Abstract
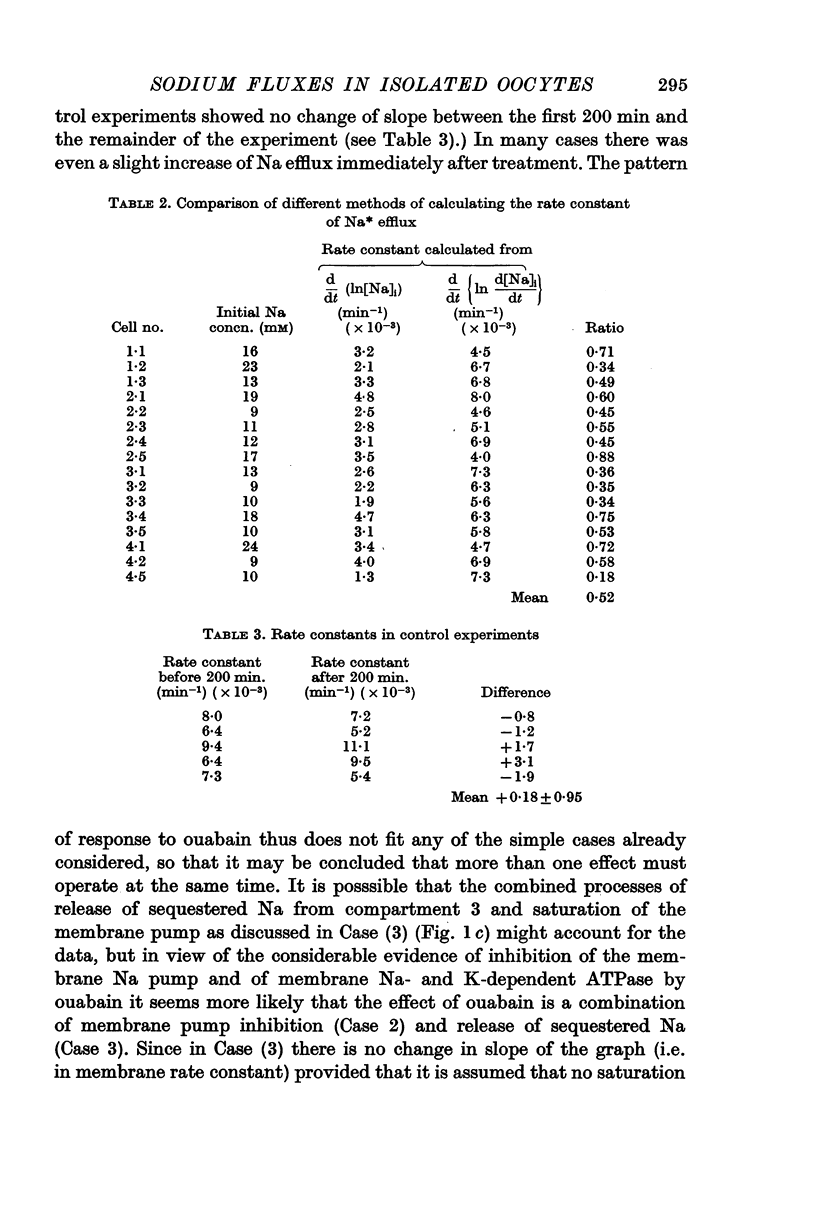
1. The rate constant for Na efflux from the oocyte calculated from (d/dt) (ln [Na*]i]) is only approximately 52% of that calculated from (d/dt)[(ln(d[Na*]i)dt)]. The difference may be interpreted by supposing that 48% of the internal Na of the oocyte is either bound to proteins or sequestered in cell organelles.
2. The mean rate constant for Na efflux was 6·4 × 10-3 min-1 corresponding to an apparent Na efflux rate of 13·3 p-mole/cm2.sec. When this is corrected for the increase in surface area produced by microvilli the true efflux rate is 1·1-1·3 p-mole/cm2.sec.
