Abstract
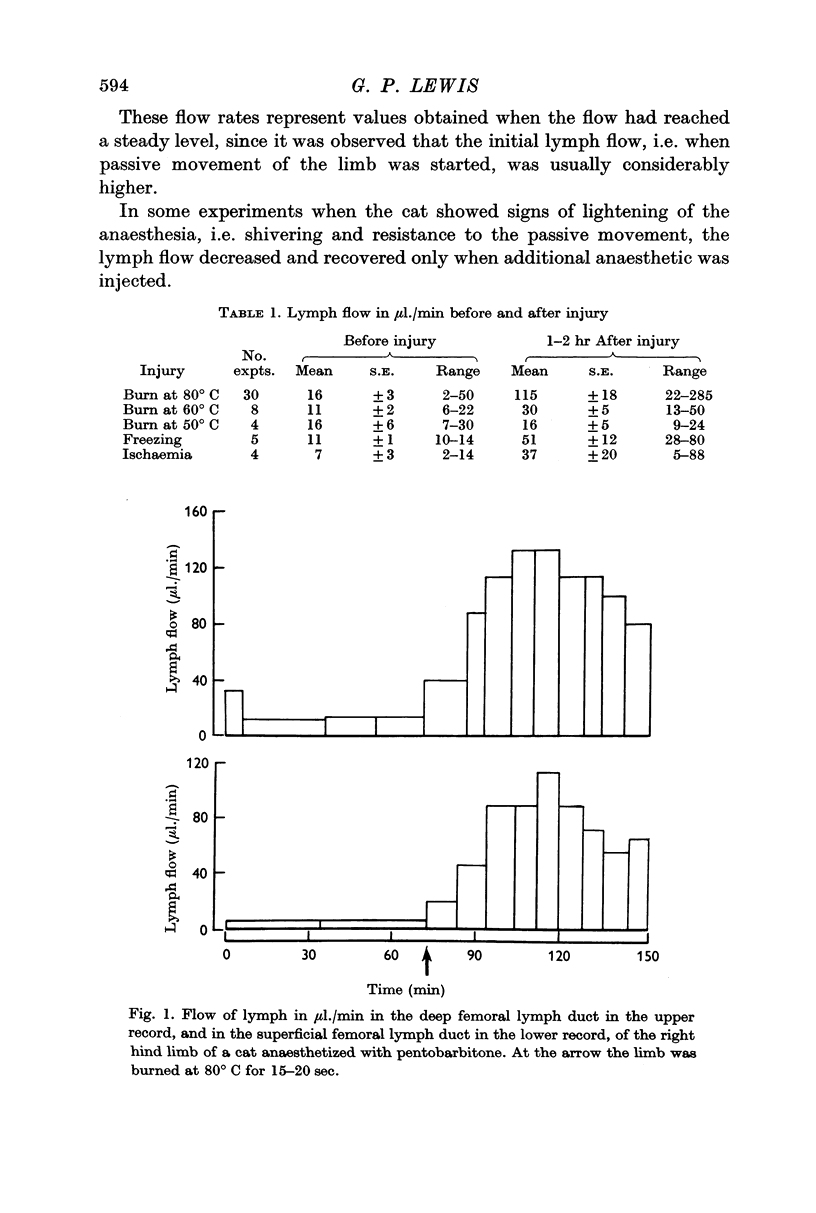
1. Lymph was collected directly from the hind limb of cats anaesthetized with pentobarbitone before and for several hours after the limb was injured.
2. After the limb was subjected to very mild injury such as hot water at 50° C or ischaemia for 1 hr there was no increase in protein or enzyme concentrations in the lymph, although after the ischaemia there was an increase in lymph flow.
