Abstract
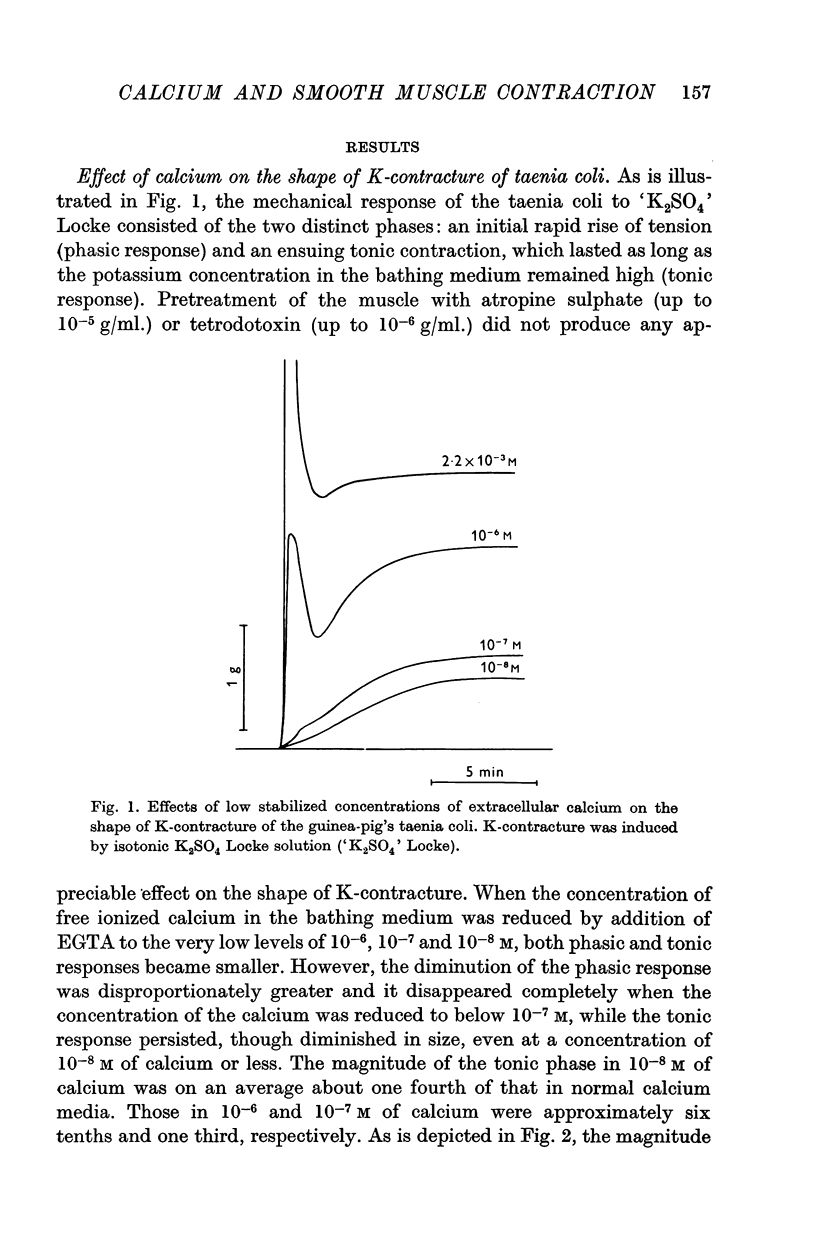
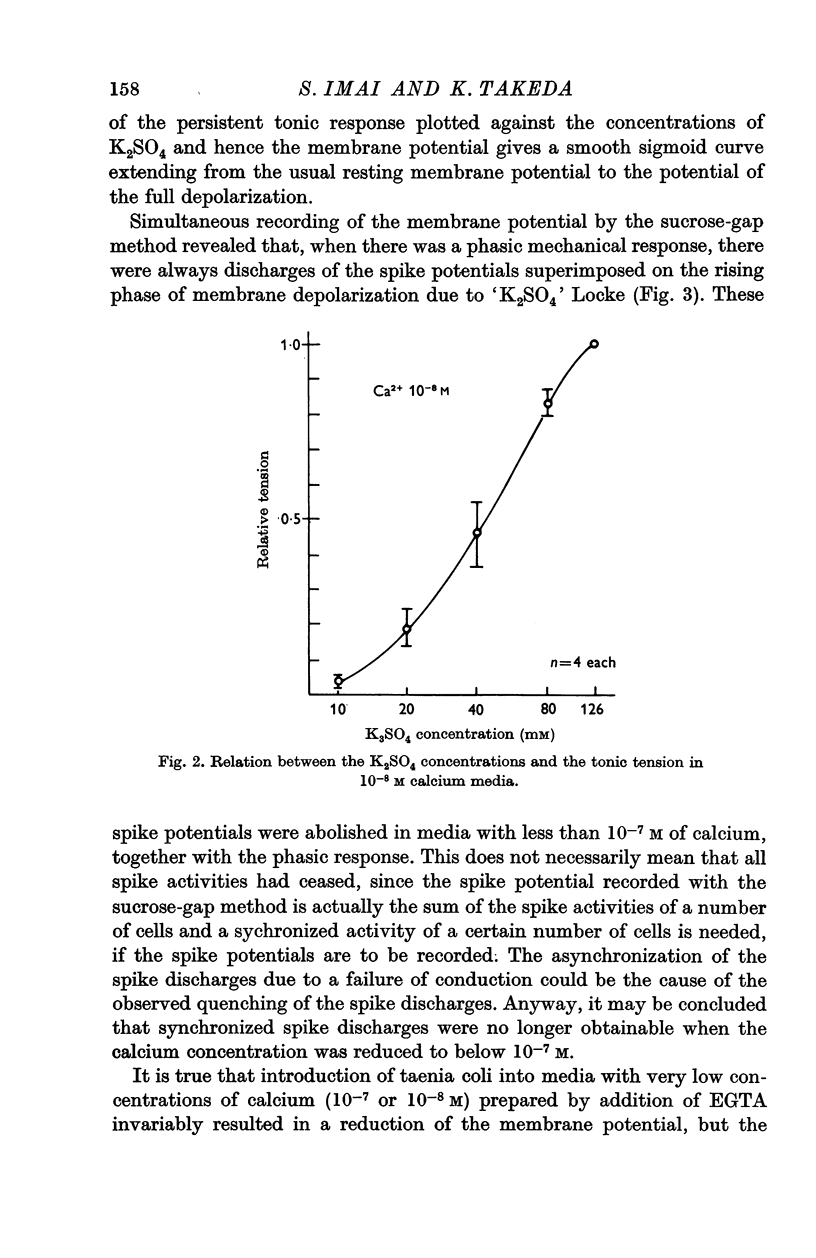
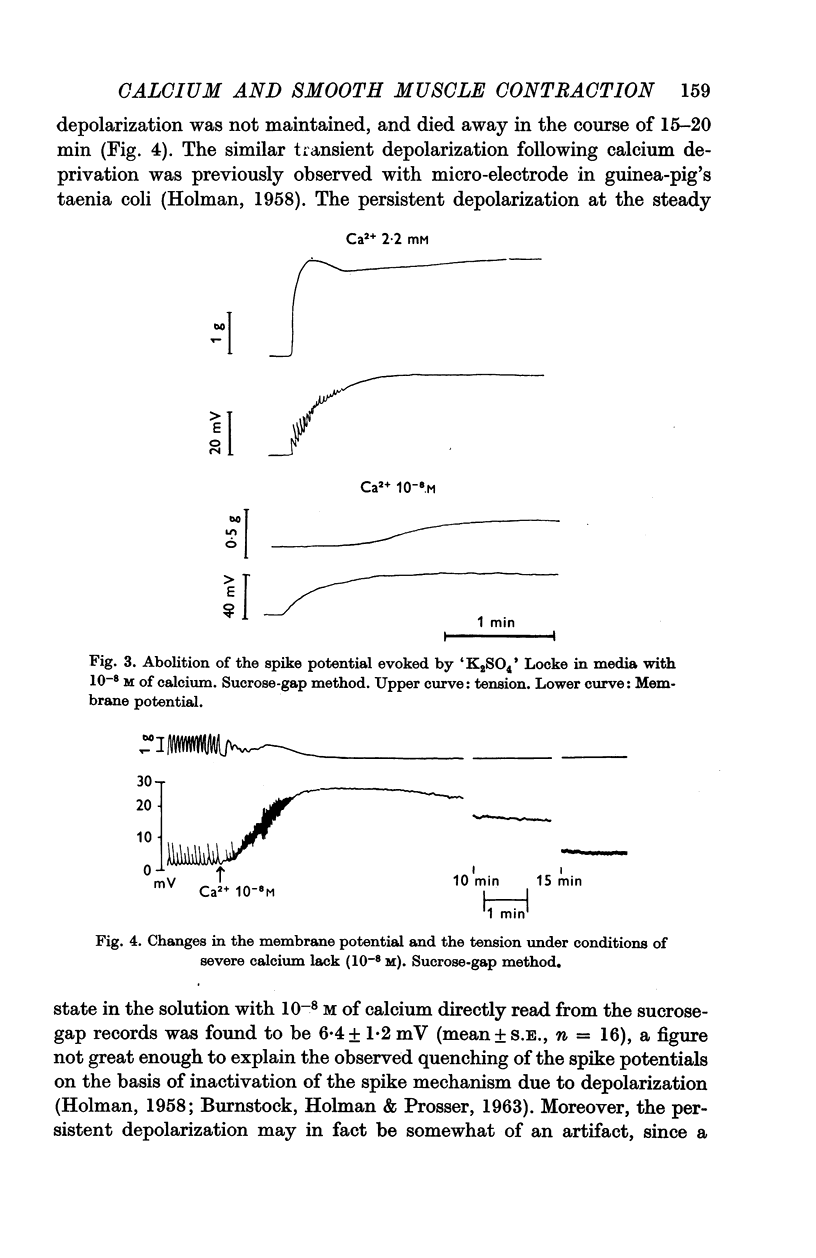
1. Using a calcium buffer system, the effect of severe calcium lack on the shape of K-contracture of the guinea-pig's taenia