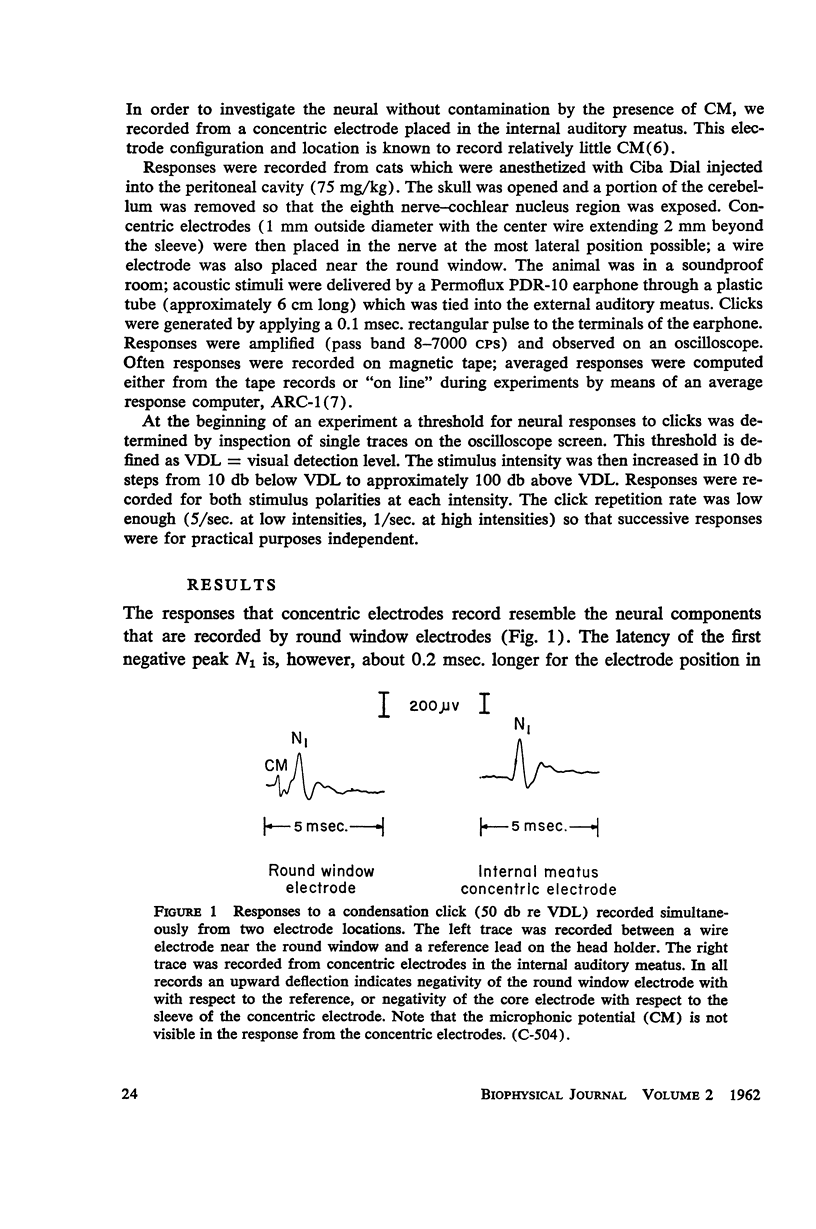
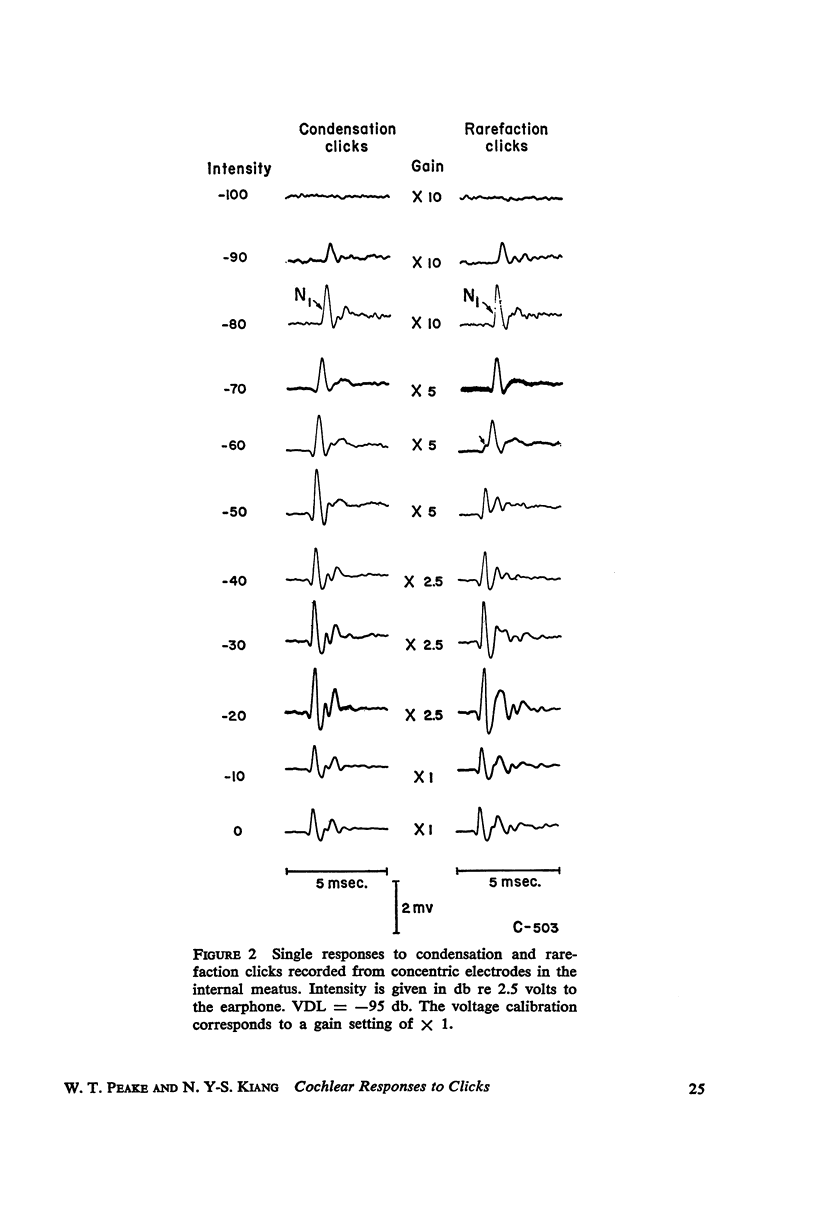
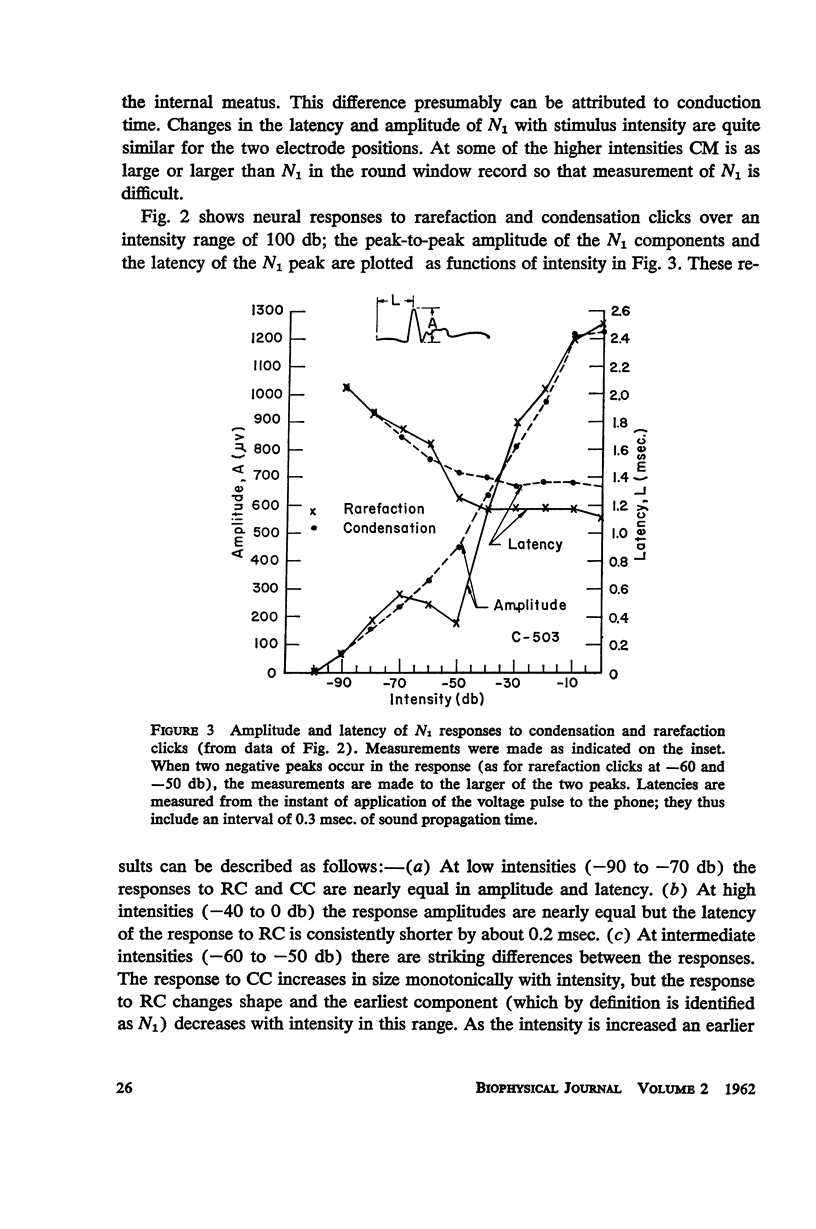
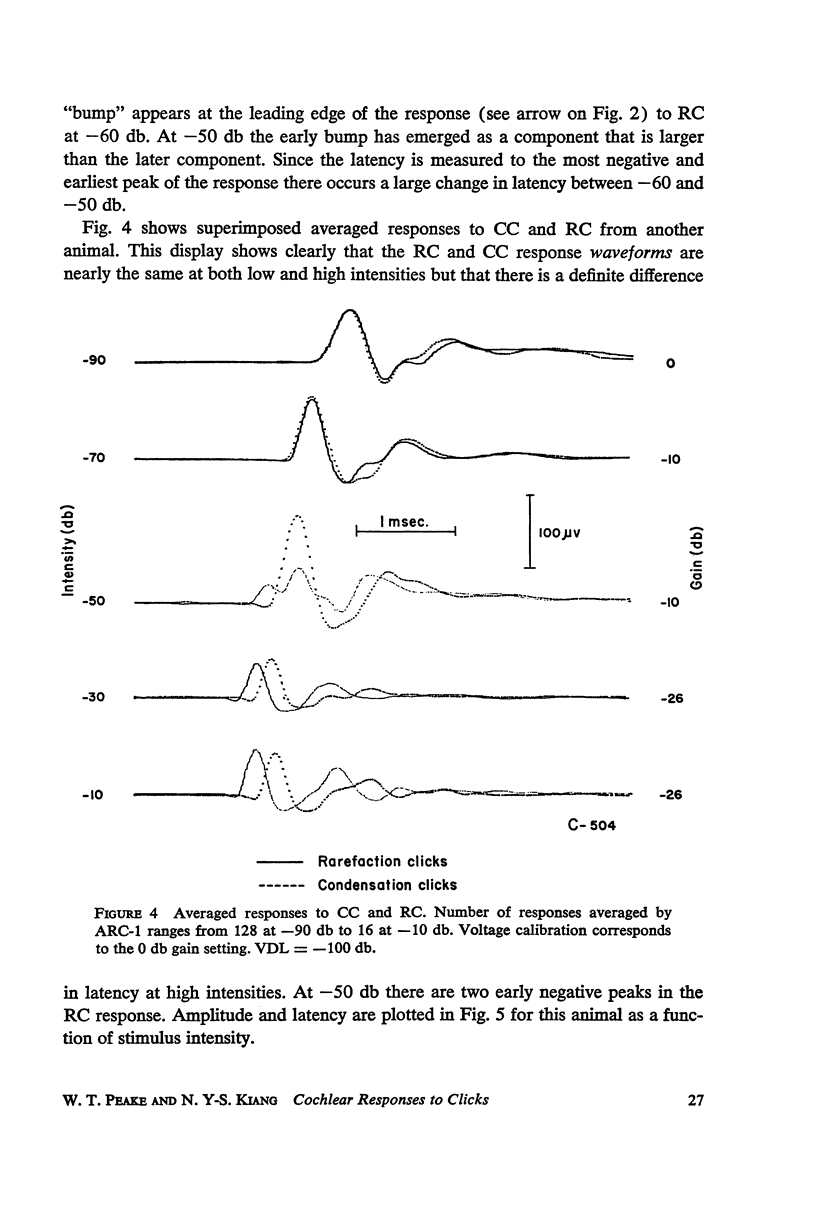
Abstract
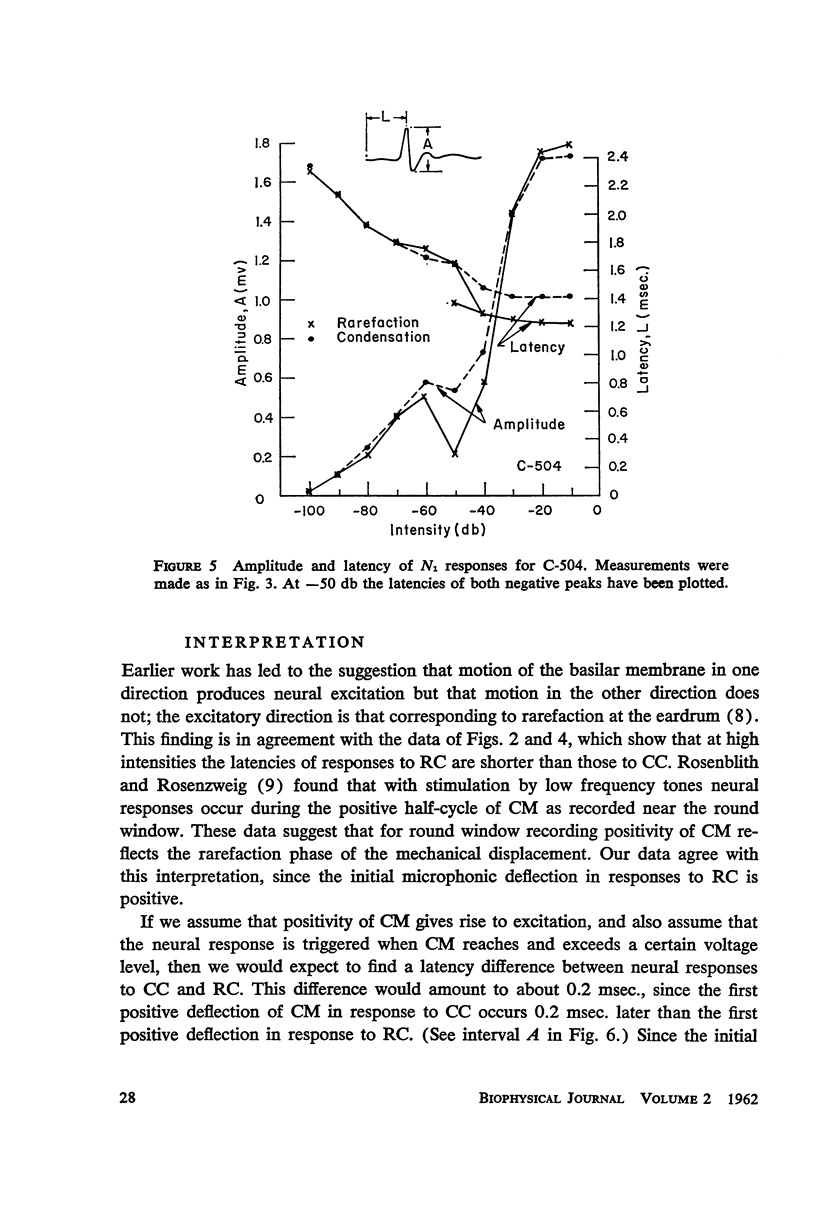
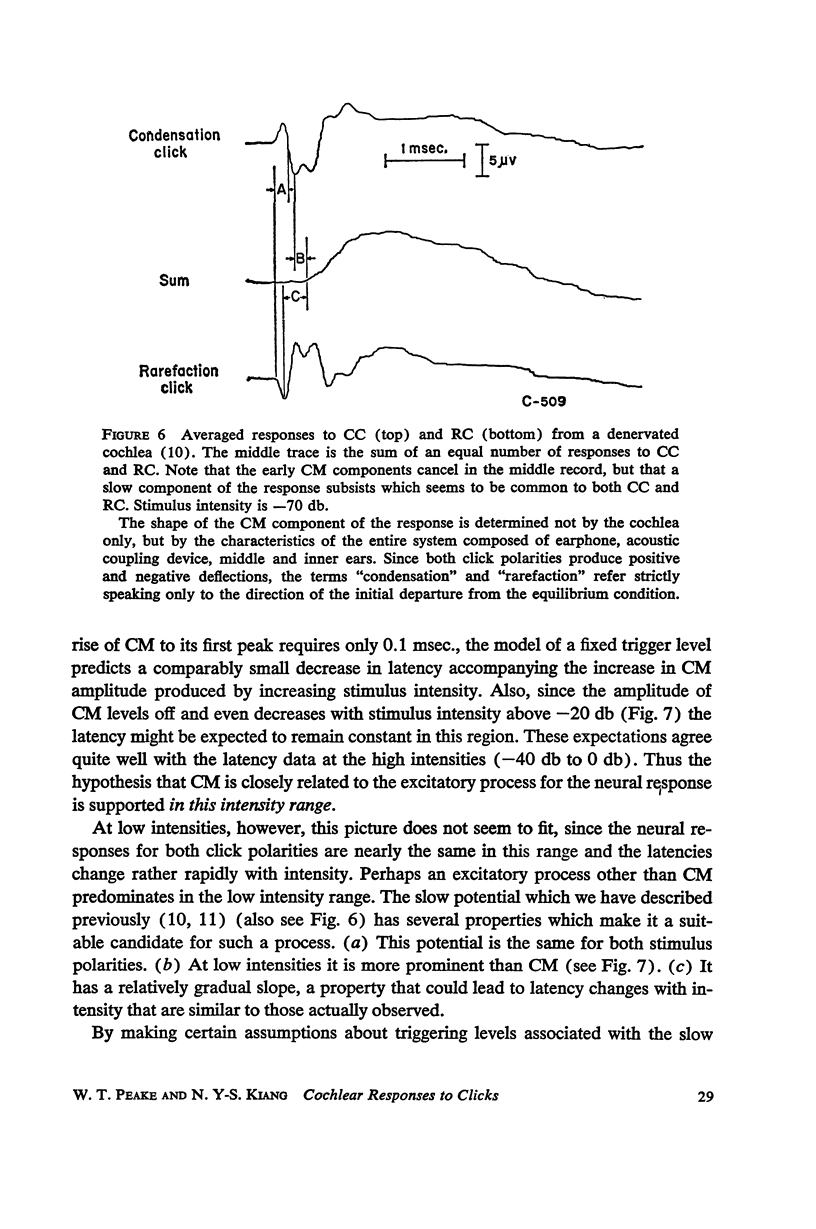
Auditory nerve responses to condensation and rarefaction clicks (CC and RC) have been recorded over a wide intensity range with gross electrodes. At low intensities the RC responses are nearly identical to CC responses. At high intensities RC and CC response