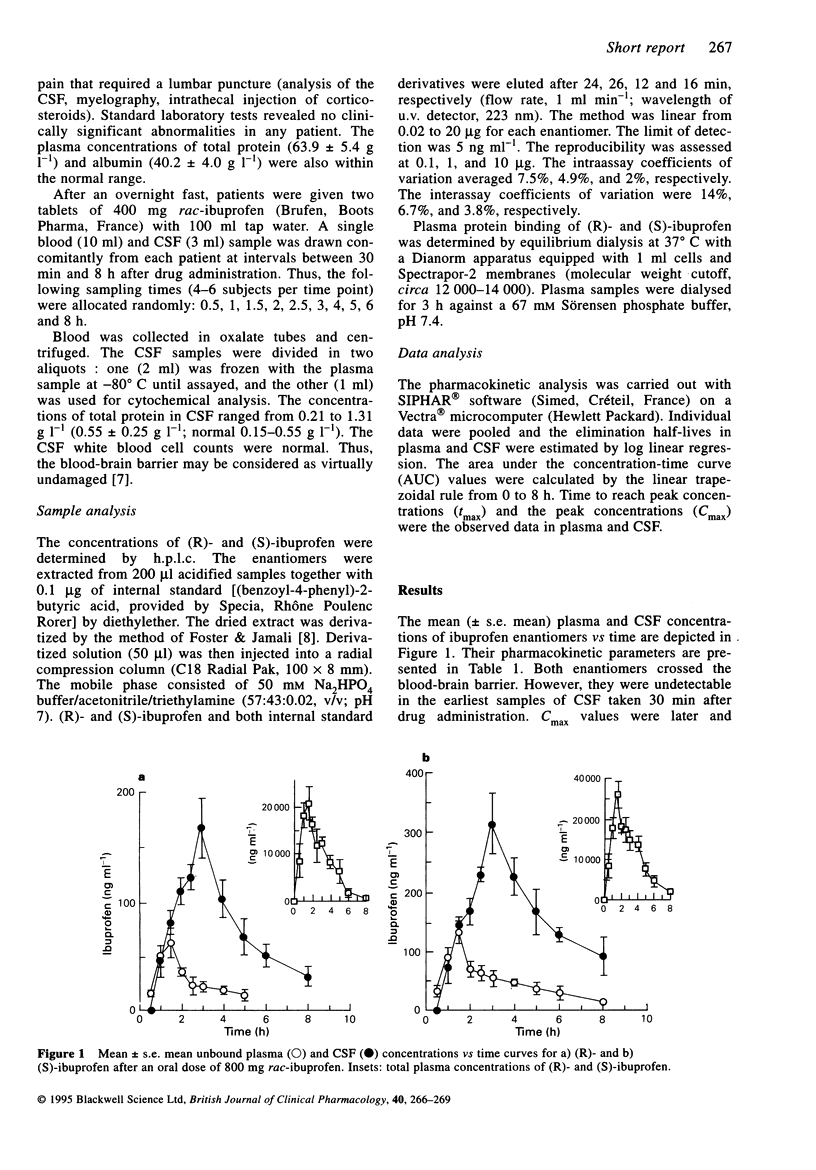
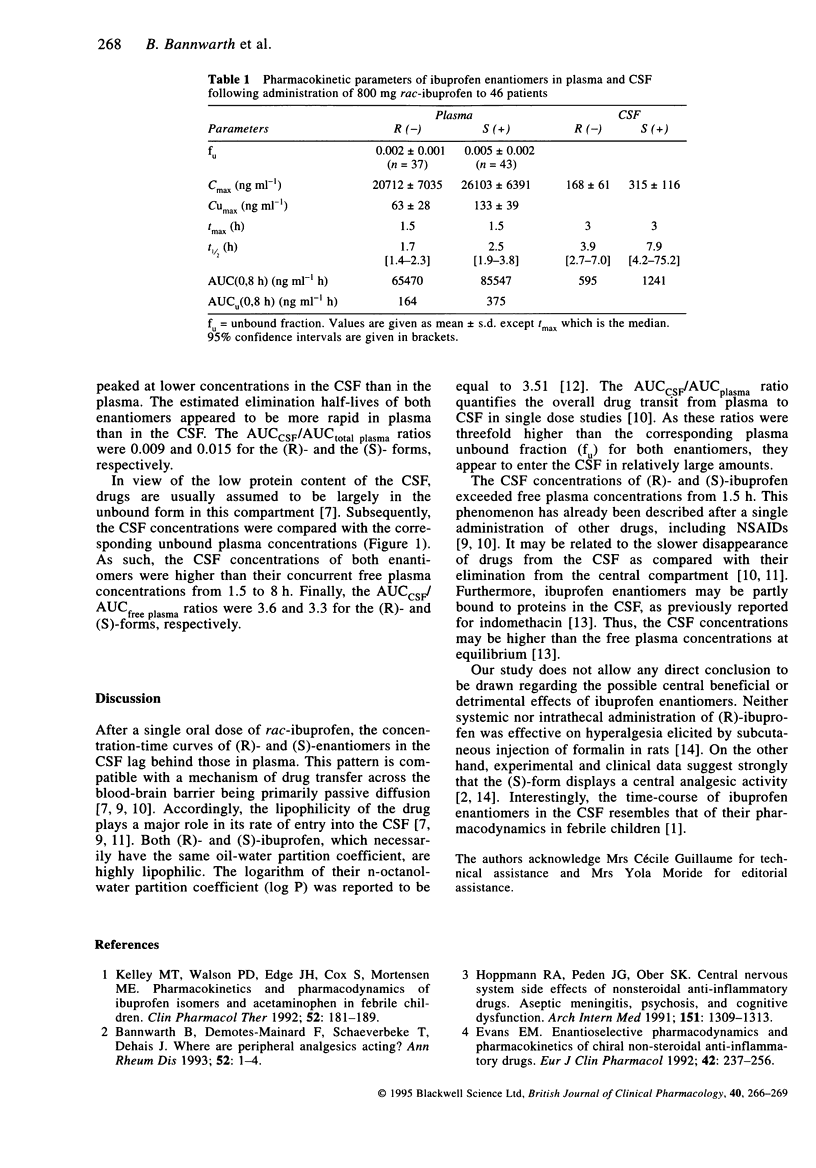
Abstract
Since both (R)- and (S)-enantiomers of ibuprofen may act on the central nervous system, we investigated their plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) concentrations in 46 patients with nerve-root compression pain requiring a lumbar puncture. Each patient received an oral dose of 800 mg rac-ibuprofen. A single blood and CSF sample was drawn concomitantly from each patient at intervals between 30 min and 8 h after dosing. Both isomers peaked later in the CSF (3 h) than in the plasma (1.5 h). Their CSF concentrations became higher than their concurrent free plasma concentrations after 90 min. The estimated elimination half-lives of (R)- and (S)-ibuprofen were 1.7 h and 2.5 h in plasma and 3.9 h and 7.9 h in CSF, respectively. The AUCCSF/AUCplasma ratios (0, 8 h) were 0.009 and 0.015 for the (R)- and (S)-forms, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bannwarth B., Demotes-Mainard F., Schaeverbeke T., Dehais J. Where are peripheral analgesics acting? Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Jan;52(1):1–4. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannwarth B., Netter P., Lapicque F., Gillet P., Péré P., Boccard E., Royer R. J., Gaucher A. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of paracetamol after a single intravenous dose of propacetamol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;34(1):79–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb04112.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannwarth B., Netter P., Lapicque F., Péré P., Thomas P., Gaucher A. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of indomethacin in humans. Relationship to analgesic activity. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;38(4):343–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00315572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonati M., Kanto J., Tognoni G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Jul-Aug;7(4):312–335. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans A. M. Enantioselective pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of chiral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1992;42(3):237–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00266343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster R. T., Jamali F. High-performance liquid chromatographic assay of ketoprofen enantiomers in human plasma and urine. J Chromatogr. 