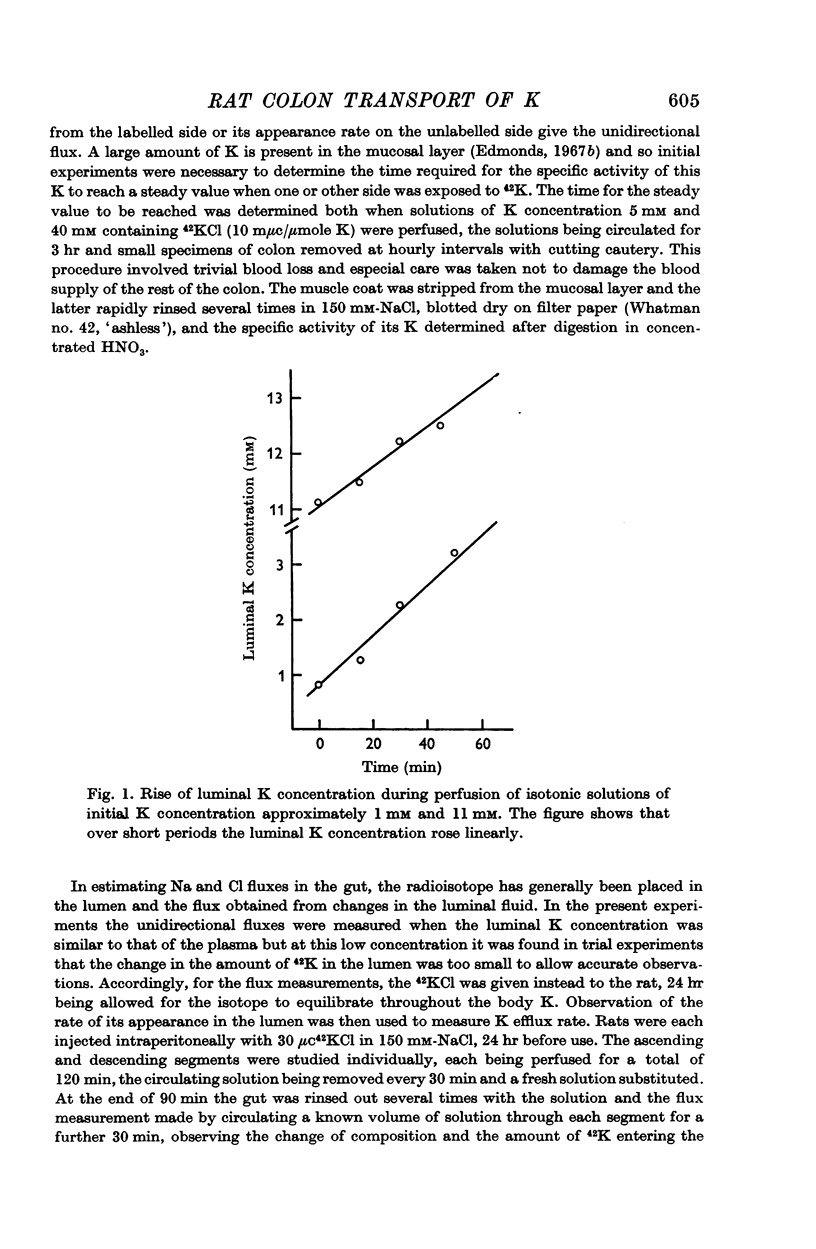
Abstract
1. Ascending and descending segments of colon of normal and Nadepleted rats were perfused with solutions of differing KCl concentration. Net K flux, electrical p.d. and, in some experiments, unidirectional K fluxes were measured.