coli was studied. Under conditions of calcium lack, the initial phasic response was preferentially affected and it disappeared completely at concentrations below 10-7 M, while the ensuing tonic response persisted, though considerably diminished in size, even at the concentration of 10-8 M.
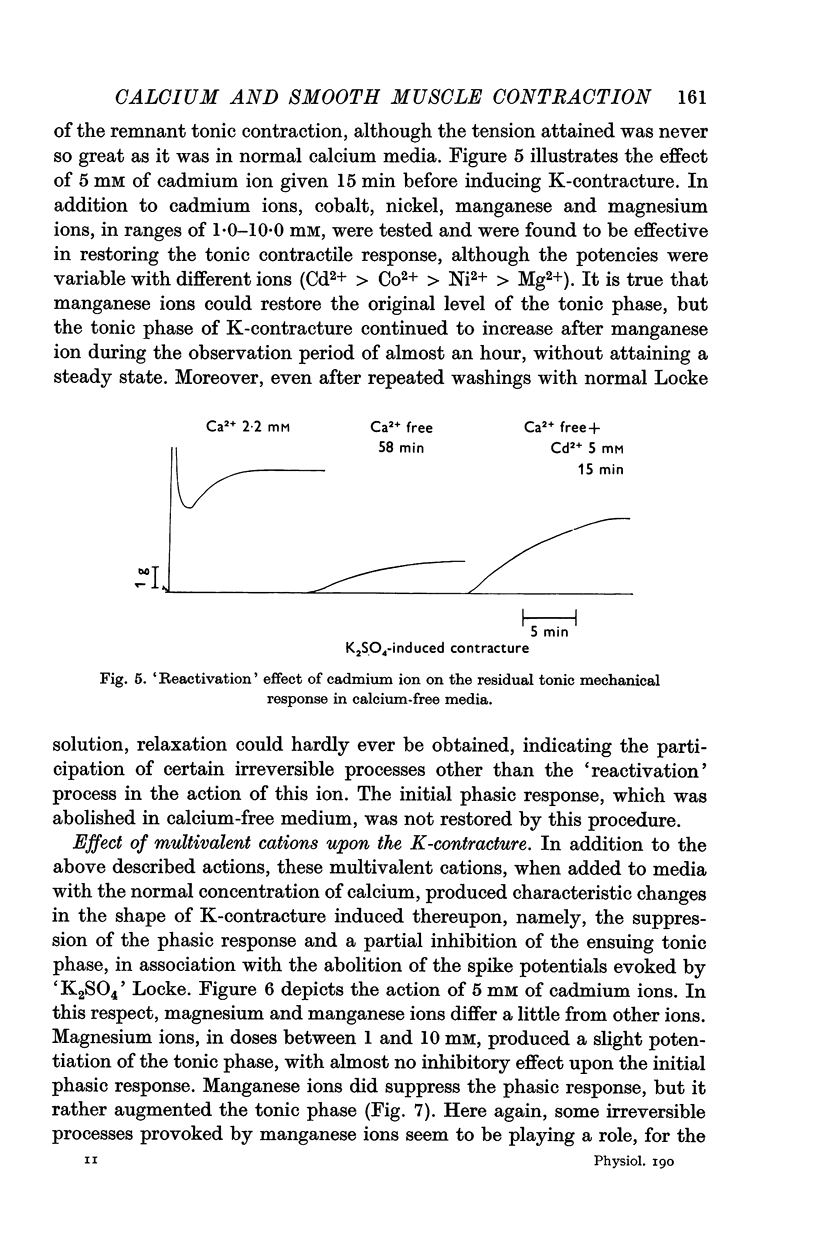
2. In calcium-free media, various multivalent cations, which according to Frank (1962) can support the K-contracture of a skeletal twitch muscle fibre in calcium-free solution, augmented the