Abstract
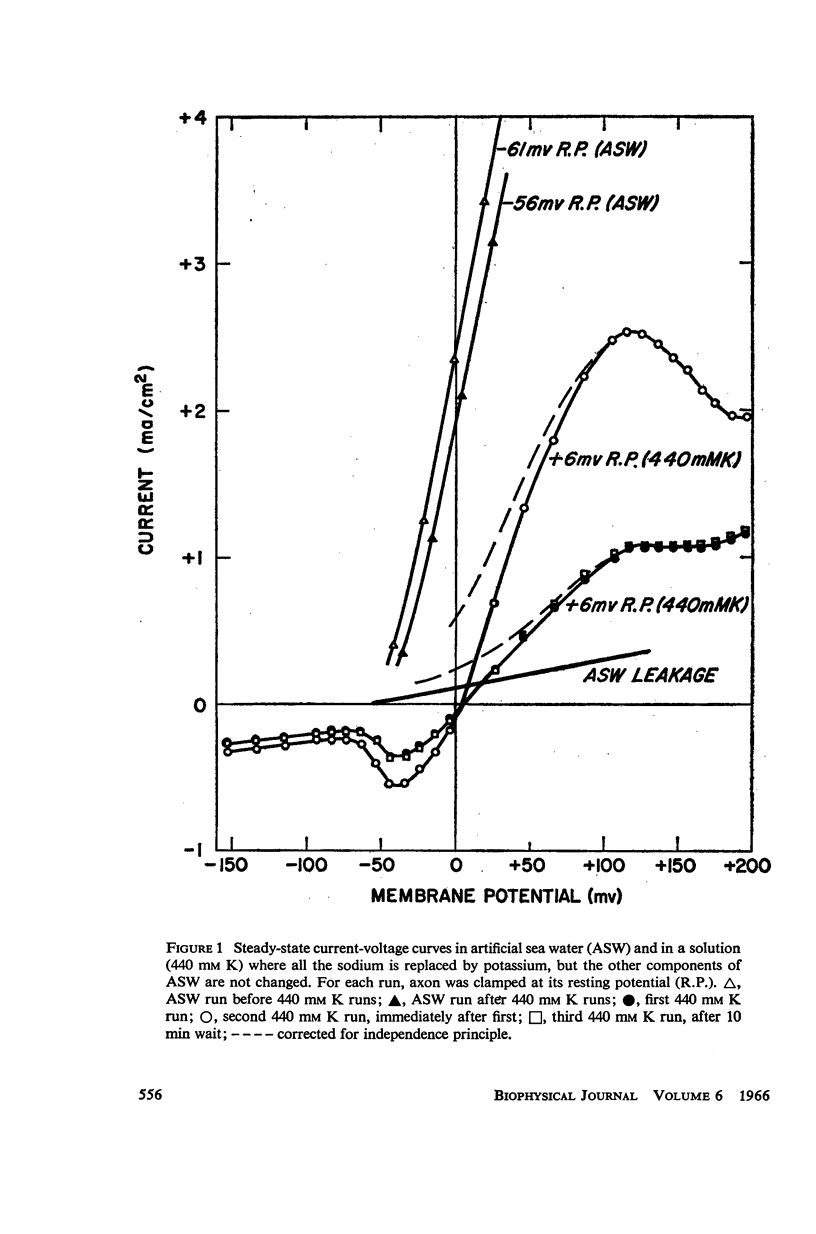
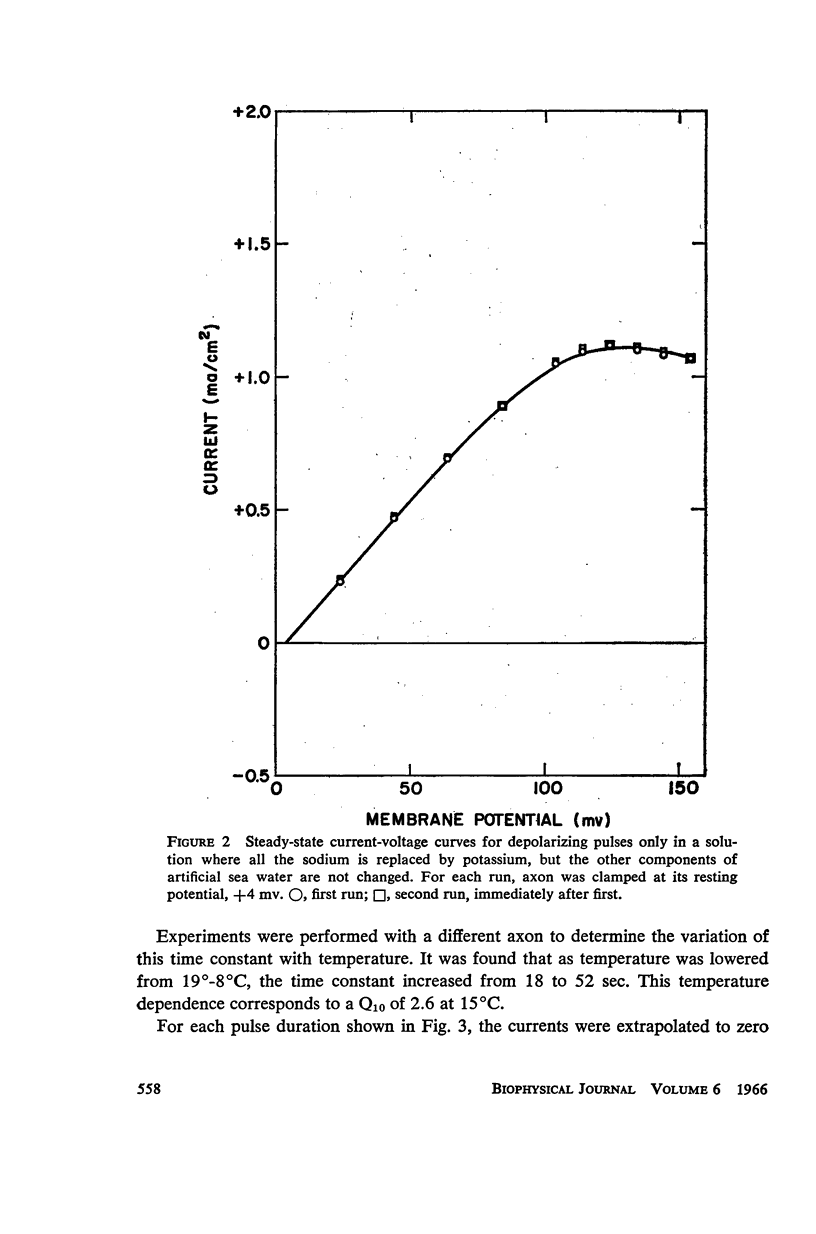
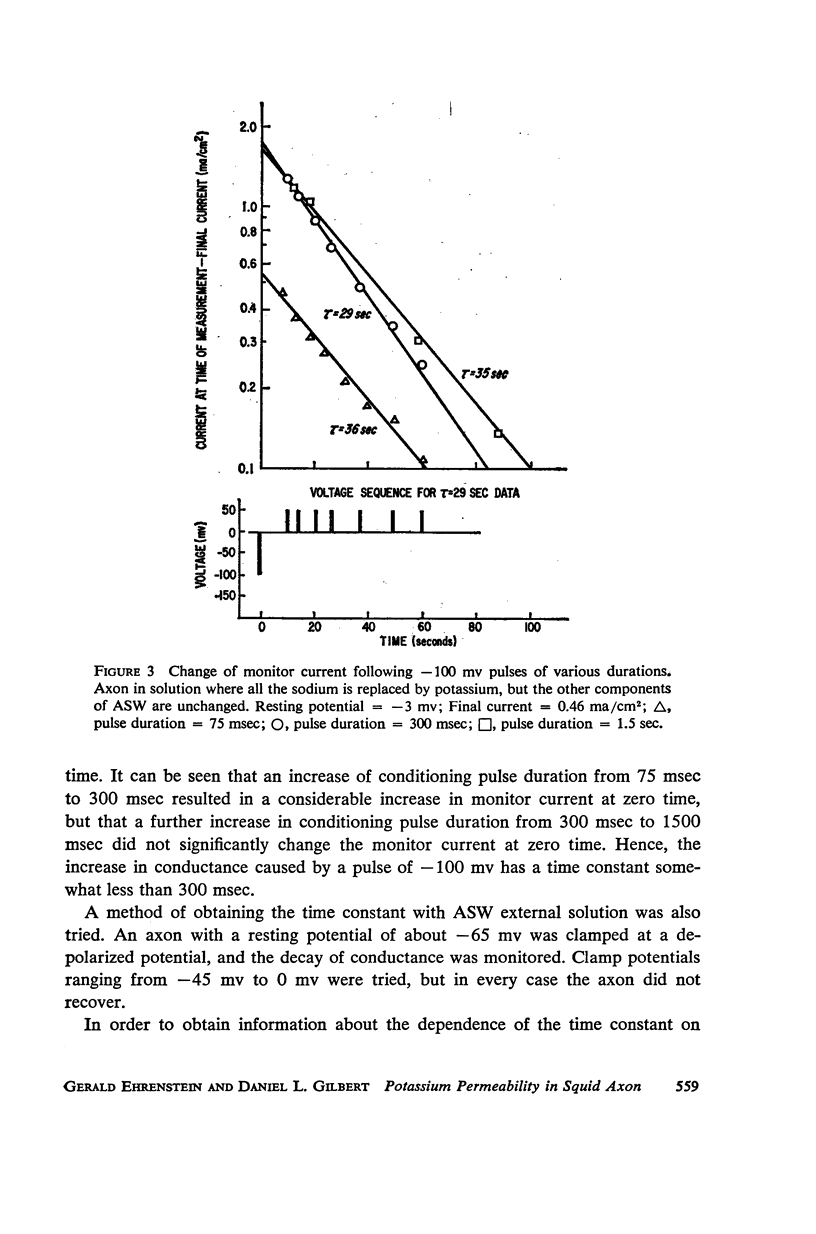
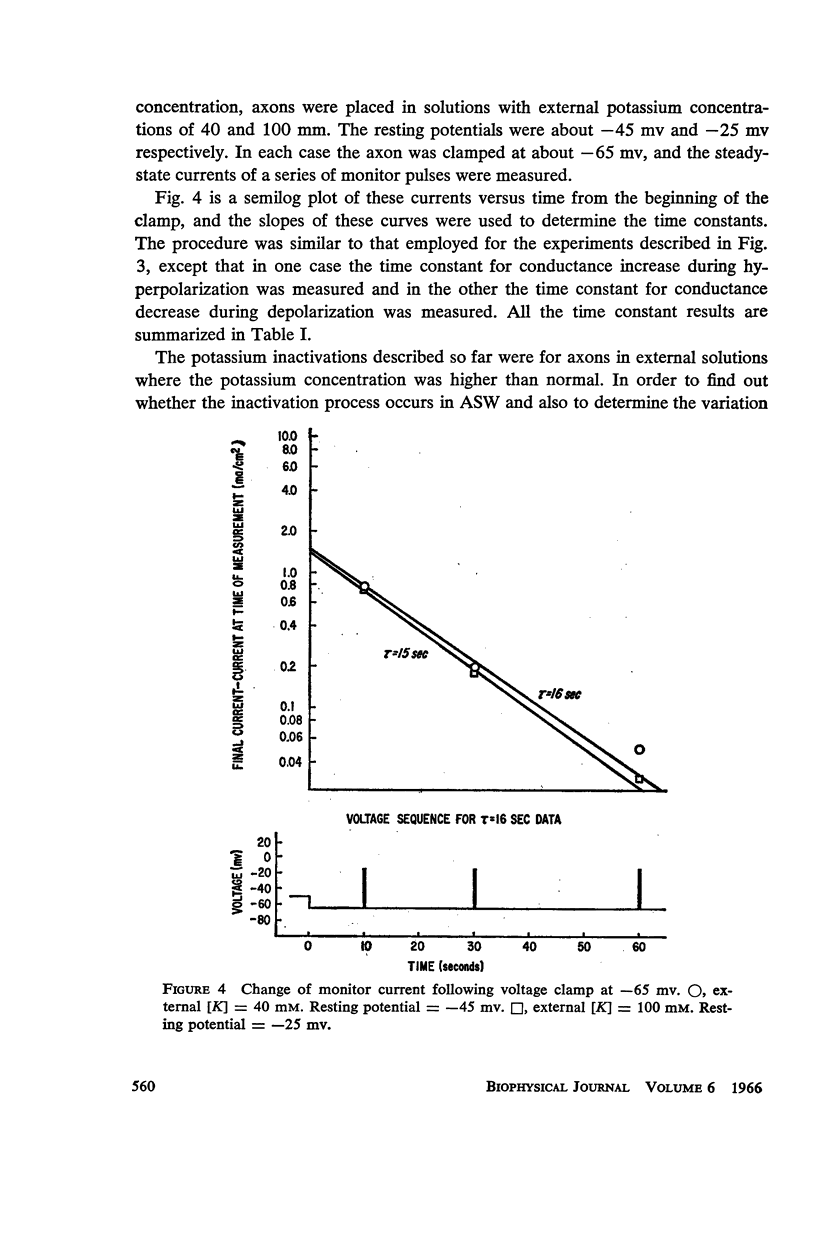
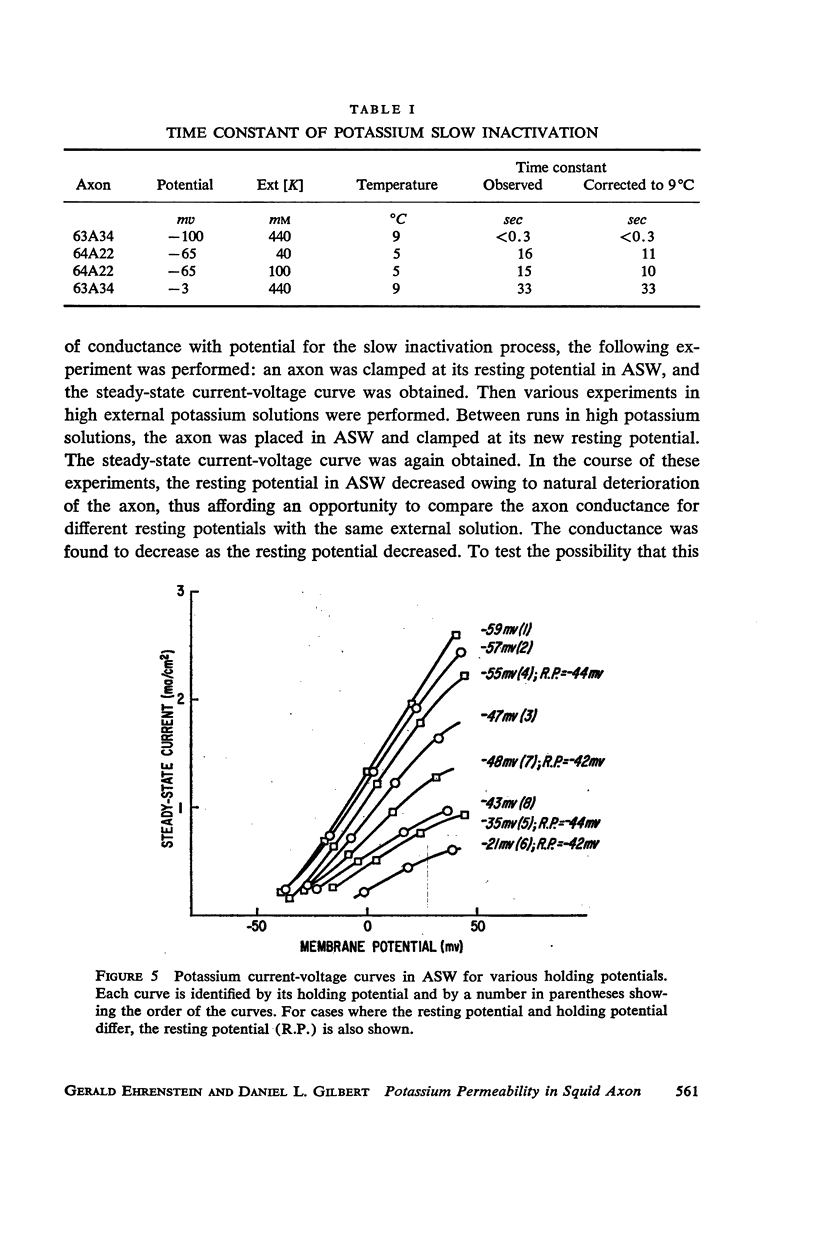
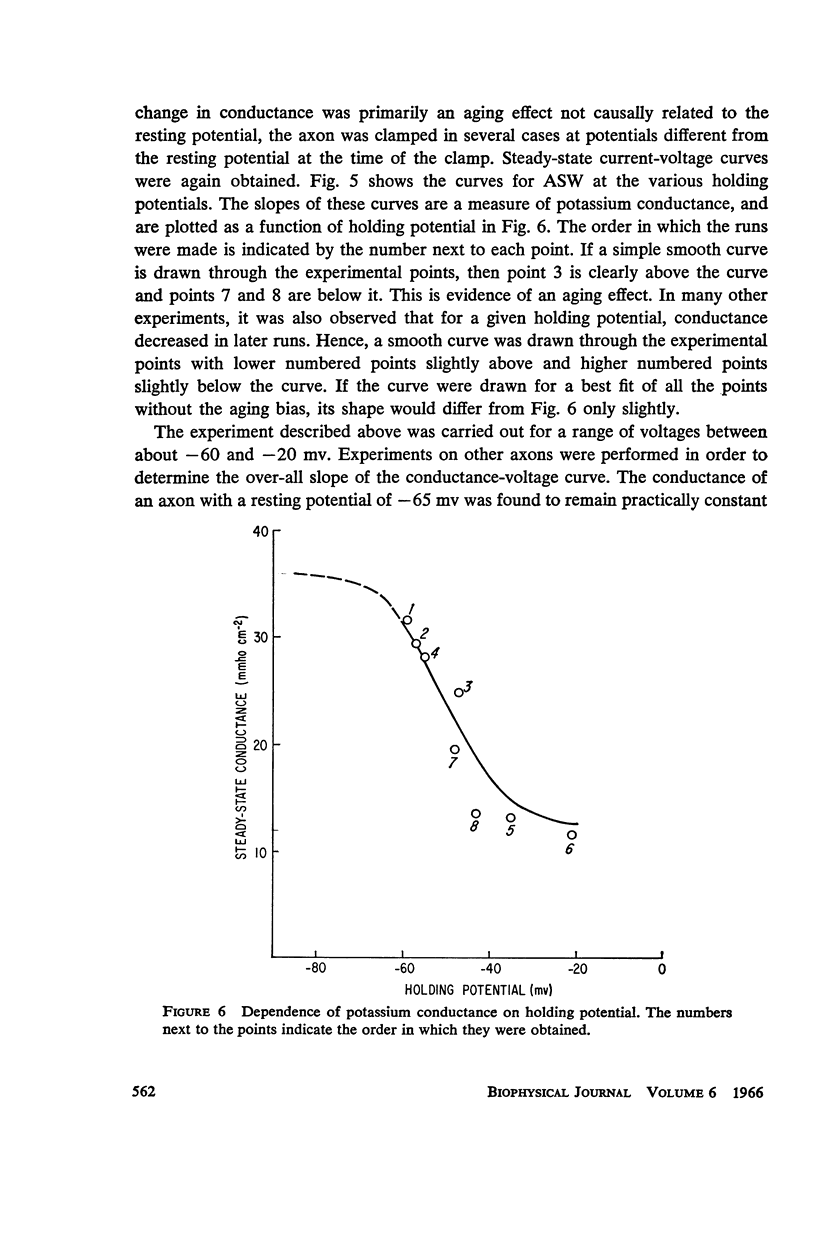
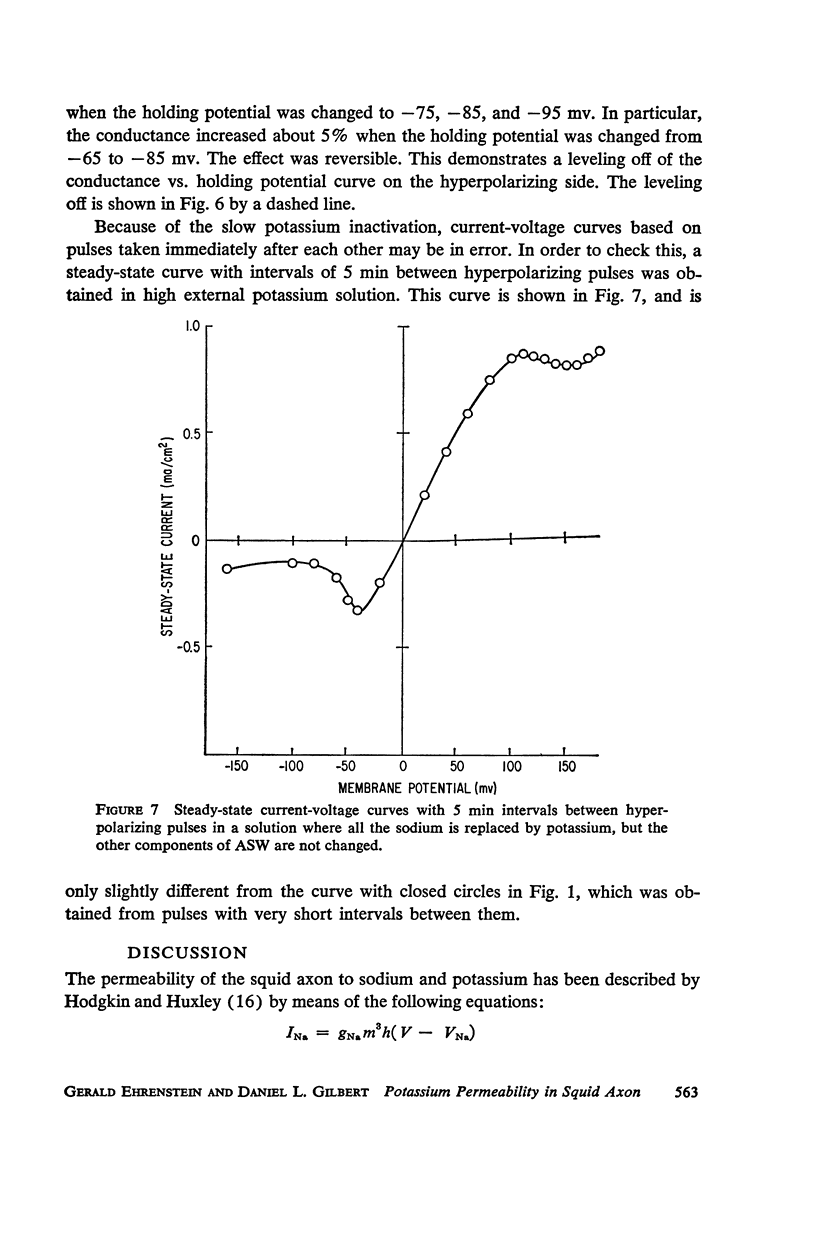
A slow potassium inactivation i.e. decrease of conductance when the inside of the membrane is made more positive with respect to the outside, has been observed for the squid axon. The conductance-potential curve is sigmoid shaped, and the ratio between maximum and minimum potassium conductance is at least 3. The time constant for the change of potassium conductance with potential