2. Variation of luminal K concentration over the range 0-40 mM did not affect p.d. or K efflux rate.
3. K secretion rate fell about 30% when Na-free choline chloride solution was perfused.
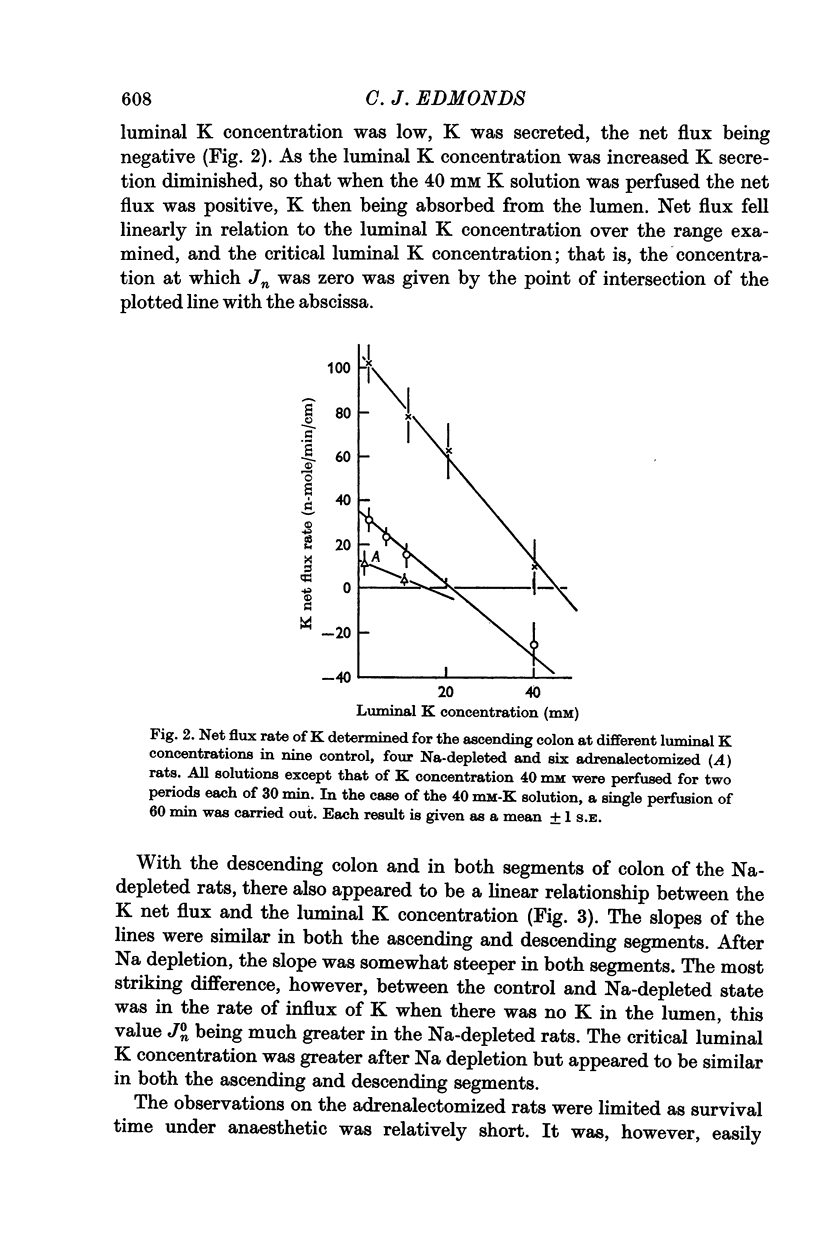
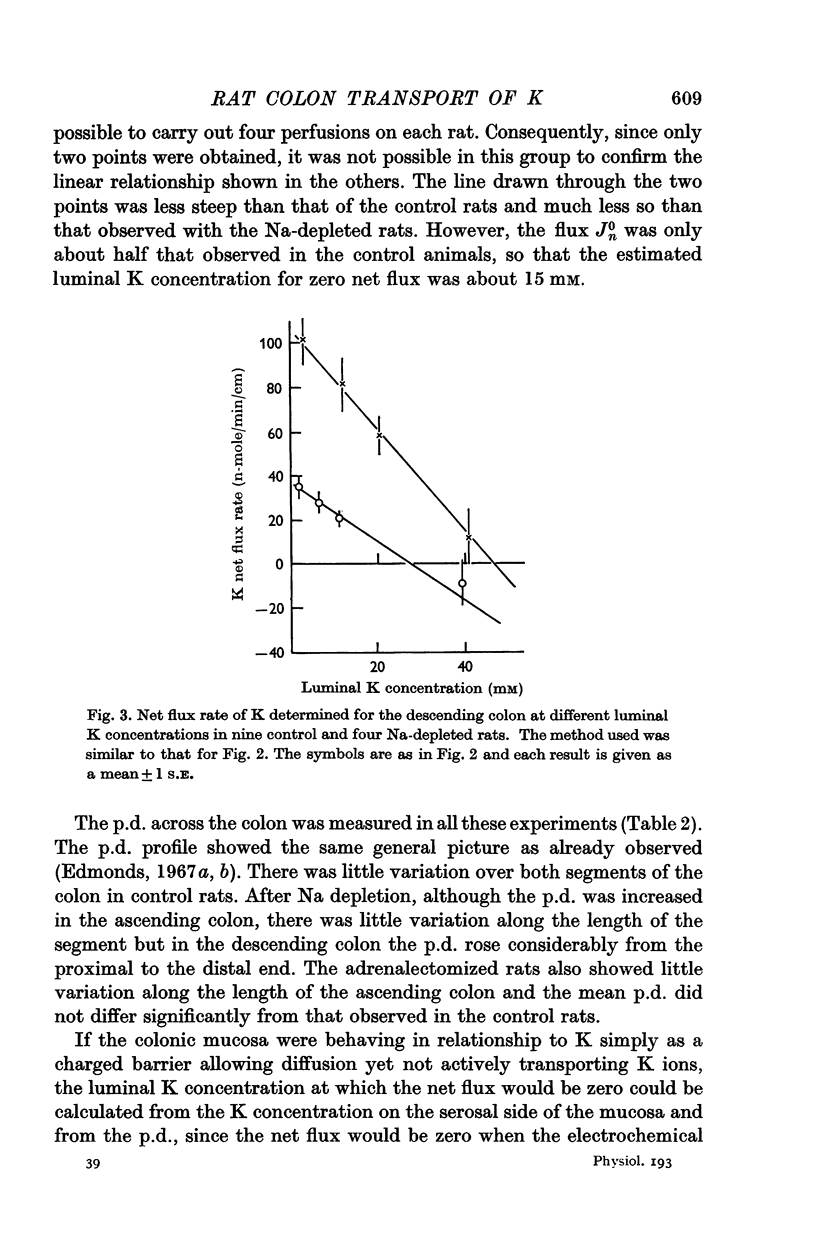
4. Net flux was a linear function of the luminal K concentration, and fell as the latter increased. Na depletion increased K secretion rate and passive permeability of the mucosa to K. Adrenalectomy had the reverse effect. The luminal K concentration, associated with zero net K flux was much greater than expected if the colonic mucosa behaved passively with respect to K.