waveforms are similar, but the latency of the N1 peak in the RC response is 0.2 msec. shorter than that for the corresponding CC response. At intermediate intensities the RC and CC response waveforms are quite different. These results can be interpreted in terms of a model in which there are two excitatory mechanisms for the neural response, which are operative in different intensity ranges. The cochlear microphonic potential and a “slow” potential are suggested as possible excitatory mechanisms.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIS H. Biophysics and physiology of the inner ear. Physiol Rev. 1957 Jan;37(1):1–49. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1957.37.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS H., DEATHERAGE B. H., ROSENBLUT B., FERNANDEZ C., KIMURA R., SMITH C. A. Modification of cochlear potentials produced by streptomycin poisoning and by extensive venous obstruction. Laryngoscope. 1958 Mar;68(3):596–627. doi: 10.1002/lary.5540680341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS H., FERNANDEZ C., McAULIFFE D. R. The excitatory process in the cochlea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1950 Oct;36(10):580–587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.36.10.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS H. [A mechano-electrical theory of cochlear action]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1958 Sep;67(3):789–801. doi: 10.1177/000348945806700315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISE G. A., ROSENBLITH W. A. Electrical responses to acoustic stimuli recorded at the round window of the pigeon. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1952 Oct;45(5):401–412. doi: 10.1037/h0060226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIANG N. Y., PEAKE W. Components of electrical responses recorded from the cochlea. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1960 Jun;69:448–458. doi: 10.1177/000348946006900213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


