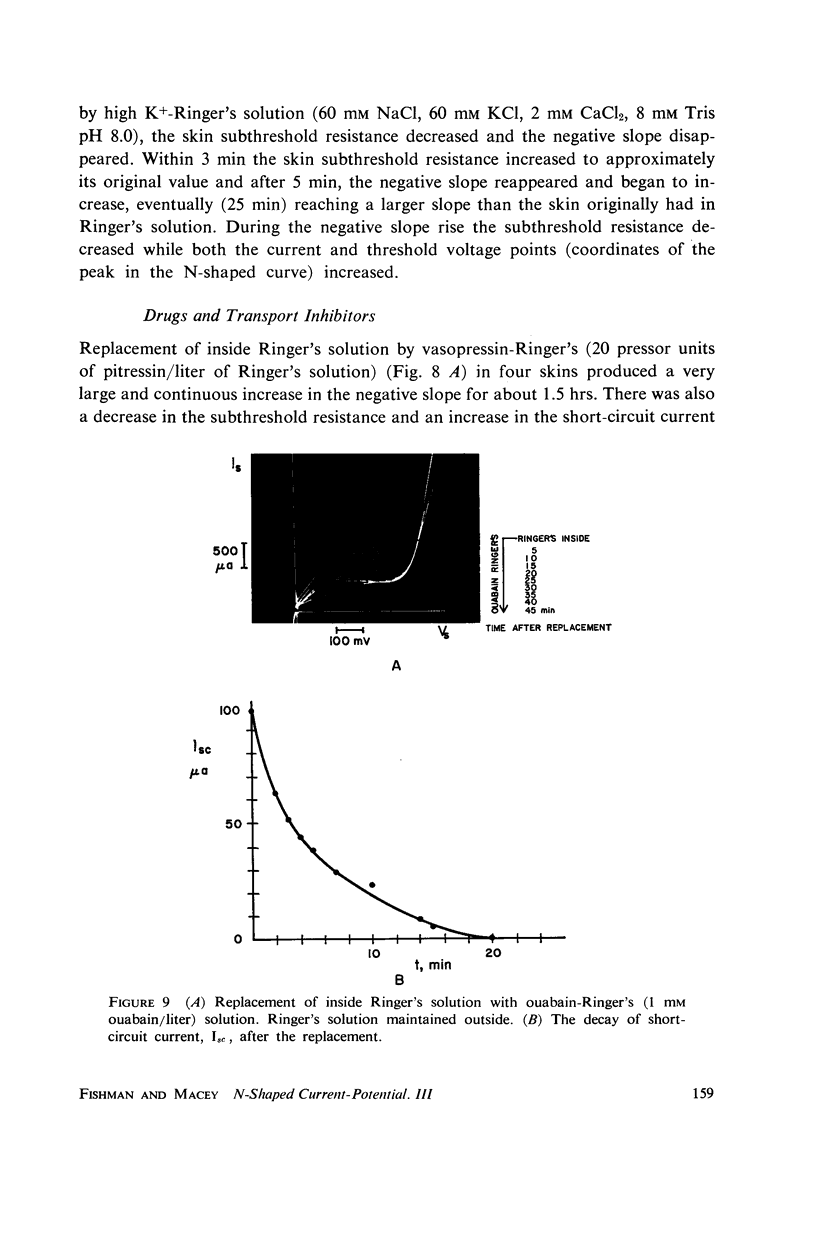
Abstract
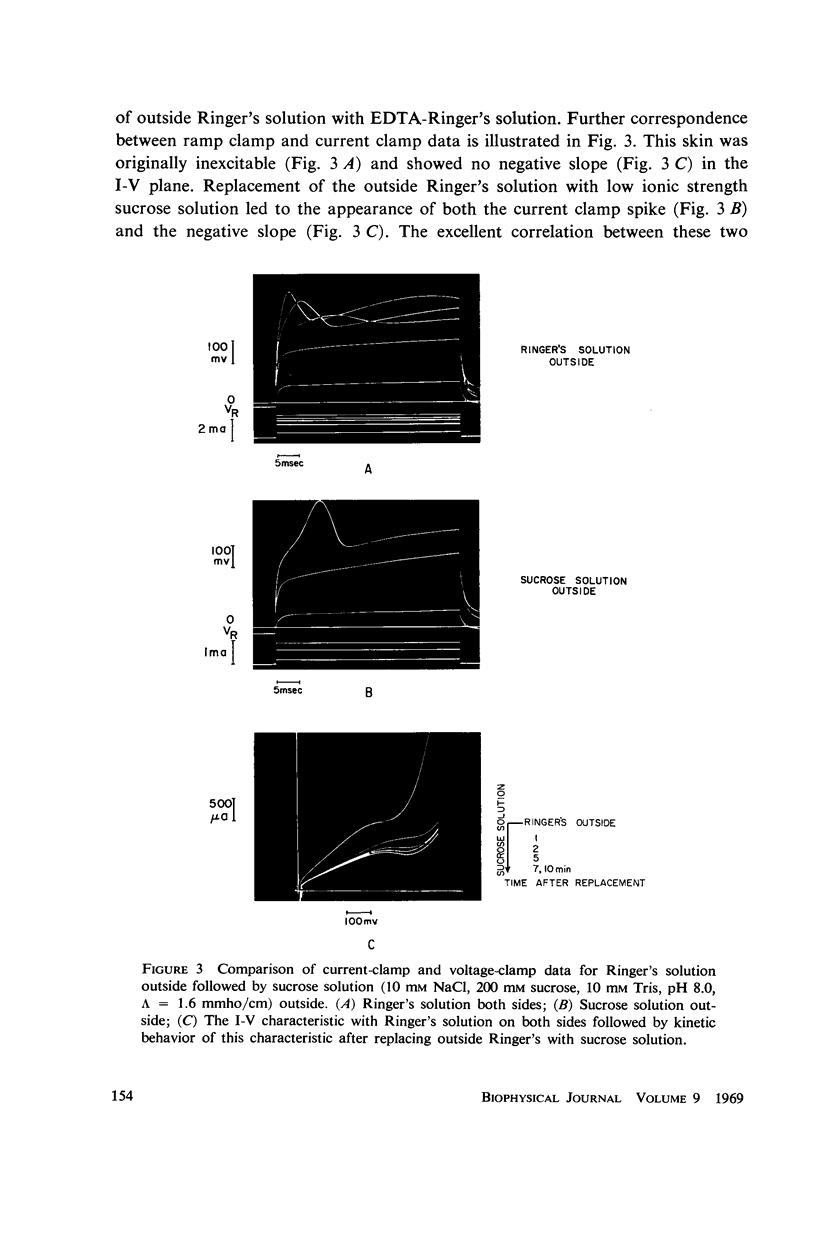
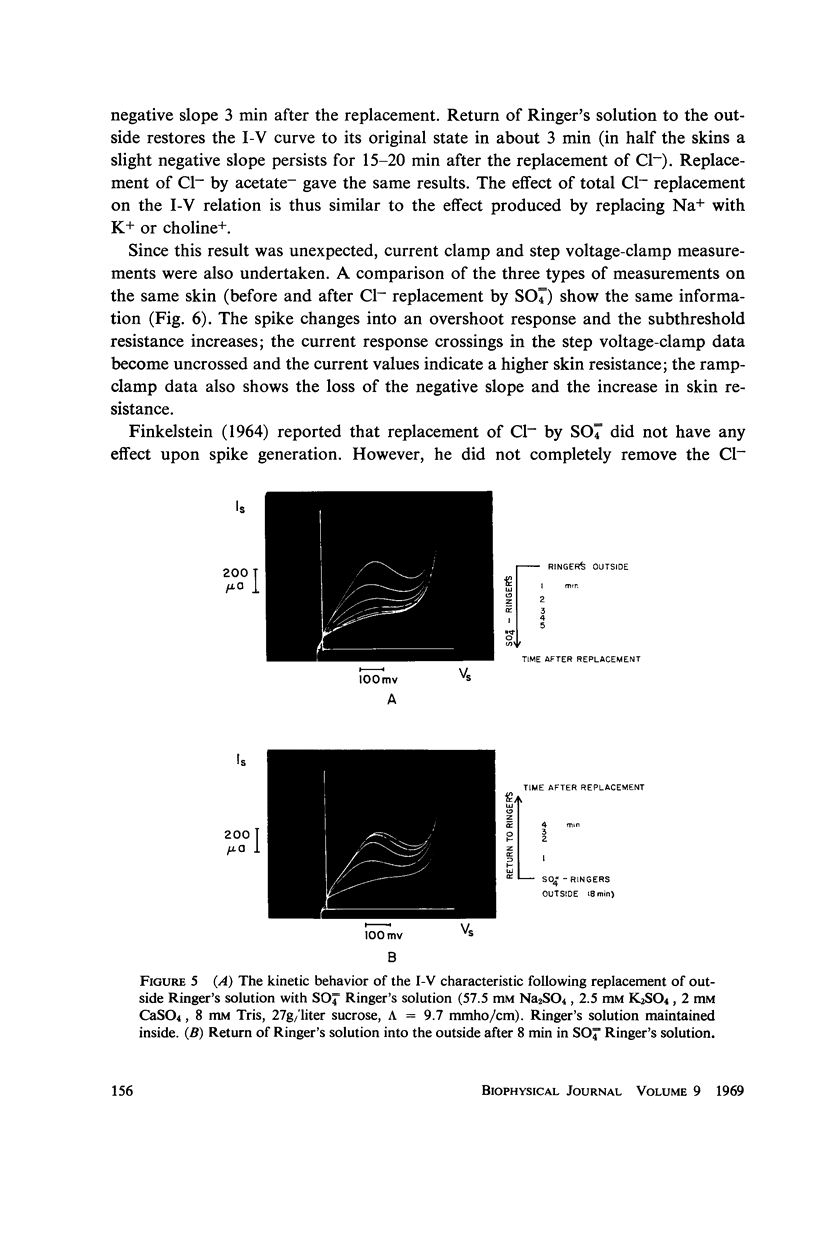
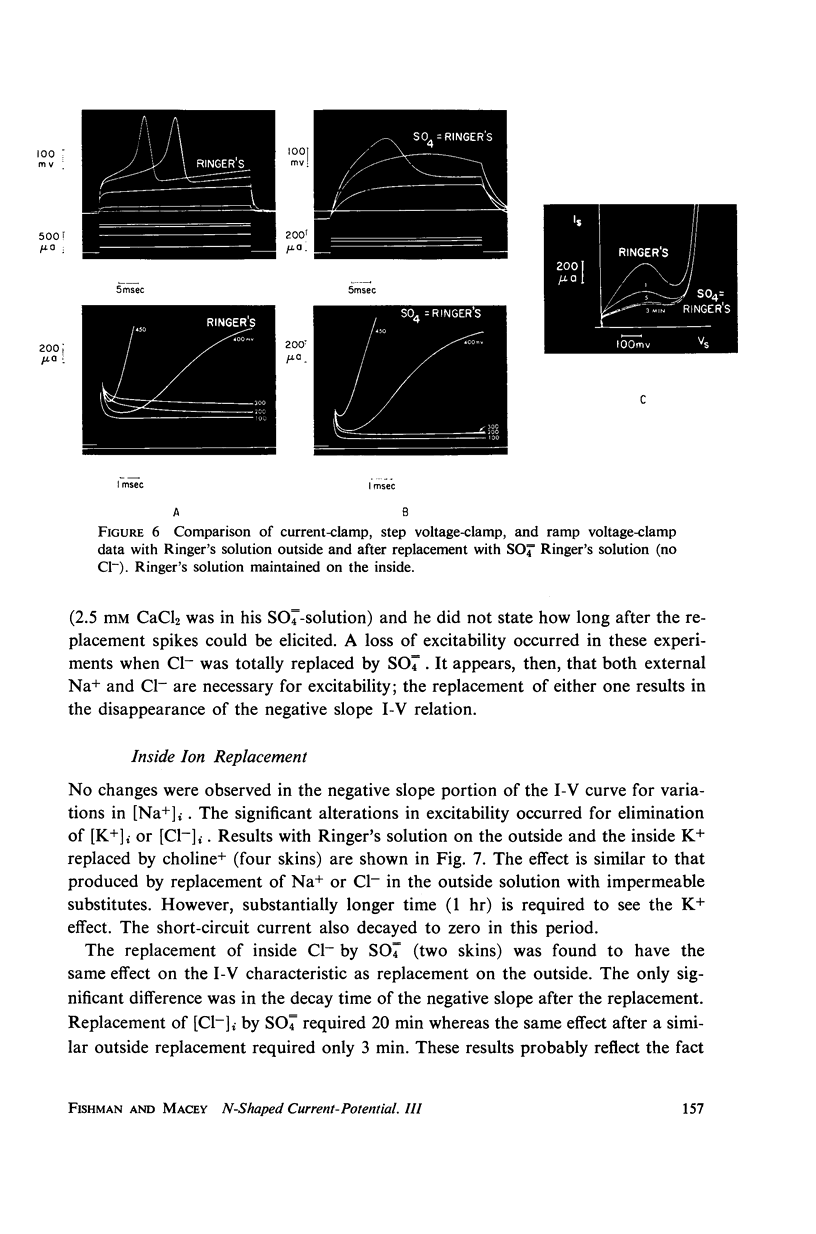
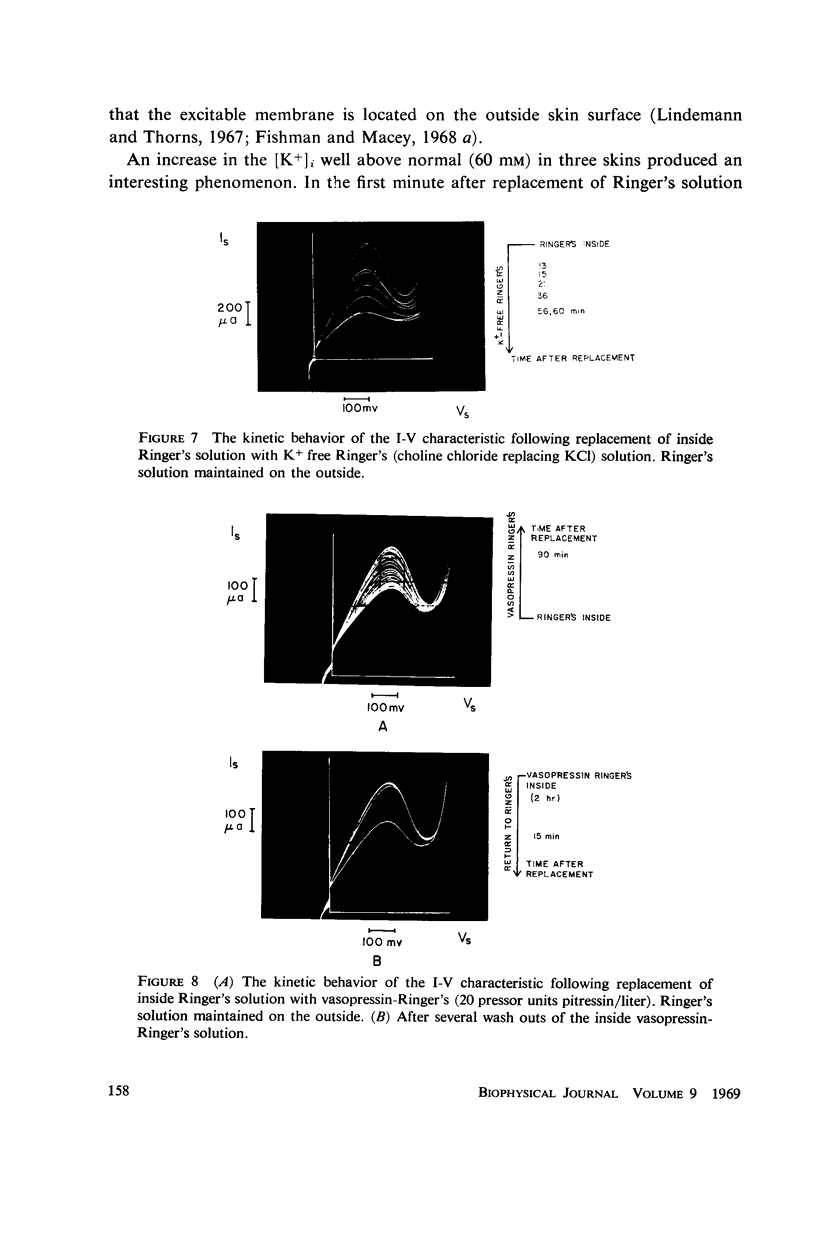
A ramp voltage clamp measurement described previously is used to detect alterations in the frog skin current-potential (I-V) characteristic following removal or replacement of various ions in the solutions bathing the skin. The ionic requirements for the maintenance of a negative-slope I-V property are the following: Ca++, Na+, and Cl- must be in the outside solution; K+ and Cl- must be in the inside solution. Removal of any one of these ions from its respective solution results in the decay and eventual disappearance of the negative slope.
