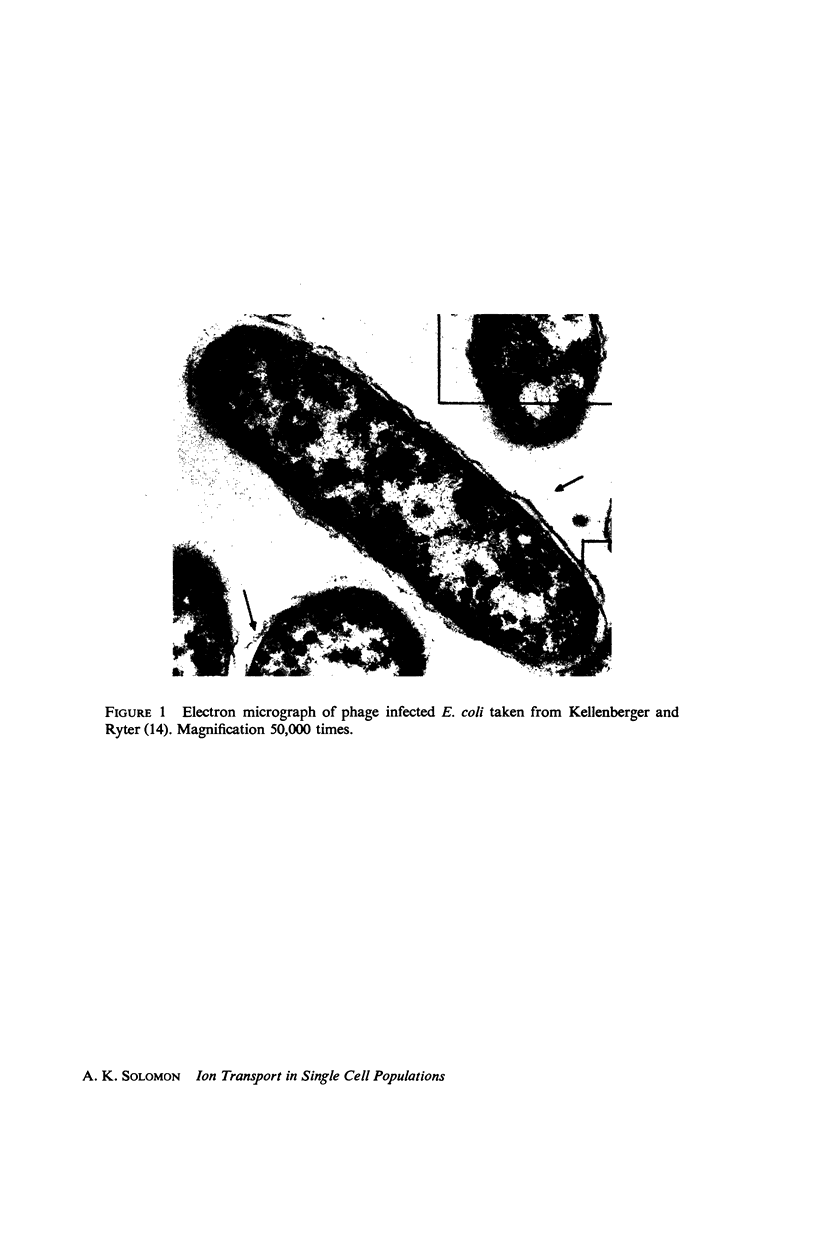
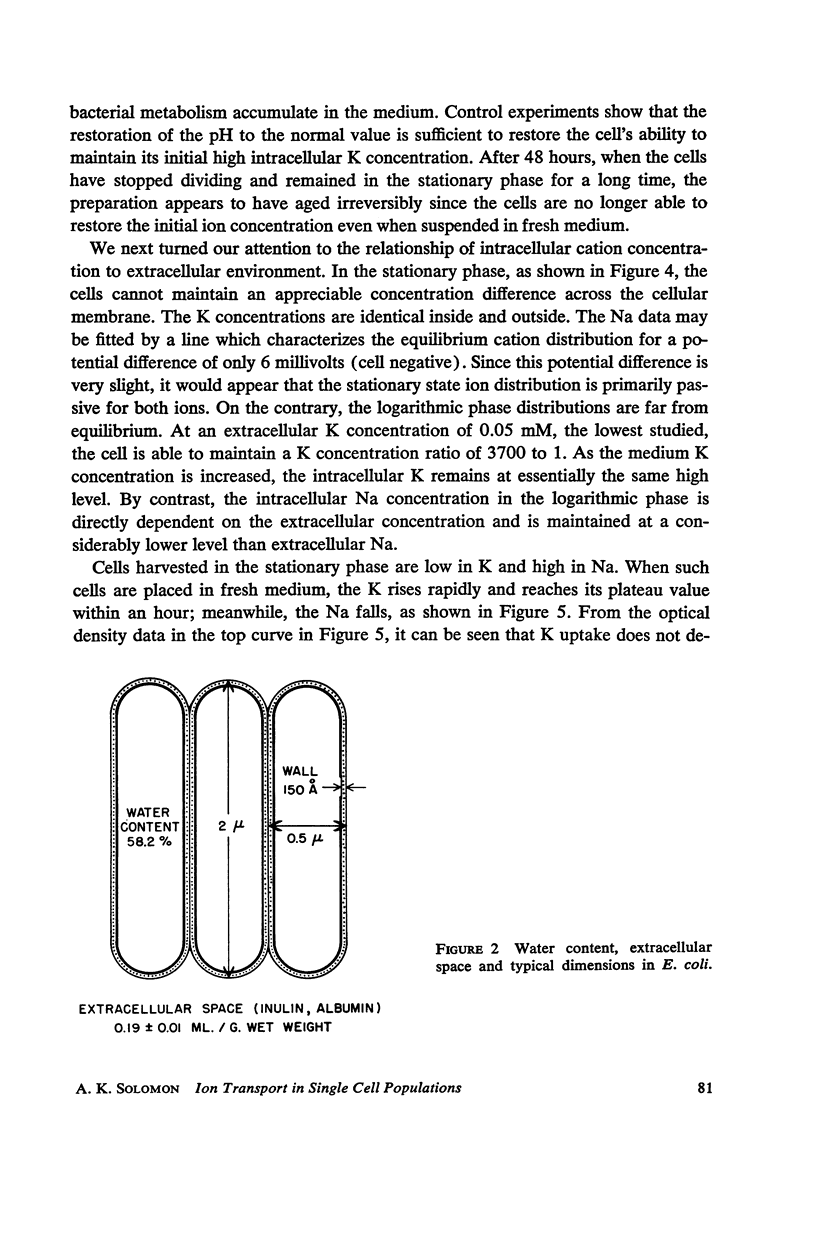
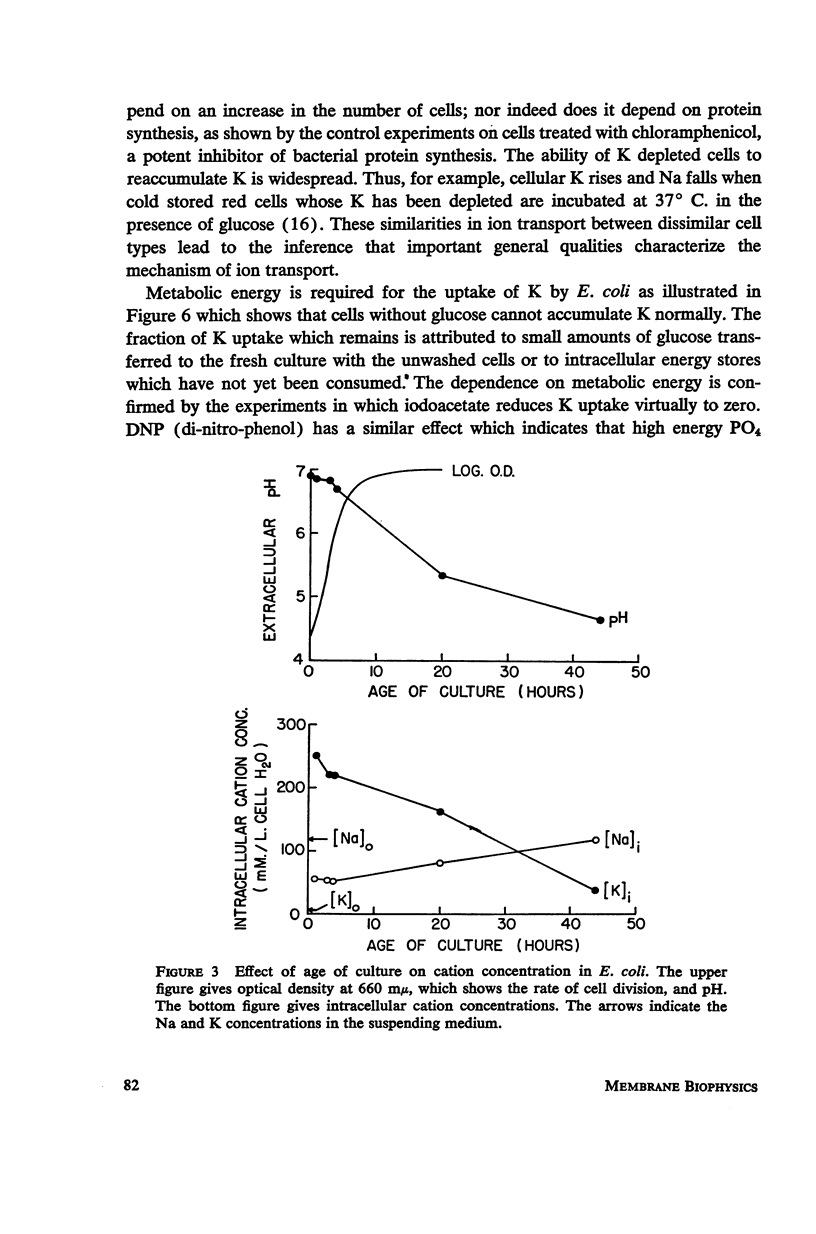
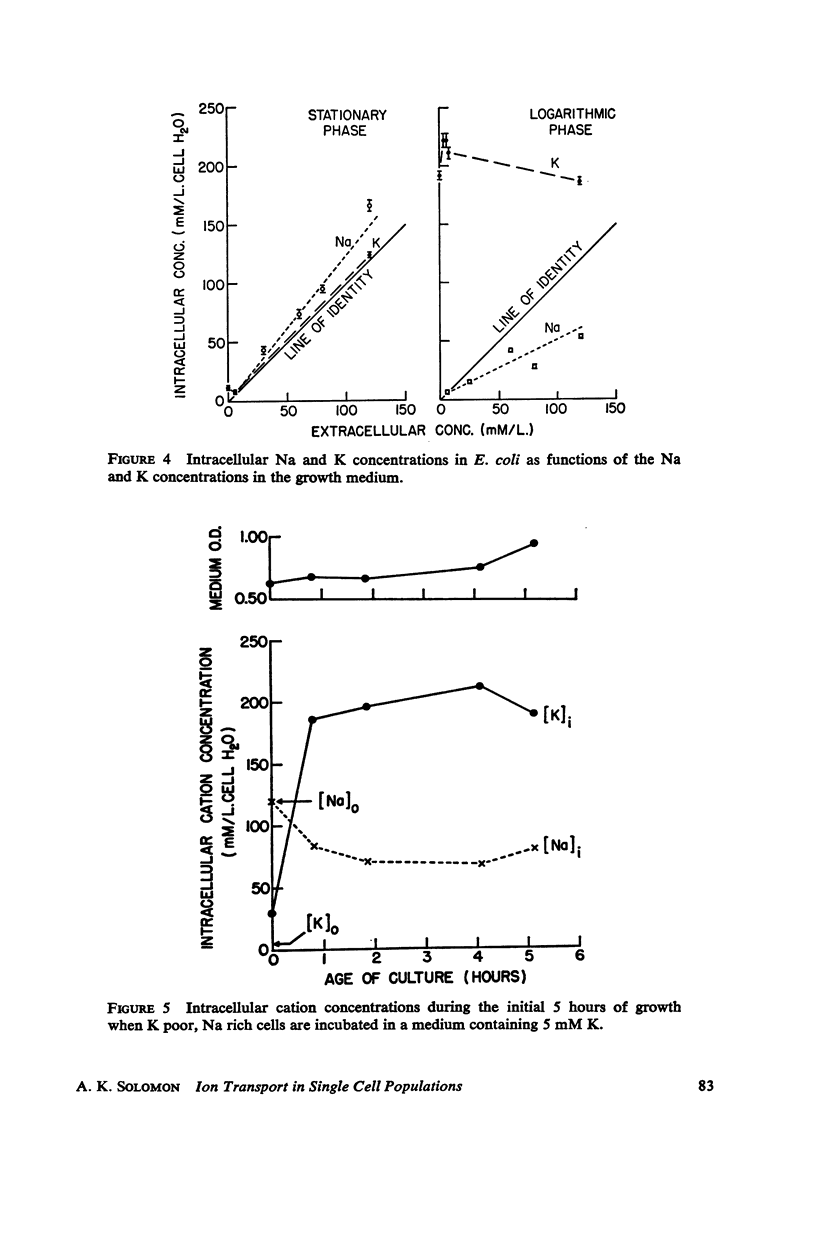
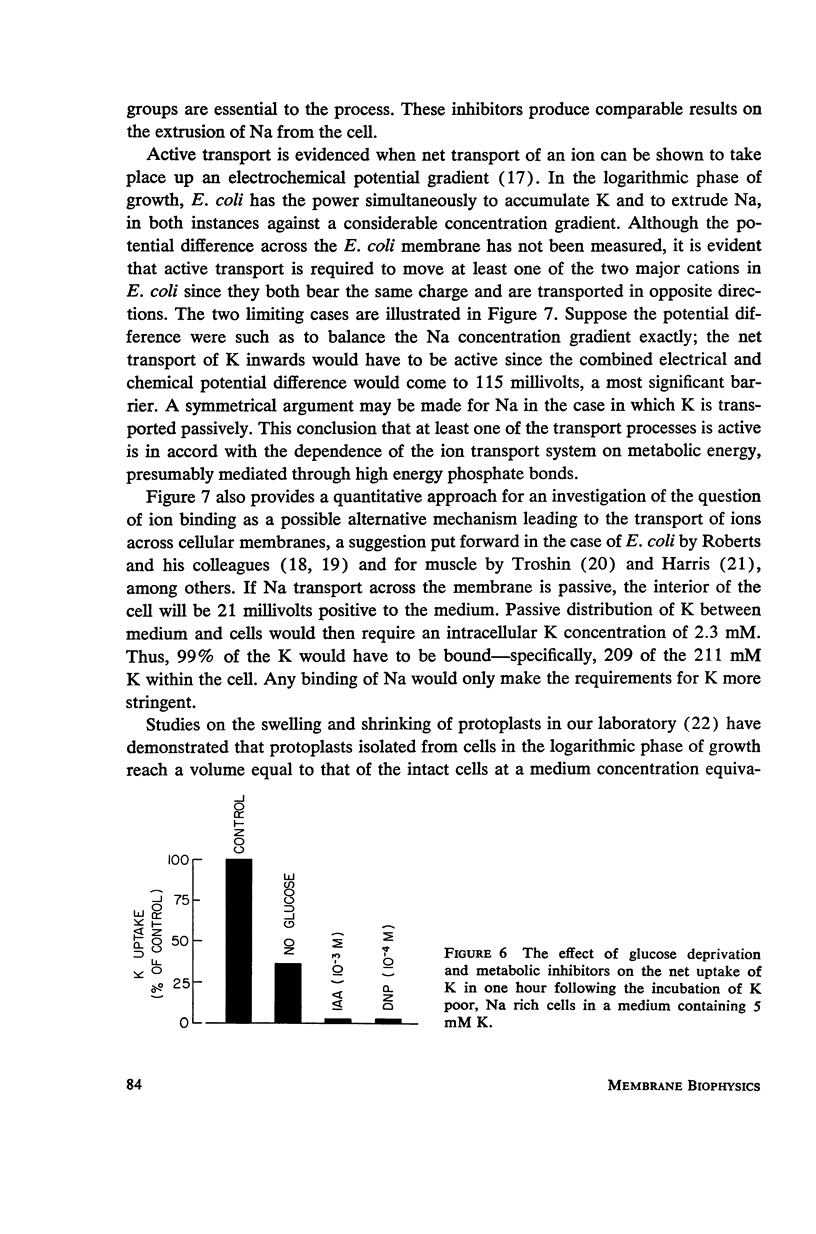
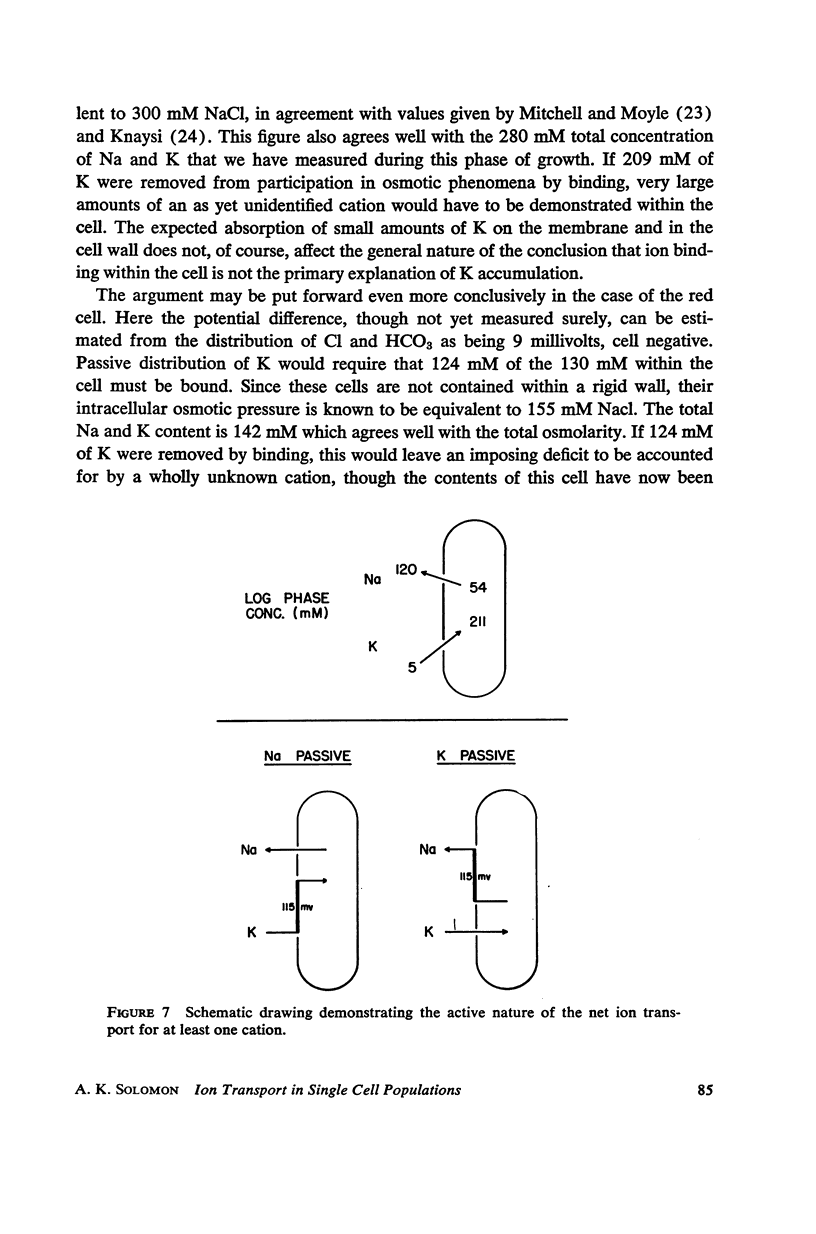
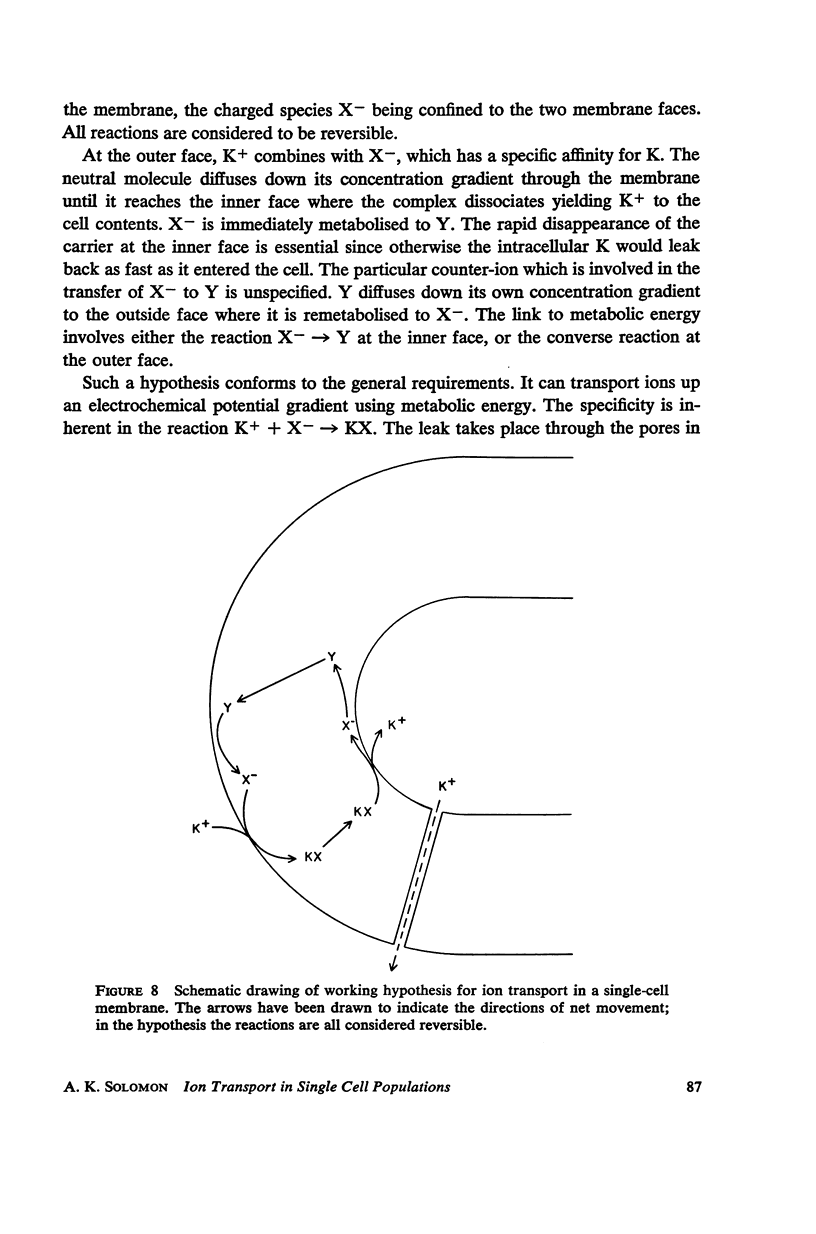
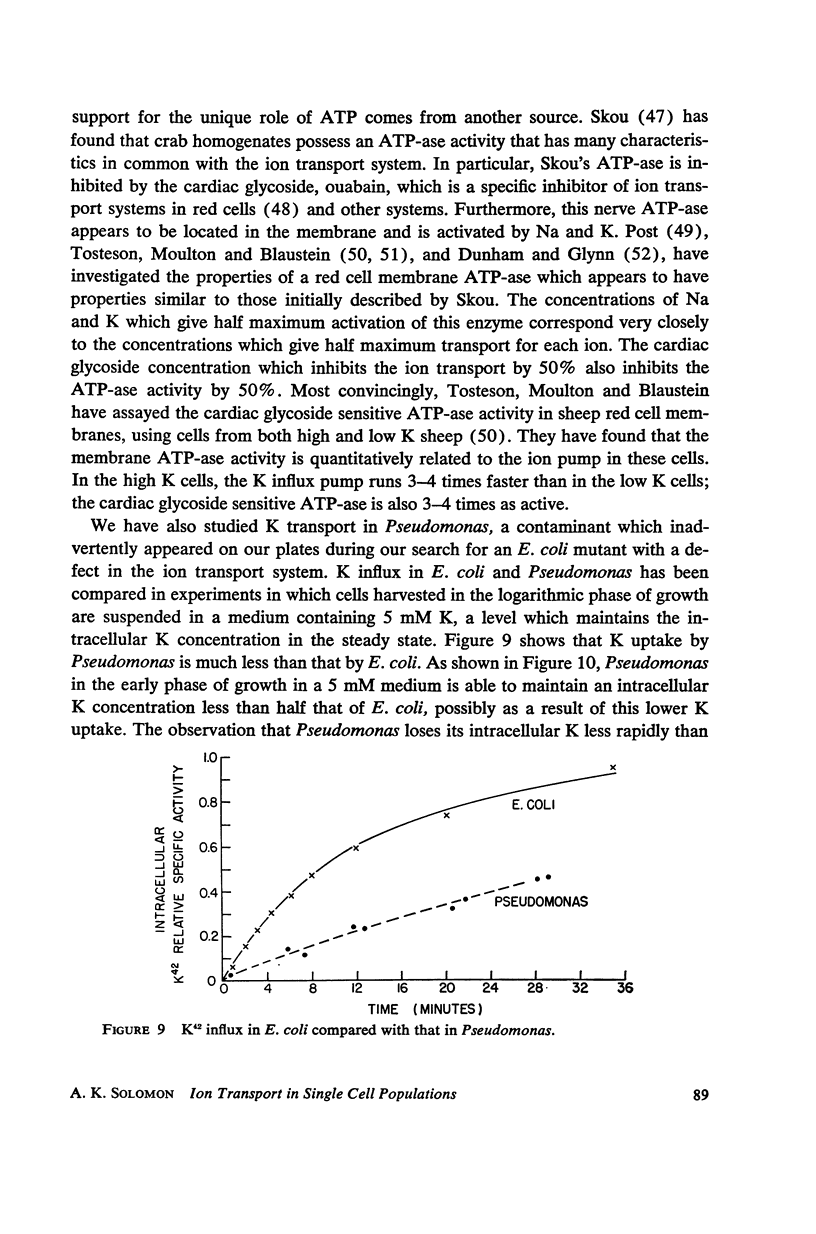
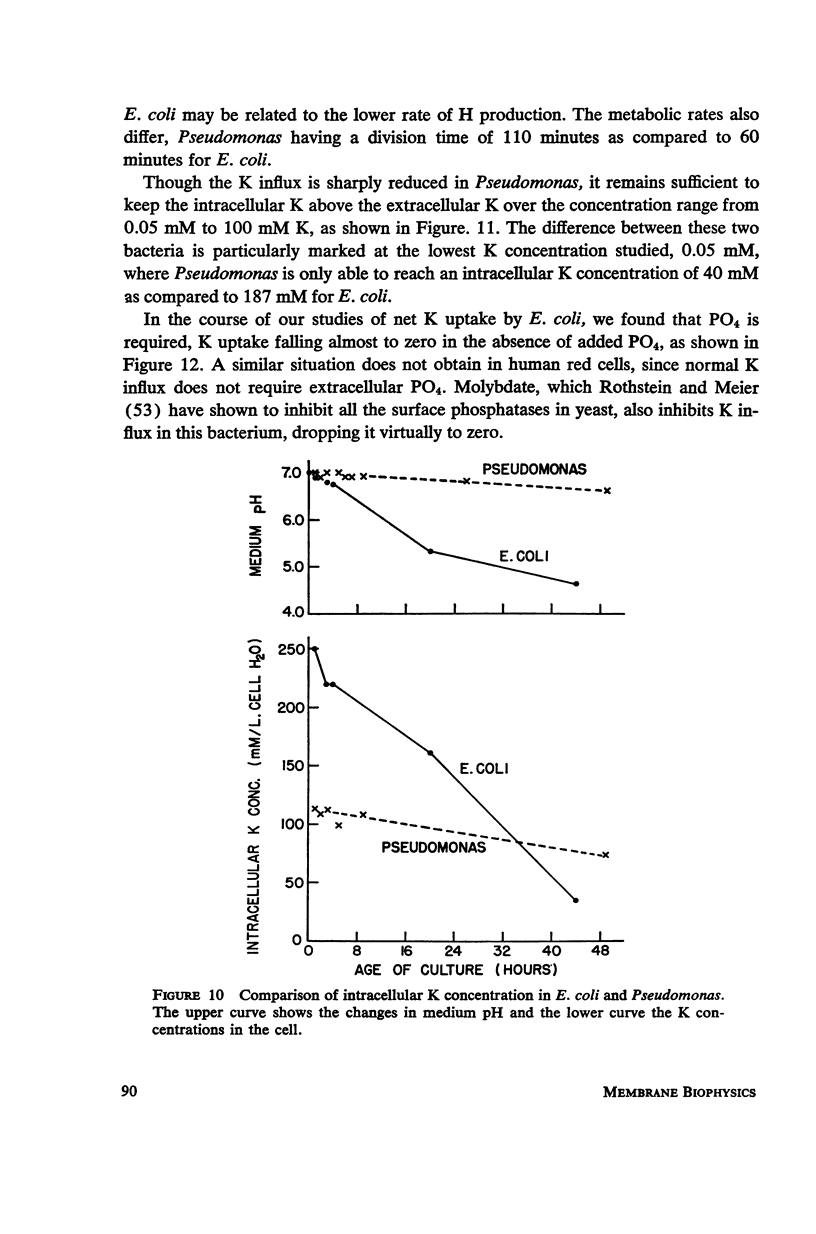
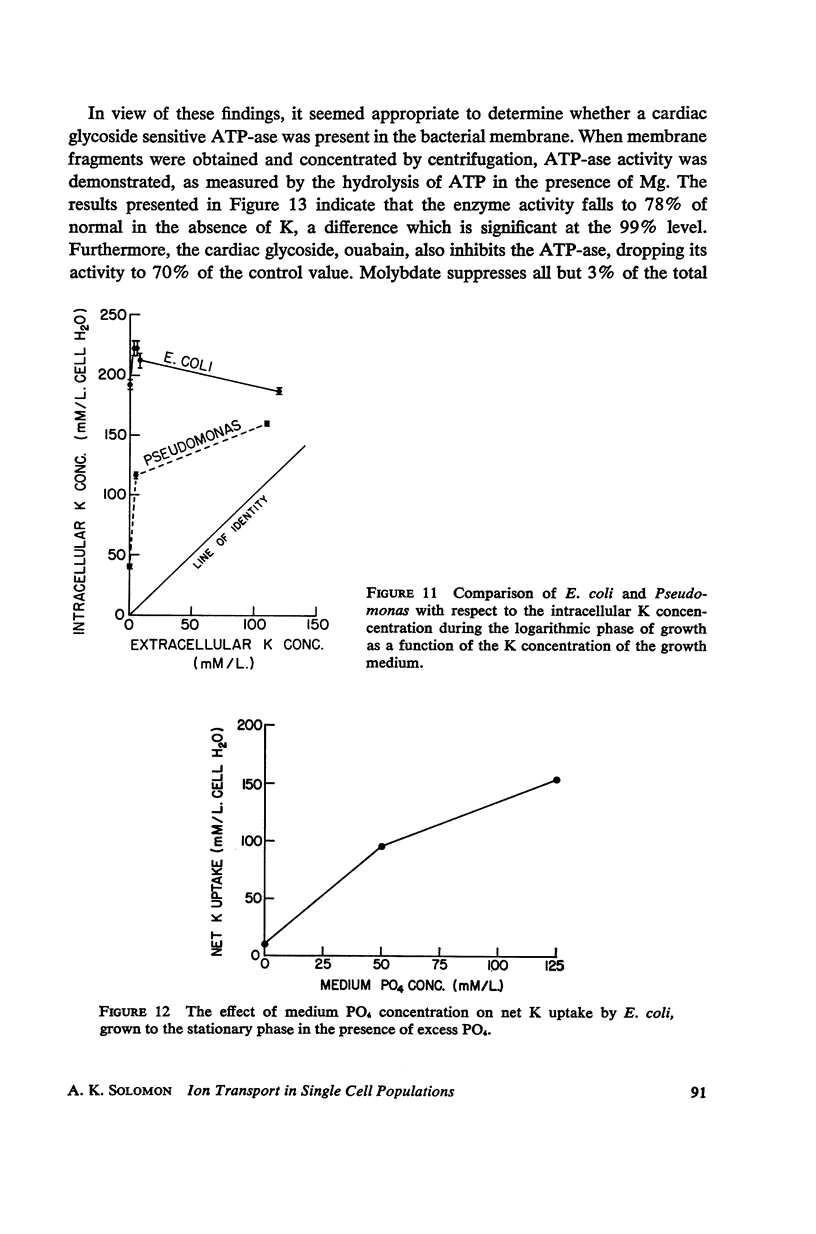
Full text
PDF


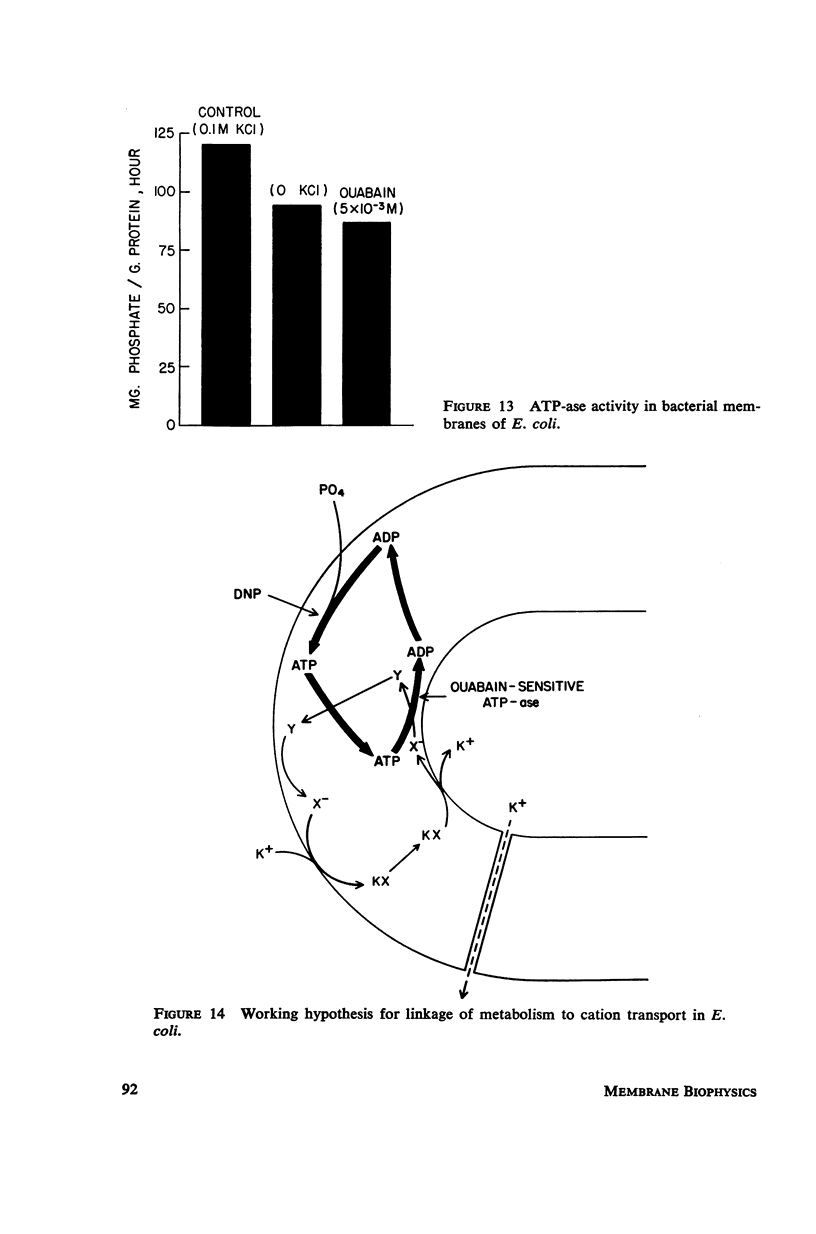



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CALDWELL P. C., HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D., SHAW T. L. The effects of injecting 'energy-rich' phosphate compounds on the active transport of ions in the giant axons of Loligo. J Physiol. 1960 Jul;152:561–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN H. N. Possible role of chelation between alkali metals and pyridoxal in biological transport. Science. 