Abstract
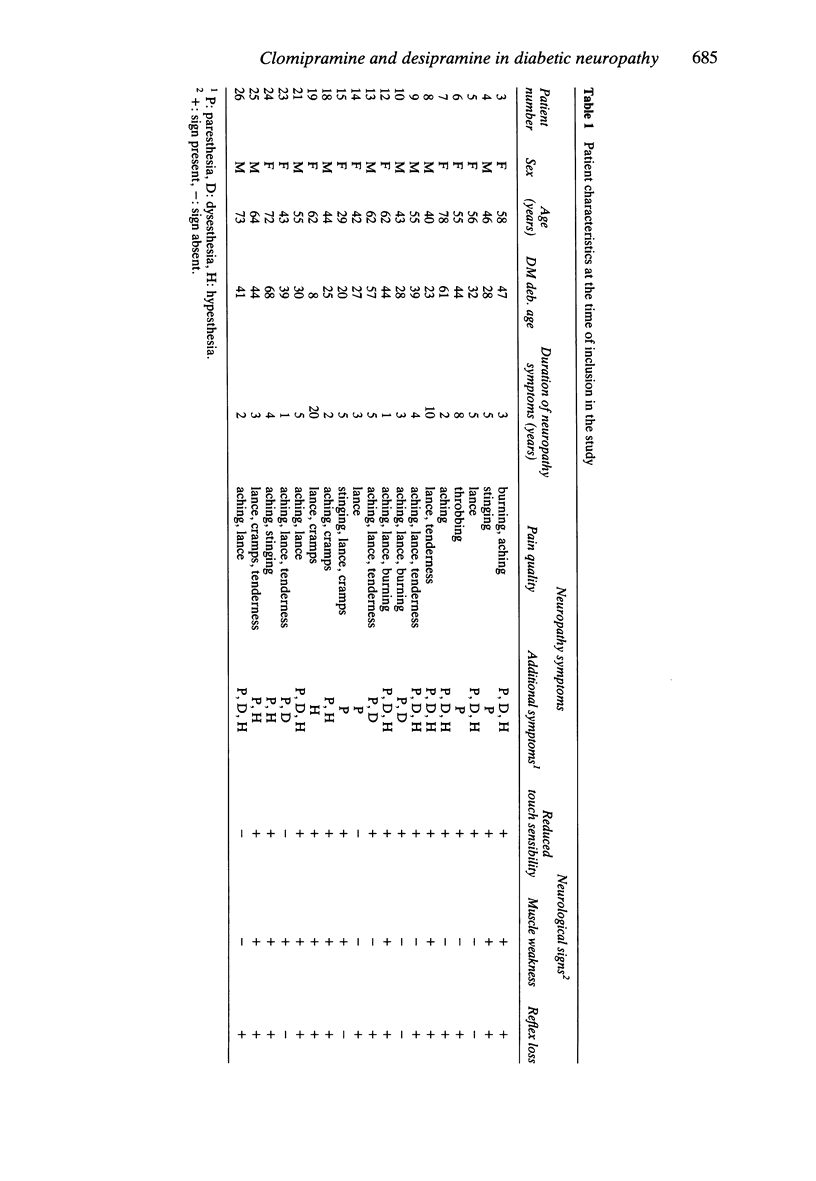
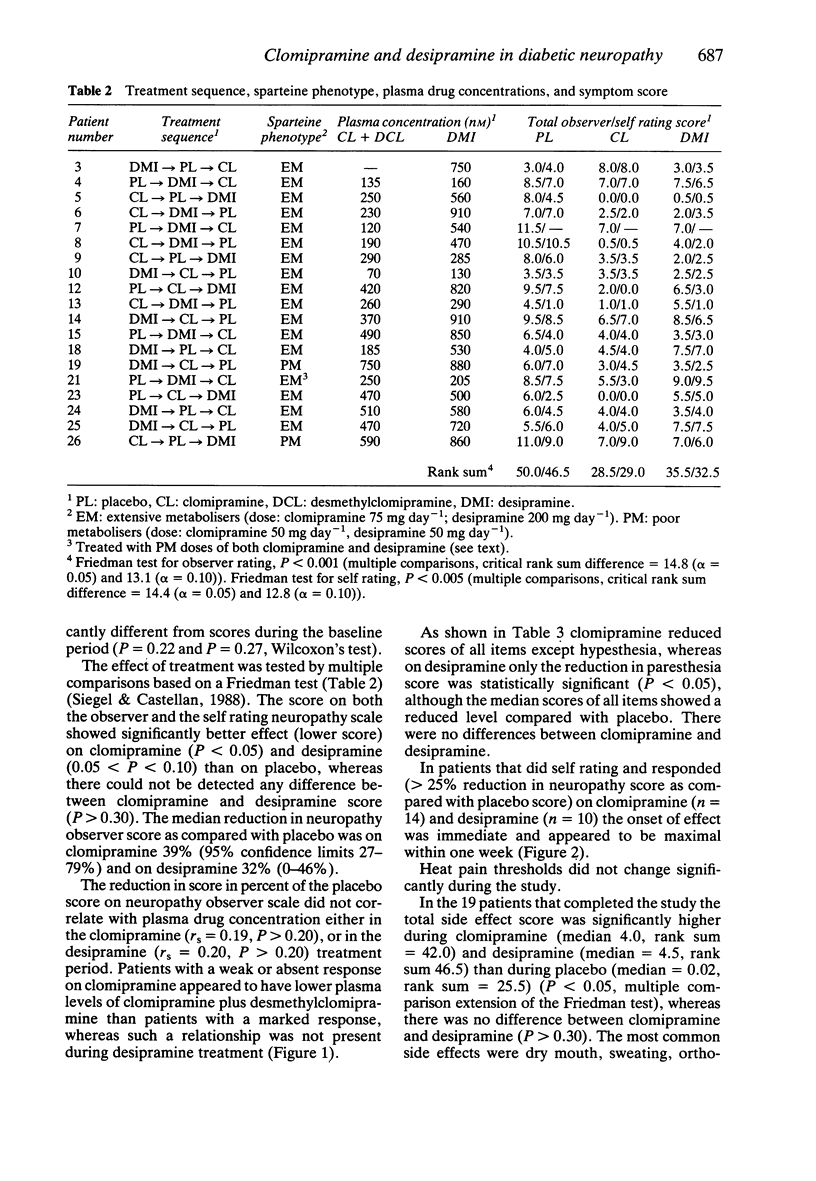
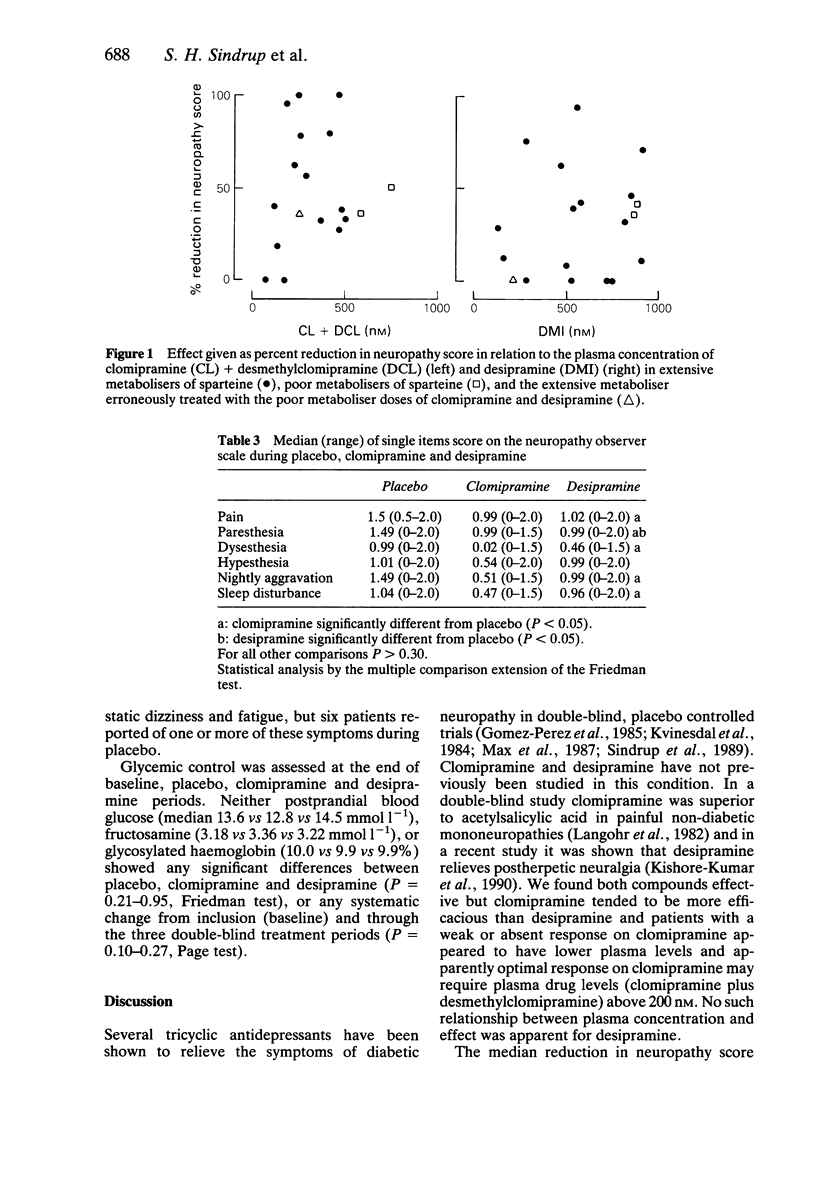
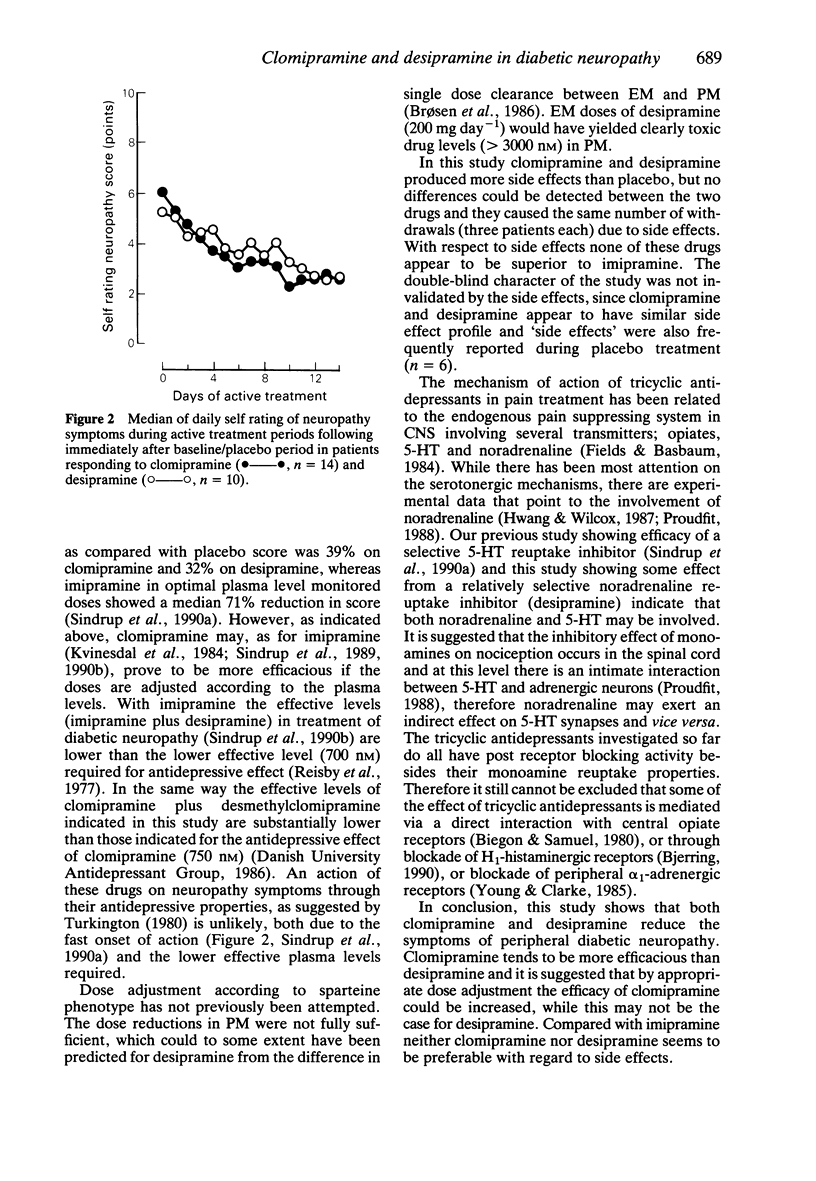
1. The effect of clomipramine and desipramine on diabetic neuropathy symptoms was examined in a double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled, cross-over study for 2 + 2 + 2 weeks. Drug doses were adjusted according to the sparteine phenotype, i.e. extensive metabolisers were treated with 75 mg clomipramine day-1 and 200 mg desipramine day-1 whereas poor metabolisers were treated with 50 mg day-1 of both drugs. Nineteen patients completed the study. 2. Plasma concentration of clomipramine plus desmethylclomipramine was 70-510 nM in extensive metabolisers, vs 590 and 750 nM in two poor metabolisers. Desipramine levels were 130-910 nM, vs 860 and 880 nM. 3. Both clomipramine and desipramine significantly reduced the symptoms of neuropathy as measured by observer- and self rating in comparison with placebo. Clomipramine tended to be more efficacious than desipramine. Patients with a weak or absent response on clomipramine had lower plasma concentrations (clomipramine plus desmethyl-clomipramine less than 200 nM) than patients with a better response. For desipramine a relationship between plasma concentration and effect was not established. 