The similarity between the I-V characteristic following Ca++ removal with EDTA from the outside solution and the I-V relation in a refractory skin suggests that the loss (refractory state) and recovery of the negative slope is a consequence of unbinding and subsequent rebinding of Ca++ to membrane sites. The role of the univalent ions is not clear—presumably some or all of these ions constitute the current through the skin; however, some of these ions may also be involved in maintaining a membrane condition necessary for the existence of a negative slope I-V relation. Further, excitation does not appear to be a direct consequence of the Na+ pump.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ehrenstein G., Gilbert D. L. Slow changes of potassium permeability in the squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1966 Sep;6(5):553–566. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(66)86677-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN A. ELECTRICAL EXCITABILITY OF ISOLATED FROG SKIN AND TOAD BLADDER. J Gen Physiol. 1964 Jan;47:545–565. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.3.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E. Adenosine triphosphatase localization in amphibian epidermis. J Cell Biol. 1966 Aug;30(2):359–379. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. M., Macey R. I. Calcium effects in the electrical excitability of "split" frog skin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):482–487. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman H. M., Macey R. I. The N-shaped current-potential characteristic in frog skin. II. Kinetic behavior during ramp voltage clamp. Biophys J. 1969 Feb;9(2):140–150. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86375-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindemann B., Thorns U. Fast potential spike of frog skin generated at the outer surface of the epithelium. Science. 1967 Dec 15;158(3807):1473–1477. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3807.1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Mohnssen H., Balk O. Relations between stationary and dynamic properties of Ranvier nodes. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1255–1257. doi: 10.1038/2071255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


