Abstract
1. Changes in temperature were determined following injection of noradrenaline, adrenaline, isoprenaline, dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) into the cerebral ventricles of the conscious mouse.
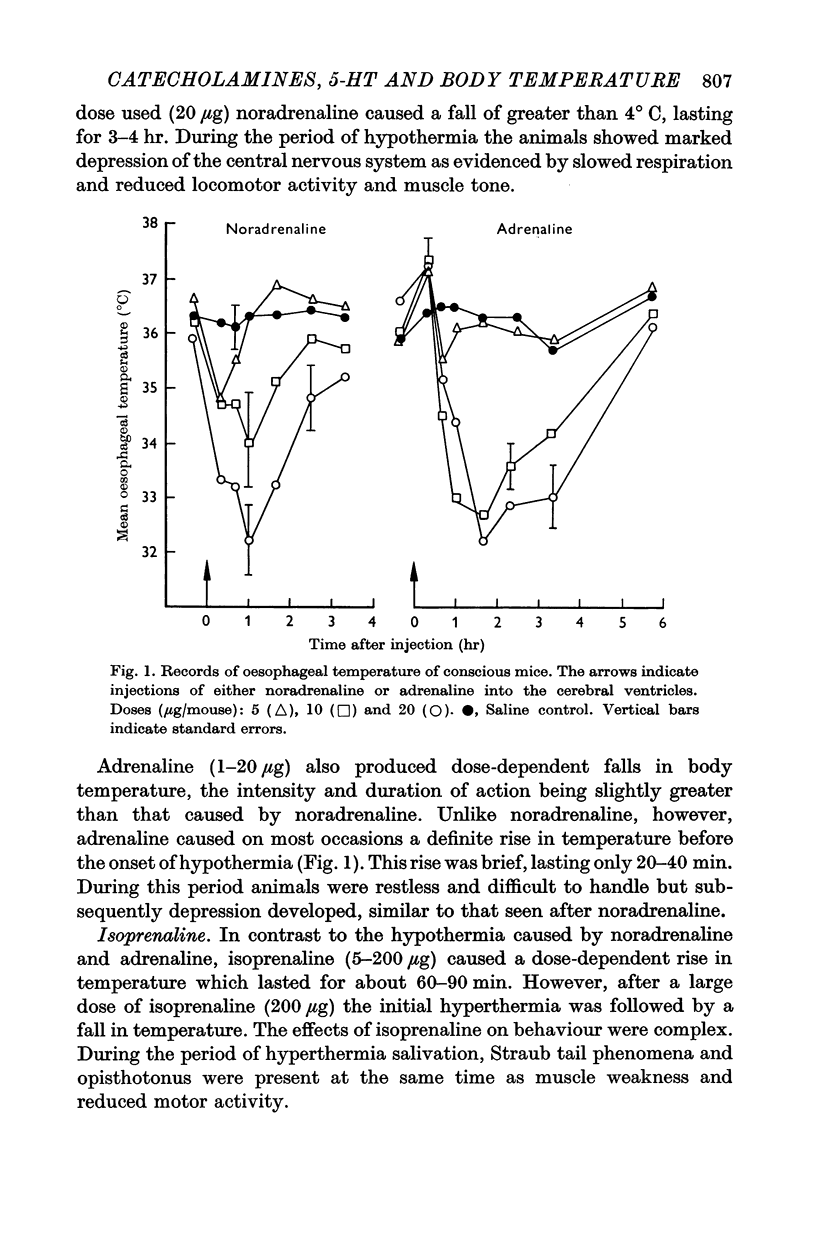
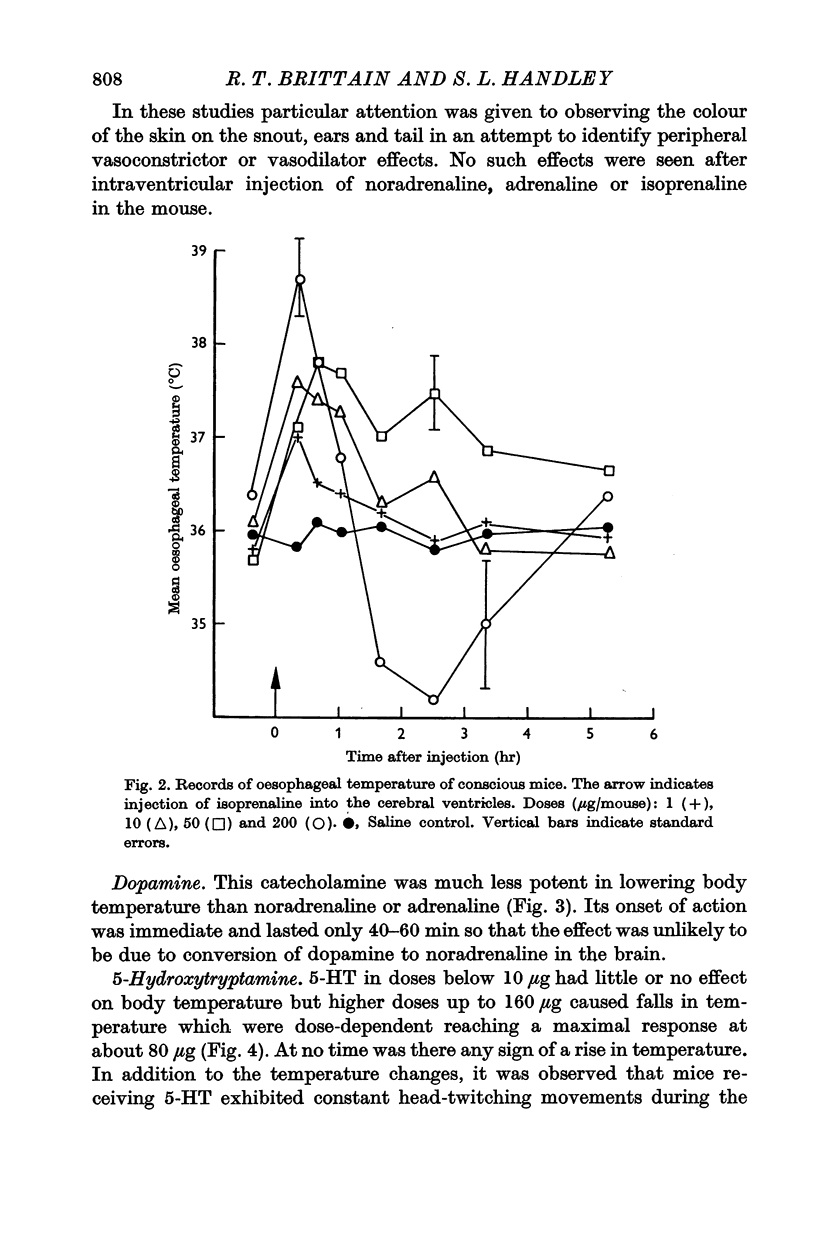
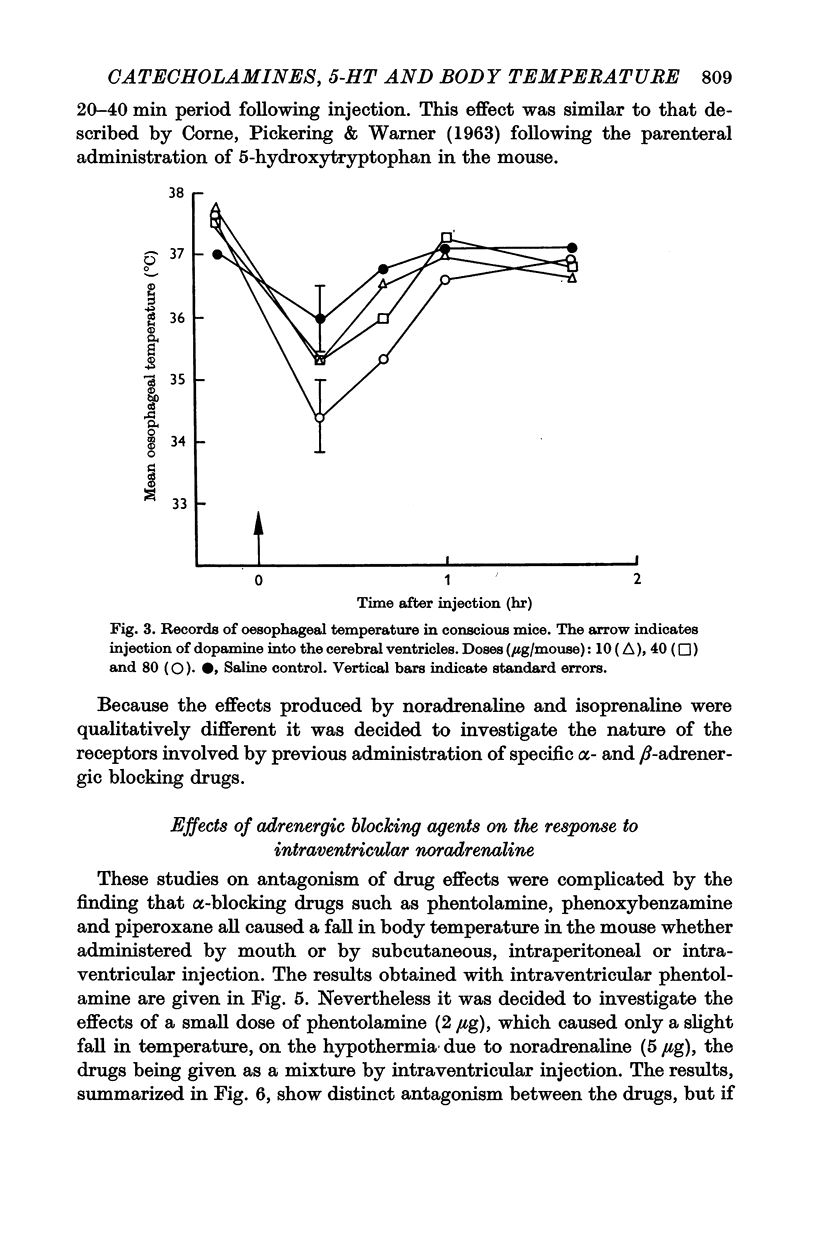
2. Noradrenaline (1-20 μg) and dopamine (10-160 μg) caused falls in body temperature. Adrenaline (1-20 μg) caused a slight and transient rise in body temperature followed by a fall. Isoprenaline (5-20 μg) caused a rise in body temperature, hypothermia only occurring after very high doses (200 μg) of this catecholamine.