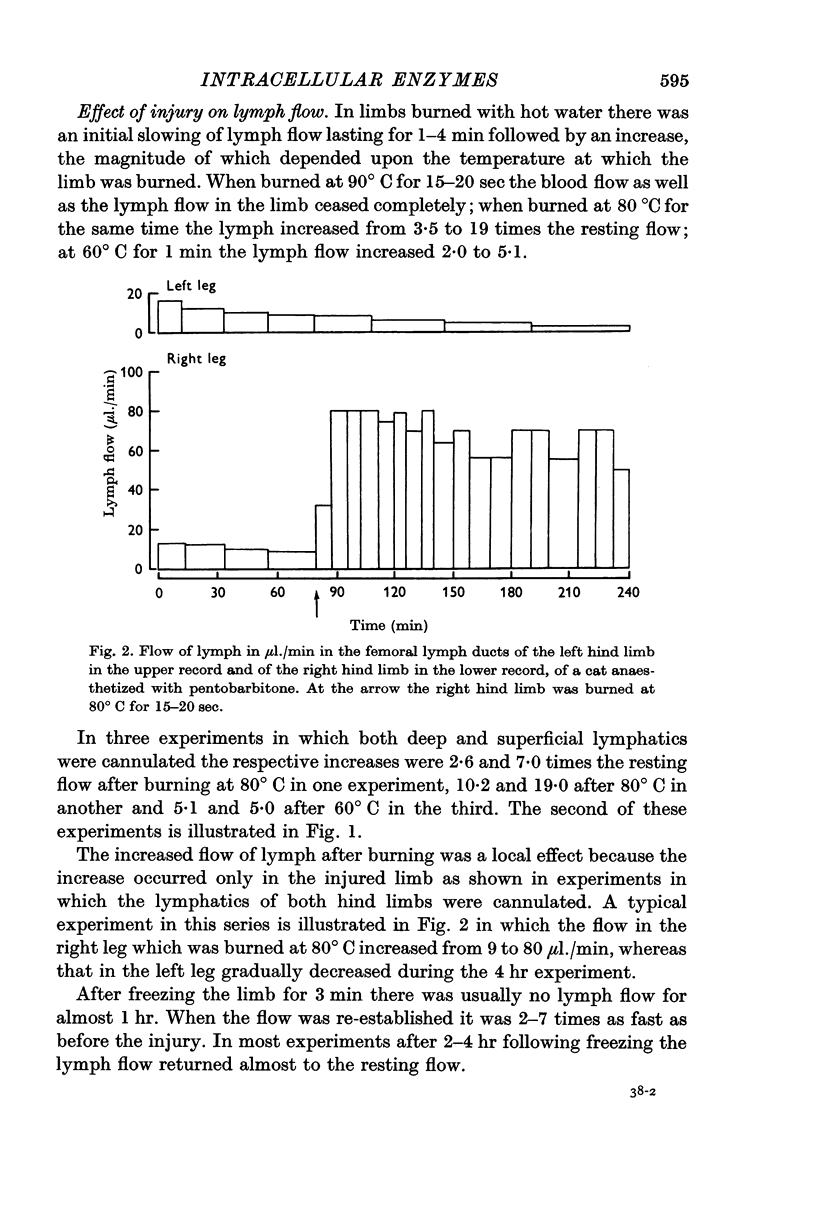
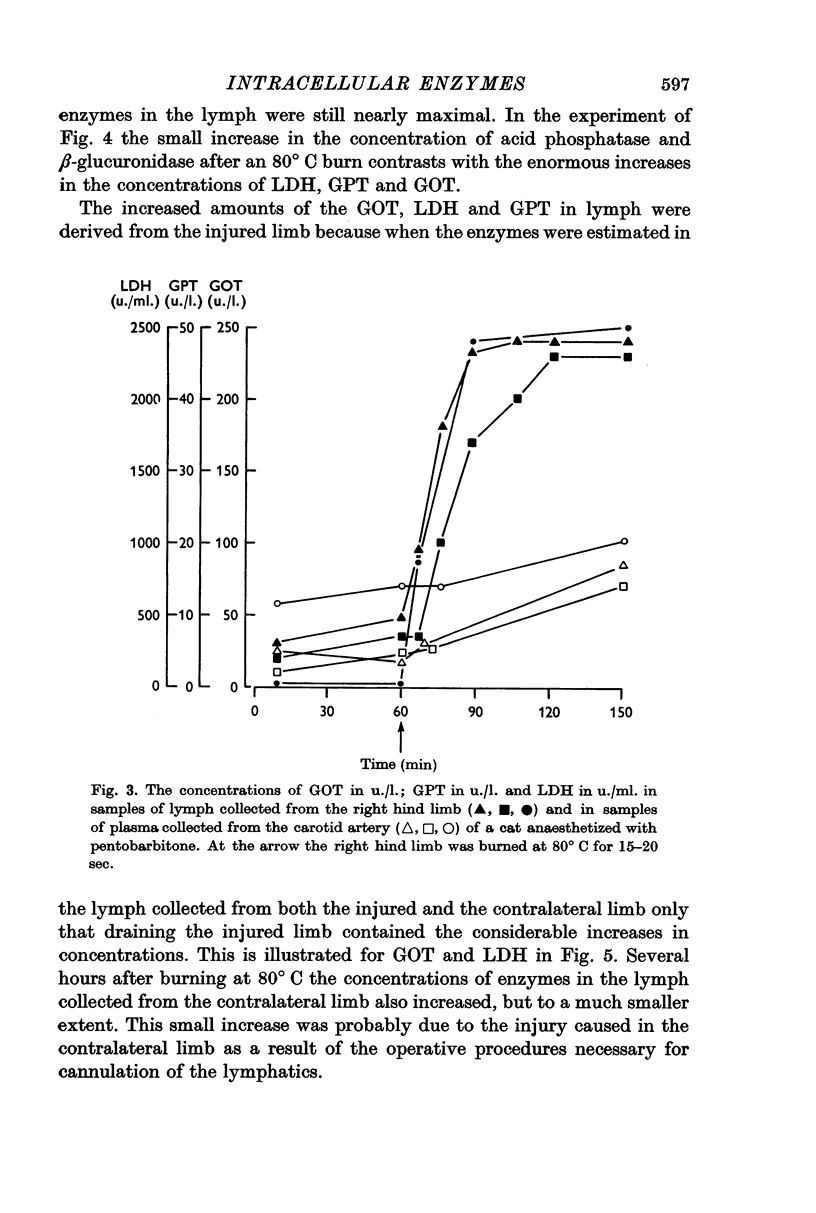
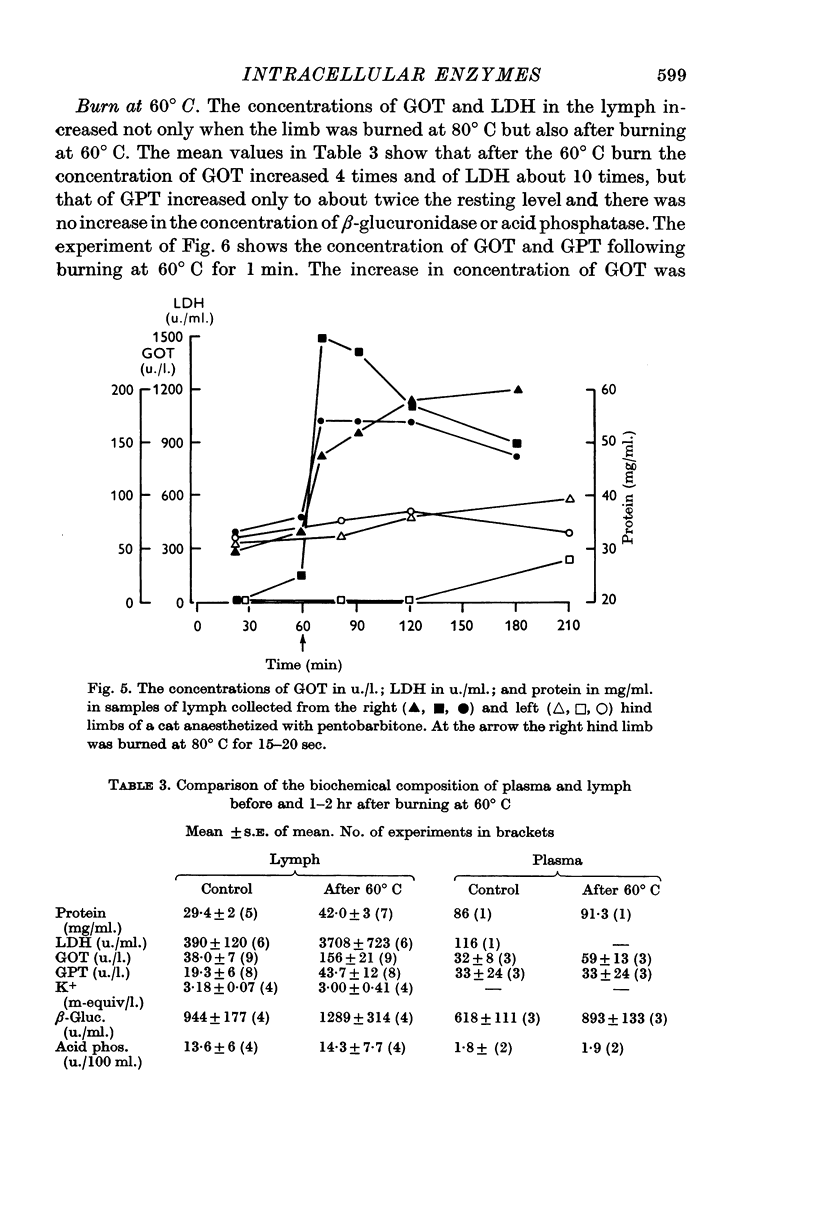
