Abstract
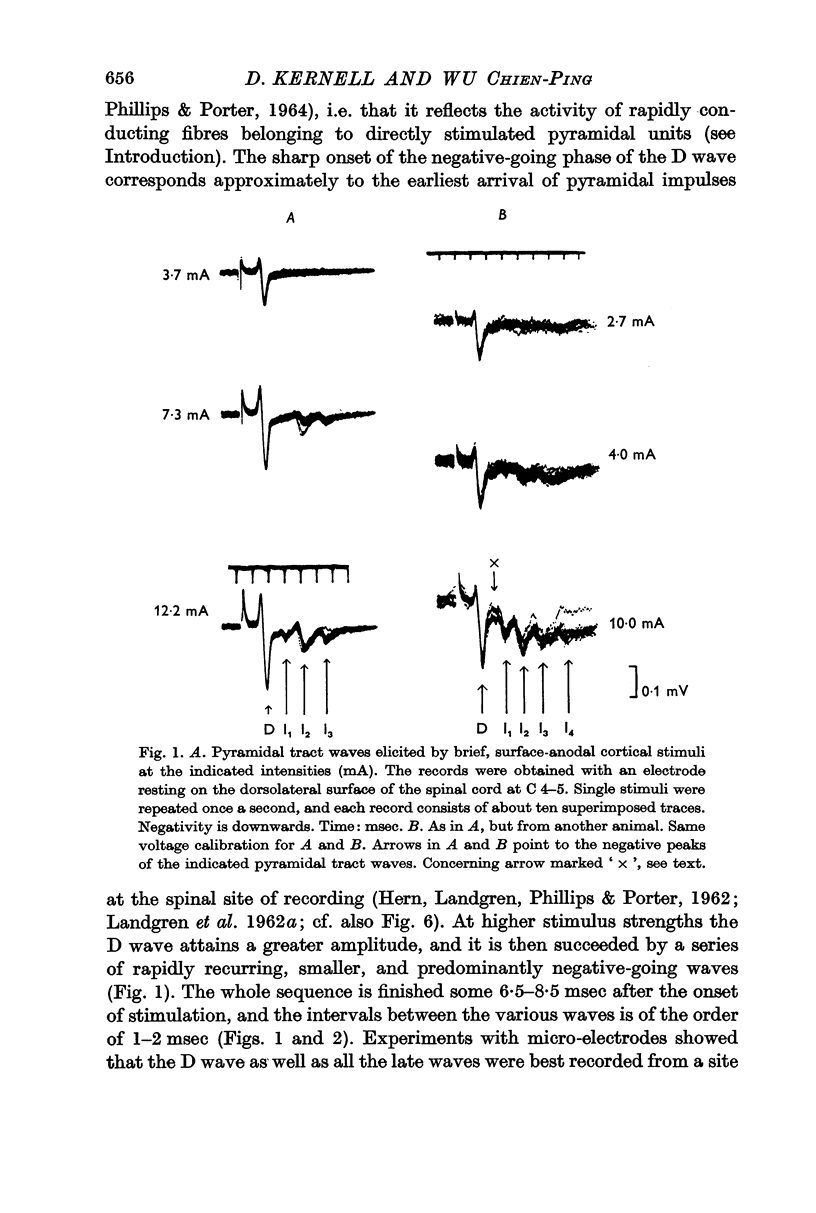
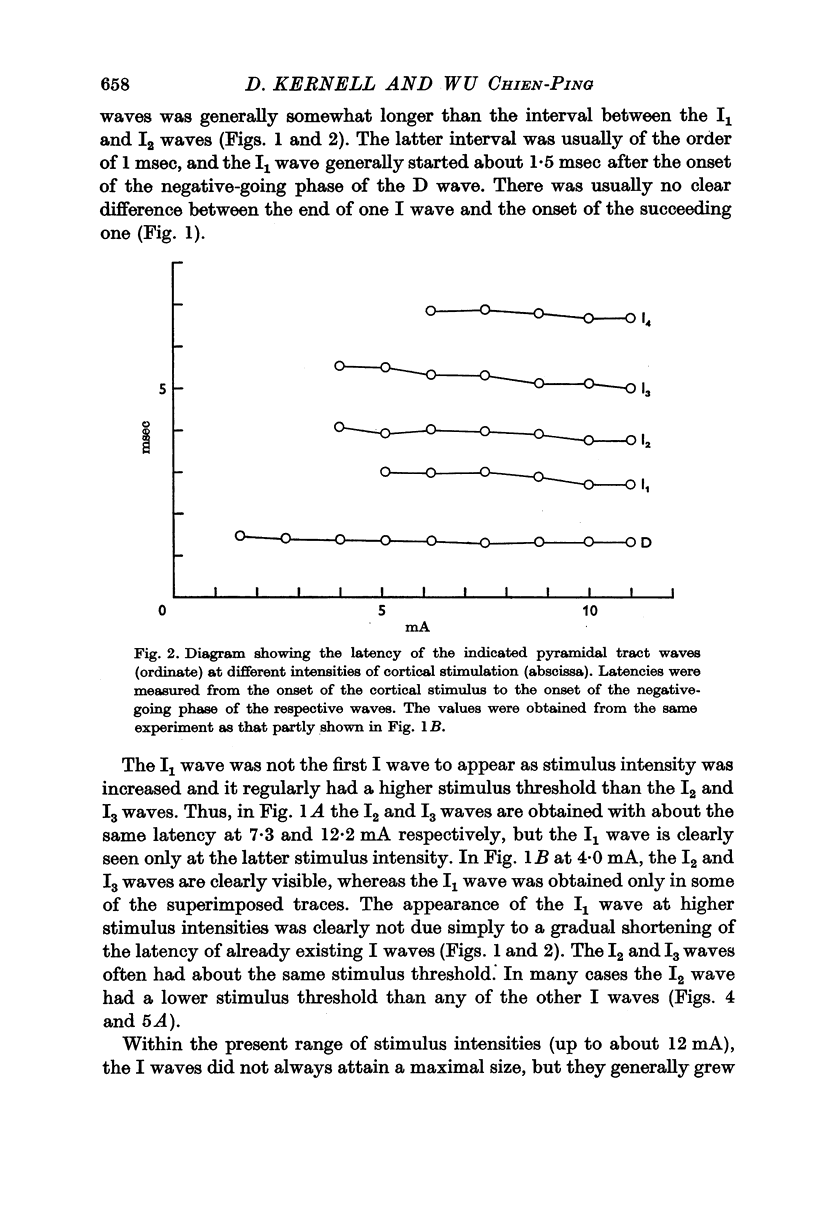
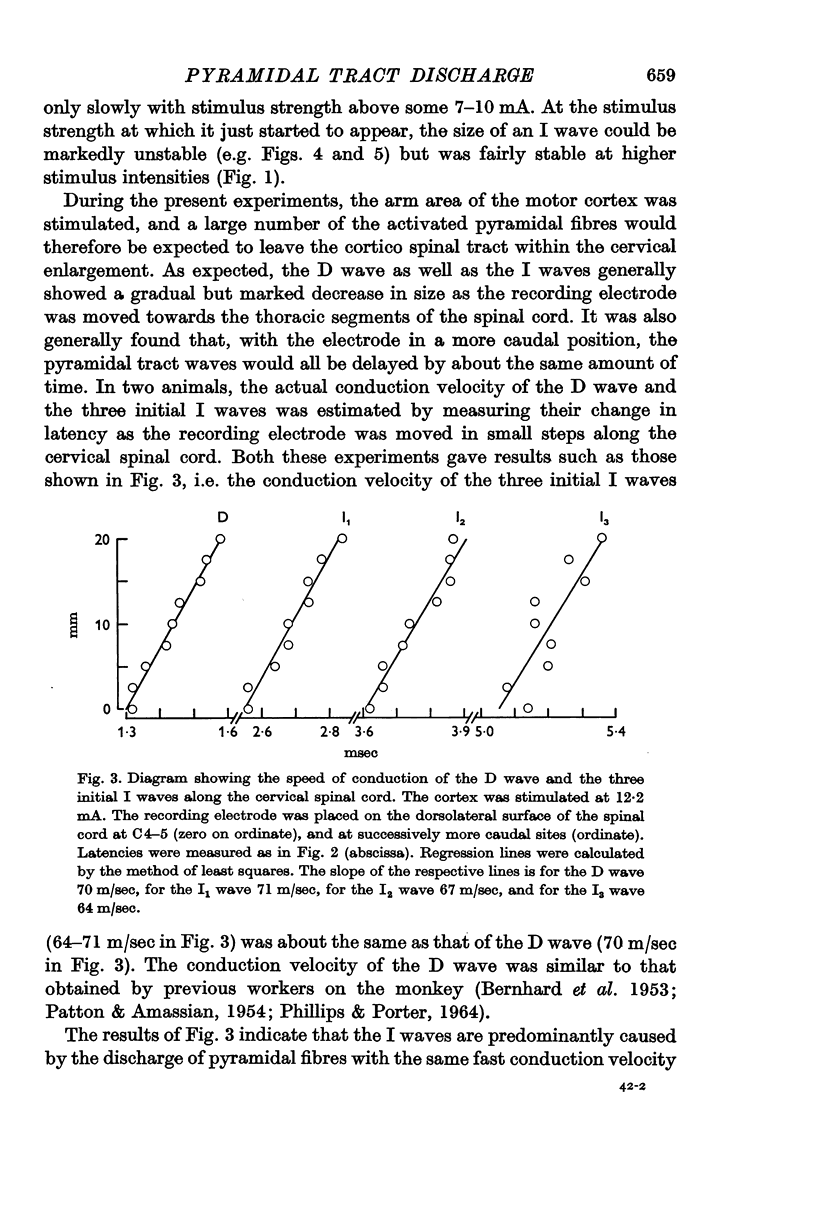
