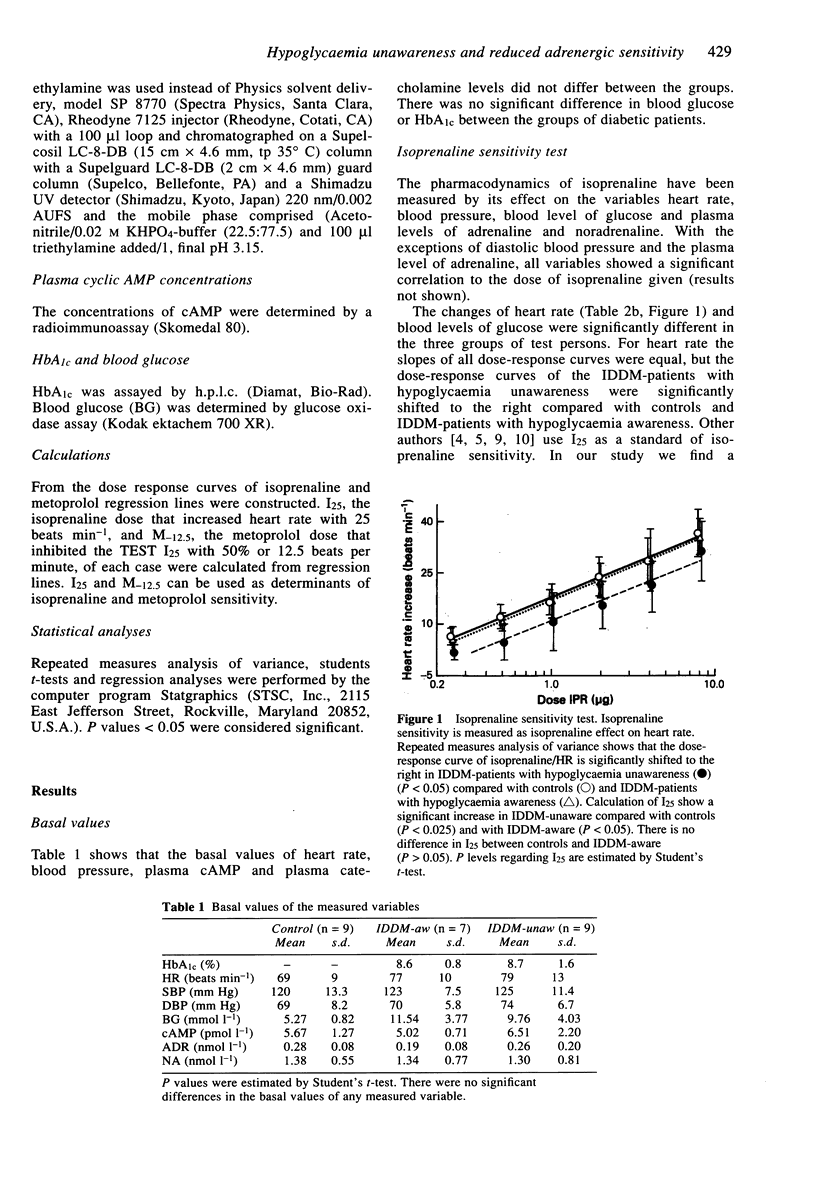
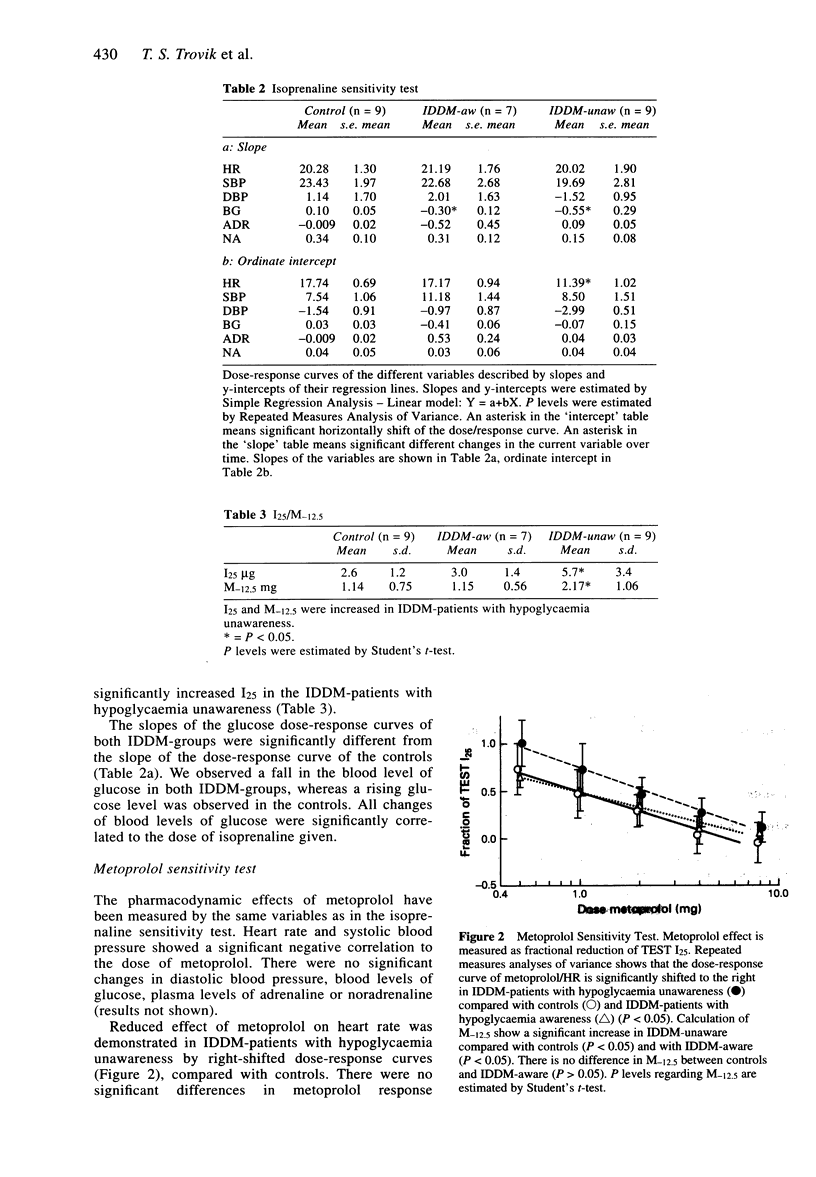
Nine IDDM-patients with hypoglycaemia unawareness, seven IDDM-patients with hypoglycemia awareness and a control group of nine healthy persons were included in this study. The patients were recruited from the medical out-patients' department of the University Hospital of Tromsø. The pathophysiological changes which cause hypoglycaemia unawareness are today not clear. Reduced peripheral tissue sensitivity to catecholamines is suggested as one of several mechanisms which may contribute. For further investigation of beta-adrenergic sensitivity an isoprenaline/metoprolol sensitivity test was performed. Isoprenaline and metoprolol were administered intravenously, and the effects on heart rate (HR), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP) and plasma levels of adrenaline (ADR) and noradrenaline (NA) were measured. All subjects were given the same doses of isoprenaline (0.25-8 micrograms) and metoprolol (0.5-8 mg). Metoprolol was given together with the dose of isoprenaline which increased heart rate by 25 beats min-1. The dose/response curves of both isoprenaline/HR and metoprolol/HR were significantly shifted to the right in IDDM-patients with hypoglycaemia unawareness compared with controls and IDDM-patients with hypoglycaemia awareness (P < 0.05). Reduced sensitivity of isoprenaline stimulation has also been shown before, whereas reduced sensitivity of a blocking agent has not earlier been shown. These findings support the hypothesis of reduced beta-adrenergic sensitivity as one pathophysiological component in hypoglycaemia unawareness.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson U., Lins P. E., Efendic S., Hamberger B., Wajngot A. Impaired counter regulation of hypoglycemia in a group of insulin-dependent diabetics with recurrent episodes of severe hypoglycemia. Acta Med Scand. 1984;216(2):215–222. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1984.tb03795.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold J. M., McDevitt D. G. Standardised isoprenaline sensitivity tests--a comparison of existent methods. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Feb;15(2):167–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balmér K., Zhang Y. Y., Lagerström P. O., Persson B. A. Determination of metoprolol and two major metabolites in plasma and urine by column liquid chromatography and fluorometric detection. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jul 3;417(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin I., Grimaldi A., Bosquet F., Puech A. J. Decreased beta-adrenergic sensitivity in insulin-dependent diabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Jul;63(1):262–265. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-1-262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin I., Grimaldi A., Landault C., Zoghbi F., Thervet F., Puech A. J., Legrand J. C. Lack of hypoglycemic symptoms and decreased beta-adrenergic sensitivity in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Feb;66(2):273–278. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin I., Grimaldi A., Payan C., Sachon C., Bosquet F., Thervet F., Puech A. J. Hypoglycemic symptoms and decreased beta-adrenergic sensitivity in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 1987 Nov-Dec;10(6):742–747. doi: 10.2337/diacare.10.6.742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. J., Schwartz N. S., Shah S. D., Clutter W. E., Cryer P. E. Plasma glucose concentrations at the onset of hypoglycemic symptoms in patients with poorly controlled diabetes and in nondiabetics. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1487–1492. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinchmann-Hansen O., Dahl-Jørgensen K., Sandvik L., Hanssen K. F. Blood glucose concentrations and progression of diabetic retinopathy: the seven year results of the Oslo study. BMJ. 1992 Jan 4;304(6818):19–22. doi: 10.1136/bmj.304.6818.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl-Jørgensen K., Bjøro T., Kierulf P., Sandvik L., Bangstad H. J., Hanssen K. F. Long-term glycemic control and kidney function in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1992 Apr;41(4):920–923. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. F., Conolly M. E., Fenyvesi T., Briant R., Dollery C. T. Intravenously administered isoproterenol sulfate dose-response curves in man. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Sep;130(3):361–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeldtke R. D., Boden G., Shuman C. R., Owen O. E. Reduced epinephrine secretion and hypoglycemia unawareness in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Apr;96(4):459–462. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitrakou A., Ryan C., Veneman T., Mokan M., Jenssen T., Kiss I., Durrant J., Cryer P., Gerich J. Hierarchy of glycemic thresholds for counterregulatory hormone secretion, symptoms, and cerebral dysfunction. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jan;260(1 Pt 1):E67–E74. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.1.E67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard P., Nilsson B. Y., Rosenqvist U. The effect of long-term intensified insulin treatment on the development of microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993 Jul 29;329(5):304–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199307293290502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager G., Slørdal L., Huseby N. E., Florholmen J. Beta-adrenoceptor regulation in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1991 May;51(3):283–288. doi: 10.3109/00365519109091616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sager G., Trovik T., Slørdal L., Jaeger R., Prytz P. S., Brox J., Reikerås O. Catecholamine binding and concentrations in acute phase plasma after surgery. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1988 Sep;48(5):419–424. doi: 10.1080/00365518809085751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonson D. C., Tamborlane W. V., DeFronzo R. A., Sherwin R. S. Intensive insulin therapy reduces counterregulatory hormone responses to hypoglycemia in patients with type I diabetes. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Aug;103(2):184–190. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-103-2-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sérusclat P., Rosen S. G., Smith E. B., Shah S. D., Clutter W. E., Cryer P. E. Mononuclear leukocyte beta 2-adrenergic receptors and adenylate cyclase sensitivity in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1983 Sep;32(9):825–829. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.9.825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trovik T. S., Jaeger R., Jorde R., Ingebretsen O., Sager G. Plasma protein binding of catecholamines, prazosin and propranolol in diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1992;43(3):265–268. doi: 10.1007/BF02333020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widom B., Simonson D. C. Glycemic control and neuropsychologic function during hypoglycemia in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Ann Intern Med. 1990 Jun 15;112(12):904–912. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-112-12-904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