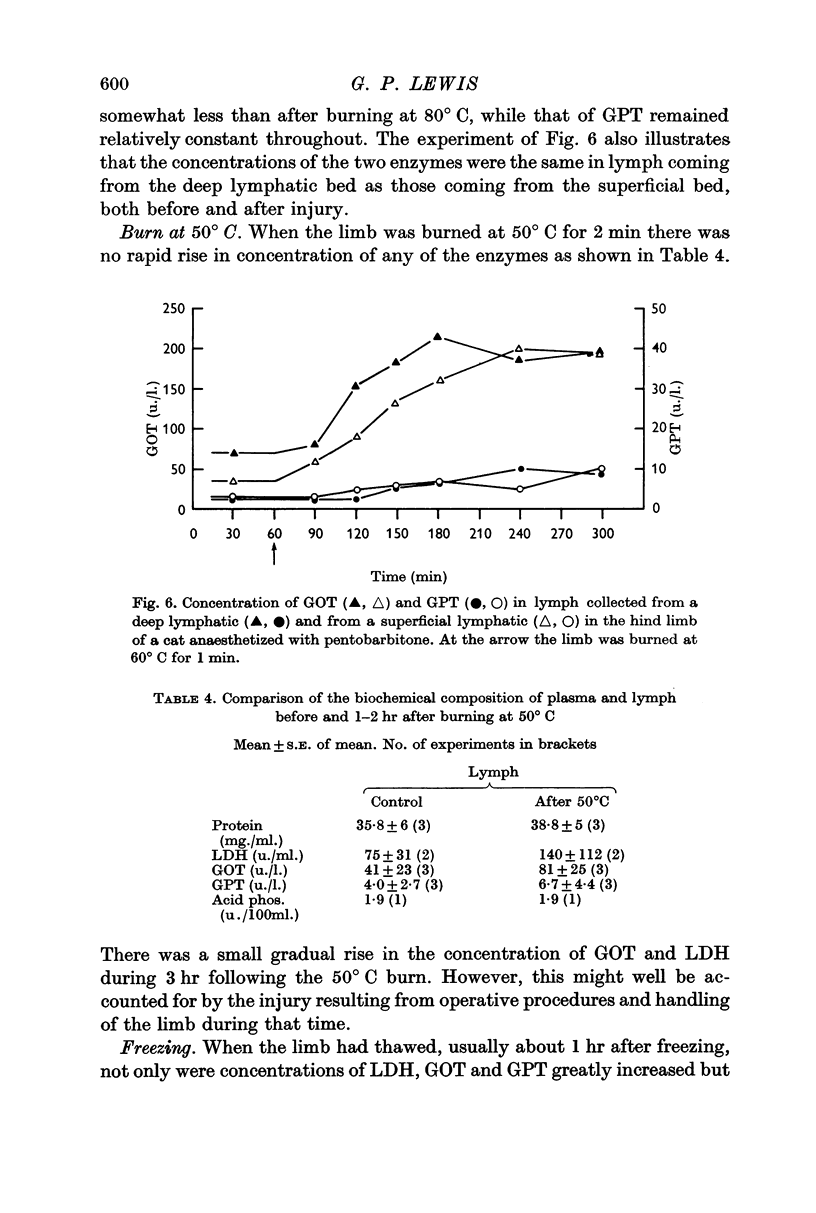
3. After burning the limb at 60° C there was a significant increase in the concentrations of the cytoplasmic enzymes glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase and lactic dehydrogenase, as a result of an increased permeability of the cell membrane.
