Abstract
1. The relationship of synaptic vesicles to the synaptic cleft was examined with the electron microscope at neuromuscular junctions in the rat diaphragm before and after bathing the preparation in a physiological salt solution for 2 hr.
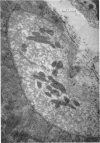
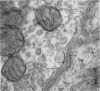
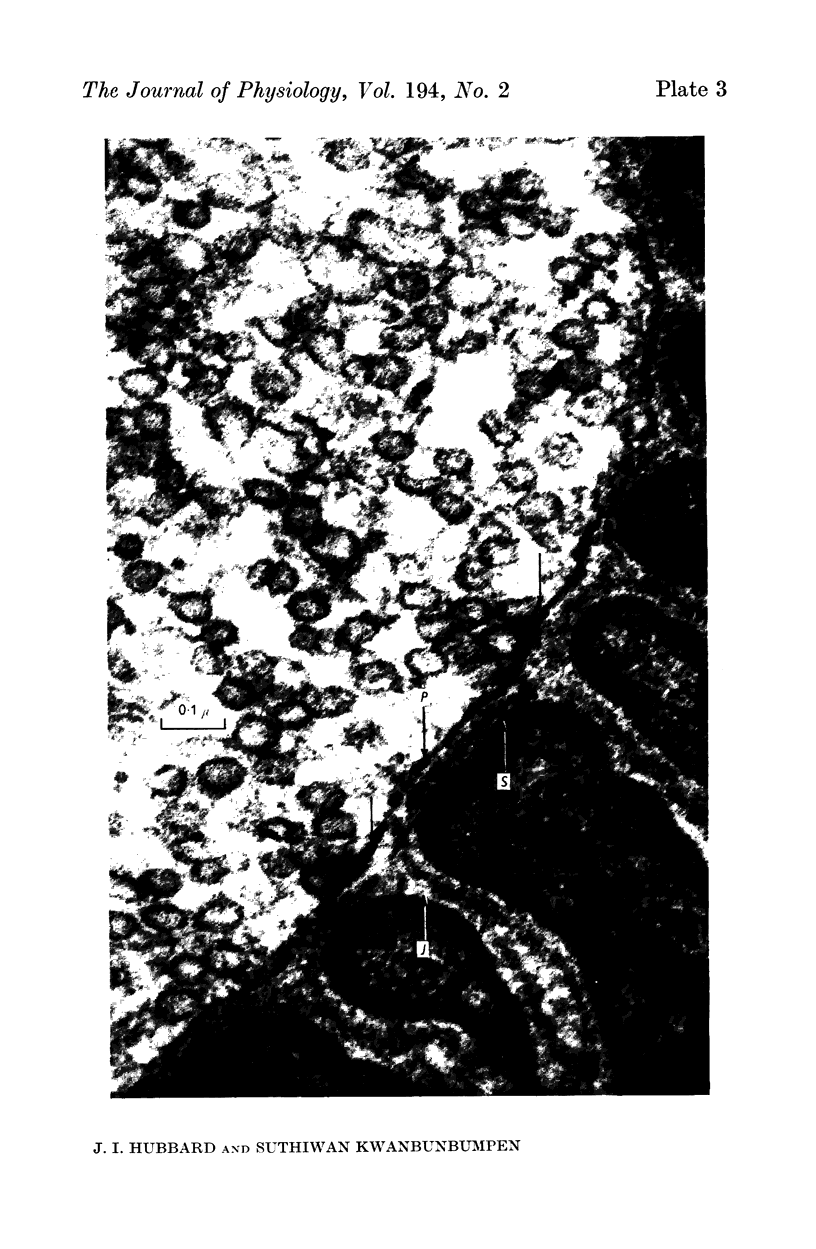
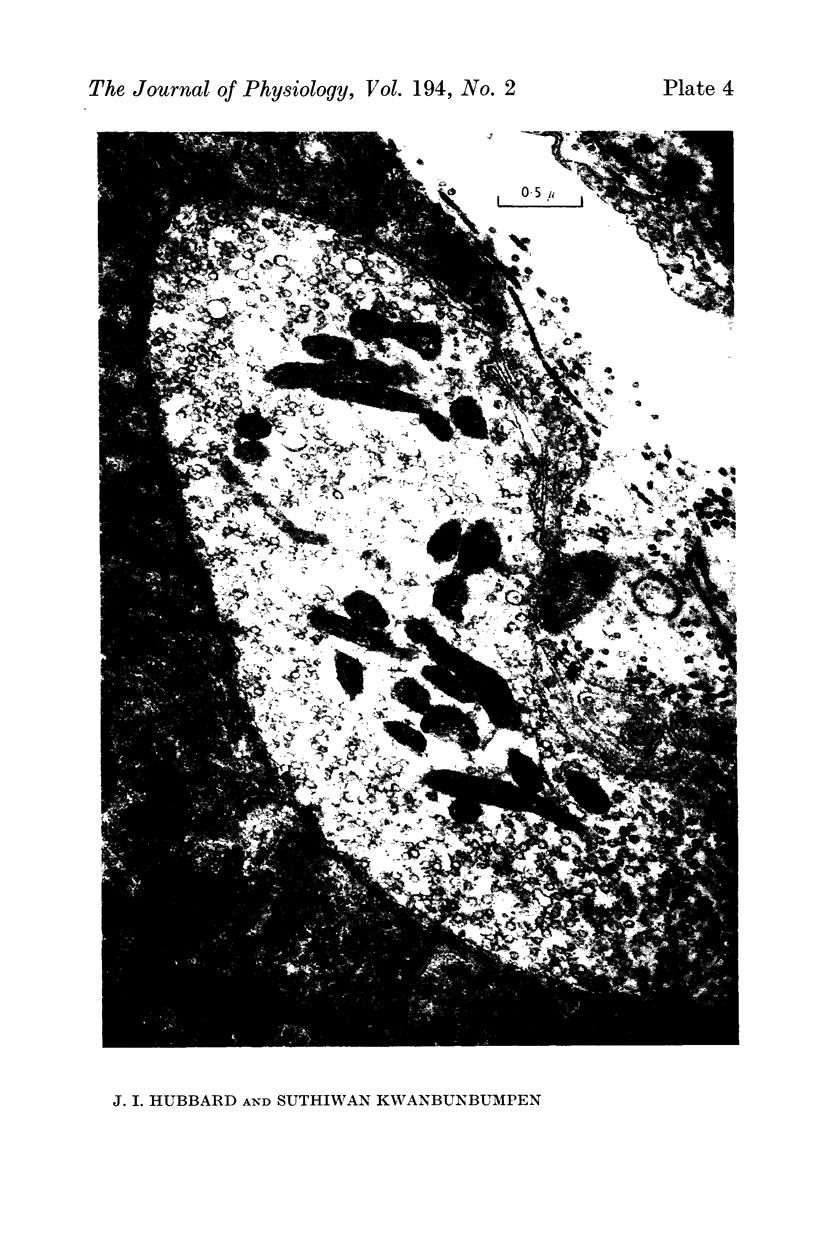
2. A population of vesicles was defined which appeared to `touch' the axoplasmic membrane. These vesicles were found to be aggregated adjacent to axoplasmic densities which lay opposite the mouths of post-synaptic junctional folds.
3. Soaking in the salt solution and modifications of this solution increased the proportion of folds opposed by presynaptic densities with associated vesicles.
4. Soaking in solutions with 20 mM-KCl depleted both the specific vesicle population and the whole population of terminal vesicles. The effect was shown in paired experiments to be a specific effect of the 20 mM-KCl, and it was prevented by a concomitant increase of the bathing MgCl2 concentration.