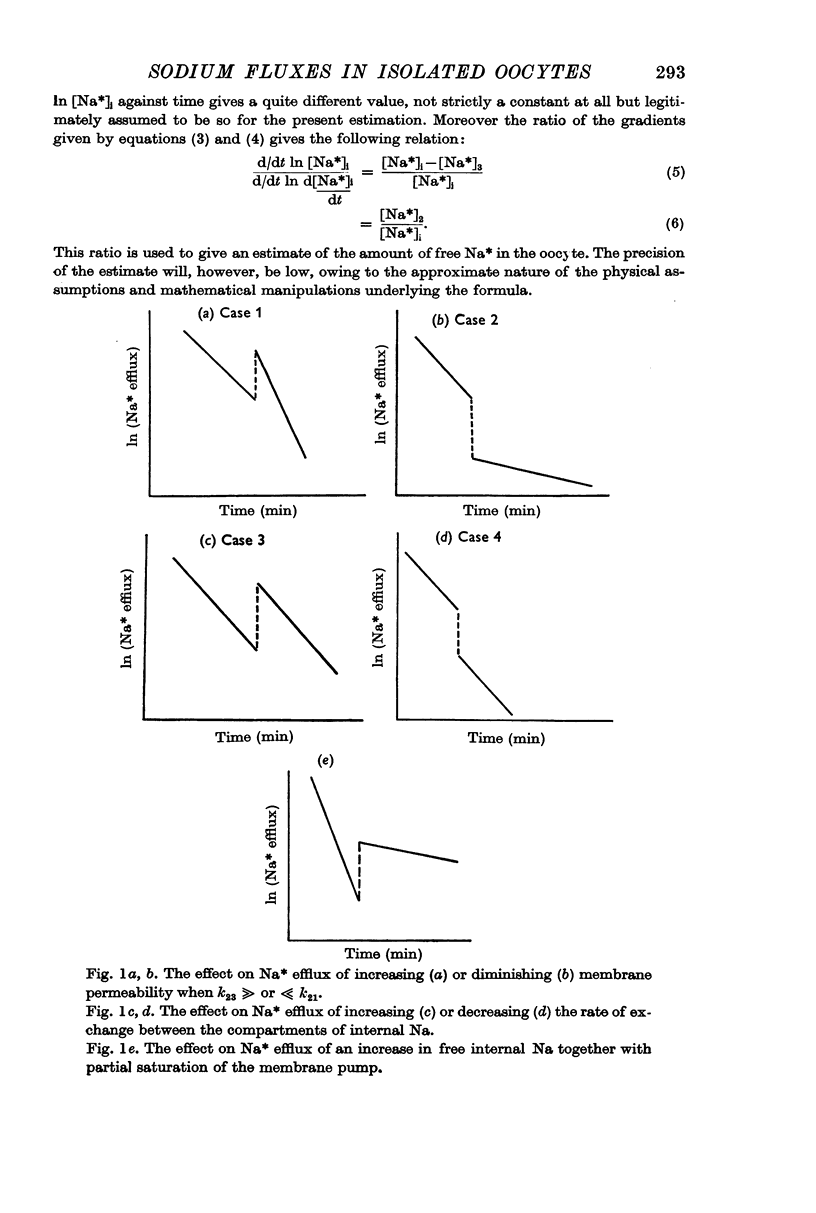
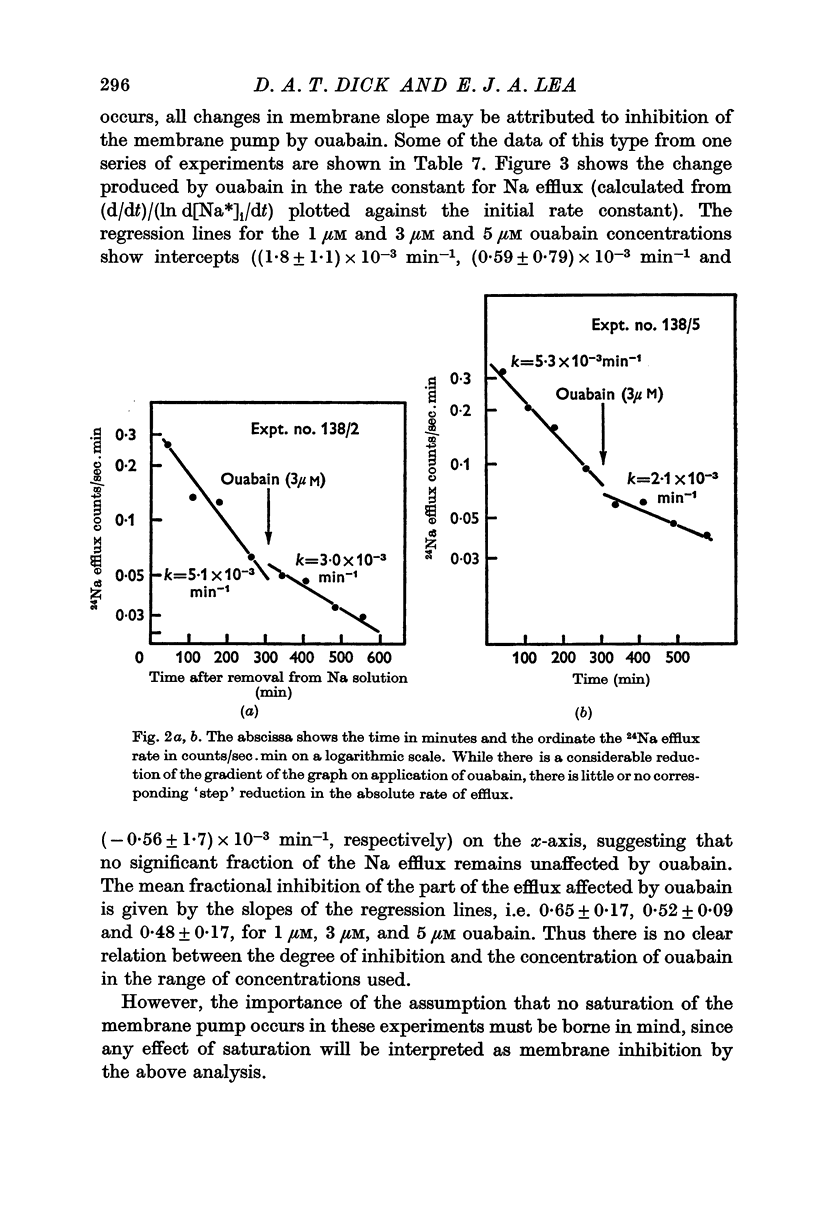
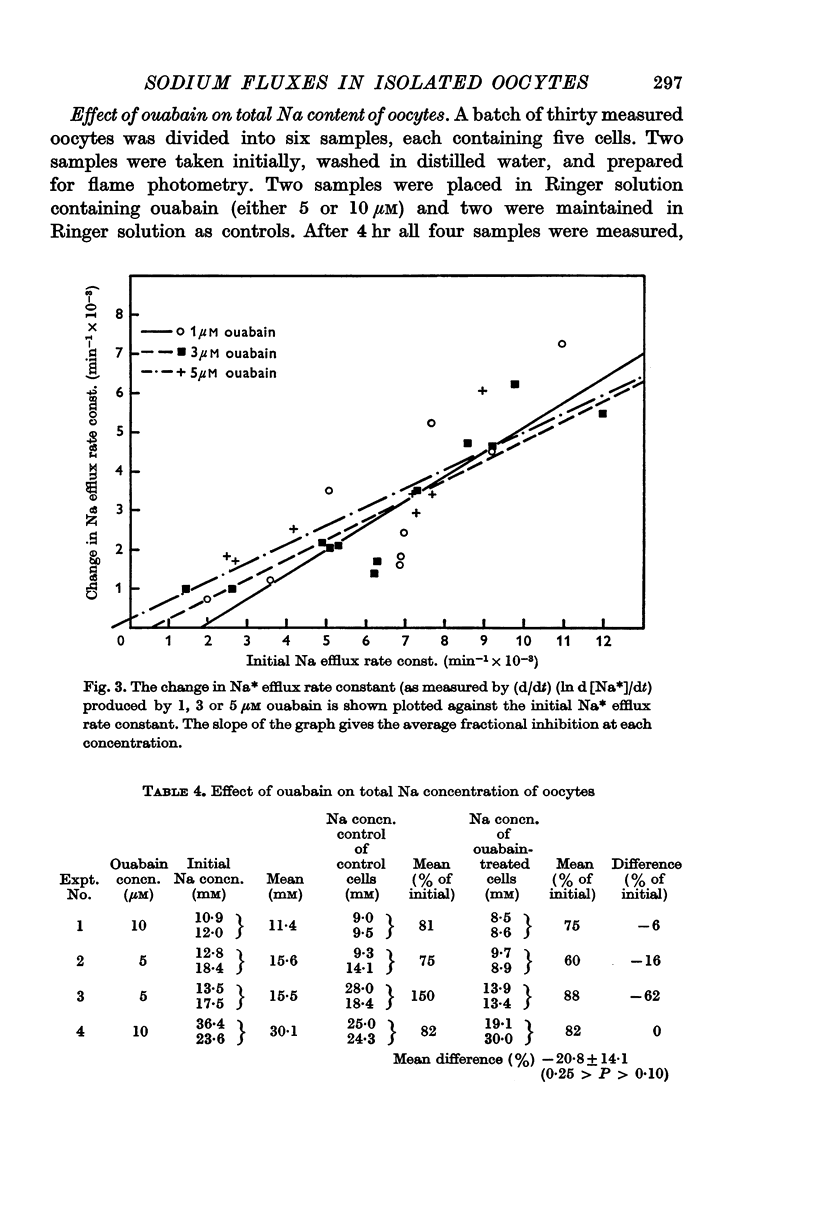
3. The action of ouabain (1-5 