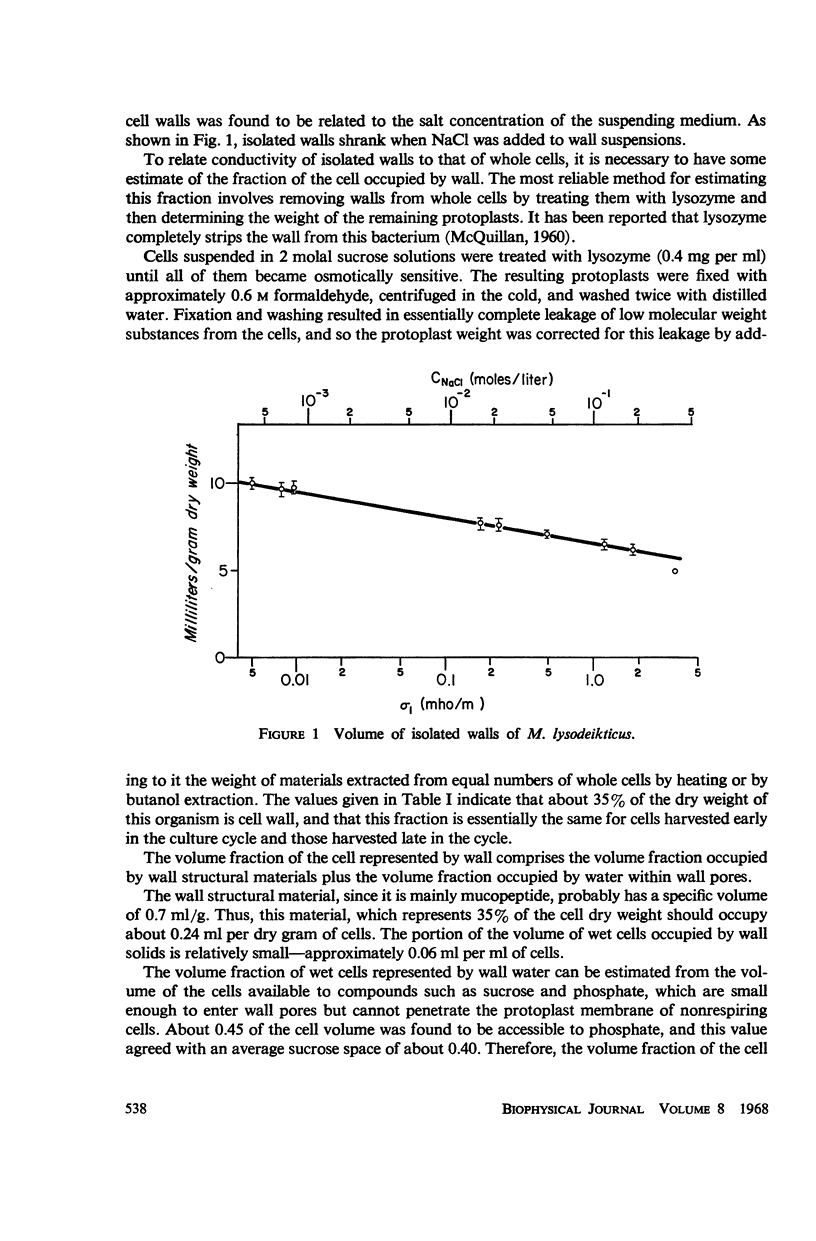
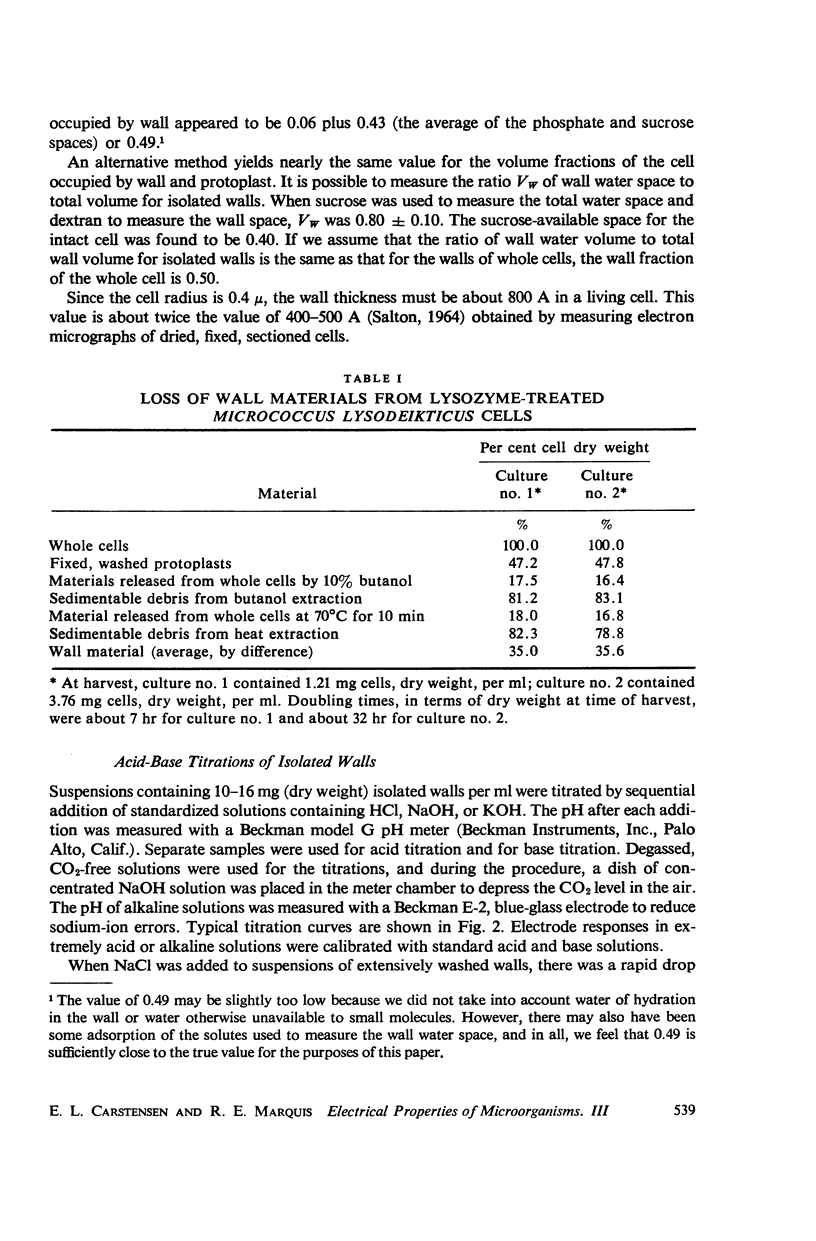
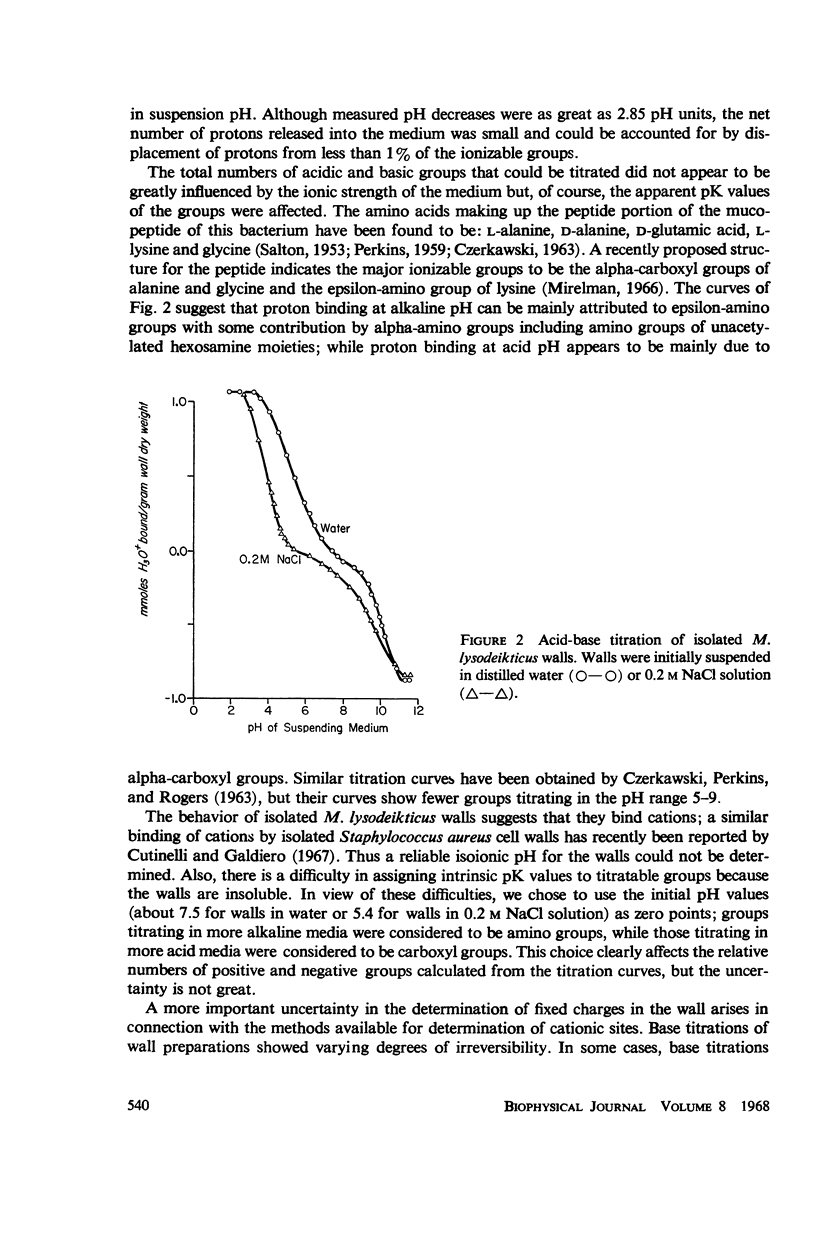
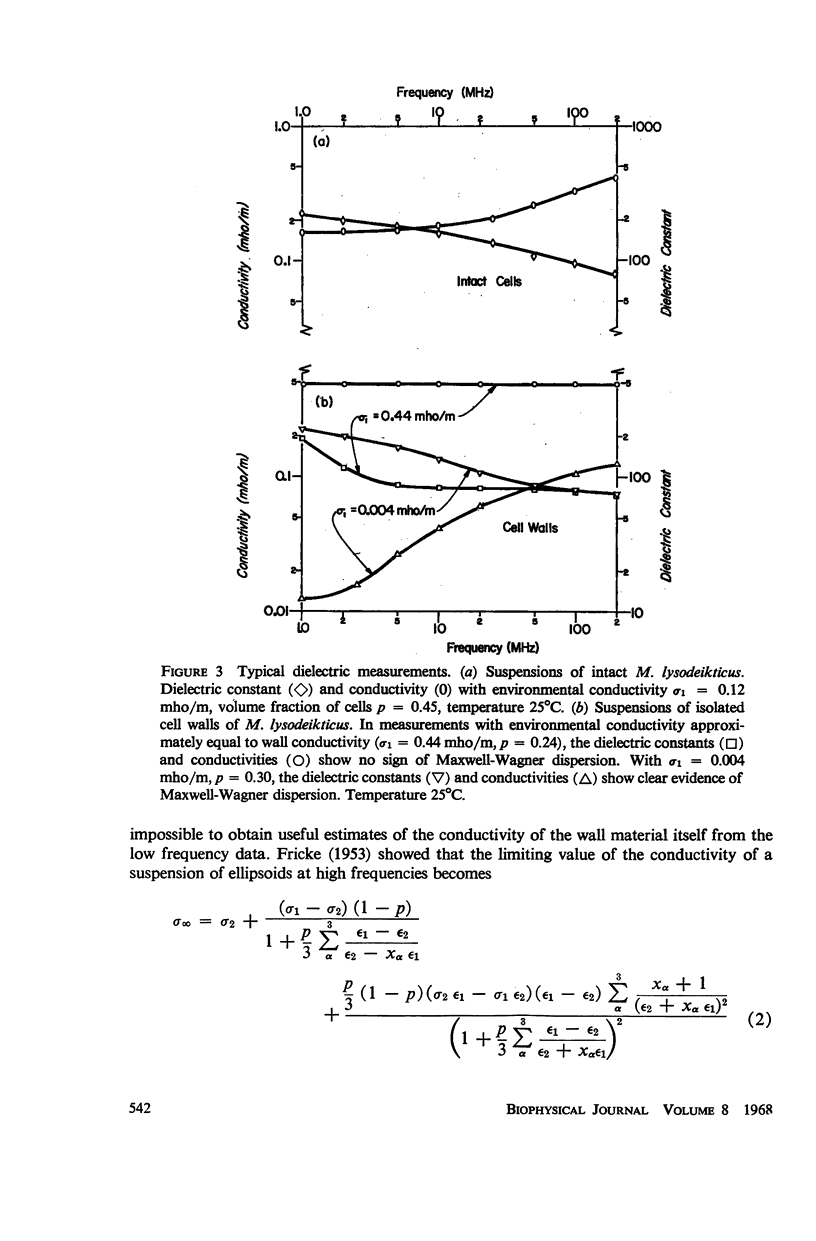
Abstract
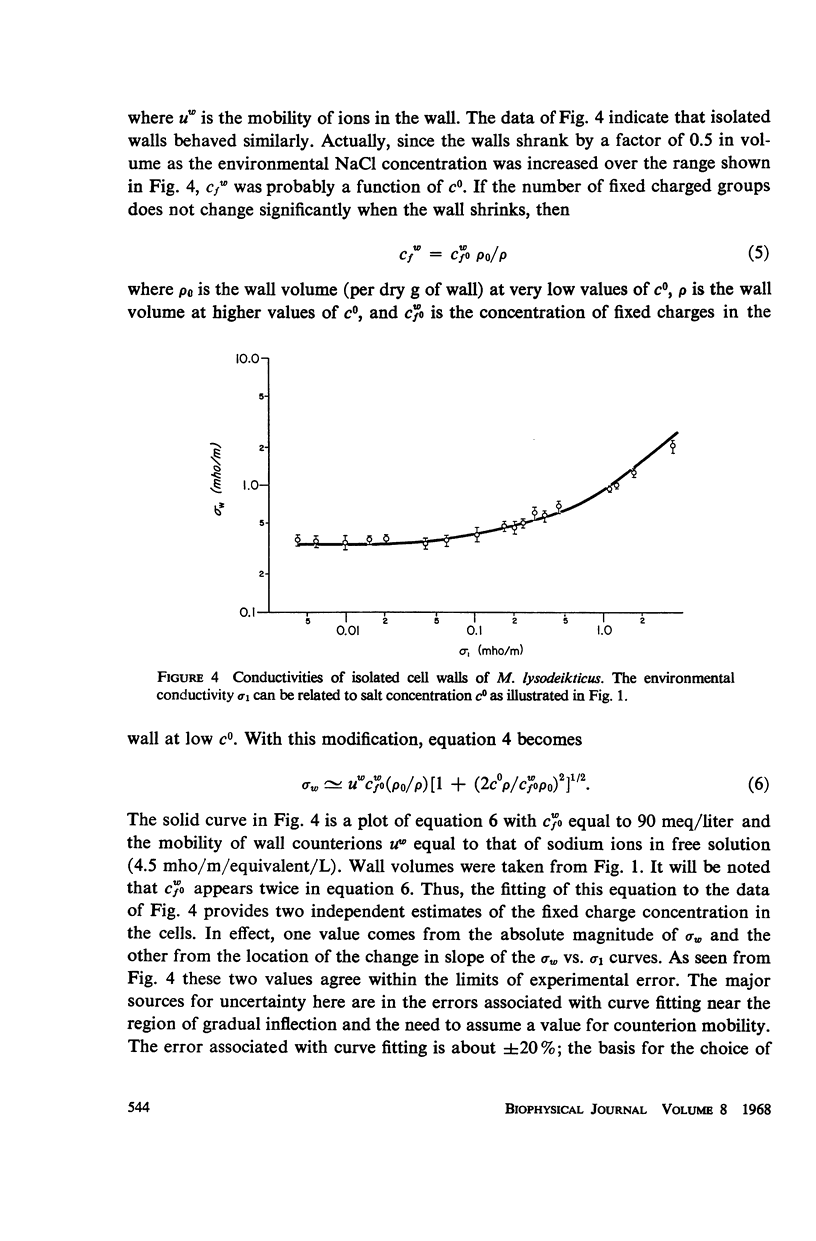
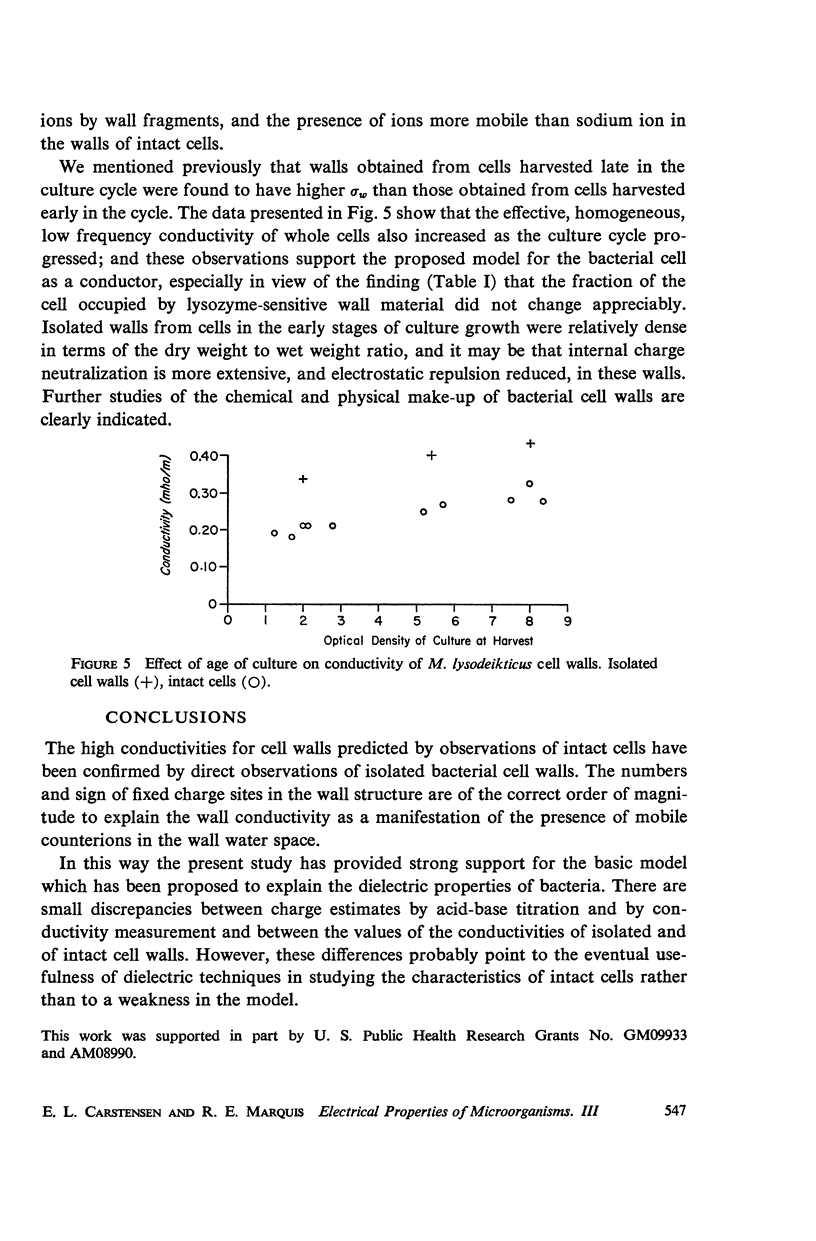
The dielectric properties of isolated Micrococcus lysodeikticus cell walls have been studied to establish more firmly the view that wall-associated ions play a major role in the conduction of low frequency electric current by intact bacterial cells. The conductivity of isolated walls was found to be about 0.40 mho/m. If counterions associated with fixed, ionized groups in the wall have average mobilities equal to that of sodium ions in free solution, the fixed charge concentration required to account for the measured conductivity is between 75 and 95 