Abstract
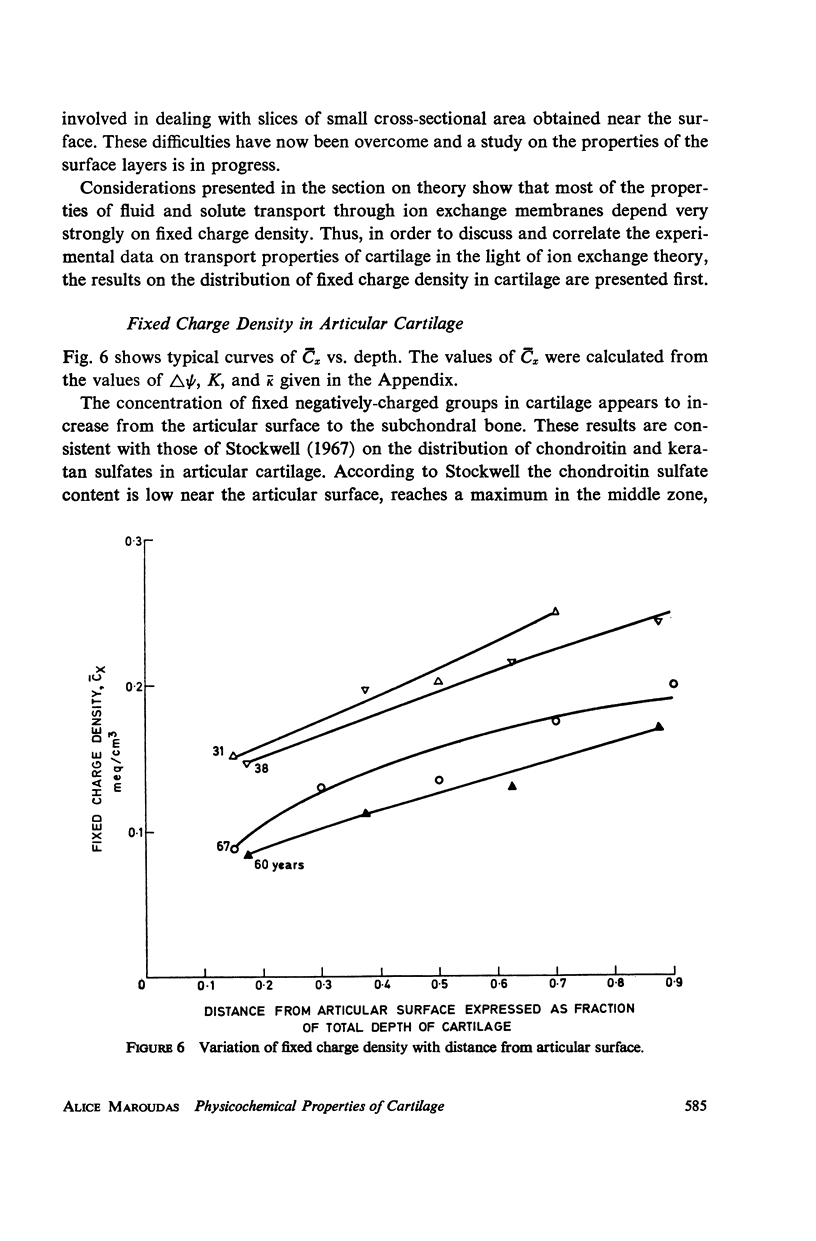
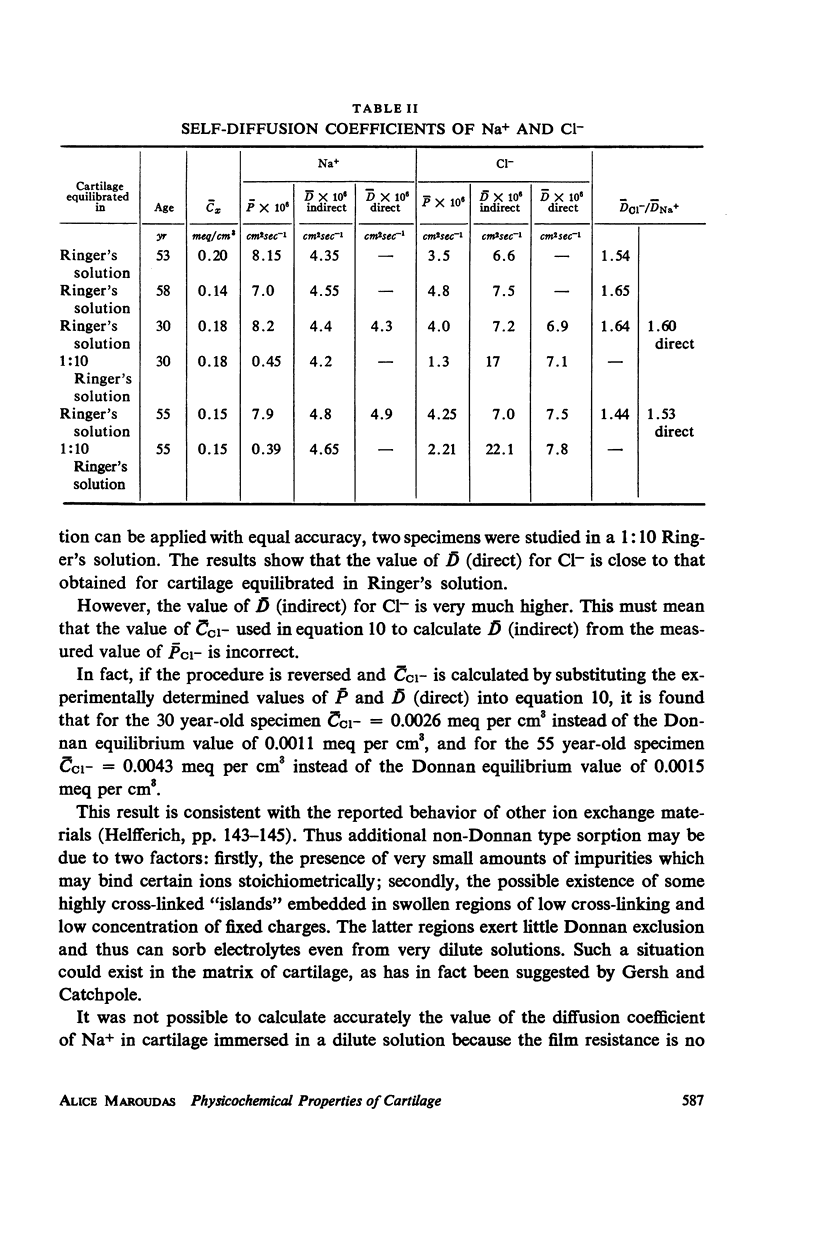
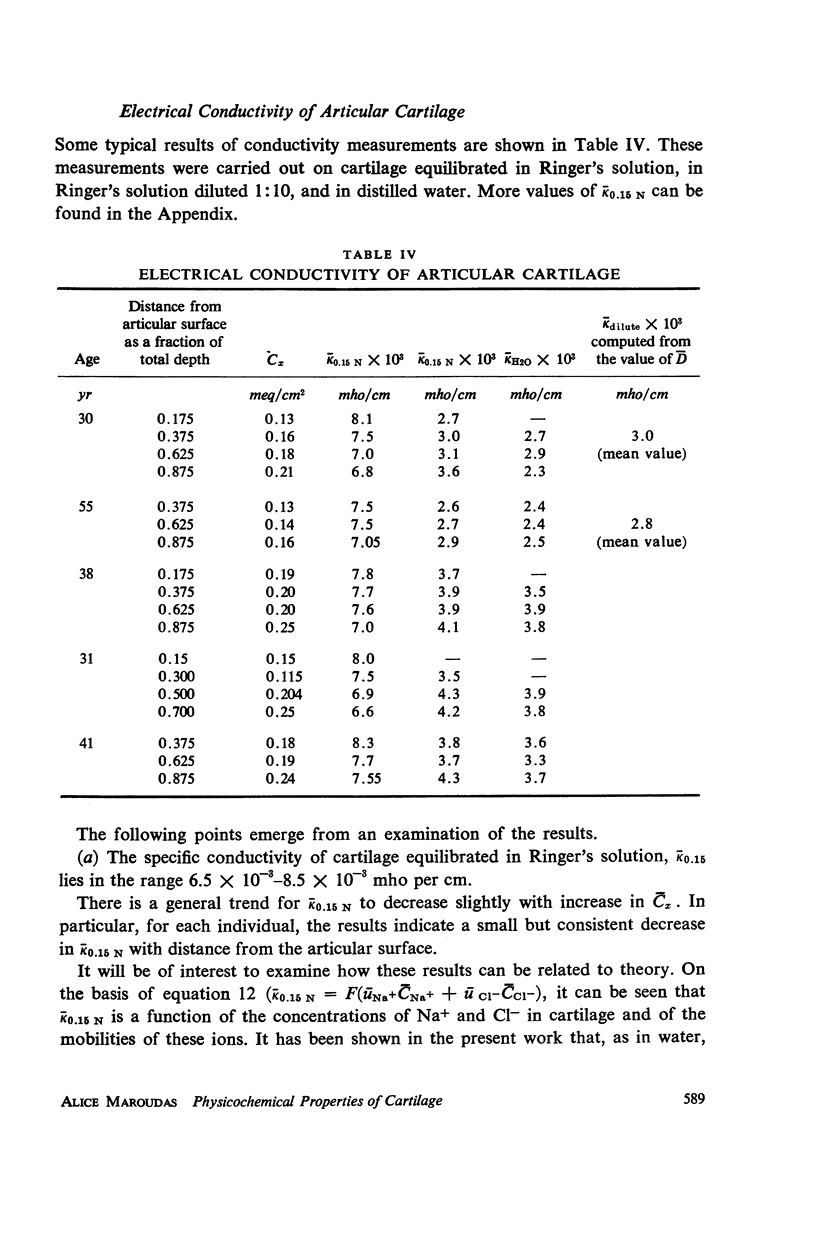
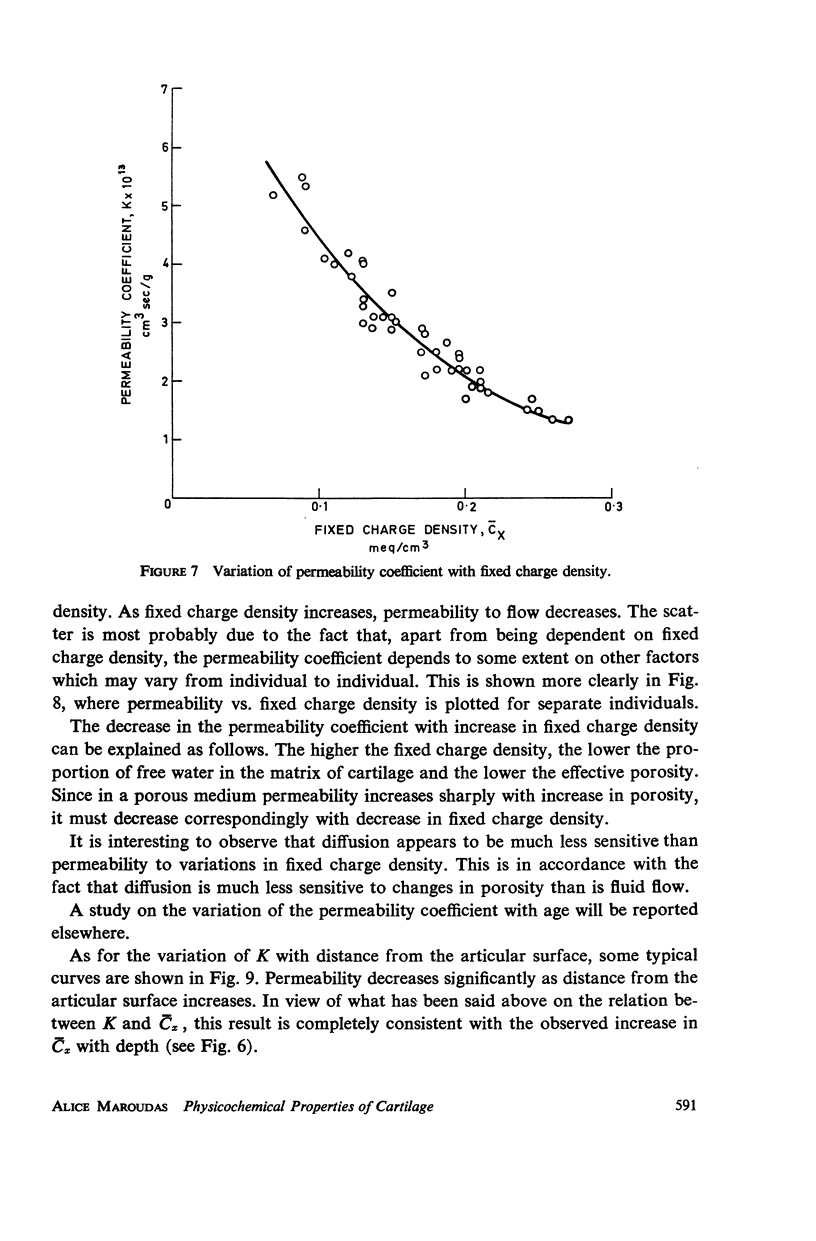
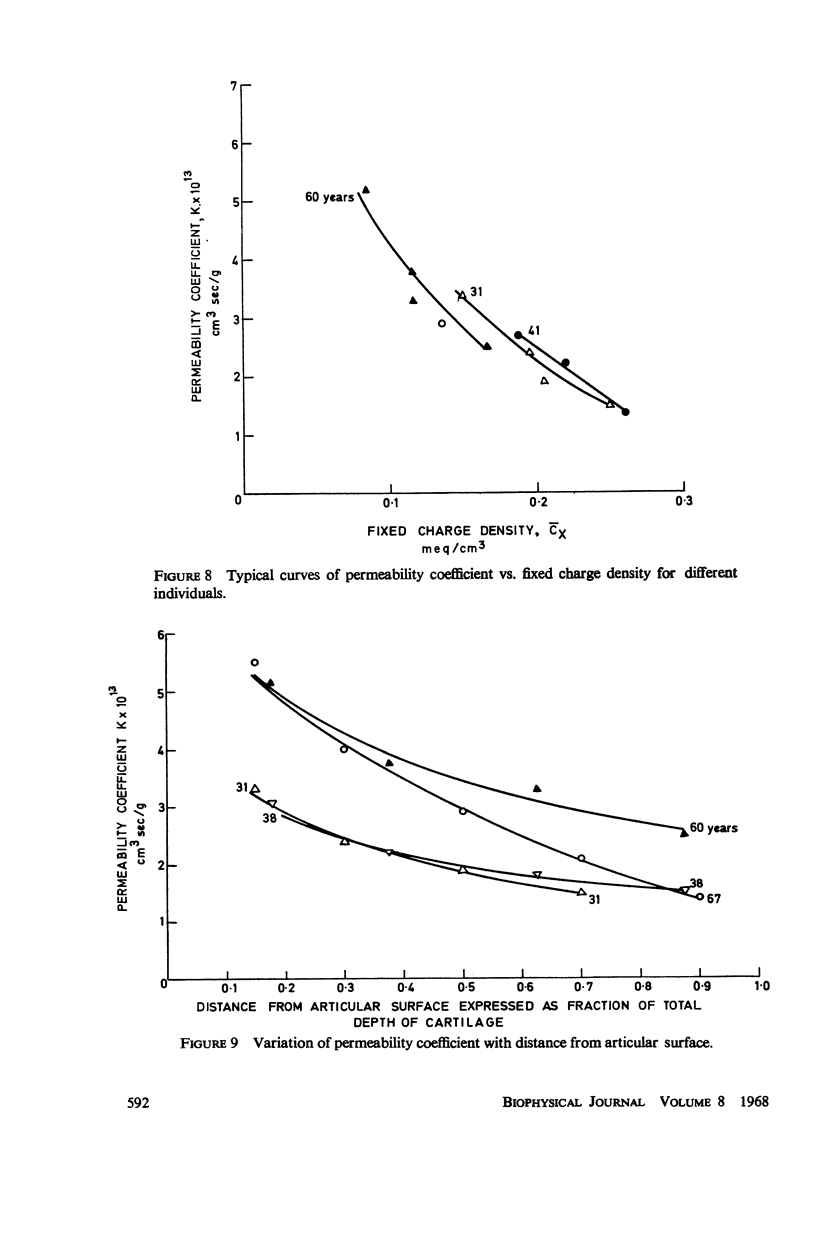