μM) appears to involve two different effects: (a) there is 48-65% inhibition of the membrane Na pump, and (b) there is a release of some of the sequestered Na in the cell.
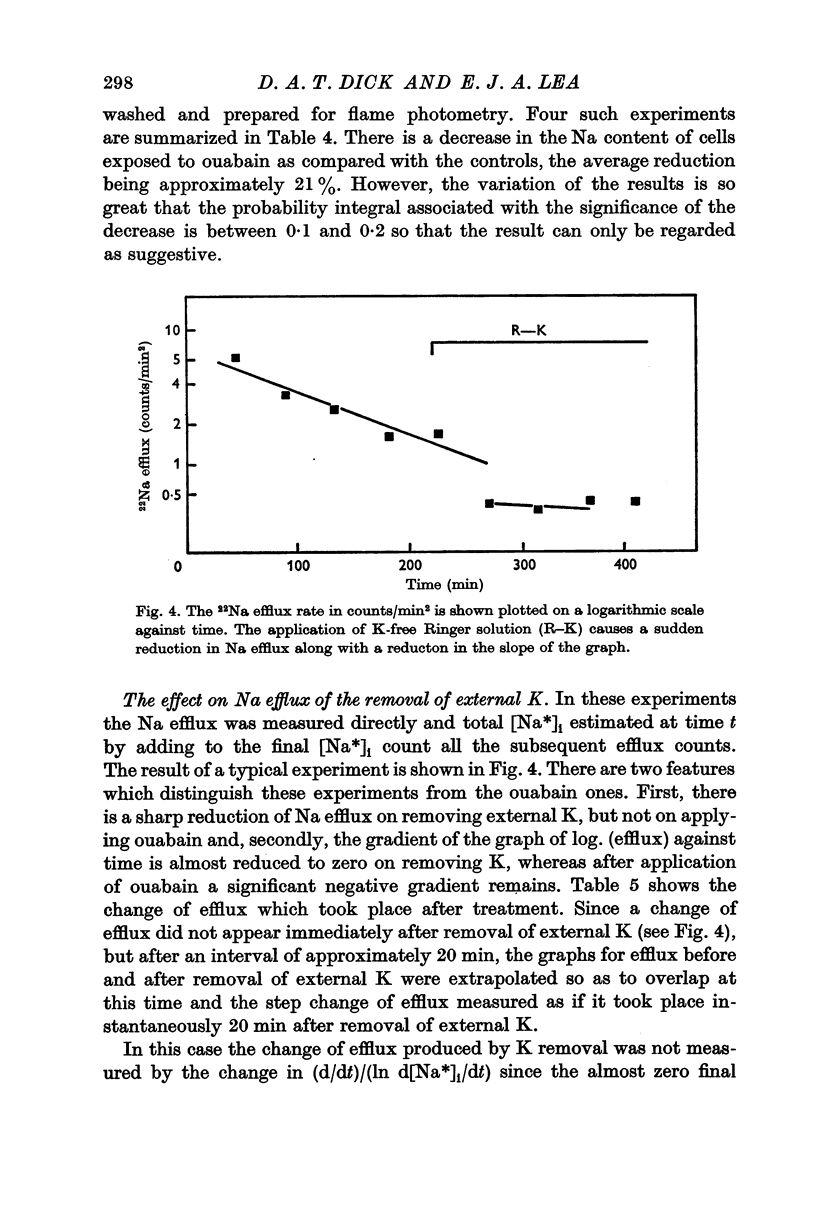
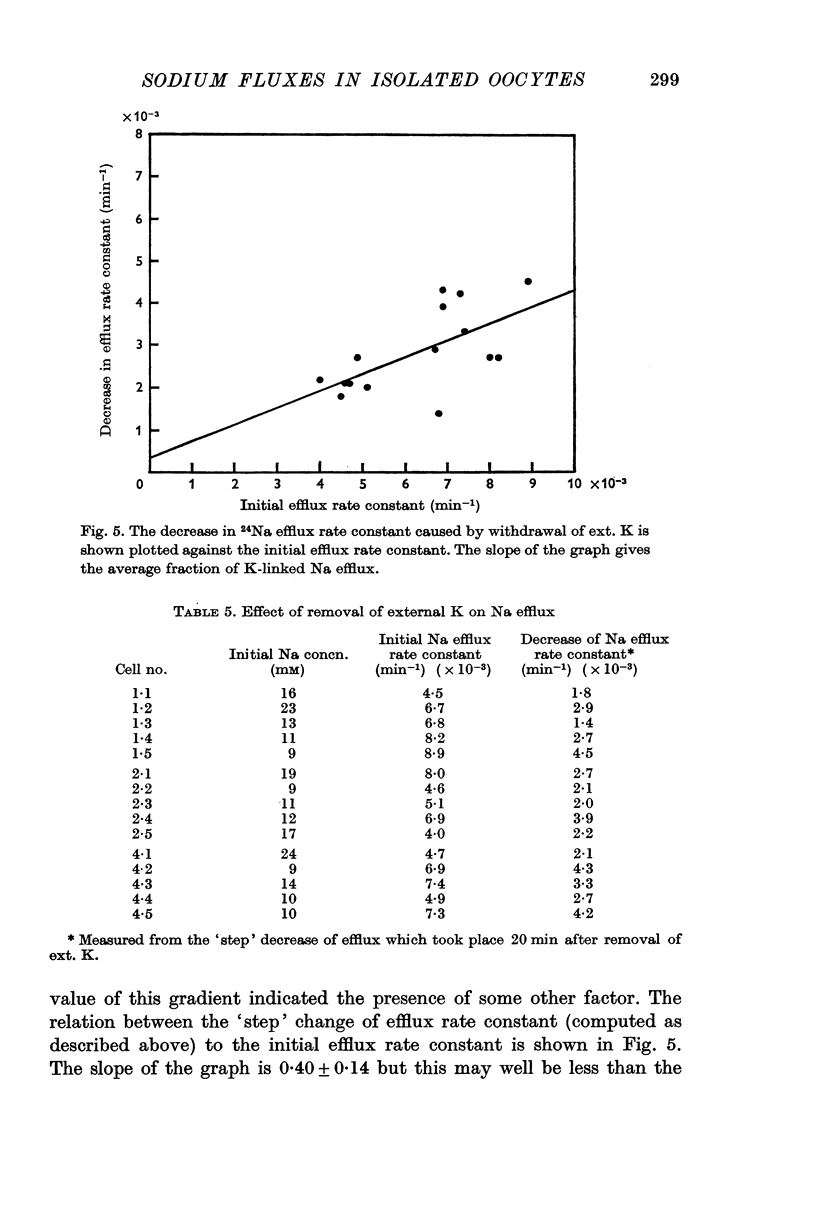
4. Removal of external K causes a 40% reduction in Na efflux although this value may be an underestimation owing to the presence of K which has leaked from the cell and may be retained near the cell surface.