5. Soaking in solutions with a raised osmotic pressure reduced the specific but not the general vesicle population.
6. It is suggested that these observations support the vesicle hypothesis and that the specific vesicle population forms part of a feed-back mechanism adjusting transmitter synthesis and mobilization to the rate of release of transmitter.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRNETT R. J. The fine structural localization of acetylcholinesterase at the myoneural junction. J Cell Biol. 1962 Feb;12:247–262. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKS R., HUXLEY H. E., KATZ B. The fine structure of the neuromuscular junction of the frog. J Physiol. 1960 Jan;150:134–144. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKS R., KATZ B., MILEDI R. Physiological and structural changes at the amphibian myoneural junction, in the course of nerve degeneration. J Physiol. 1960 Jan;150:145–168. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COUTEAUX R. THE DIFFERENTIATION OF SYNAPTIC AREAS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1963 Nov 19;158:457–480. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1963.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. Synaptic action during and after repetitive stimulation. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:374–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E. D., BENNETT H. S. Some features of the submicroscopic morphology of synapses in frog and earthworm. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Jan;1(1):47–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E., FERREIRA A. V. Submicroscopic changes of the nerve endings in the adrenal medulla after stimulation of the splanchnic nerve. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 Jul 25;3(4):611–614. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.4.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE ROBERTIS E., FRANCHI C. M. Electron microscope observations on synaptic vesicles in synapses of the retinal rods and cones. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 May 25;2(3):307–318. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.3.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Biophysical aspects of neuro-muscular transmission. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1956;6:121–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Local activity at a depolarized nerve-muscle junction. J Physiol. 1955 May 27;128(2):396–411. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FATT P., KATZ B. Spontaneous subthreshold activity at motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1952 May;117(1):109–128. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G. The granule cells, mossy synapses and Purkinje spine synapses of the cerebellum: light and electron microscope observations. J Anat. 1961 Jul;95:345–356. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Hubbard J. I. The origin of the post-tetanic hyperpolarization of mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1966 May;184(2):335–352. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage P. W., Quastel D. M. Dual effect of potassium on transmitter release. Nature. 1965 May 8;206(984):625–626. doi: 10.1038/206625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I. REPETITIVE STIMULATION AT THE MAMMALIAN NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION, AND THE MOBILIZATION OF TRANSMITTER. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:641–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I. The effect of calcium and magnesium on the spontaneous release of transmitter from mammalian motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1961 Dec;159:507–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess A. Developmental changes in the structure of the synapse on the myelinated cell bodies of the chicken ciliary ganglion. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jun;25(3 Suppl):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.3.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. I., Jones S. F., Landau E. M. On the mechanism by which calcium and magnesium affect the spontaneous release of transmitter from mammalian motor nerve terminals. J Physiol. 1968 Feb;194(2):355–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. An investigation of spontaneous activity at the neuromuscular junction of the rat. J Physiol. 1956 Jun 28;132(3):650–666. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILEY A. W. The effects of presynaptic polarization on the spontaneous activity at the mammalian neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1956 Nov 28;134(2):427–443. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOUNTFORD S. EFFECTS OF LIGHT AND DARK ADAPTATION ON THE VESICLE POPULATIONS OF RECEPTOR-BIPOLAR SYNAPSES. J Ultrastruct Res. 1963 Dec;52:403–418. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(63)80075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALAY S. L. The morphology of synapses in the central nervous system. Exp Cell Res. 1958;14(Suppl 5):275–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Hofmann W. W., Feigen G. A. Presynaptic effects of potassium ion on the mammalian neuromuscular junction. Nature. 1965 Nov 6;208(5010):590–591. doi: 10.1038/208590a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGER J. F. The ultrastructure of normal and denervated neuromuscular synapses in mouse gastrocnemius muscle. Exp Cell Res. 1957 Jun;12(3):662–665. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(57)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON J. D. The ultrastructure of a reptilian myoneural junction. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1956 Jul 25;2(4):381–394. doi: 10.1083/jcb.2.4.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMALBRUCH H. UBER WIRKUNGEN VON ALKALI- UND ERDALKALI-IONEN (NA+, K+, LI+, MG2+, CA2+) AUF EINIGE STRUKTUREN DES ZWERCHFELLS DER MAUS. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1964 Mar 5;62:246–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. Changes in potassium concentration around motor nerve terminals, produced by current flow, and their effects on neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1961 Jan;155:46–58. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAEMERT J. C. The ultrastructure and disposition of vesiculated nerve processes in smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1963 Feb;16:361–377. doi: 10.1083/jcb.16.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. Some properties of synaptic membranes isolated from the central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):982–998. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P. The application of subcellular fractionation techniques to the study of brain function. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1965;15:39–96. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(65)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]