remaining tonic response, but did not restore the phasic response, when it was eliminated in calcium free environment.
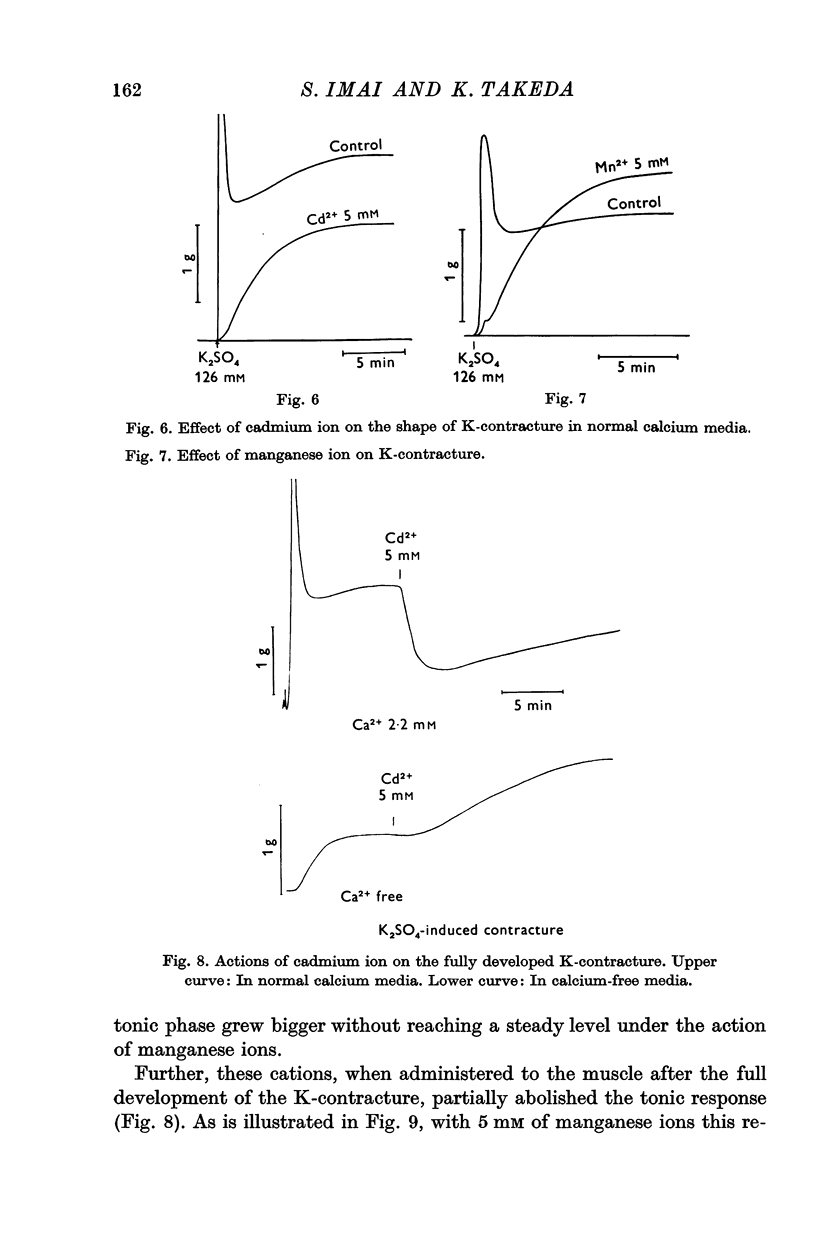
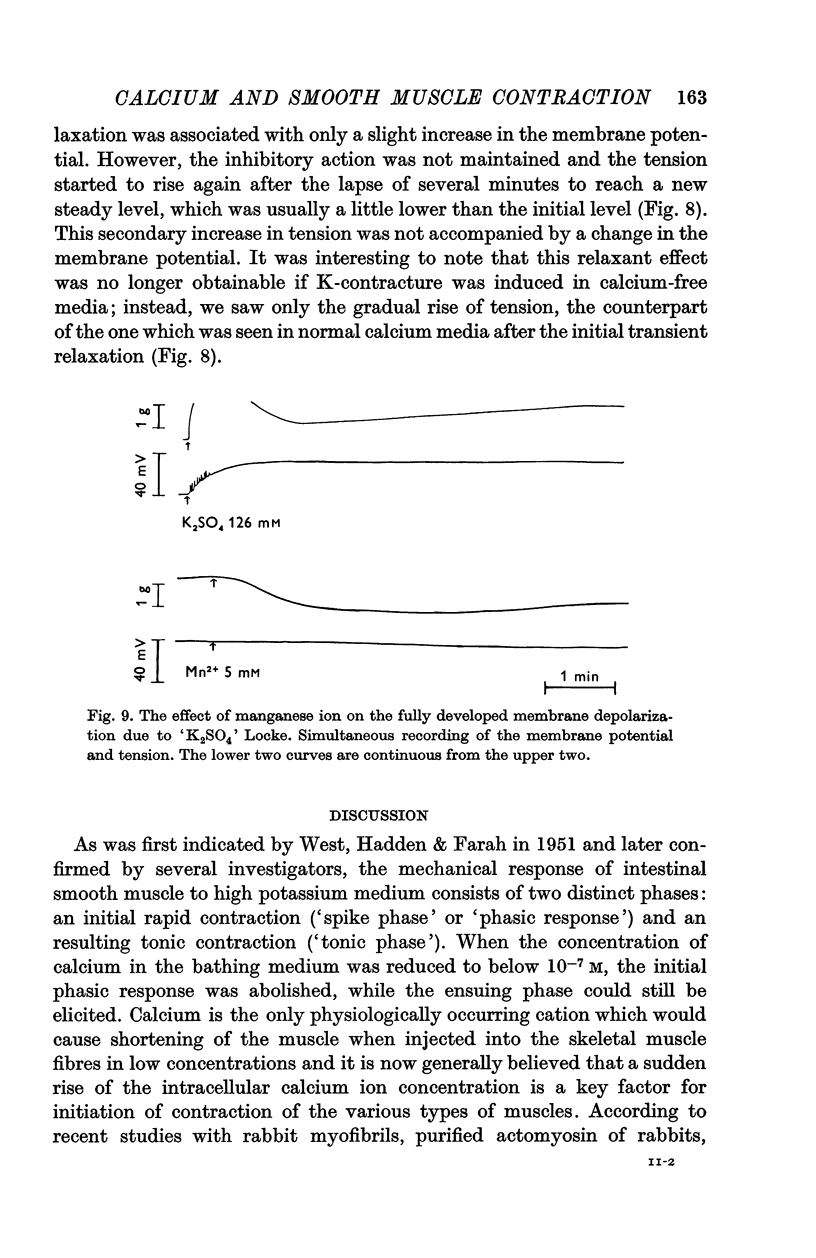
3. When K-contractures were induced in normal calcium media, these cations produced, in contrast, an abolition of the phasic response together with a partial depression of the tonic phase. They also inhibited a part of the fully developed contracture. The last effect was no longer obtainable in calcium-free media.