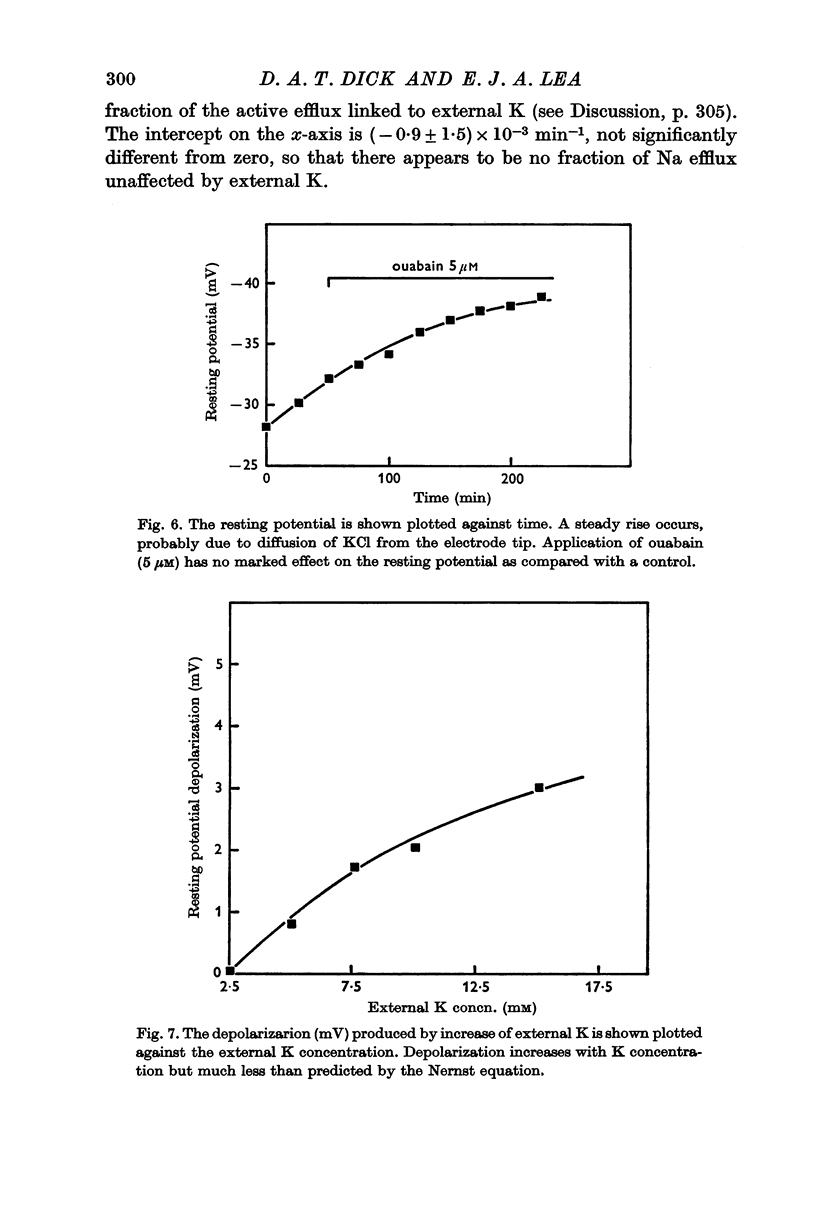
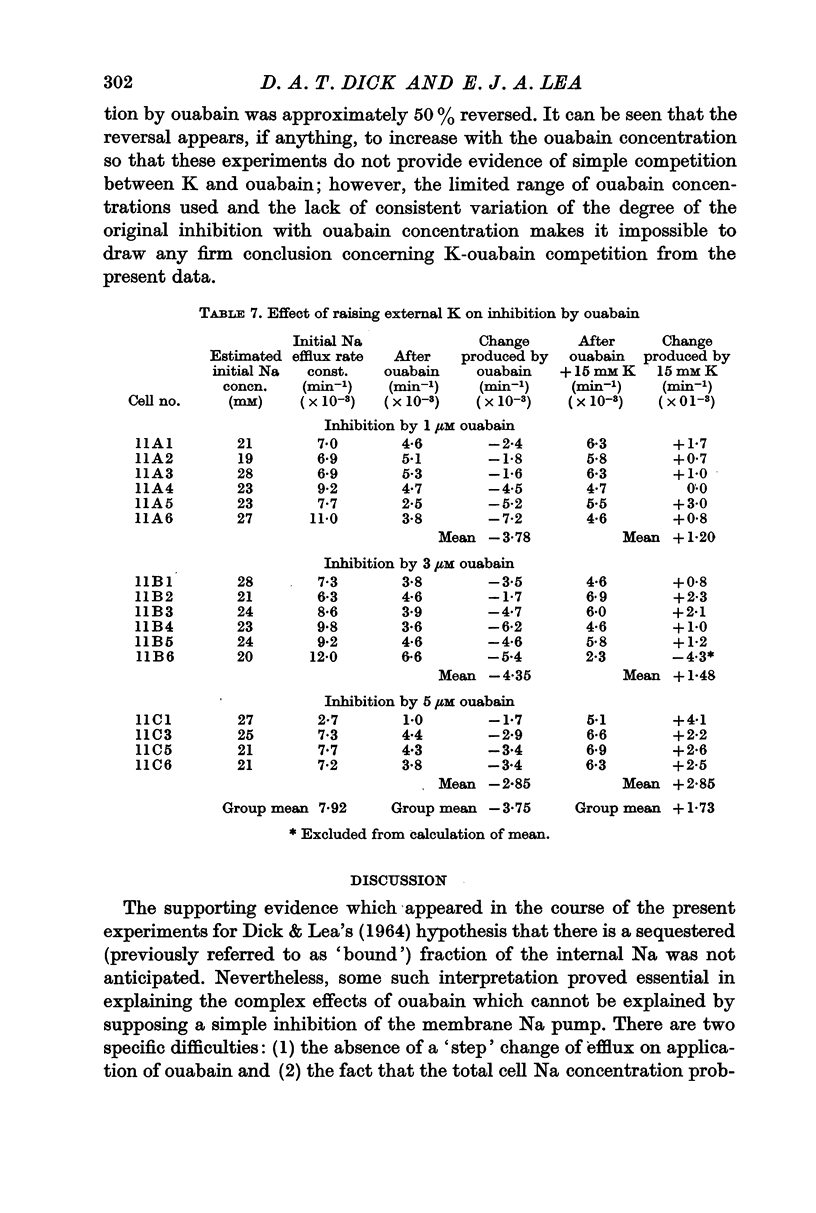
5. Raising the external K concentration to 15 mM reduces the inhibitory effect of ouabain by approximately a half.
6. It was concluded that the Na pump in the toad oocyte may have a slightly lower level of activity than that in frog muscle, but that its general properties are similar to those in frog muscle and some other animal cells.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Slayman C. L. Membrane potential and conductance during transport of sodium, potassium and rubidium in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):970–1014. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHARNOCK J. S., ROSENTHAL A. S., POST R. L. STUDIES OF THE MECHANISM OF CATION TRANSPORT. II. A PHOSPHORLATED INTERMEDIATE IN THE CATION STIMULATED ENZYMIC HYDROLYSIS OF ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1963 Dec;41:675–686. doi: 10.1038/icb.1963.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY E. J., KERNAN R. P., ZADUNAISKY J. A. The sodium pump in skeletal muscle in relation to energy barriers. J Physiol. 1961 Feb;155:263–279. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cope F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance evidence for complexing of sodium ions in muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):225–227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. B., Keynes R. D., Rybová R. The coupling of sodium efflux and potassium influx in frog muscle. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(4):865–880. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEE E., KERNAN R. P. Energetics of sodium transport in Rana pipiens. J Physiol. 1963 Mar;165:550–558. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DICK D. A., LEA E. J. NA FLUXES IN SINGLE TOAD OOCYTES WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE EFFECT OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL NA CONCENTRATION ON NA EFFLUX. J Physiol. 1964 Oct;174:55–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS C., HARRIS E. J. Factors influencing the sodium movement in frog muscle with a discussion of the mechanism of sodium movement. J Physiol. 1957 Mar 11;135(3):567–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. Sodium and potassium movements in human red cells. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):278–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. THE ACTION OF CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES ON ION MOVEMENTS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Dec;16:381–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. The action of cardiac glycosides on sodium and potassium movements in human red cells. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):148–173. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J. THE DEPENDENCE OF EFFLUX OF SODIUM FROM FROG MUSCLE ON INTERNAL SODIUM AND EXTERNAL POTASSIUM. J Physiol. 1965 Apr;177:355–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINKE J. A. The measurement of sodium and potassium activities in the squid axon by means of cation-selective glass micro-electrodes. J Physiol. 1961 Apr;156:314–335. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Movements of Na and K in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1959 Mar 3;145(2):405–432. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Active transport of cations in giant axons from Sepia and Loligo. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):28–60. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOROWICZ P., GERBER C. J. EFFECTS OF EXTERNAL POTASSIUM AND STROPHANTHIDIN ON SODIUM FLUXES IN FROG STRIATED MUSCLE. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Jan;48:489–514. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.3.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMP N. E. Electron microscopy of growing oocytes of Rana pipiens. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 May 25;2(3):281–292. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERKUT G. A., THOMAS R. C. AN ELECTROGENIC SODIUM PUMP IN SNAIL NERVE CELLS. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1965 Jan;14:167–183. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(65)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. SOME FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON THE SODIUM EFFLUX IN FROG MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:305–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., SWAN R. C. The effect of external sodium concentration on the sodium fluxes in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;147:591–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEV A. A. DETERMINATION OF ACTIVITY AND ACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS OF POTASSIUM AND SODIUM IONS IN FROG MUSCLE FIBRES. Nature. 