Abstract
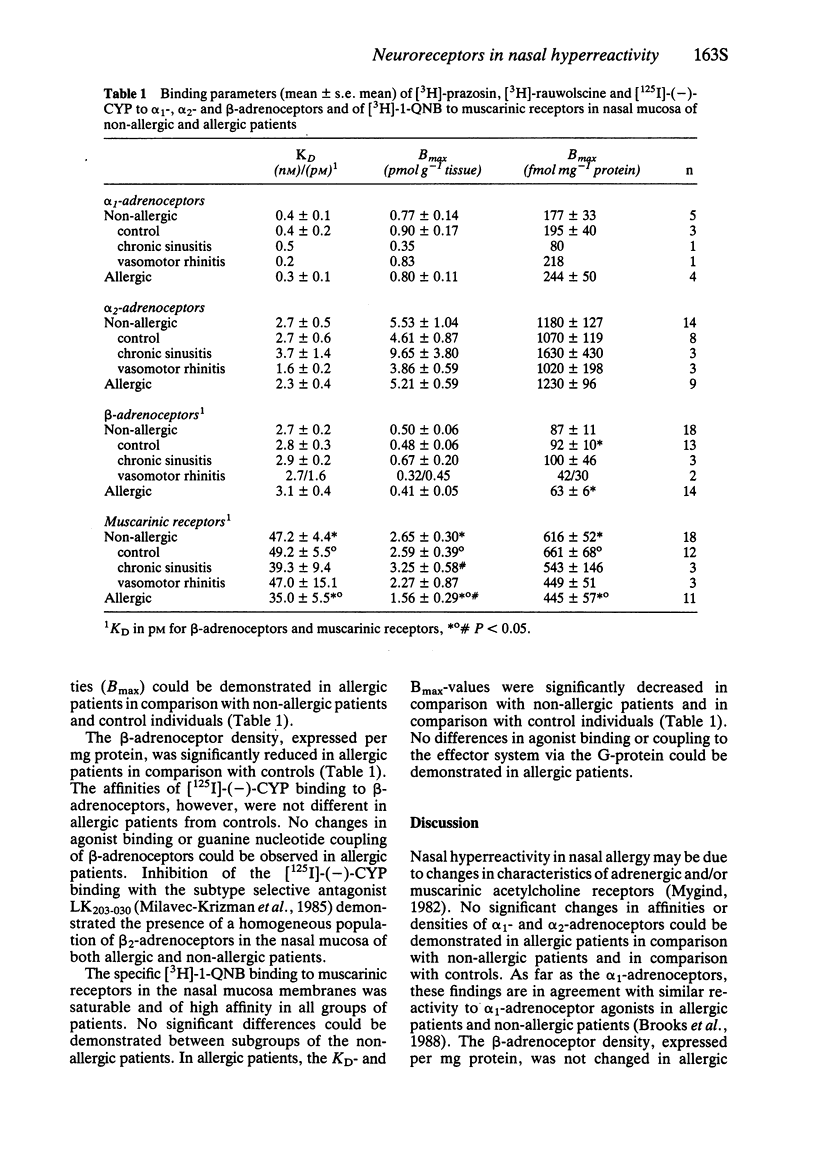
Cholinergic and adrenergic abnormalities have been observed in nasal allergy and may be due to changes in pharmacological characteristics of neuroreceptors. Radioligand receptor binding studies demonstrated no significant changes in affinities or densities of α-adrenoceptors, a decreased number of β-adrenoceptors and a decreased affinity combined with a decreased number of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
Keywords: nasal hyperreactivity, adrenoceptors, muscarinic receptors
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes P. J. Neural control of human airways in health and disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Dec;134(6):1289–1314. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.5.1289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. D., Spenner G. C., Karl K. J., Heissler C. T., Metzler C. M. Nasal airway response to infused phenylephrine in normals and in patients with allergic and non-allergic rhinitis. Rhinology. 1988 Mar;26(1):51–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milavec-Krizman M., Evenou J. P., Wagner H., Berthold R., Stoll A. P. Characterization of beta-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat kidney with new highly selective beta 1 blockers and their role in renin release. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Nov 15;34(22):3951–3957. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90371-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mygind N. Mediators of nasal allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Sep;70(3):149–159. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90036-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues de Miranda J. F., Scheres H. M., Salden H. J., Beld A. J., Klaassen A. B., Kuijpers W. Muscarinic receptors in rat nasal mucosa are predominantly of the low affinity agonist type. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 31;113(3):441–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90094-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelhamer J. H., Marom Z., Kaliner M. Abnormal beta-adrenergic responsiveness in allergic subjects. II. The role of selective beta 2-adrenergic hyporeactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Jan;71(1 Pt 1):57–61. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90547-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Megen Y. J., Klaassen A. B., Rodrigues de Miranda J. F., Wentges R. T., van Ginneken C. A. Demonstration of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat nasal mucosa. J Recept Res. 1989;9(3):221–234. doi: 10.3109/10799898909066056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


