Abstract
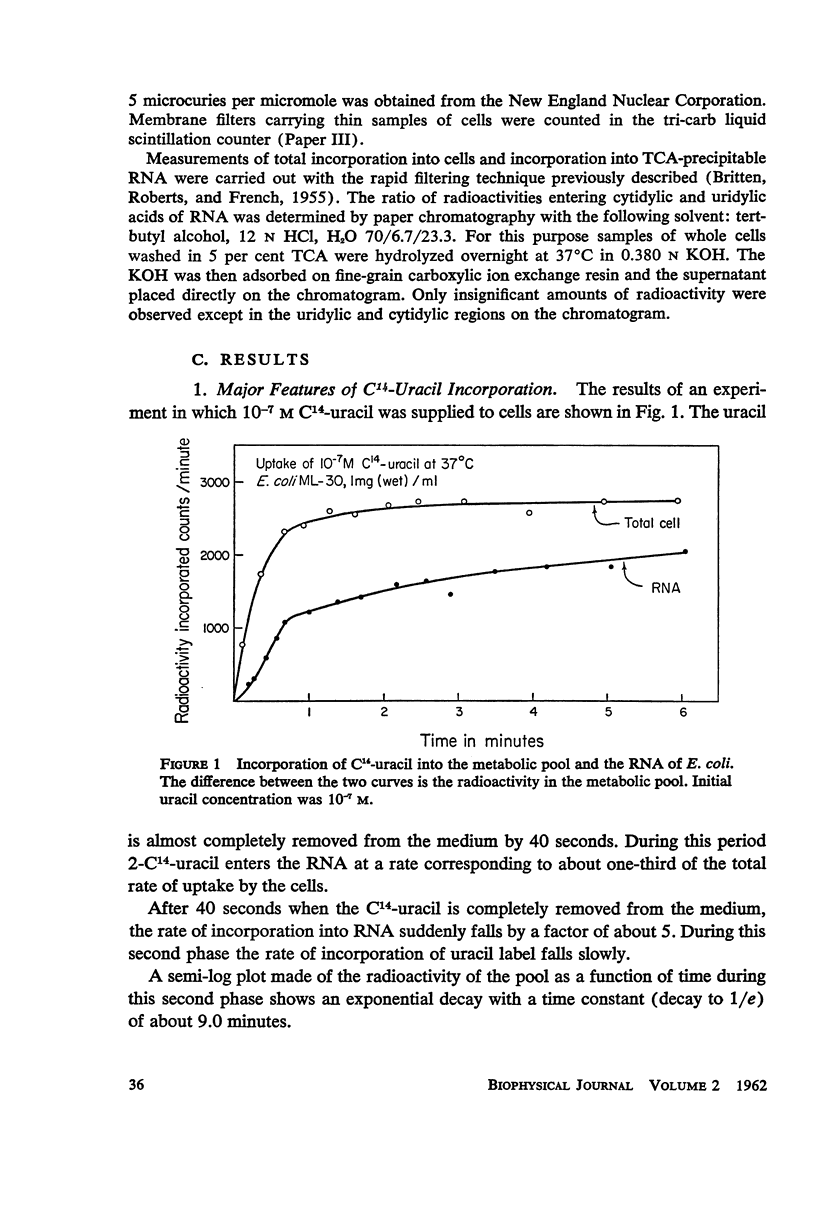
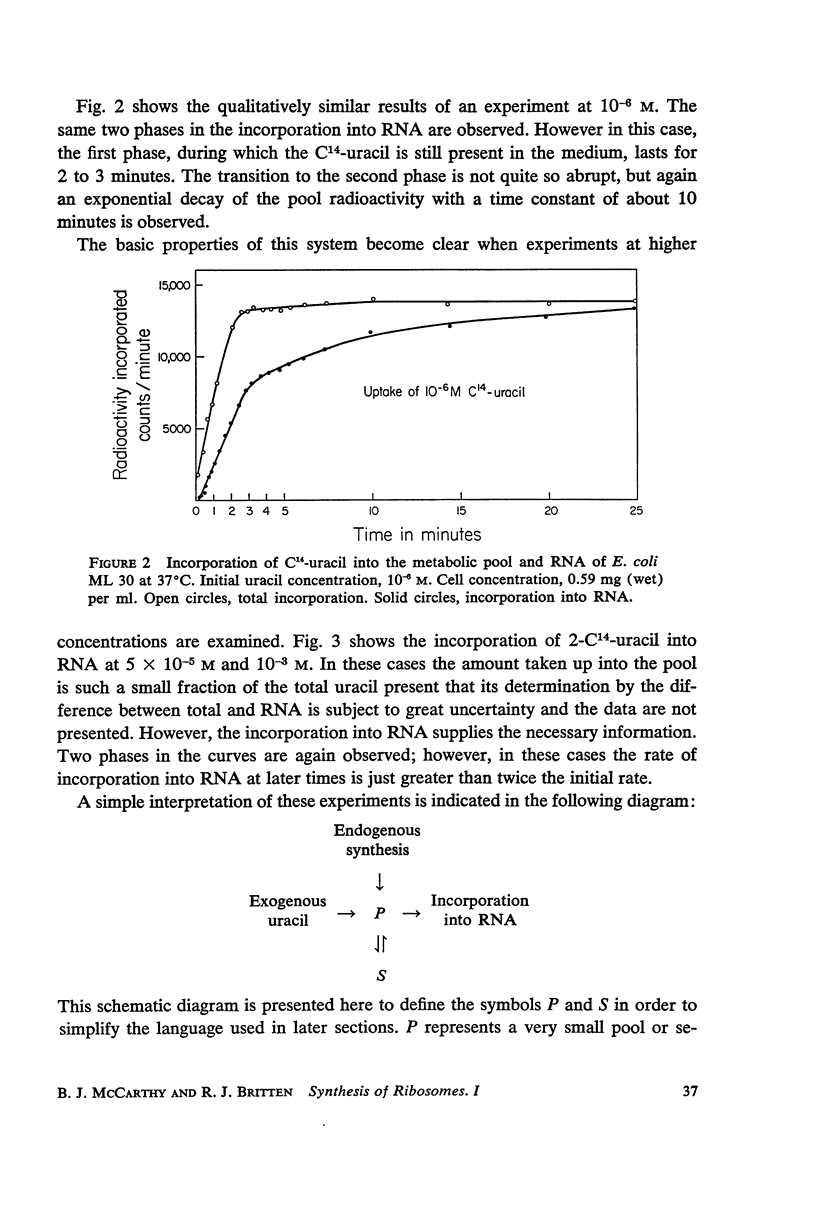
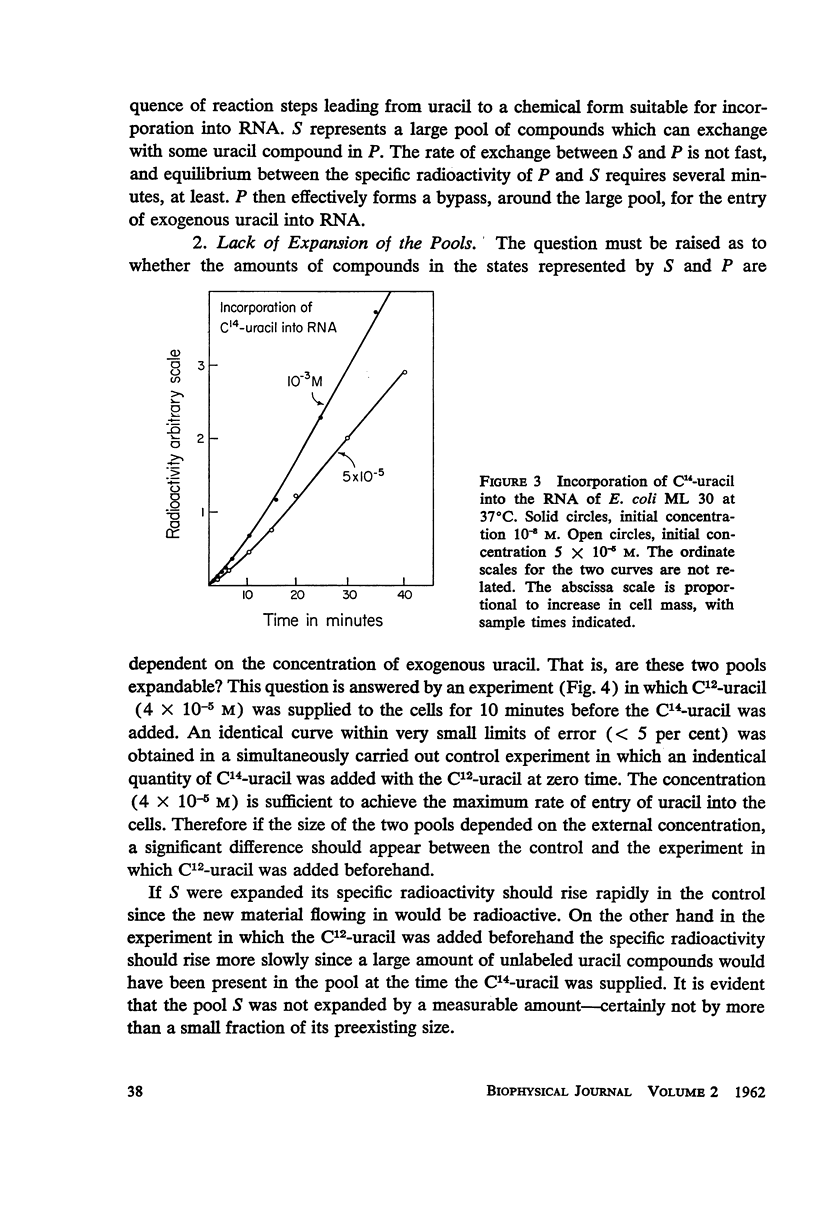
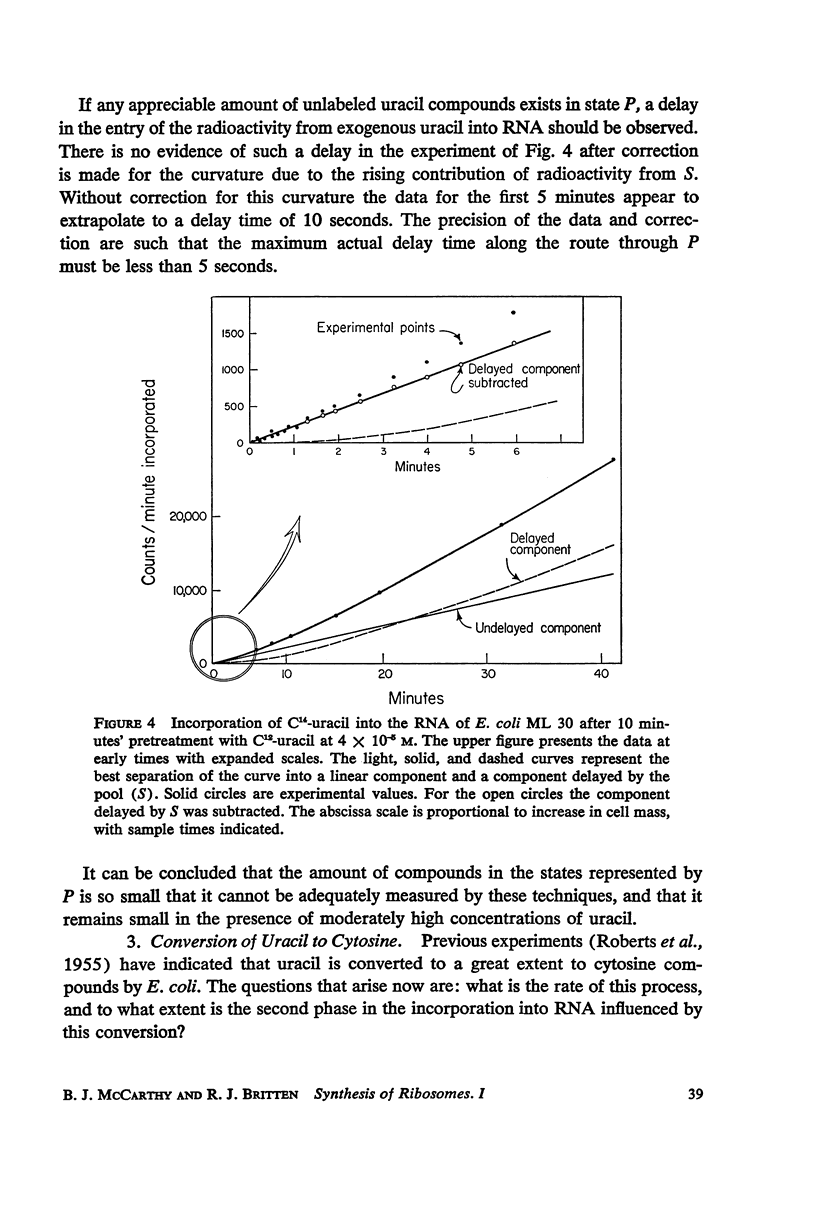
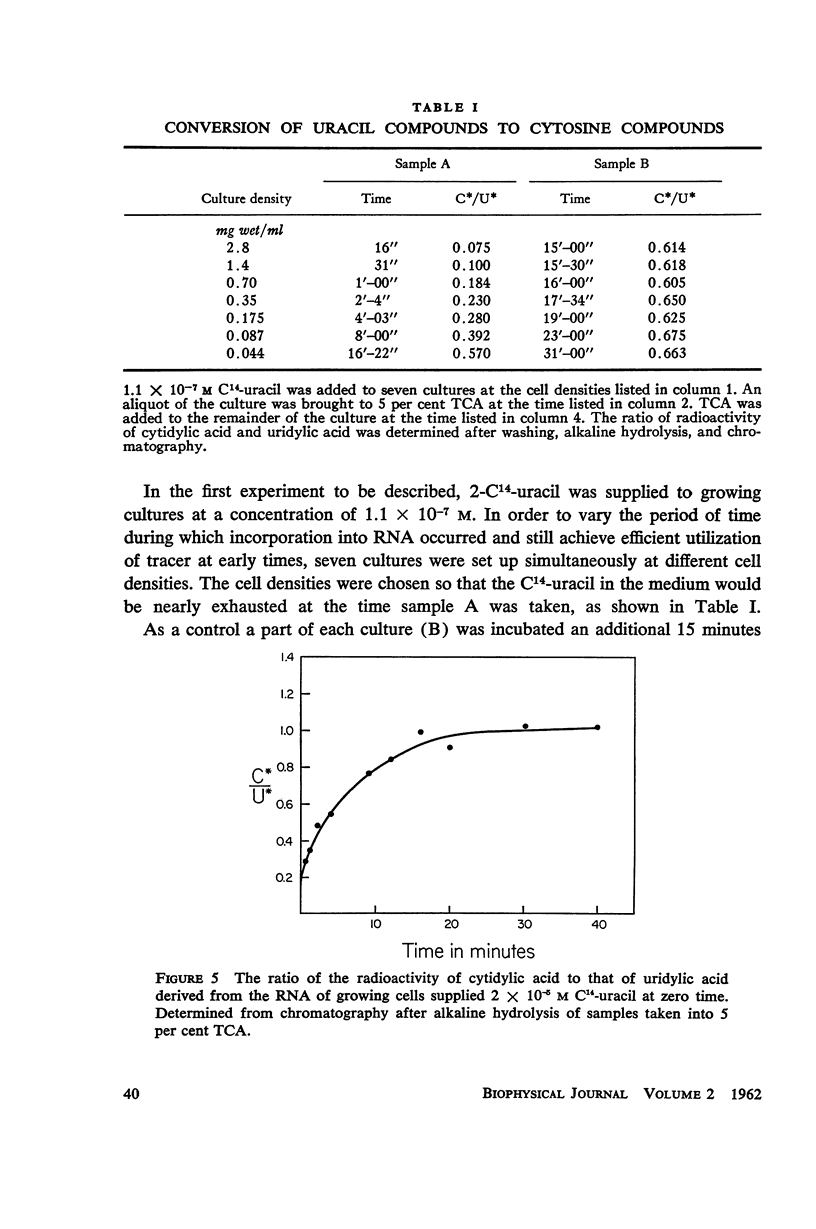
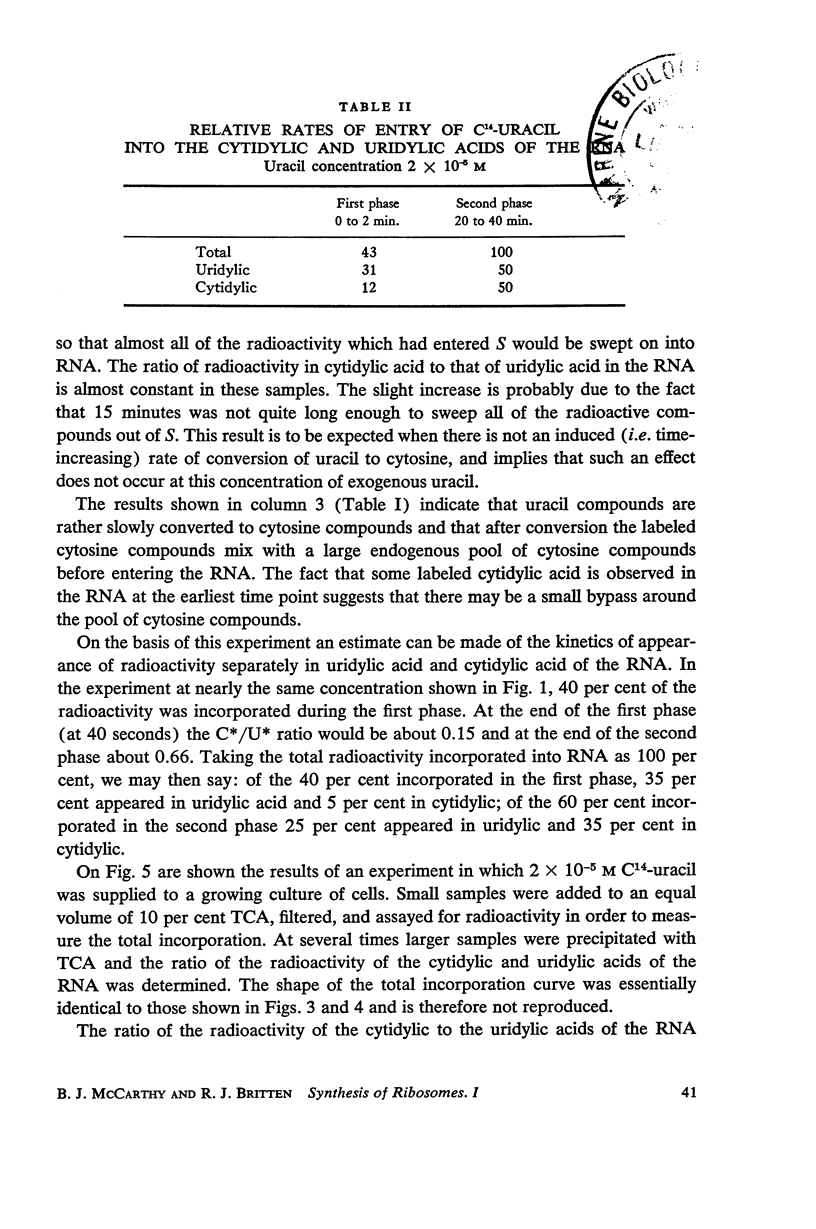
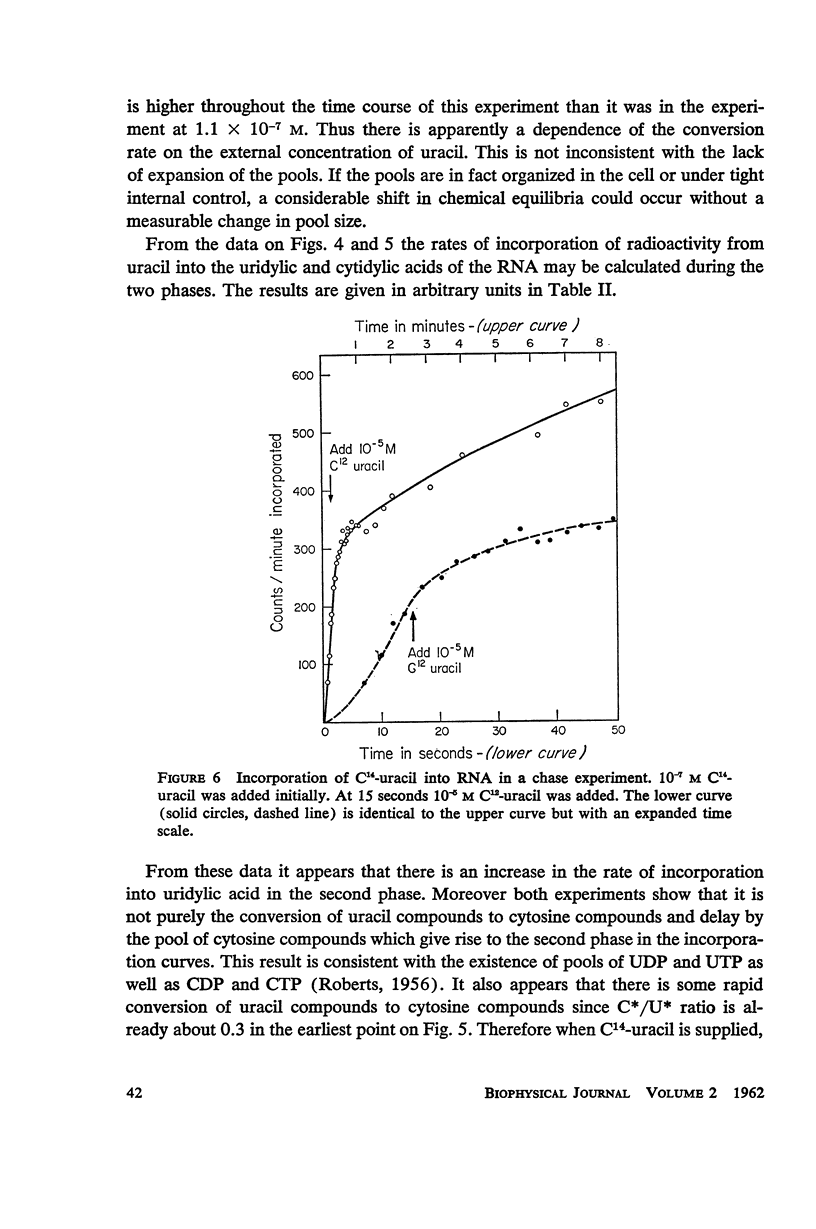
C14-uracil is rapidly incorporated by E. coli at low concentrations. Approximately half the radioactivity passes directly into RNA with very little delay. The remaining half enters a large metabolic pool and later is incorporated into RNA. The total rate of uptake (growing cells) is not greater than the requirement for uracil and cytosine for RNA synthesis. The size of the metabolic pool is not influenced measurably by the external uracil concentration. No evidence is found for the existence of a fraction of RNA which is rapidly synthesized and degraded.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOEZI J. A., COWIE D. B. Kinetic studies of beta-galactosidase induction. Biophys J. 1961 Nov;1:639–647. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(61)86913-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J., Roberts R. B., French E. F. AMINO ACID ADSORPTION AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS IN Escherichia Coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1955 Nov 15;41(11):863–870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.41.11.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROS F., HIATT H., GILBERT W., KURLAND C. G., RISEBROUGH R. W., WATSON J. D. Unstable ribonucleic acid revealed by pulse labelling of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1961 May 13;190:581–585. doi: 10.1038/190581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., MONOD J. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1961 Jun;3:318–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(61)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