5. Unidirectional fluxes determined when 5 mM-KCl was in the lumen showed that the ratio influx/efflux was much less than predicted by Ussing's flux ratio equation.
6. It was concluded that K influx was due to simple diffusion and K efflux to diffusion and active transport, both processes being increased by Na depletion.
Full text
PDF











Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLAPP J. R., RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W. Effect of unreabsorbed anions on proximal and distal transtubular potentials in rats. Am J Physiol. 1962 Apr;202:781–786. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.4.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., SCHWARTZ G. F. Na, Cl, and water transport by rat colon. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:555–571. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., SOLOMON A. K. Ion and water fluxes in the ileum of rats. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Sep 20;41(1):143–168. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'AGOSTINO A., LEADBETTER W. F., SCHWARTZ W. B. Alterations in the ionic composition of isotonic saline solution instilled into the colon. J Clin Invest. 1953 May;32(5):444–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI102757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIETSCHY J. M., MOORE E. W. DIFFUSION POTENTIALS AND POTASSIUM DISTRIBUTION ACROSS THE GALLBLADDER WALL. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1551–1560. doi: 10.1172/JCI105032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J. The gradient of electrical potential difference and of sodium and potassium of the gut contents along the caecum and colon of normal and sodium-depleted rats. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):571–588. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C. J. Transport of sodium and secretion of potassium and bicarbonate by the colon of normal and sodium-depleted rats. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):589–602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD H., Jr, DAILEY R. E., BOYD R. S., SWELL L. Effect of restriction of dietary sodium on electrolyte composition of the contents of the terminal ileum. Am J Physiol. 1954 Dec;179(3):477–480. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.179.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIEBISCH G., WINDHAGER E. E. RENAL TUBULAR TRANSFER OF SODIUM, CHLORIDE AND POTASSIUM. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:643–669. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILMAN A., KOELLE E., RITCHIE J. M. Transport of potassium ions in therat's intestine. Nature. 1963 Mar 23;197:1210–1211. doi: 10.1038/1971210b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. Sodium and potassium movements in human red cells. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):278–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J., MAIZELS M. The permeability of human erythrocytes to sodium. J Physiol. 1951 May;113(4):506–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J. B., EDELMAN I. S. Transport of potassium by the gastric mucosa of the frog. Am J Physiol. 1960 Feb;198:280–284. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L. Ionic movements and electrical activity in giant nerve fibres. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):1–37. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. The potassium permeability of a giant nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1955 Apr 28;128(1):61–88. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KHURI R. N., GOLDSTEIN D. A., MAUDE D. L., EDMONDS C., SOLOMON A. K. Single proximal tubules of Necturus kidney. VIII. Na and K determination by glass electrodes. Am J Physiol. 1963 May;204:743–748. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.5.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEFOED-JOHNSEN V., USSING H. H. The nature of the frog skin potential. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Jun 2;42(3-4):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKEN D. E., SOLOMON A. K. Single proximal tubules of Necturus kidney. VI. Nature of potassium transport. Am J Physiol. 1963 Mar;204:377–380. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SJODIN R. A. THE POTASSIUM FLUX RATIO IN SKELETAL MUSCLE AS A TEST FOR INDEPENDENT ION MOVEMENT. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:777–795. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELER H. O. TRANSPORT OF ELECTROLYTES AND WATER ACROSS WALL OF RABBIT GALL BLADDER. Am J Physiol. 1963 Sep;205:427–438. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRONG O., METCALFE-GIBSON A., MORRISON R. B., NG S. T., HOWARD A. V. IN VIVO DIALYSIS OF FAECES AS A METHOD OF STOOL ANALYSIS. I. TECHNIQUE AND RESULTS IN NORMAL SUBJECTS. Clin Sci. 1965 Apr;28:357–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