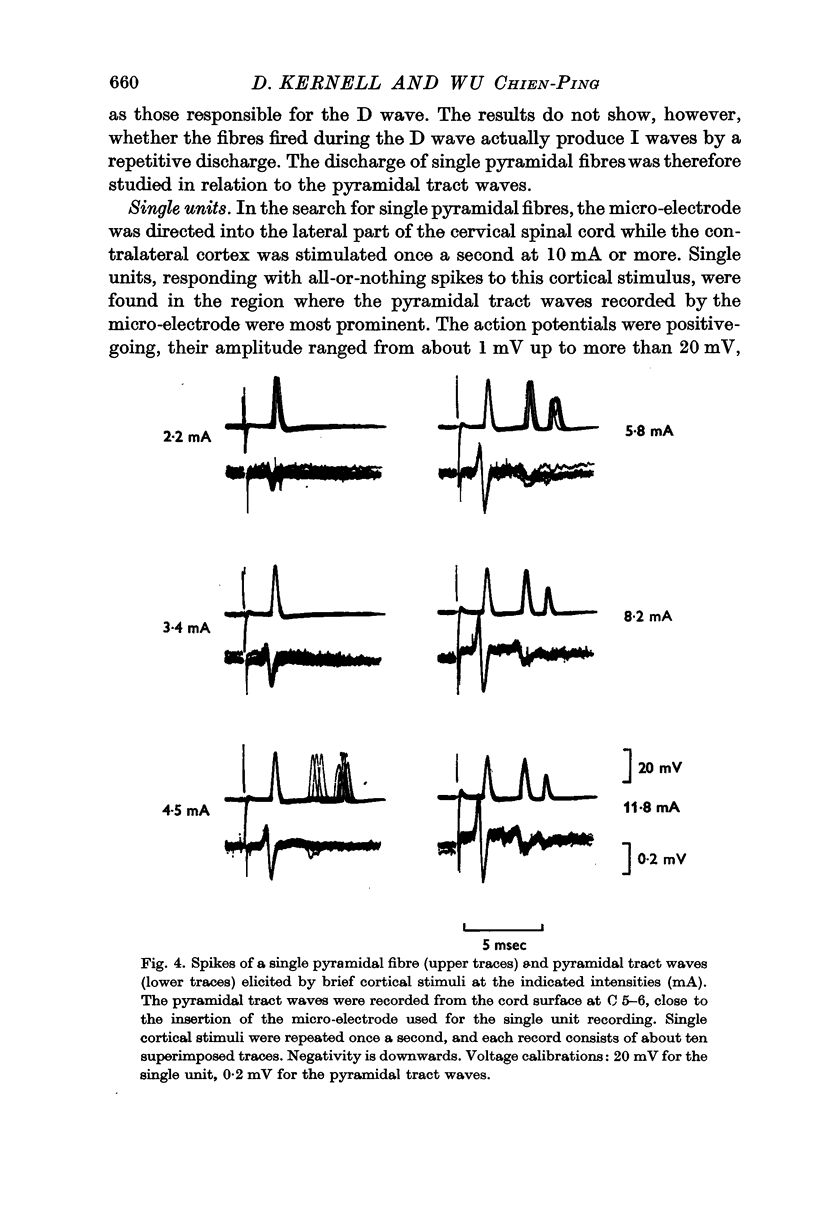
1. The arm area of the baboon's precentral motor cortex was stimulated by brief surface-anodal pulses, and the discharge of the corticospinal tract (the `pyramidal tract waves') was recorded by an electrode resting on the dorsolateral surface of the cervical spinal cord.