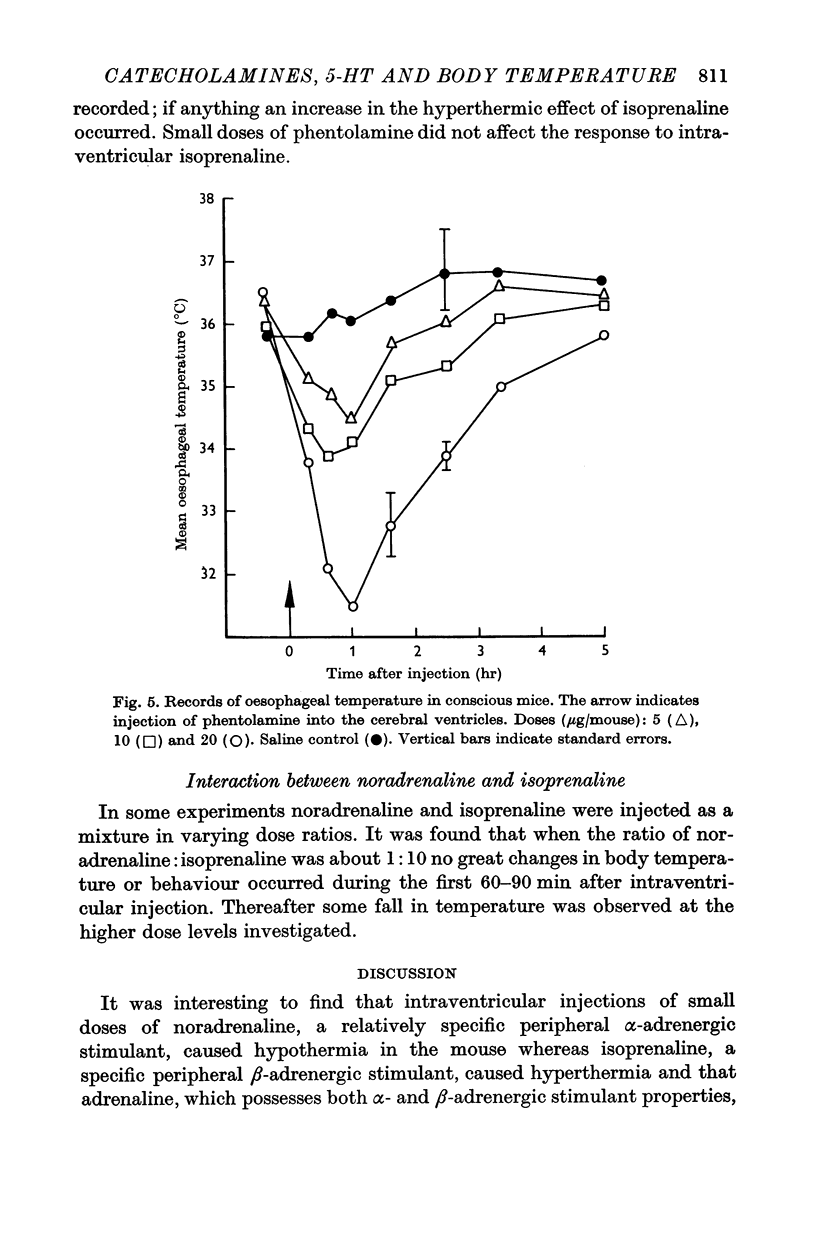
3. α- and β-adrenergic blocking agents, phentolamine (> 2 μg) and propranolol (> 5 μg) respectively, caused falls in body temperature when injected into the cerebral ventricles of the mouse.
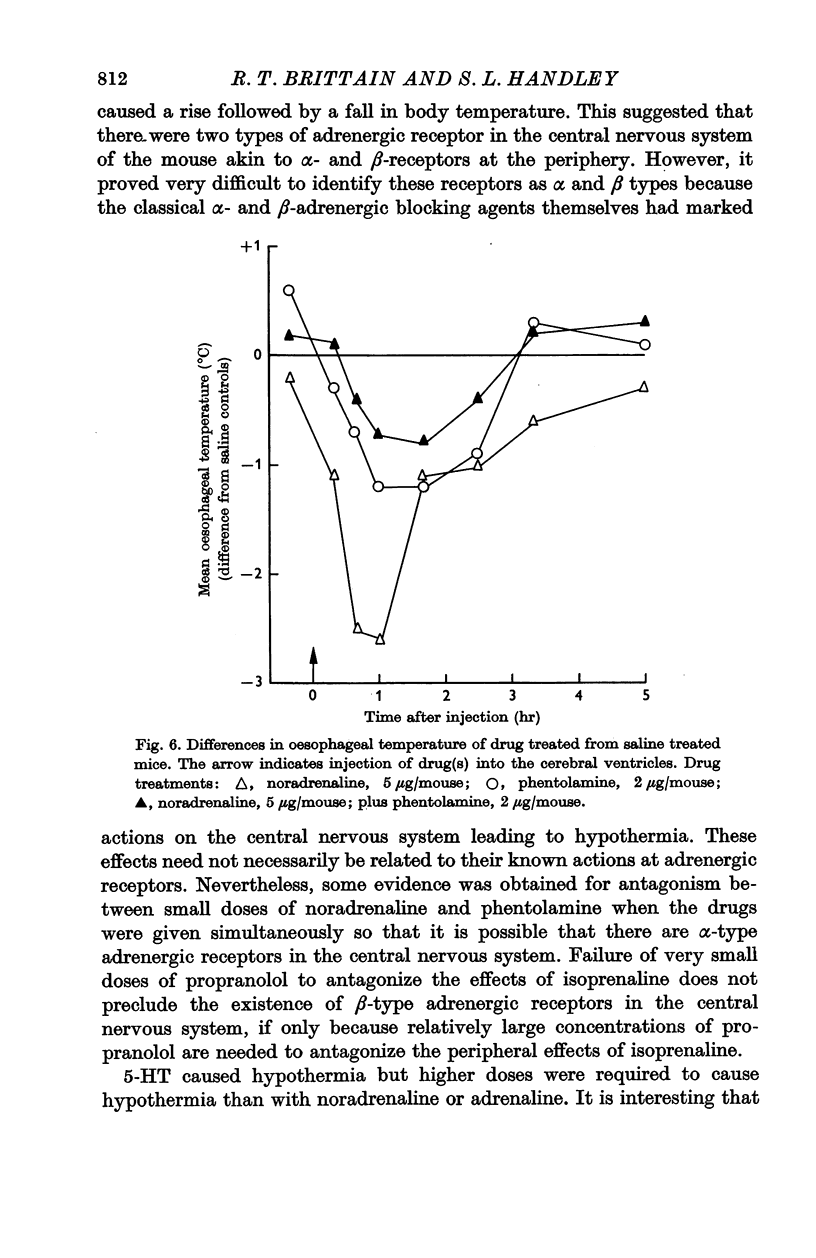
4. Specific drug antagonism studies were limited owing to the intrinsic effects of the α- and β-adrenergic blocking agents. However, some evidence was obtained to indicate that noradrenaline mediated its effects through a central α-type adrenergic receptor.
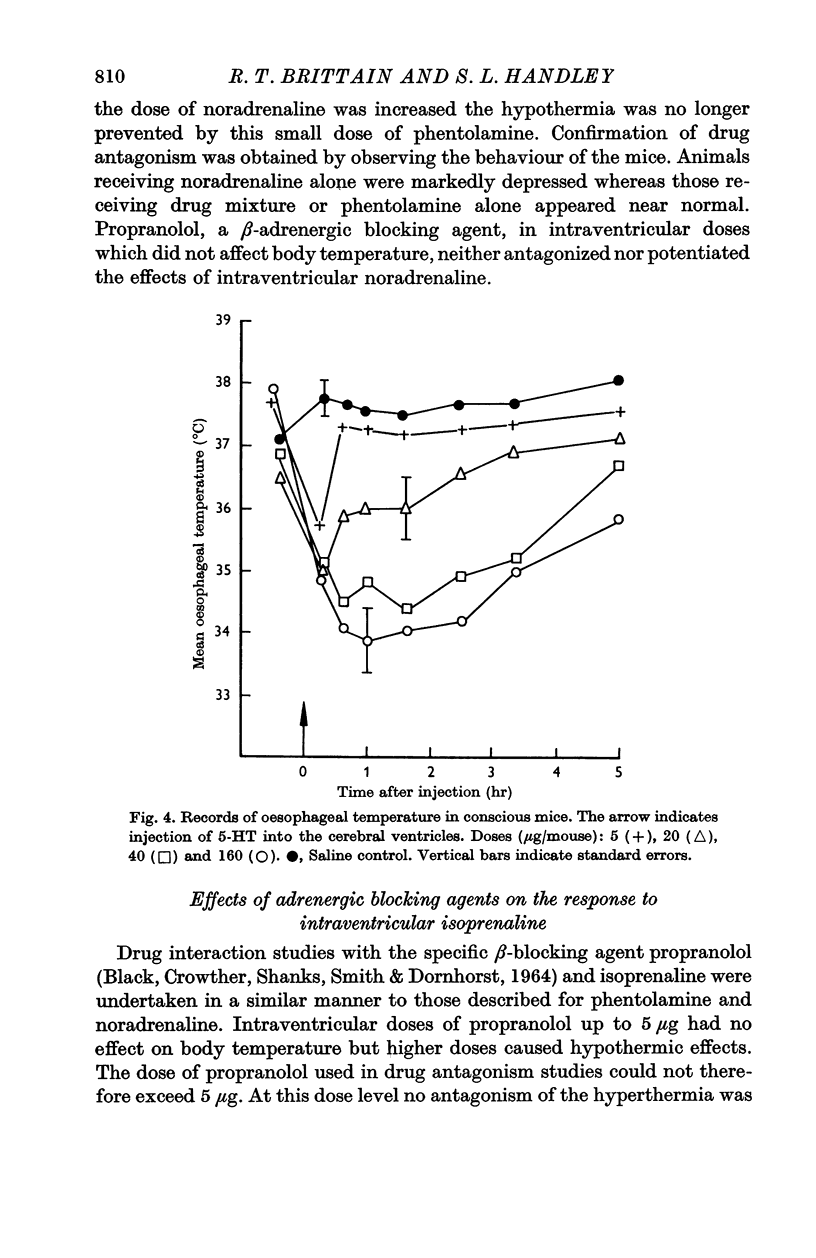
5. 5-HT (10-160 μg) caused a fall in body temperature. The action of this indoleamine and the catecholamines in regard to thermoregulatory function is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK J. W., CROWTHER A. F., SHANKS R. G., SMITH L. H., DORNHORST A. C. A NEW ADRENERGIC BETARECEPTOR ANTAGONIST. Lancet. 1964 May 16;1(7342):1080–1081. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91275-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTAIN R. T., SPENCER P. S. MEASUREMENT OF BODY TEMPERATURE IN CONSCIOUS SMALL LABORATORY ANIMALS BY MEANS OF AN OESOPHAGEAL THERMOCOUPLE. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1964 Jul;16:497–499. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1964.tb07501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittain R. T. The intracerebral effects of noradrenaline and its modification by drugs in the mouse. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966 Sep;18(9):621–623. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1966.tb07944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORNE S. J., PICKERING R. W., WARNER B. T. A method for assessing the effects of drugs on the central actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1963 Feb;20:106–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1963.tb01302.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper K. E., Cranston W. I., Honour A. J. Effects of intraventricular and intrahypothalamic injection of noradrenaline and 5-HT on body temperature in conscious rabbits. J Physiol. 1965 Dec;181(4):852–864. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MYERS R. D. EFFECTS ON TEMPERATURE OF AMINES INJECTED INTO THE CEREBRAL VENTRICLES. A NEW CONCEPT OF TEMPERATURE REGULATION. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:226–231. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Hellon R. F., Myers R. D. Effects on temperature of monoamines injected into the cerebral ventricles of anaesthetized dogs. J Physiol. 1966 Oct;186(2):416–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp008043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldberg W., Lotti V. J. Temperature changes produced in the unanaesthetized rat by monoamines and tranylcypromine injected into the cerebral ventricles. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):35P–36P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALEY T. J., MCCORMICK W. G. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):12–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