1987 May 15;416(2):388–393. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80525-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppmann R. A., Peden J. G., Ober S. K. Central nervous system side effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Aseptic meningitis, psychosis, and cognitive dysfunction. Arch Intern Med. 1991 Jul;151(7):1309–1313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M. T., Walson P. D., Edge J. H., Cox S., Mortensen M. E. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ibuprofen isomers and acetaminophen in febrile children. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Aug;52(2):181–189. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1992.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. J., Williams K., Day R., Graham G., Champion D. Stereoselective disposition of ibuprofen enantiomers in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985 May;19(5):669–674. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1985.tb02694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg A. B., Yaksh T. L. Antinociceptive actions of spinal nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents on the formalin test in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Oct;263(1):136–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller N., Lapicque F., Monot C., Payan E., Gillet P., Bannwarth B., Netter P. Protein binding of indomethacin in human cerebrospinal fluid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 25;42(4):799–804. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau R., Zysk G., Thiel A., Prange H. W. Pharmacokinetic quantification of the exchange of drugs between blood and cerebrospinal fluid in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1993;45(5):469–475. doi: 10.1007/BF00315520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva M., Heckenberger R., Strobach H., Palmér M., Schrör K. Equipotent inhibition by R(-)-, S(+)- and racemic ibuprofen of human polymorphonuclear cell function in vitro. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;35(3):235–242. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1993.tb05690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano T., Nakagawa A., Tsuji M., Noda K. Skin permeability of various non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in man. Life Sci. 1986 Sep 22;39(12):1043–1050. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90195-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