1955 Dec 2;122(3179):1087–1088. doi: 10.1126/science.122.3179.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., LIONETTI F., SOLOMON A. K. Possible cation-carrier substances in blood. Nature. 1956 Sep 15;178(4533):582–583. doi: 10.1038/178582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNHAM E. T., GLYNN I. M. Adenosinetriphosphatase activity and the active movements of alkali metal ions. J Physiol. 1961 Apr;156:274–293. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENMAN G., RUDIN D. O., CASBY J. U. Glass electrode for measuring sodium ion. Science. 1957 Oct 25;126(3278):831–834. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3278.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. V. Electrolyte concentrations in red blood cells of British breeds of sheep. Nature. 1954 Nov 13;174(4437):931–932. doi: 10.1038/174931a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. V., HARRIS H., WARREN F. L. The distribution of haemoglobin and blood potassium types in British breeds of sheep. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Dec 4;149(935):249–262. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS J. V., PHILLIPSON A. T. Electrolyte concentrations in the erythrocytes of the goat and ox. J Physiol. 1957 Nov 14;139(1):87–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRAZIER H. S., SICULAR A., SOLOMON A. K. Potassium uptake by the dog erythrocyte. J Gen Physiol. 1954 May 20;37(5):631–641. doi: 10.1085/jgp.37.5.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDOS G. Akkumulation der Kaliumionen durch menschliche Blutkörperchen. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1954;6(2-3):191–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERLACH E., FLECKENSTEIN A., GROSS E. Der intermediäre Phosphat-Stoffwechsel des Menschen-Erythrocyten; papierchromatographische Studien unter Verwendung von 32P-markiertem Orthophosphat. Pflugers Arch. 1958;266(5):528–555. doi: 10.1007/BF00362257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIEBEL O., PASSOW H. [The permeability of erythrocyte membranes for organic anions. On the problem of diffusion through the pores]. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1960;271:378–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILL T. J., 3rd, GOLD G. L., SOLOMON A. K. The kinetics of cardiac glycoside inhibition of potassium transport in human erythrocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1956 Nov 20;40(2):327–350. doi: 10.1085/jgp.40.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLD G. L., SOLOMON A. K. The transport of sodium into human erythrocytes in vivo. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Jan 20;38(3):389–404. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSTEIN D. A., SOLOMON A. K. Determination of equivalent pore radius for human red cells by osmotic pressure measurement. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Sep;44:1–17. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS E. J., MAIZELS M. The permeability of human erythrocytes to sodium. J Physiol. 1951 May;113(4):506–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINZ E., DURBIN R. P. Studies of the chloride transport in the gastric mucosa of the frog. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Sep 20;41(1):101–117. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEMPLING H. G. Potassium and sodium movements in the Ehrlich mouse ascites tumor cell. