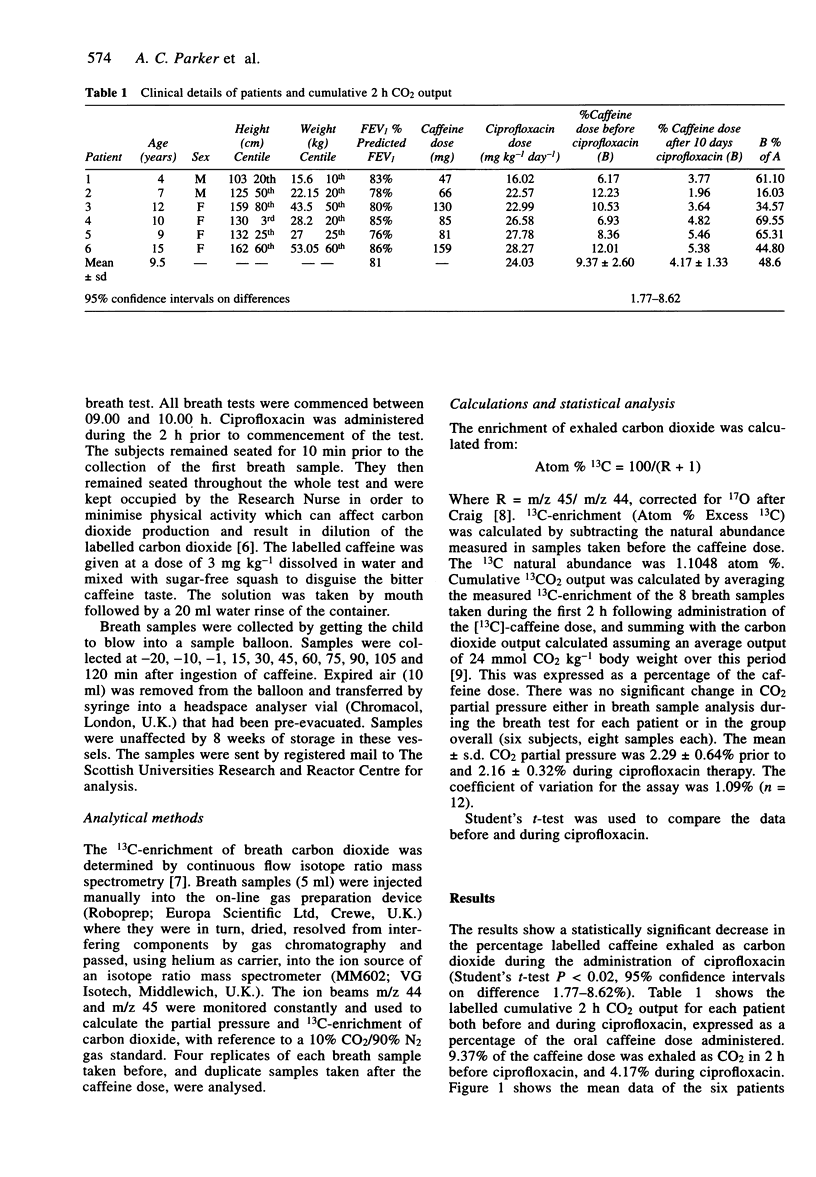
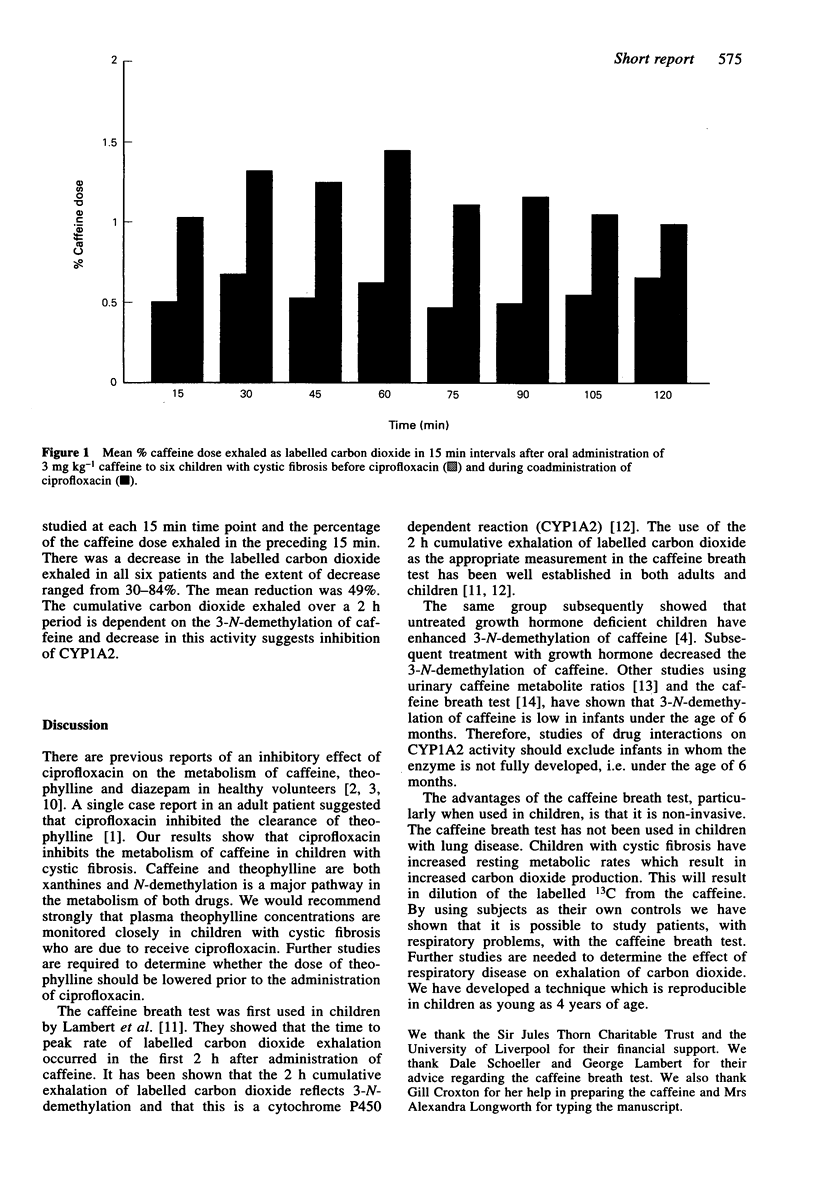
Abstract
The caffeine breath test was carried out in six children with cystic fibrosis, before and during a course of ciprofloxacin. There was a significant decrease in the 2 h cumulative labelled CO2 exhaled during ciprofloxacin treatment, mean difference (s.d.) -5.2(3.3)%, P < 0.02. The results suggest an inhibition of 3-N-demethylation of caffeine (CYP1A2 enzyme activity) by ciprofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin may cause significant drug interactions in children with cystic fibrosis. The caffeine breath test can be used to study drug interactions involving CYP1A2 in children.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butler M. A., Iwasaki M., Guengerich F. P., Kadlubar F. F. Human cytochrome P-450PA (P-450IA2), the phenacetin O-deethylase, is primarily responsible for the hepatic 3-demethylation of caffeine and N-oxidation of carcinogenic arylamines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7696–7700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrier O., Pons G., Rey E., Richard M. O., Moran C., Badoual J., Olive G. Maturation of caffeine metabolic pathways in infancy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Aug;44(2):145–151. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1988.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder S., Staib A. H., Beer C., Papenburg A., Stille W., Shah P. M. 4-quinolones inhibit biotransformation of caffeine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1988;35(6):651–656. doi: 10.1007/BF00637602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert G. H., Kotake A. N., Schoeller D. The CO2 breath tests as monitors of the cytochrome P450 dependent mixed function monooxygenase system. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1983;135:119–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert G. H., Schoeller D. A., Kotake A. N., Flores C., Hay D. The effect of age, gender, and sexual maturation on the caffeine breath test. