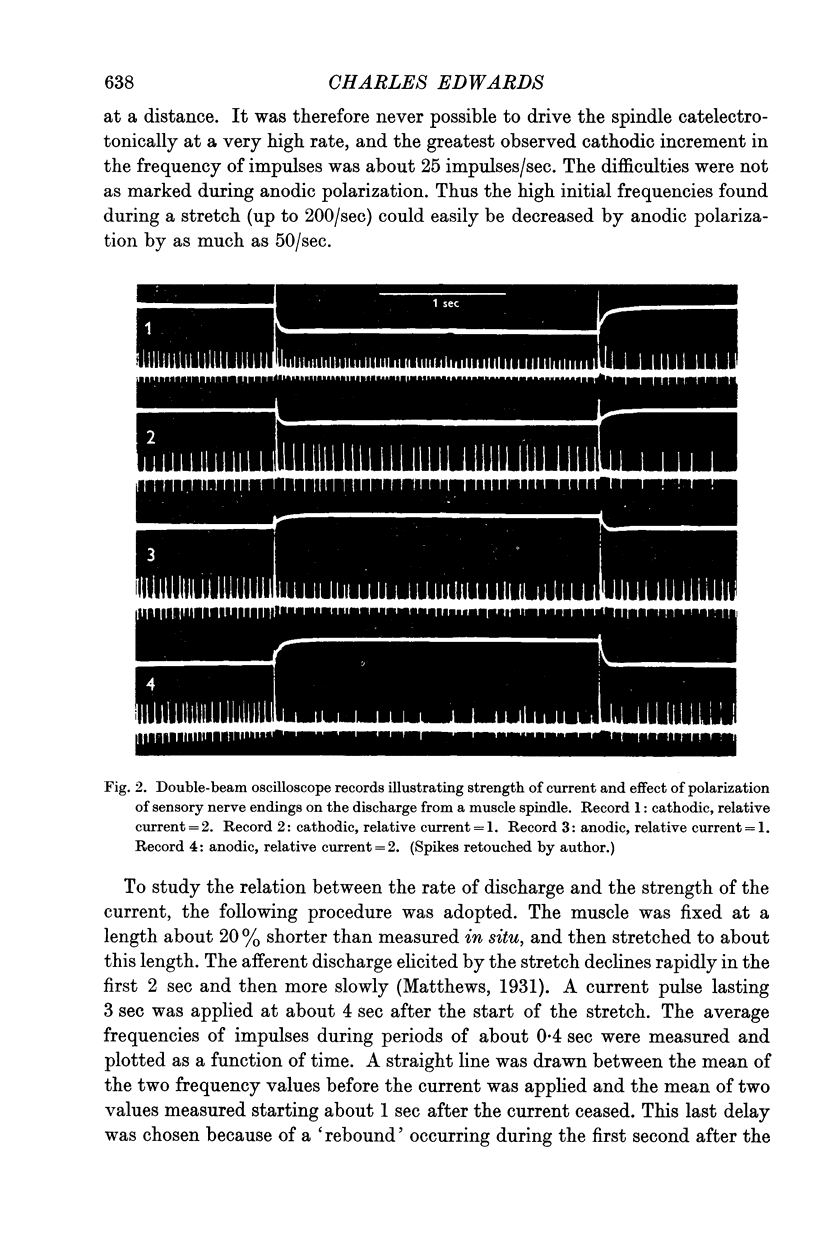
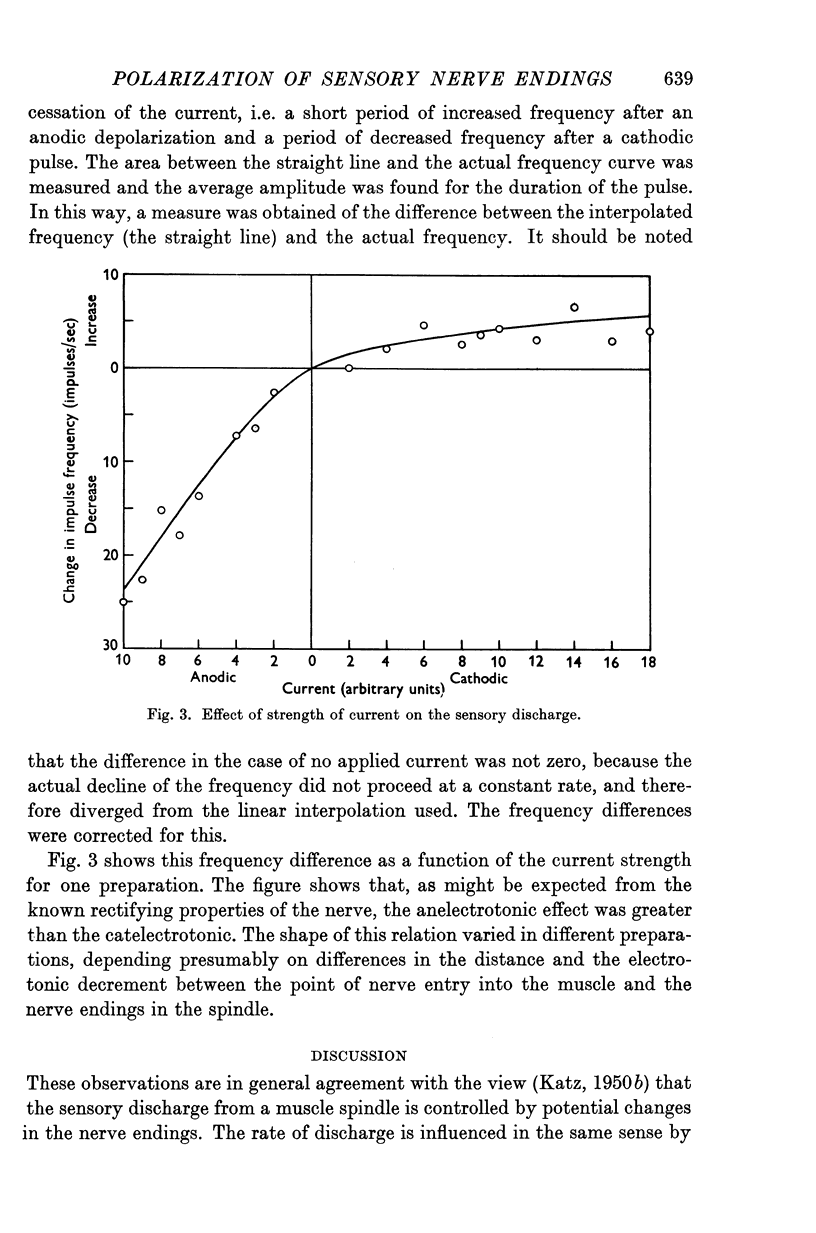
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- KATZ B. Action potentials from a sensory nerve ending. J Physiol. 1950 Oct 16;111(3-4):248–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B. Depolarization of sensory terminals and the initiation of impulses in the muscle spindle. J Physiol. 1950 Oct 16;111(3-4):261–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1950.sp004479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWENSTEIN O. Effect of galvanic polarization on the impulse discharge from the horizontal ampulla of the isolated elasmobranch labyrinth. Nature. 1953 Sep 19;172(4377):549–550. doi: 10.1038/172549a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews B. H. The response of a single end organ. J Physiol. 1931 Jan 21;71(1):64–110. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1931.sp002718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TASAKI I., FERNANDEZ C. Modification of cochlear microphonics and action potentials by KC1 solution and by direct currents. J Neurophysiol. 1952 Nov;15(6):497–512. doi: 10.1152/jn.1952.15.6.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



