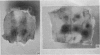
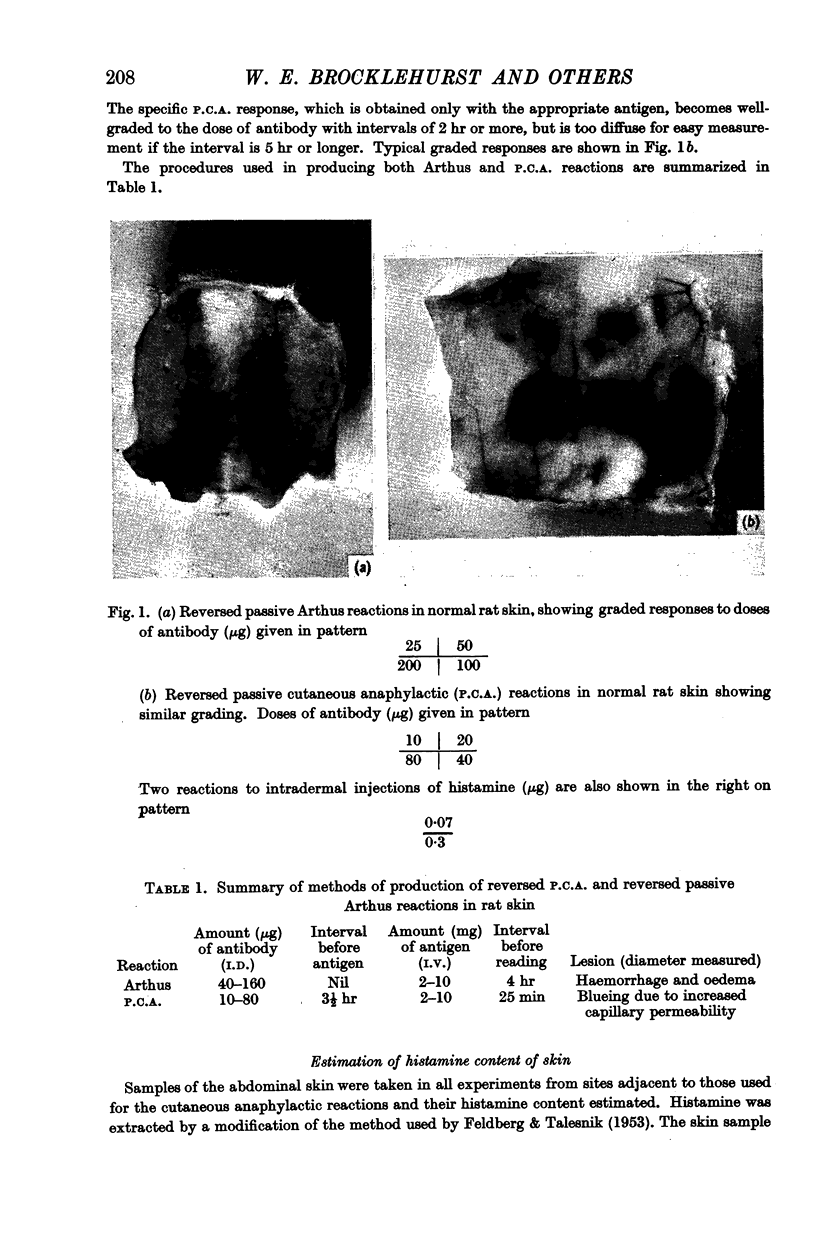
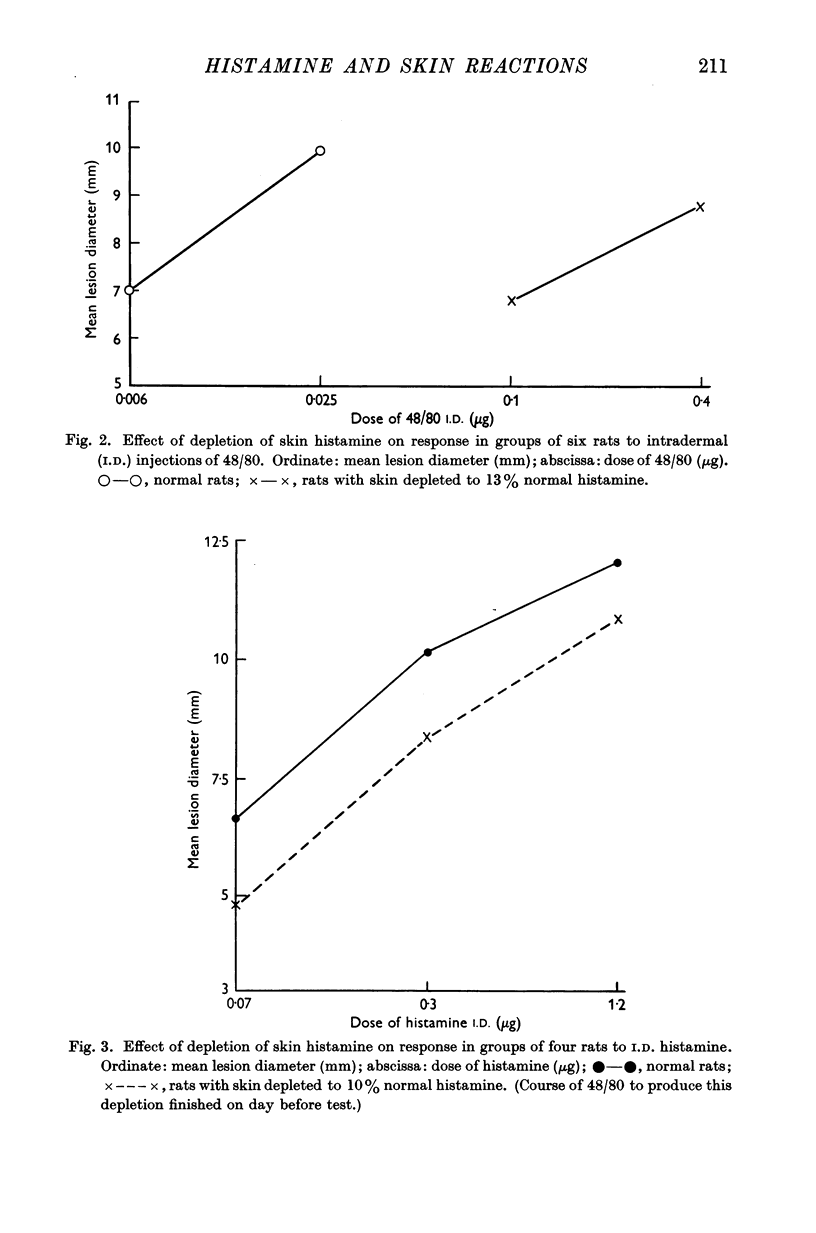
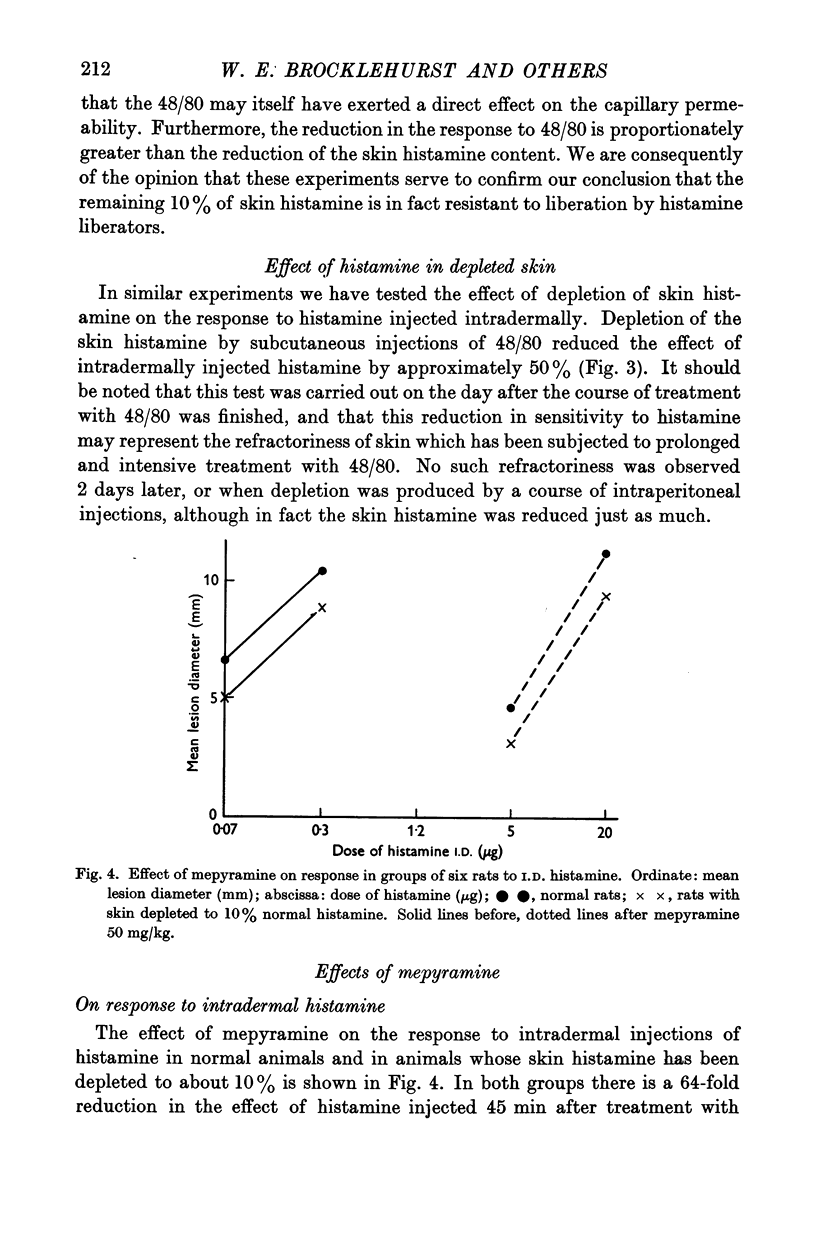
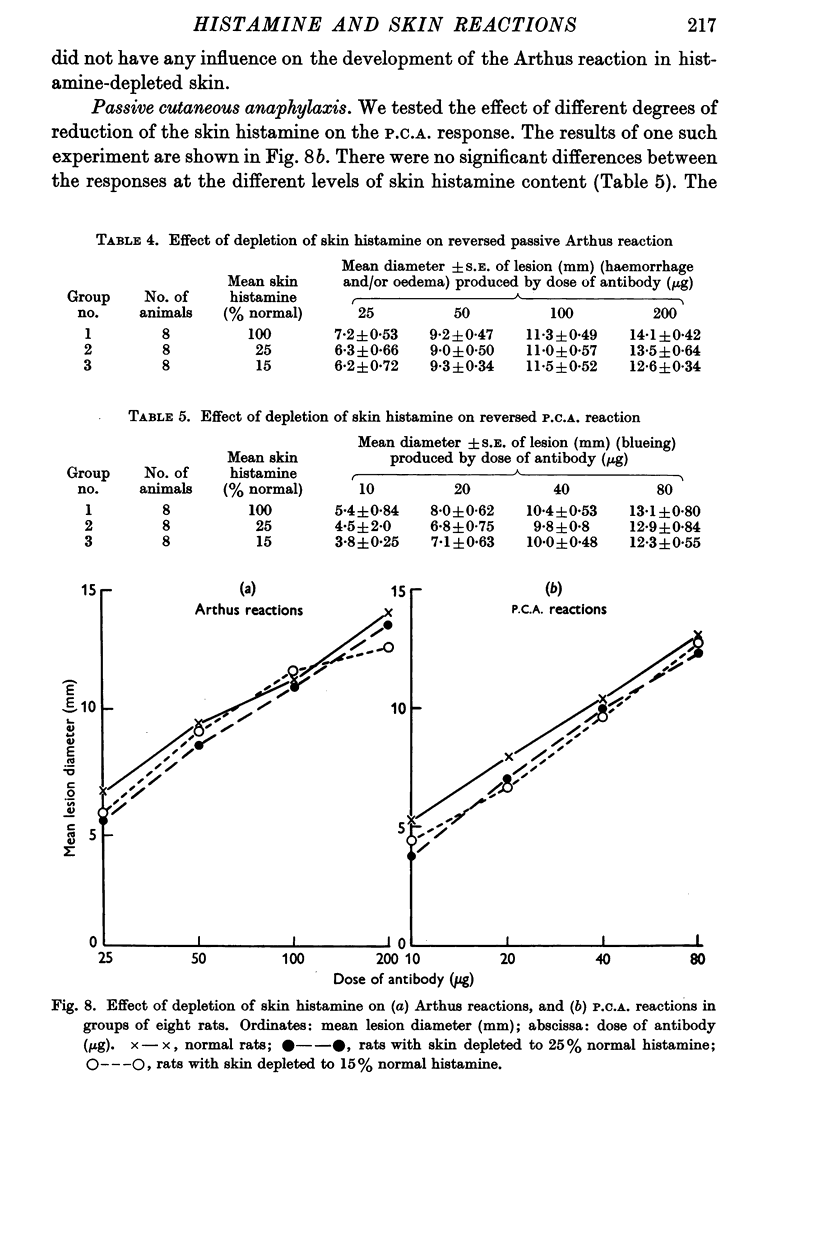
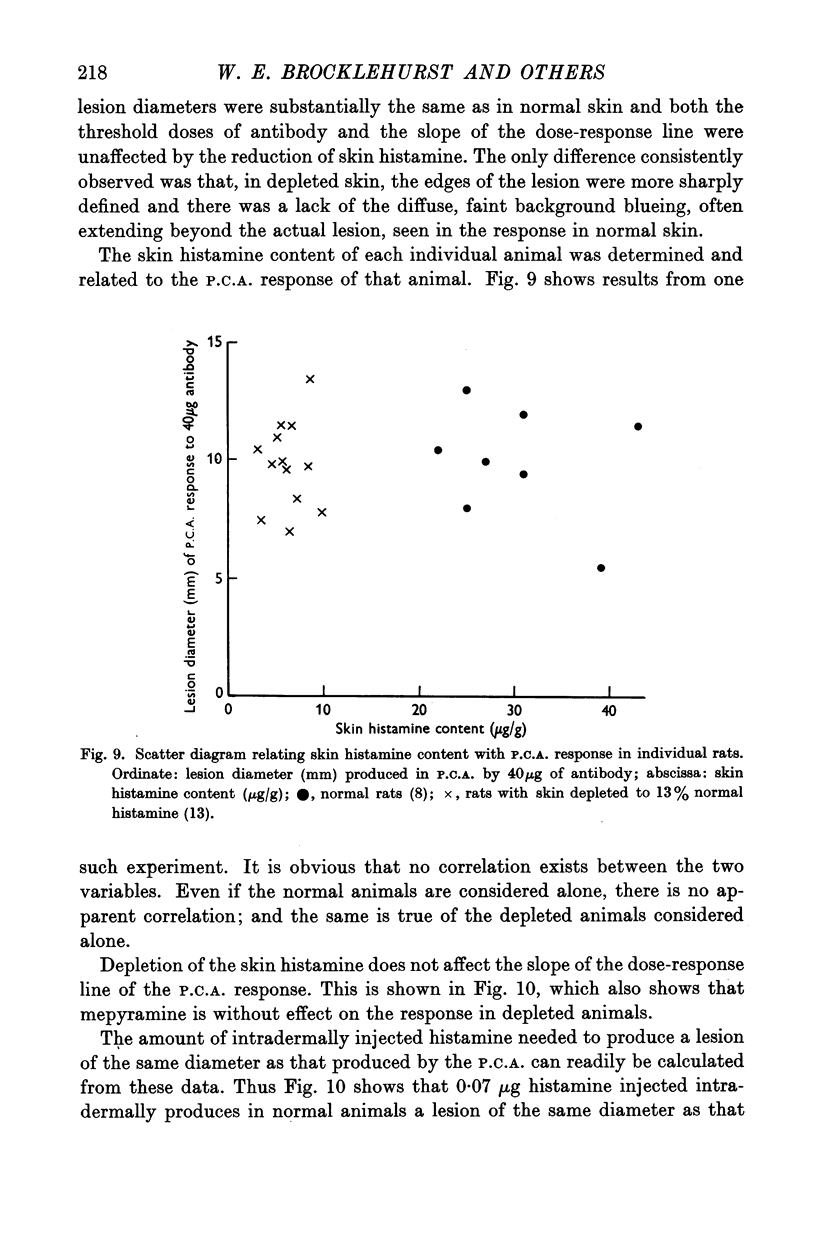
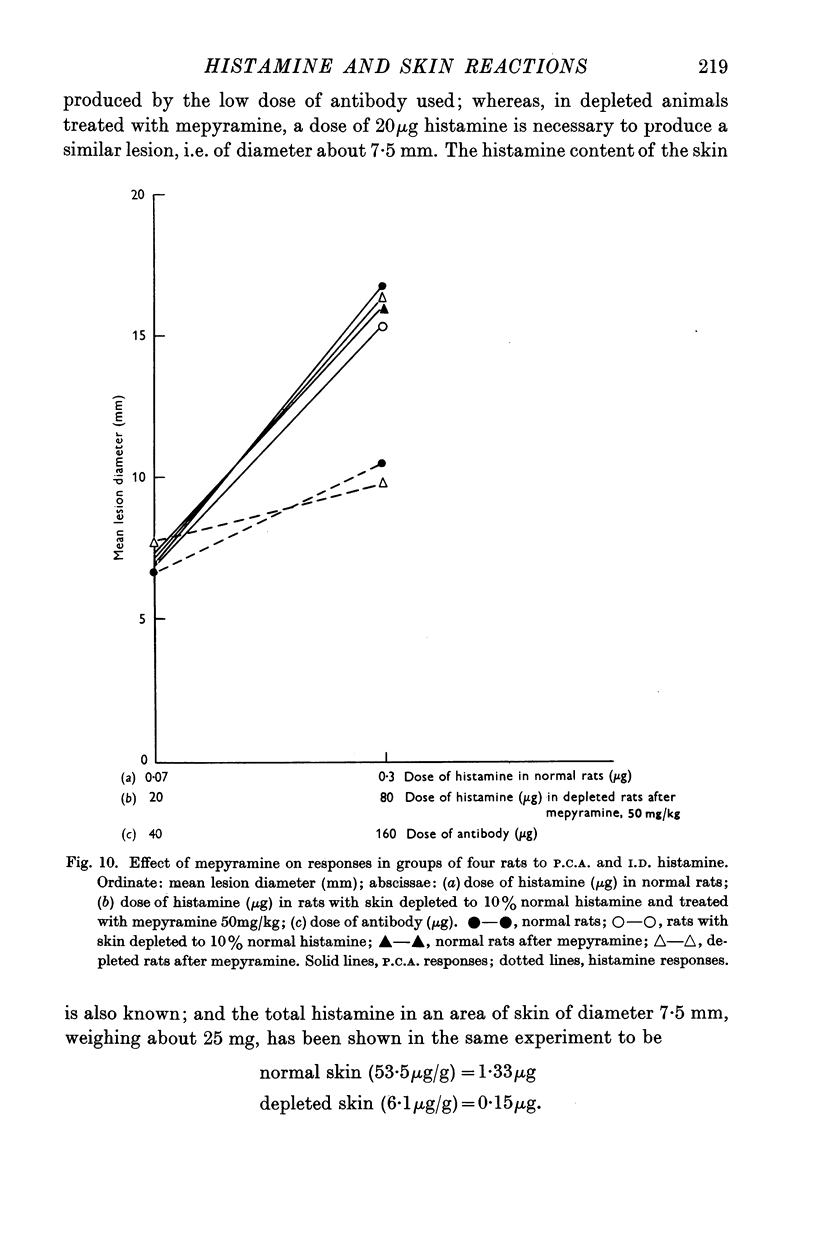
Full text
PDF




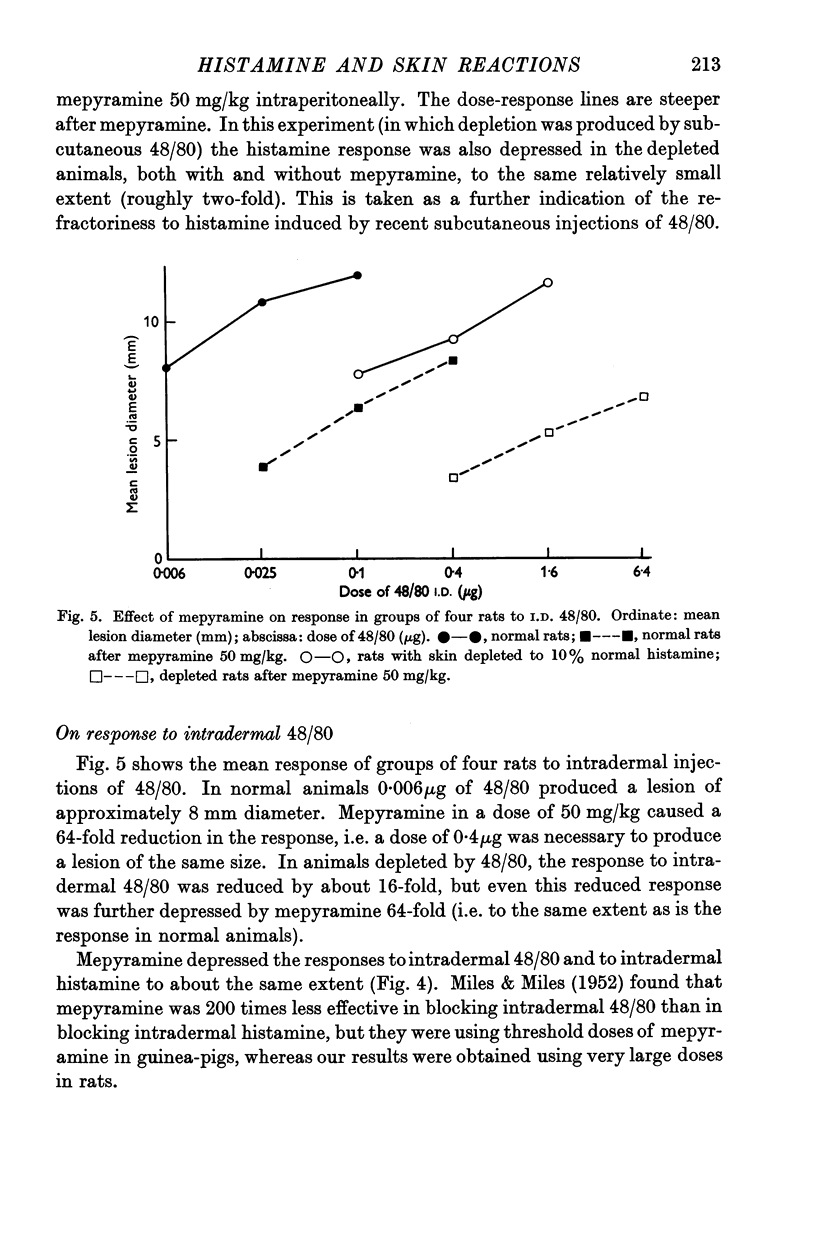
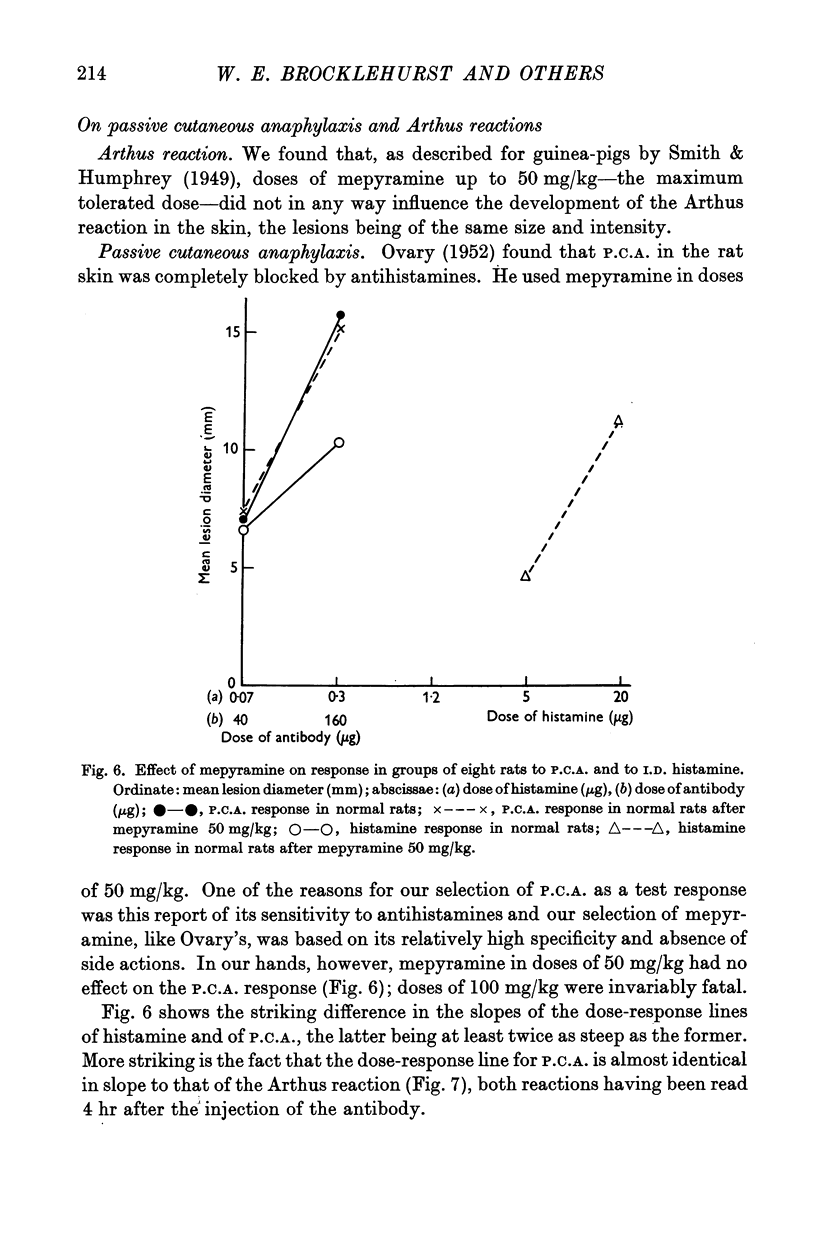
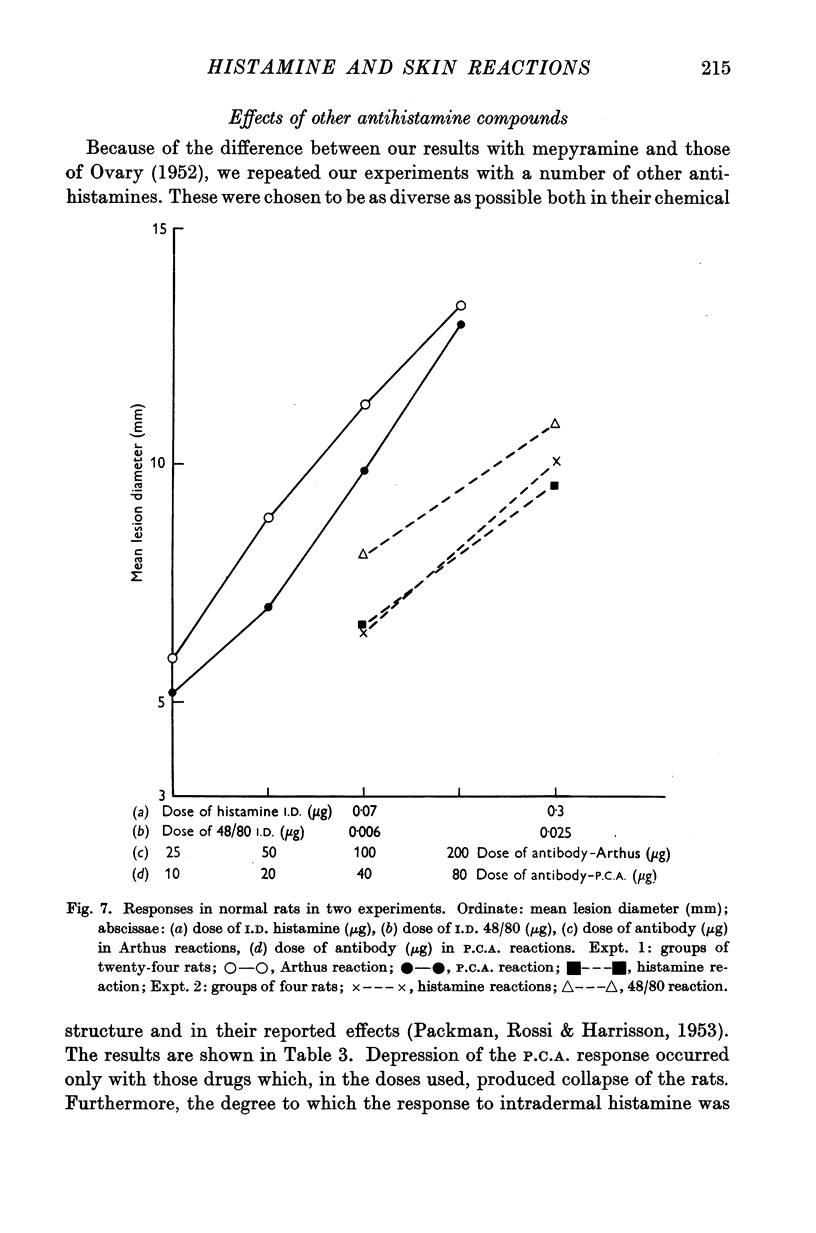





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENACERRAF B., KABAT E. A. A