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1986;9(6):375–388. doi: 10.1159/000457262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitsky L. L., Schoeller D. A., Lambert G. H., Edidin D. V. Effect of growth hormone therapy in growth hormone-deficient children on cytochrome P-450-dependent 3-N-demethylation of caffeine as measured by the caffeine 13CO2 breath test. Dev Pharmacol Ther. 1989;12(2):90–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loi C. M., Parker B. M., Cusack B. J., Vestal R. Individual and combined effects of cimetidine and ciprofloxacin on theophylline metabolism in male nonsmokers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;36(3):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1993.tb04216.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons G., Blais J. C., Rey E., Plissonnier M., Richard M. O., Carrier O., d'Athis P., Moran C., Badoual J., Olive G. Maturation of caffeine N-demethylation in infancy: a study using the 13CO2 breath test. Pediatr Res. 1988 Jun;23(6):632–636. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198806000-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston T., McMillan D. C. Rapid sample throughput for biomedical stable isotope tracer studies. Biomed Environ Mass Spectrom. 1988 Oct;16(1-12):229–235. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200160142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rost K. L., Brösicke H., Brockmöller J., Scheffler M., Helge H., Roots I. Increase of cytochrome P450IA2 activity by omeprazole: evidence by the 13C-[N-3-methyl]-caffeine breath test in poor and extensive metabolizers of S-mephenytoin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Aug;52(2):170–180. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1992.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeller D. A., Schneider J. F., Solomons N. W., Watkins J. B., Klein P. D. Clinical diagnosis with the stable isotope 13C in CO2 breath tests: methodology and fundamental considerations. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Sep;90(3):412–421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. H., Thomson G. D., Hepburn M., Whiting B. A clinically significant interaction between ciprofloxacin and theophylline. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;33(4):435–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00637645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