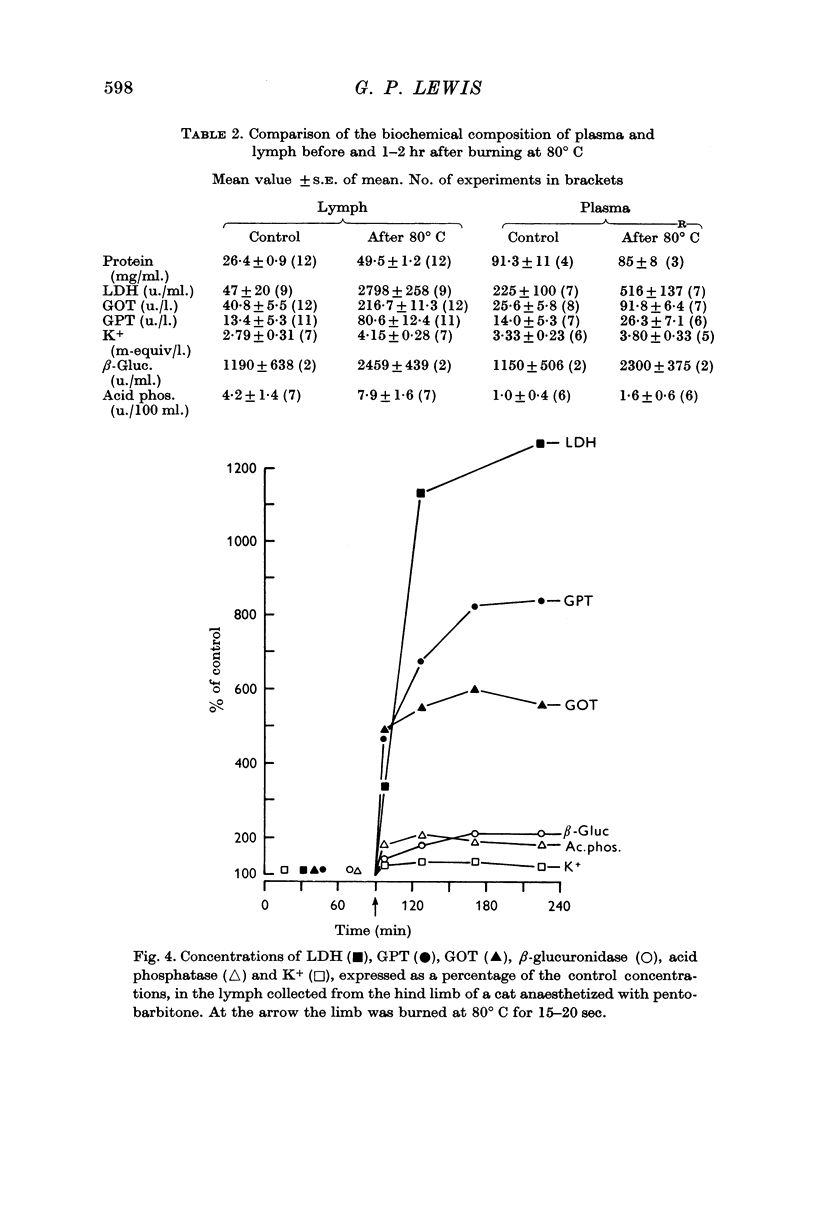
4. When the limb was burned at 80° C there was a marked increase not only in the cytoplasmic enzymes but also in the mitochondrial enzyme glutamic pyruvic transaminase. Thus with the stronger burn the permeability of the intracellular mitochondrial membrane was also increased.