1964 Mar 14;201:1132–1134. doi: 10.1038/2011132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAIZELS M., REMINGTON M., TRUSCOE R. The effects of certain physical factors and of the cardiac glycosides on sodium transfer by mouse ascites tumour cells. J Physiol. 1958 Jan 23;140(1):61–79. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCLANE T. K. A BIPHASIC ACTION OF OUABAIN ON SODIUM TRANSPORT IN THE TOAD BLADDER. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1965 Apr;148:106–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J., FRUMENTO A. S. The concentration dependence of sodium efflux from muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Mar;46:629–654. doi: 10.1085/jgp.46.4.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin S. G., Hinke J. A. Sodium and water binding in single striated muscle fibers of the giant barnacle. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1966 Sep;44(5):837–848. doi: 10.1139/y66-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGE E., GOERKE R. J., STORM S. R. CAT HEART MUSCLE IN VITRO. IV. INHIBITION OF TRANSPORT IN QUIESCENT MUSCLES. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jan;47:531–543. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.3.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATLAK C. S. Derivation of an equation for the diffusion potential. Nature. 1960 Dec 10;188:944–945. doi: 10.1038/188944b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., MERRITT C. R., KINSOLVING C. R., ALBRIGHT C. D. Membrane adenosine triphosphatase as a participant in the active transport of sodium and potassium in the human erythrocyte. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jun;235:1796–1802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. F., Lasseter K. C., Melvin S. L. Stimulation of Na+ and K+ dependent adenosine triphosphatase by ouabain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Mar;113(3):629–633. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