is independent of the concentration of potassium in the external solution, but dependent upon potential and temperature. At 9°C and at the normal sea water resting potential, the time constant is 11 sec. For lower temperature or more depolarizing potentials, the time constant is greater. The inactivation can be described by modifying the Hodgkin-Huxley equation for potassium current, using one additional parameter. The modified equation is similar in form to the Hodgkin-Huxley equation for sodium current, suggesting that the mechanism for the passive transport of potassium through the axon membrane is similar to that for sodium.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERMAN M., SHAHN E., WEISS M. F. The routine fitting of kinetic data to models: a mathematical formalism for digital computers. Biophys J. 1962 May;2:275–287. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(62)86855-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLE K. S., MOORE J. W. Liquid junction and membrane potentials of the squid giant axon. J Gen Physiol. 1960 May;43:971–980. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.5.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. A QUANTITATIVE DESCRIPTION OF POTASSIUM CURRENTS IN MYELINATED NERVE FIBRES OF XENOPUS LAEVIS. J Physiol. 1963 Nov;169:424–430. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The after-effects of impulses in the giant nerve fibres of Loligo. J Physiol. 1956 Feb 28;131(2):341–376. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., WALTMAN B. Membrane resistance and conduction velocity of large myelinated nerve fibres from Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:677–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUNDFEST H. The mechanisms of discharge of the electric organs in relation to general and comparative electrophysiology. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:1–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALL A. E., HUTTER O. F., NOBLE D. Current-voltage relations of Purkinje fibres in sodium-deficient solutions. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:225–240. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. Currents carried by sodium and potassium ions through the membrane of the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):449–472. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The components of membrane conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):473–496. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEISSNER H. P. DAS VERHALTEN DER SCHNUERRINGMEMBRAN UNTER DEM EINFLUSS STARKER DEPOLARISIERENDER STROEME. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965 Apr 6;283:213–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE J. W. Excitation of the squid axon membrane in isosmotic potassium chloride. Nature. 1959 Jan 24;183(4656):265–266. doi: 10.1038/183265b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P., Rudin D. O. Induced excitability in reconstituted cell membrane structure. J Theor Biol. 1963 May;4(3):268–280. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(63)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REUBEN J. P., GAINER H. Membrance conductance during depolarizing postsynaptic potentials of crayfish muscle fibres. Nature. 1962 Jan 13;193:142–143. doi: 10.1038/193142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