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Jan 20;41(3):565–583. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.3.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOKIN L. E., HOKIN M. R. Diglyceride kinase and phosphatidic acid phosphatase in erythrocyte membranes. Nature. 1961 Mar 11;189:836–837. doi: 10.1038/189836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A. Cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 May 25;4(3):323–326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRSCHNER L. B. The cation content of phospholipides from swine erythrocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Nov 20;42(2):231–241. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MITCHELL P. Structure and function in microorganisms. Biochem Soc Symp. 1959;16:73–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., JOLLY P. C. The linkage of sodium, potassium, and ammonium active transport across the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Jul;25(1):118–128. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSTEIN A., MEIER R. The relationship of the cell surface to metabolism; the role of cell surface phosphatases of yeast. J Cell Physiol. 1949 Aug;34(1):97–114. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030340107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHATZMANN H. J. Herzglykoside als Hemmstoffe für den aktiven Kalium- und Natriumtransport durch die Erythrocytenmembran. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1953;11(4):346–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A. K., GOLD G. L. Potassium transport in human erythrocytes: evidence for a three compartment system. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Jan 20;38(3):371–388. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOLOMON A. K. The permeability of the human erythrocyte to sodium and potassium. J Gen Physiol. 1952 May;36(1):57–110. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.1.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach H. B. On the Sodium and Potassium Balance of Isolated Frog Muscles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 May;38(5):451–455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.5.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VILLEGAS R., BARNOLA F. V. Characterization of the resting axolemma in the giant axon of the squid. J Gen Physiol. 1961 May;44:963–977. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.5.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]