2. Some properties of the pyramidal tract waves were described, and they were also studied in relation to the firing of single cortico spinal fibres.
3. The results led to the conclusion that the later pyramidal tract waves (the `I waves') were almost exclusively due to a semi-synchronous repetitive discharge of the same fast cortico spinal fibres as those responsible for the initial wave (the `D wave').
4. Some problems concerning the origin and significance of the I waves were discussed.
Full text
PDF



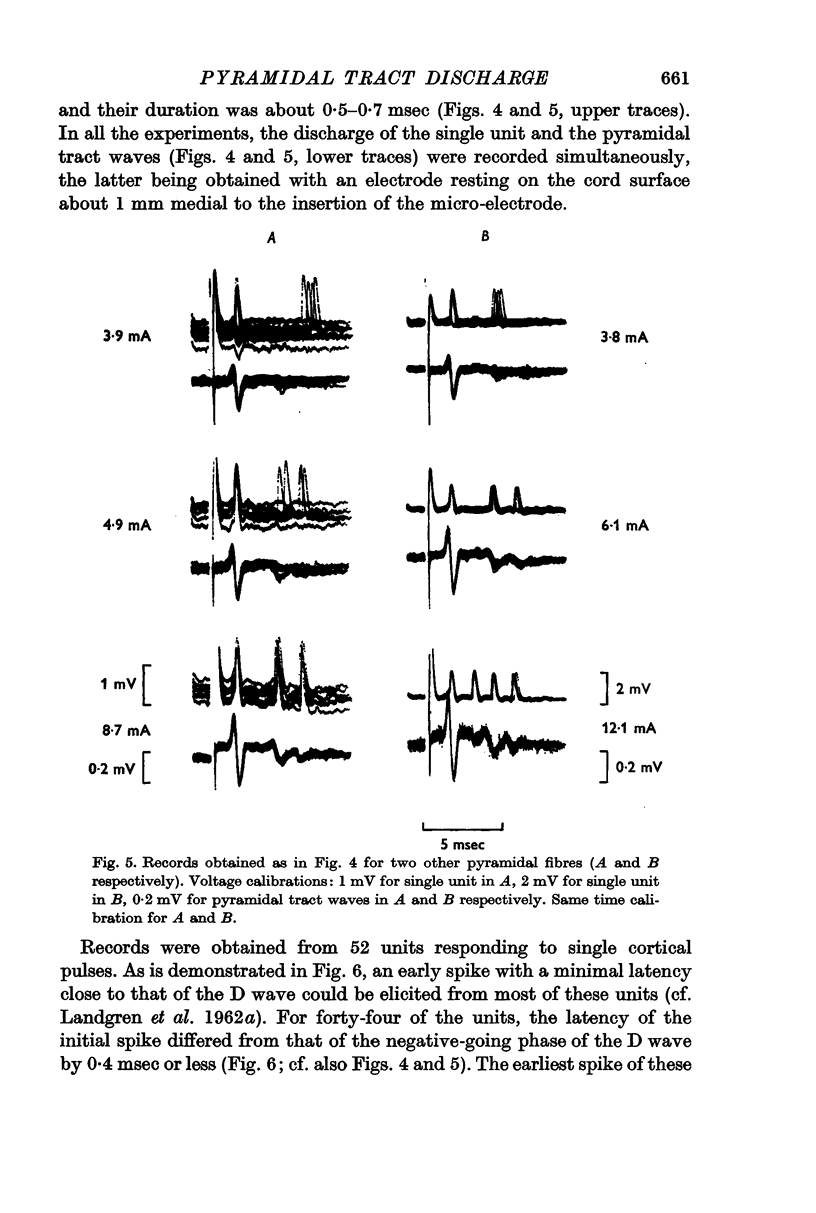
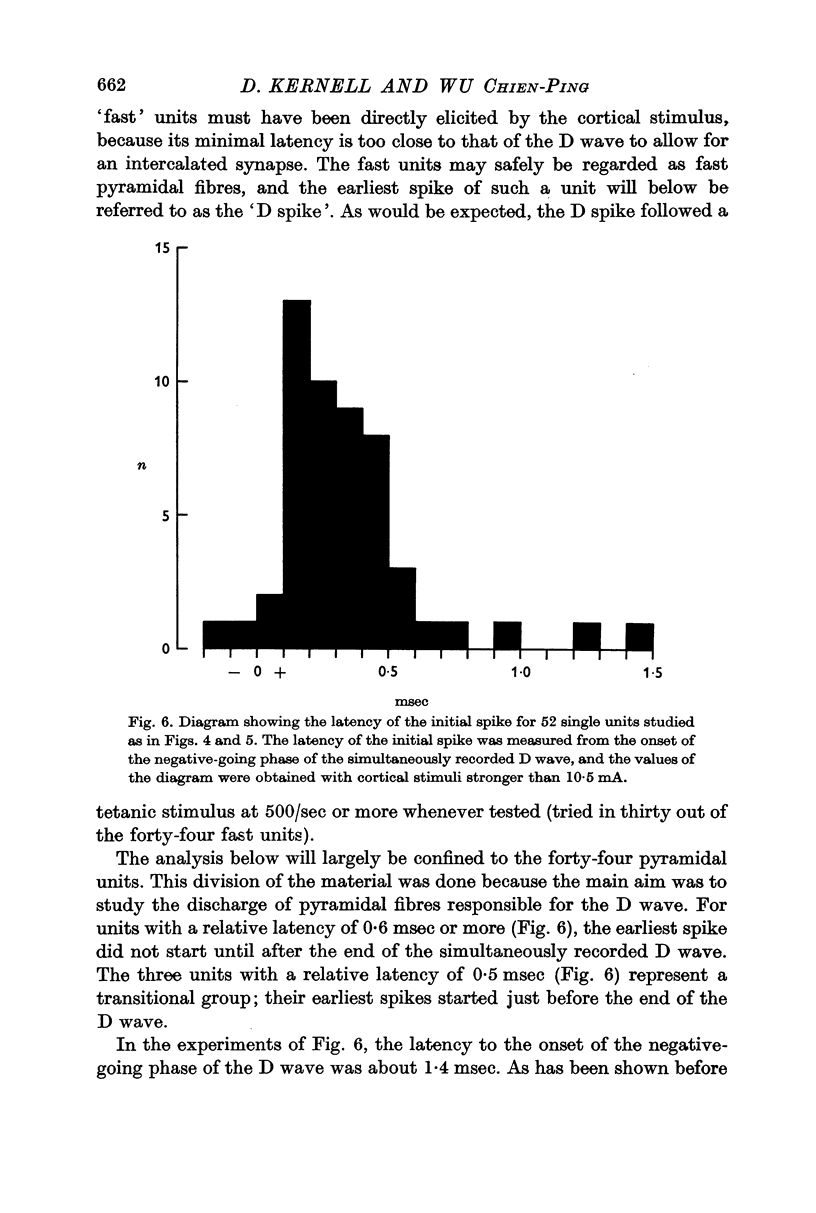

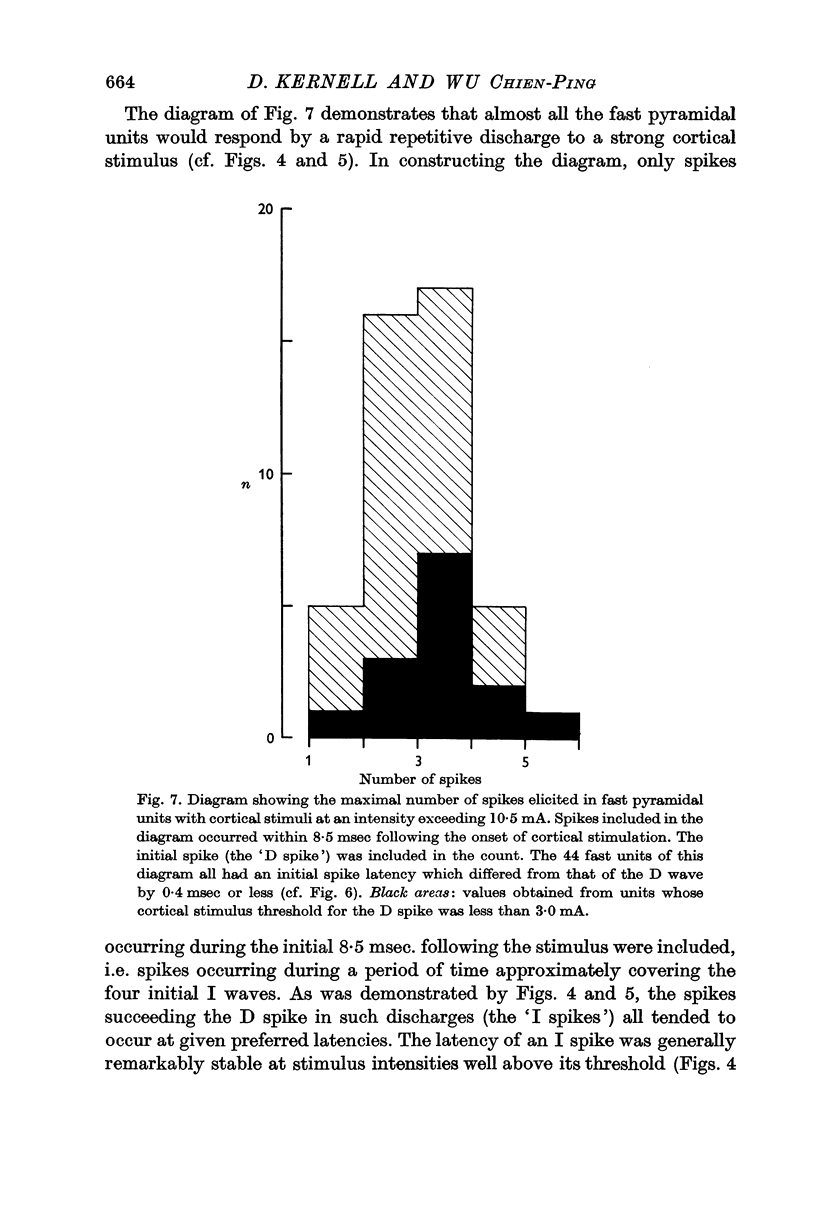
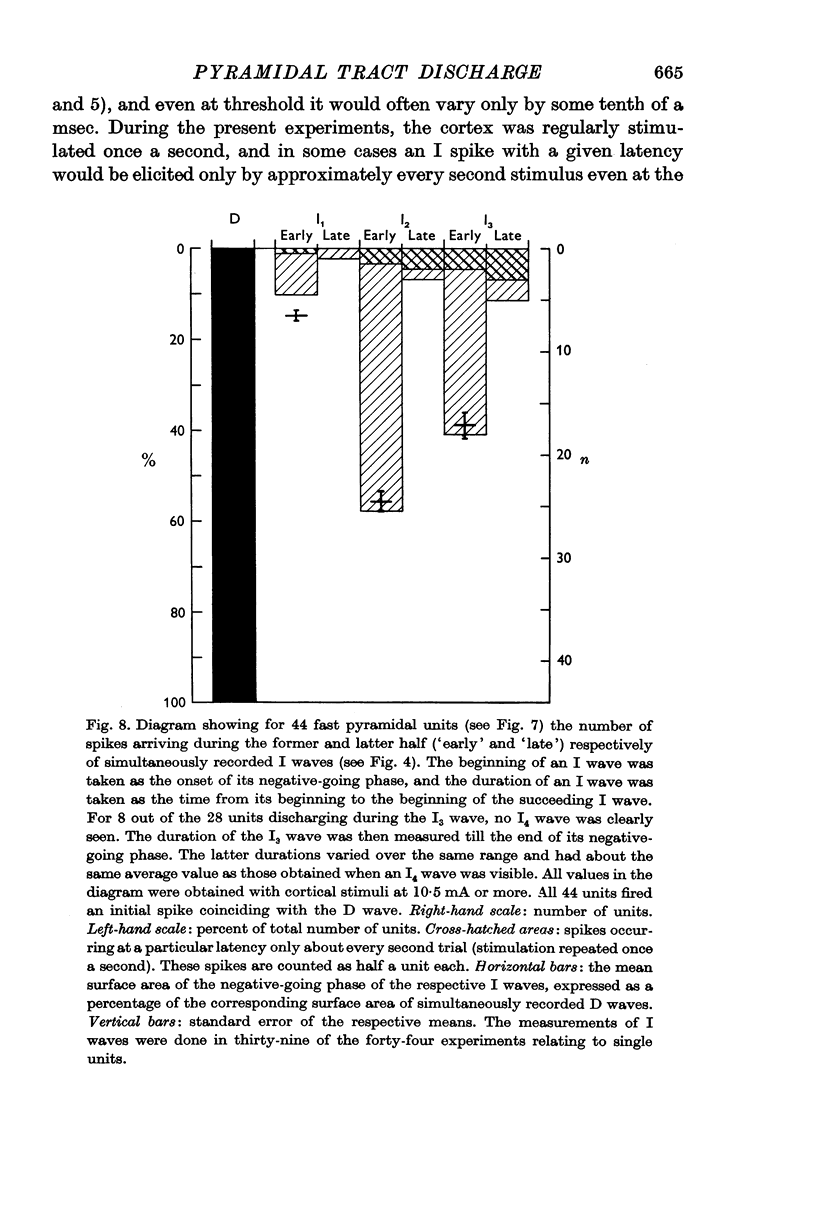







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian E. D., Moruzzi G. Impulses in the pyramidal tract. J Physiol. 1939 Dec 14;97(2):153–199. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1939.sp003798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERLIN L. EFFECTS OF SEIZURES ON SINGLE PYRAMIDAL TRACT NEURONS. Arch Neurol. 1964 Mar;10:271–282. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460150041004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTRAND G. Spinal efferent pathways from the supplementary motor area. Brain. 1956 Sep;79(3):461–473. doi: 10.1093/brain/79.3.