Abstract
1. Test meals containing various concentrations of glucose, maltose, sucrose, fructose, lactose, galactose and mixtures of these solutes were given to six healthy subjects. All meals contained 40 mM sodium citrate.
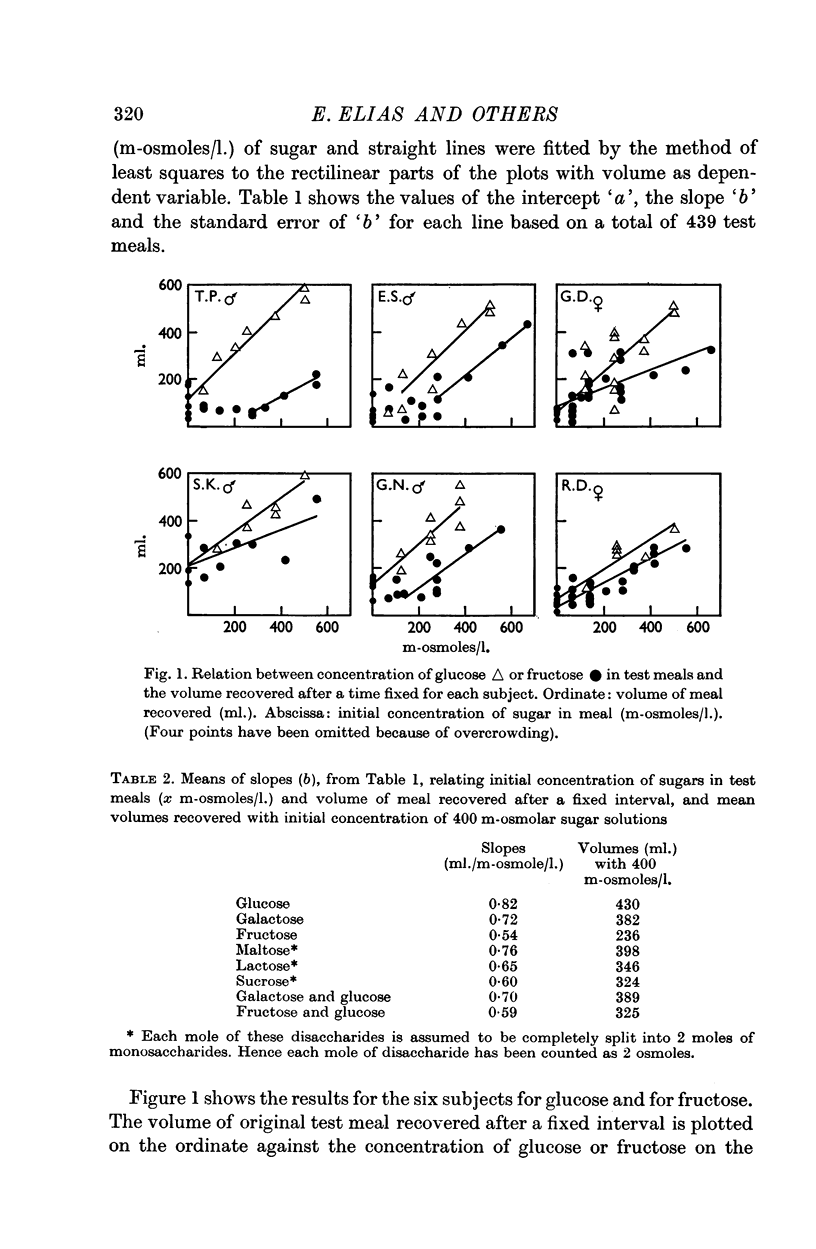
2. The slowing of gastric emptying produced by the disaccharides in test meals was generally consistent with the stimulation of duodenal osmoreceptors occuring after the hydrolysis of the disaccharides.
3. Glucose was slightly more effective, per osmole, in slowing gastric emptying than was galactose.
4. By comparison with glucose or galactose, fructose was much less effective in slowing gastric emptying. In three subjects out of six there was a threshold for its effect.
5. The results may be indicative of the relative activities of disaccharidases in the brush border of the small intestine. They are consistent with there being an osmoreceptor deep to these enzymes which slows gastric emptying.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON C. M., KERRY K. R., TOWNLEY R. R. AN INBORN DEFECT OF INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF CERTAIN MONOSACCHARIDES. Arch Dis Child. 1965 Feb;40:1–6. doi: 10.1136/adc.40.209.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K., Forstner G., Eichholz A. Studies on the mechanism of the intestinal absorption of sugars. X. An effect of Na+ concentration on the apparent Michaelis constants for intestinal sugar transport, in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 29;109(2):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. M., Santiago N. A. Disaccharide absorption in normal and diseased human intestine. Gastroenterology. 1966 Oct;51(4):489–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groen J. THE ABSORPTION OF HEXOSES FROM THE UPPER PART OF THE SMALL INTESTINE IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1937 Mar;16(2):245–255. doi: 10.1172/JCI100854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSWORTH C. D., DAWSON A. M. ABSORPTION OF FRUCTOSE IN MAN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:142–145. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT J. N., KNOX M. T. The regulation of gastric emptying of meals containing citric acid and salts of citric acid. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163:34–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT J. N. Some properties of an alimentary osmoreceptor mechanism. J Physiol. 1956 May 28;132(2):267–288. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT J. N. The site of receptors slowing gastric emptying in response to starch in test meals. J Physiol. 1960 Dec;154:270–276. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt J. N., Pathak J. D. The osmotic effects of some simple molecules and ions on gastric emptying. J Physiol. 1960 Dec;154(2):254–269. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D., CRANE R. K. The digestive function of the epithelium of the small intestine. II. Localization of disaccharide hydrolysis in the isolated brush border portion of intestinal epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Sep 16;52:293–298. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90678-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer A. D., McGill D. B. Distribution of disaccharidase activity in the small bowel of normal and lactase-deficient subjects. Gastroenterology. 1966 Oct;51(4):481–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTINI R., Jr, AVILES J., SHEEHY T. W. Sucrase activity in the intestinal mucosa of patients with sprue and normal subjects. Am J Dig Dis. 1960 Dec;5:1059–1062. doi: 10.1007/BF02231951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



