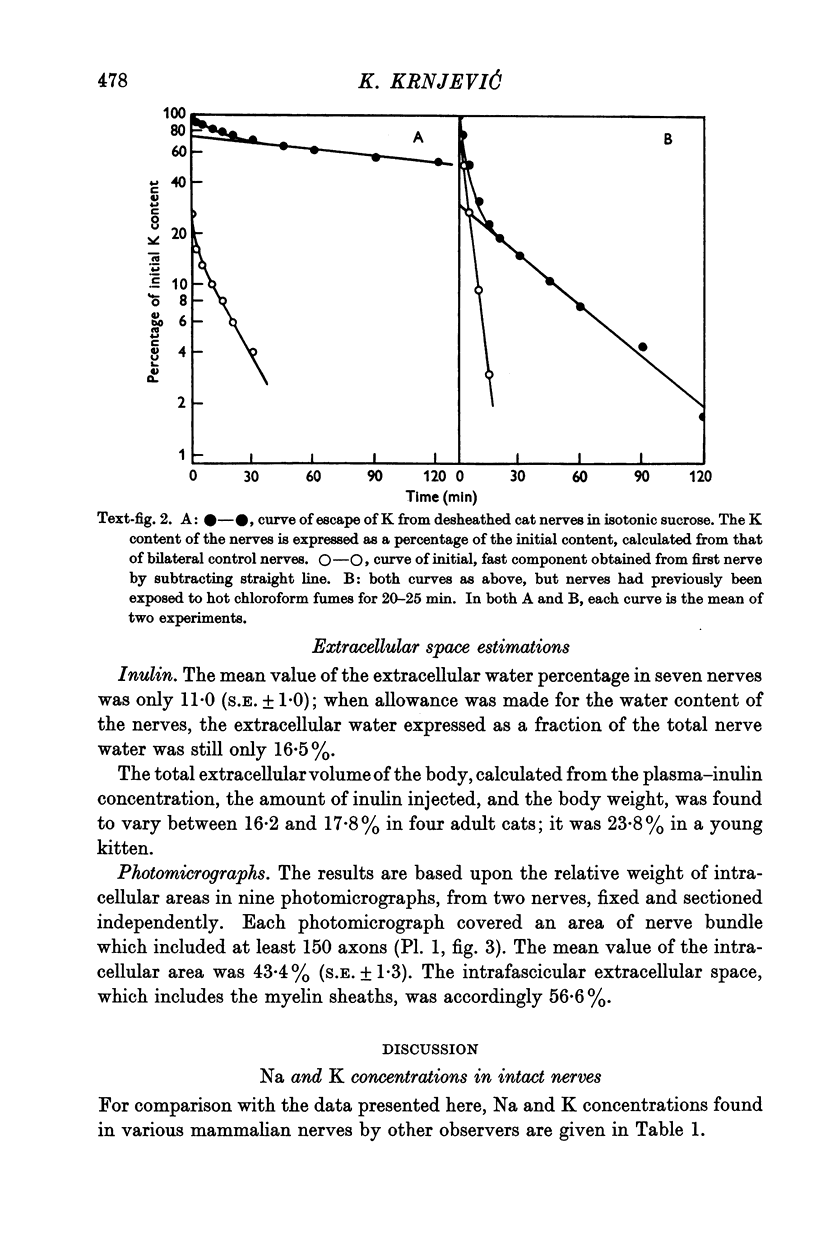
Full text
PDF



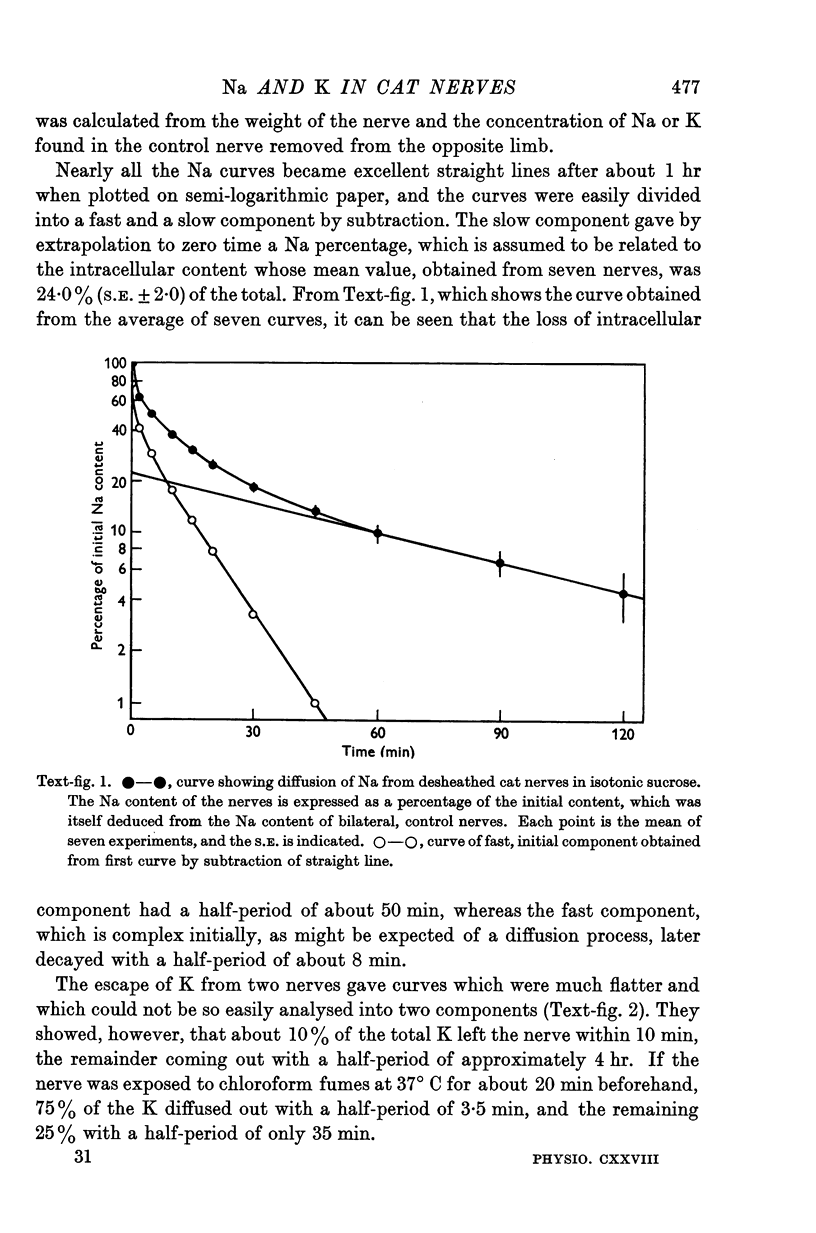










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcock N. H., Lynch G. R. On the relation between the physical, chemical, and electrical properties of the nerves: Part I. J Physiol. 1907 Nov 29;36(2-3):93–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1907.sp001220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. J., Conway E. J. Potassium accumulation in muscle and associated changes. J Physiol. 1941 Aug 11;100(1):1–63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAUSEY G., PALMER E. The epineural sheath of a nerve as a barrier to the diffusion of phosphate ions. J Anat. 1953 Jan;87(1):30–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAINTY J., KRNJEVIC K. The rate of exchange of 24Na in cat nerves. J Physiol. 1955 Jun 28;128(3):489–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES F., DAVIES R. F., FRANCIS E. T. B., WHITTAM R. The sodium and potassium content of cardiac and other tissues of the ox. J Physiol. 1952 Oct;118(2):276–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggleton M. G., Eggleton P., Hamilton A. M. Distribution of chloride in frog's skeletal muscle immersed in saline solution. J Physiol. 1937 Jul 15;90(2):167–182. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1937.sp003506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellison F. O. On the relation between the physical, chemical and electrical properties of the nerves: Part II. The tissues composing a nerve trunk. J Physiol. 1910 Mar 8;39(6):397–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1910.sp001348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J., McLENNAN H. Cation exchanges in sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1953 Sep;121(3):629–637. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D. The ionic fluxes in frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):359–382. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K. Some observations on perfused frog sciatic nerves. J Physiol. 1954 Feb 26;123(2):338–356. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K. The connective tissue of the frog sciatic nerve. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1954;39(1):55–72. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1954.sp001048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS P. R. The free amino-acids of invertebrate nerve. Biochem J. 1952 Oct;52(2):330–338. doi: 10.1042/bj0520330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLENNAN H., HARRIS E. J. The effect of temperature on the content and turnover of sodium and potassium in rabbit nerve. Biochem J. 1954 Jun;57(2):329–334. doi: 10.1042/bj0570329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLS G., Jr, NICHOLS N., WEIL W. B., WALLACE W. M. The direct measurement of the extracellular phase of tissues. J Clin Invest. 1953 Dec;32(12):1299–1308. doi: 10.1172/JCI102858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON W. V., DUNIHUE F. W. Water and electrolyte distribution in cardiac muscle. Am J Physiol. 1954 May;177(2):292–298. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.177.2.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Effects of sheath removal on bullfrog nerve. J Cell Physiol. 1953 Apr;41(2):305–311. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030410208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Effects of sheath removal on the sciatic of the toad, Bufo marinus. J Cell Physiol. 1954 Feb;43(1):87–98. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030430107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]