4. It is concluded that the phasic response and a part of the tonic response of taenia coli depend upon the extracellular calcium for their initiation (and also for maintenance of tension in the case of the latter) and that the rest of the tonic response draws on a store of `bound' calcium for its evolution.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNSTOCK G., HOLMAN M. E., PROSSER C. L. Electrophysiology of smooth muscle. Physiol Rev. 1963 Jul;43:482–527. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1963.43.3.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNSTOCK G., STRAUB R. W. A method for studying the effects of ions and drugs on the resting and action potentials in smooth muscle with external electrodes. J Physiol. 1958 Jan 23;140(1):156–167. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Burnstock G. Application of the sucrose-gap method to determine the ionic basis of the membrane potential of smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):637–648. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohr D. F. Vascular Smooth Muscle: Dual Effect of Calcium. Science. 1963 Feb 15;139(3555):597–599. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3555.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL E. E. ON ROLES OF CALCIUM STRONTIUM AND BARIUM IN CONTRACTION AND EXCITABILITY OF RAT UTERINE MUSCLE. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1963 Dec 1;146:298–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMAN K. A., SCHILD H. O. The need for calcium in the contractile responses induced by acetylcholine and potassium in the rat uterus. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:424–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. H., SCHILD H. O., THESLEFF S. Effects of drugs on depolarized plain muscle. J Physiol. 1958 Oct 31;143(3):474–485. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FILO R. S., BOHR D. F., RUEGG J. C. GLYCERINATED SKELETAL AND SMOOTH MUSCLE: CALCIUM AND MAGNESIUM DEPENDENCE. Science. 1965 Mar 26;147(3665):1581–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3665.1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK G. B. Utilization of bound calcium in the action of caffeine and certain multivalent cations on skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1962 Sep;163:254–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMAN M. E. Membrane potentials recorded with high-resistance micro-electrodes; and the effects of changes in ionic environment on the electrical and mechanical activity of the smooth muscle of the taenia coli of the guineapig. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):464–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Differences in Na and Ca spikes as examined by application of tetrodotoxin, procaine, and manganese ions. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):793–806. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Nakajima S. Effects of the intracellular Ca ion concentration upon the excitability of the muscle fiber membrane of a barnacle. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Mar;49(4):807–818. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.4.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUETTGAU H. C. THE ACTION OF CALCIUM IONS ON POTASSIUM CONTRACTURES OF SINGLE MUSCLE FIBRES. J Physiol. 1963 Oct;168:679–697. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARK J. S. An electron microscope study of uterine smooth muscle. Anat Rec. 1956 Jul;125(3):473–493. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091250306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonomura Y., Hotta Y., Ohashi H. Tetrodotoxin and manganese ions: effects on electrical activity and tension in taenia coli of guinea pig. Science. 1966 Apr 1;152(3718):97–98. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3718.97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFAFFMAN M., URAKAWA N., HOLLAND W. C. ROLE OF METABOLISM IN K-INDUCED TENSION CHANGES IN GUINEA PIG TAENIA COLI. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jun;208:1203–1205. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.6.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTZEHL H., CALDWELL P. C., RUEEGG J. C. THE DEPENDENCE OF CONTRACTION AND RELAXATION OF MUSCLE FIBRES FROM THE CRAB MAIA SQUINADO ON THE INTERNAL CONCENTRATION OF FREE CALCIUM IONS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 May 25;79:581–591. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- URAKAWA N., HOLLAND W. C. CA45 UPTAKE AND TISSUE CALCIUM IN K-INDUCED PHASIC AND TONIC CONTRACTION IN TAENIA COLI. Am J Physiol. 1964 Oct;207:873–876. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.4.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST T. C., HADDEN G., FARAH A. Effect of anoxia on response of the isolated intestine to various drugs and enzyme inhibitors. Am J Physiol. 1951 Feb;164(2):565–572. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.164.2.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