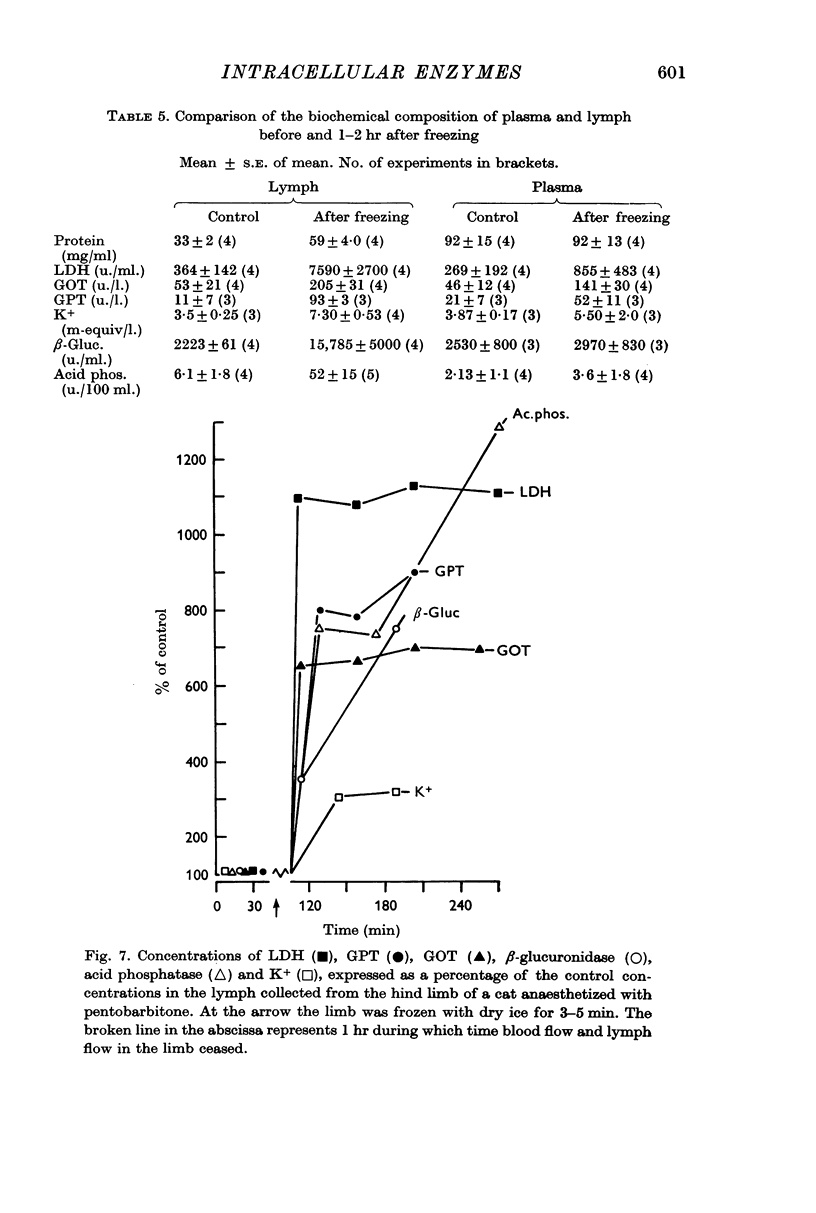
5. Not until the most severe injury of all, i.e. freezing the limb solid, was there an increase in the concentration of lysosomal enzymes in the lymph.
6. It is concluded that estimation of intracellular enzymes in the lymph draining an injured tissue affords a method of assessing the extent of cellular injury.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DE DUVE C., BEAUFAY H. Tissue fractionation studies. 10. Influence of ischaemia on the state of some bound enzymes in rat liver. Biochem J. 1959 Dec;73:610–616. doi: 10.1042/bj0730610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAUSS W. H., LEPPELMANN H. J. Reactive changes of enzyme activities in serum and liver as symptoms of acute syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Oct 13;75(1):250–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb36871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARMEN A., WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Transaminase activity in human blood. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jan;34(1):126–131. doi: 10.1172/JCI103055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LADUE J. S., WROBLEWSKI F., KARMEN A. Serum glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase activity in human acute transmural myocardial infarction. Science. 1954 Sep 24;120(3117):497–499. doi: 10.1126/science.120.3117.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REES K. R., SINHA K. P. Blood enzymes in liver injury. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1960 Oct;80:297–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater T. F., Greenbaum A. L. Changes in lysosomal enzymes in acute experimental liver injury. Biochem J. 1965 Aug;96(2):484–491. doi: 10.1042/bj0960484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater T. F., Sträuli U. D., Sawyer B. C. Changes in liver nucleotide concentrations in experimental liver injury. 1. Carbon tetrachloride poisoning. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):260–266. doi: 10.1042/bj0930260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase in cardiac with hepatic disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Apr;91(4):569–571. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