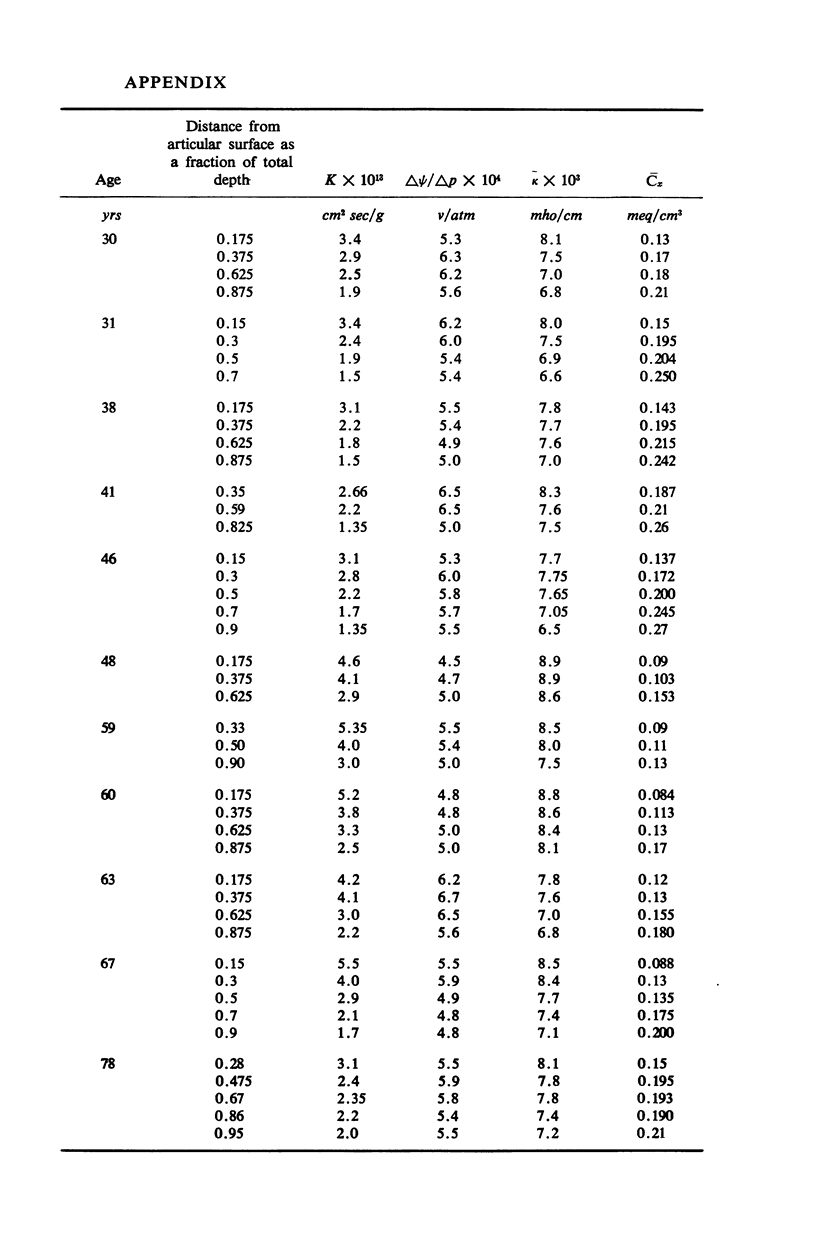
Ion exchange theory has been applied to articular cartilage. Relationships were derived between permeability, diffusivity, electrical conductivity, and streaming potential. Systematic measurements were undertaken on these properties. Experimental techniques are described and data tabulated. Theoretical correlations were found to hold within the experimental error. The concentration of fixed negatively-charged groups in cartilage was shown to be the most important parameter. Fixed charge density was found to increase with distance from the articular surface and this variation was reflected in the other properties.
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Stockwell R. A., Scott J. E. Distribution of acid glycosaminoglycans in human articular cartilage. Nature. 1967 Sep 23;215(5108):1376–1378. doi: 10.1038/2151376a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