meq/liter of wet wall volume. Estimates of the numbers of titratable amino and carboxyl groups in wall polymers indicate that conductivity is more closely related to net wall charge than to total wall charge. The measured wall conductivity was used to predict a value of 0.15 ± 0.03 mho/m for whole cell conductivity. This prediction is close to the measured value of 0.25 ± 0.05 mho/m and it is thought that much of the disparity in values is related to changes in wall structure and composition during the isolation procedures.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRITT E. M., GERHARDT P. Bacterial permeability; total uptake of lysine by intact cells, protoplasts, and cell walls of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):288–293. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.288-293.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CZERKAWSKI J. W., PERKINS H. R., ROGERS H. J. A study of the composition and structure of the cell-wall mucopeptide of micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem J. 1963 Mar;86:468–474. doi: 10.1042/bj0860468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen E. L., Cox H. A., Mercer W. B., Natale L. A. Passive Electrical Properties of Microorganisms: I. Conductivity of Escherichia coli and Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biophys J. 1965 May;5(3):289–300. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(65)86717-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen E. L. Passive electrical properties of microorganisms. II. Resistance of the bacterial membrane. Biophys J. 1967 Sep;7(5):493–503. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86600-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutinelli C., Galdiero F. Ion-binding properties of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):2022–2023. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.2022-2023.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einolf C. W., Jr, Carstensen E. L. Bacterial conductivity in the determination of surface charge by microelectrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 28;148(2):506–516. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GERHARDT P., JUDGE J. A. POROSITY OF ISOLATED CELL WALLS OF SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE AND BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:945–951. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.4.945-951.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARQUIS R. E., GERHARDT P. RESPIRATION-COUPLED AND PASSIVE UPTAKE OF ALPHA-AMINOISOBUTYRIC ACID, A METABOLICALLY INERT TRANSPORT ANALOGUE, BY BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3361–3371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Sharon N. Isolation and characterization of two disaccharide-peptides from lysozyme digests of Micrococcus lysodeikticus cell walls. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jul 20;24(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90726-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKINS H. R., ROGERS H. J. The products of the partial acid hydrolysis of the mucopeptide from cell walls of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:647–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0720647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauly H., Schwan H. P. Dielectric properties and ion mobility in erythrocytes. Biophys J. 1966 Sep;6(5):621–639. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(66)86682-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SALTON M. R. Studies of the bacterial cell wall. IV. The composition of the cell walls of some Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1953 Apr;10(4):512–523. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(53)90296-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWAN H. P. Electrical properties of tissue and cell suspensions. Adv Biol Med Phys. 1957;5:147–209. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4832-3111-2.50008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