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREUTZFELDT O. D., LUX H. D., NACIMIENTO A. C. INTRACELLULAERE REIZUNG CORTICALER NERVENZELLEN. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1964 Oct 5;281:129–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVARTS E. V. RELATION OF DISCHARGE FREQUENCY TO CONDUCTION VELOCITY IN PYRAMIDAL TRACT NEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Mar;28:216–228. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evarts E. V. Pyramidal tract activity associated with a conditioned hand movement in the monkey. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Nov;29(6):1011–1027. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.6.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman A. L. Differential patterns of activation of the pyramidal system elicited by surface anodal and cathodal cortical stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1966 Jul;29(4):547–564. doi: 10.1152/jn.1966.29.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERN J. E., LANDGREN S., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Selective excitation of corticofugal neurones by surface-anodal stimulation of the baboon's motor cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:73–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERN J. E., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Electrical thresholds of unimpaled corticospinal cells in the cat. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1962 Apr;47:134–140. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1962.sp001584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell D., Chien-Ping W. Post-synaptic effects of cortical stimulation on forelimb motoneurones in the baboon. J Physiol. 1967 Aug;191(3):673–690. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Cortical fields of origin of the monosynaptic pyramidal pathways to some alpha motoneurones of the baboon's hand and forearm. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:112–125. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S., PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Minimal synaptic actions of pyramidal impulses on some alpha motoneurones of the baboon's hand and forearm. J Physiol. 1962 Apr;161:91–111. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landau W. M., Bishop G. H., Clare M. H. Site of excitation in stimulation of the motor cortex. J Neurophysiol. 1965 Nov;28(6):1206–1222. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.6.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATTON H. D., AMASSIAN V. E. Single and multiple-unit analysis of cortical stage of pyramidal tract activation. J Neurophysiol. 1954 Jul;17(4):345–363. doi: 10.1152/jn.1954.17.4.345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. THE PYRAMIDAL PROJECTION TO MOTONEURONES OF SOME MUSCLE GROUPS OF THE BABOON'S FORELIMB. Prog Brain Res. 1964;12:222–245. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60625-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. G., PORTER R. Unifocal and bifocal stimulation of the motor cortex. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;162:532–538. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTON J. B., WHITLOCK D. G. Intracellular potentials recorded from motoneurons following precentral gyrus stimulation in primate. J Neurophysiol. 1961 Jan;24:91–100. doi: 10.1152/jn.1961.24.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTON J. B., WHITLOCK D. G. Precentral facilitation and inhibition of spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol. 1960 Mar;23:154–170. doi: 10.1152/jn.1960.23.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALL P. D., REMOND A. G., DOBSON R. L. Studies on the mechanism of the action of visual afferents on motor cortex excitability. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1953 Aug;5(3):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(53)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