quantitative study of the Arthus phenomenon induced passively in the guinea pig. J Immunol. 1950 Jan;64(1):1–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAWCETT D. W. Cytological and pharmacological observations on the release of histamine by mast cells. J Exp Med. 1954 Aug 1;100(2):217–224. doi: 10.1084/jem.100.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., MILES A. A. Regional variations of increased permeability of skin capillaries induced by a histamine liberator and their relation to the histamine content of the skin. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):205–213. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELDBERG W., TALESNIK J. Reduction of tissue histamine by compound 48/80. J Physiol. 1953 Jun 29;120(4):550–568. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDWICK D. C. Age changes in the histamine content of rat skin. J Physiol. 1954 Apr 28;124(1):157–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekwick R. A., Cannan R. K. The hydrogen ion dissociation curve of the crystalline albumin of the hen's egg. Biochem J. 1936 Feb;30(2):227–234. doi: 10.1042/bj0300227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACINTOSH F. C., PATON W. D. M. The liberation of histamine by certain organic bases. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):190–219. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILES A. A., MILES E. M. Vascular reactions to histamine, histamine-liberator and leukotaxine in the skin of guinea-pigs. J Physiol. 1952 Oct;118(2):228–257. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONGAR J. L., SCHILD H. O. Quantitative measurement of the histamine-releasing activity of a series of mono-alkyl-amines using minced guinea-pig lung. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1953 Mar;8(1):103–109. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1953.tb00760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z., BIER O. G. Quantitative studies on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in the guinea pig and its relationship to the Arthus phenomenon. J Immunol. 1953 Jul;71(1):6–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z., BIER O. G. Quantitative study of Arthus reaction and of cutaneous anaphylaxis induced passively in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Dec;81(3):584–586. doi: 10.3181/00379727-81-19949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OVARY Z. [Cutaneous anaphylaxis in the albino rat]. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1952;3(4):293–301. doi: 10.1159/000227977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PACKMAN E. W., ROSSI G. V., HARRISSON J. W. E. The effect of histamine and antihistamines on body temperature. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1953 May;5(5):301–310. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1953.tb13990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. M. Compound 48/80: a potent histamine liberator. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1951 Sep;6(3):499–508. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1951.tb00661.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILEY J. F. The effects of histamine-liberators on the mast cells of the rat. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Apr;65(2):471–479. doi: 10.1002/path.1700650219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILEY J. F., WEST G. B. The presence of histamine in tissue mast cells. J Physiol. 1953 Jun 29;120(4):528–537. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]