4. Side effect ratings did not differ for clomipramine and desipramine and on both drugs three patients withdrew due to side effects. 5. Compared with earlier results obtained with imipramine dosed on the basis of plasma level monitoring, clomipramine and desipramine on fixed doses appeared less efficacious whereas the side effect profiles were the same. At least for clomipramine, appropriate dose adjustment on the basis of plasma level monitoring may increase the efficacy.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biegon A., Samuel D. Interaction of tricyclic antidepressants with opiate receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;29(3):460–462. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90531-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegon A., Samuel D. The in vivo distribution of an antidepressant drug (DMI) in male and female rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1979 Nov;65(3):259–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00492213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brøsen K., Otton S. V., Gram L. F. Imipramine demethylation and hydroxylation: impact of the sparteine oxidation phenotype. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Nov;40(5):543–549. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brøsen K., Otton S. V., Gram L. F. Sparteine oxidation polymorphism in Denmark. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1985 Nov;57(5):357–360. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1985.tb00058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruhstorfer H., Lindblom U., Schmidt W. C. Method for quantitative estimation of thermal thresholds in patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Nov;39(11):1071–1075. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.11.1071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Perez F. J., Rull J. A., Dies H., Rodriquez-Rivera J. G., Gonzalez-Barranco J., Lozano-Castañeda O. Nortriptyline and fluphenazine in the symptomatic treatment of diabetic neuropathy. A double-blind cross-over study. Pain. 1985 Dec;23(4):395–400. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(85)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram L. F., Bjerre M., Kragh-Sørensen P., Kvinesdal B., Molin J., Pedersen O. L., Reisby N. Imipramine metabolites in blood of patients during therapy and after overdose. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Mar;33(3):335–342. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall H., Ogren S. O. Effects of antidepressant drugs on different receptors in the brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 26;70(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang A. S., Wilcox G. L. Analgesic properties of intrathecally administered heterocyclic antidepressants. Pain. 1987 Mar;28(3):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(87)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishore-Kumar R., Max M. B., Schafer S. C., Gaughan A. M., Smoller B., Gracely R. H., Dubner R. Desipramine relieves postherpetic neuralgia. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1990 Mar;47(3):305–312. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1990.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvinesdal B., Molin J., Frøland A., Gram L. F. Imipramine treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. JAMA. 1984 Apr 6;251(13):1727–1730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langohr H. D., Stöhr M., Petruch F. An open and double-blind cross-over study on the efficacy of clomipramine (Anafranil) in patients with painful mono- and polyneuropathies. Eur Neurol. 1982;21(5):309–317. doi: 10.1159/000115497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max M. B., Culnane M., Schafer S. C., Gracely R. H., Walther D. J., Smoller B., Dubner R. Amitriptyline relieves diabetic neuropathy pain in patients with normal or depressed mood. Neurology. 1987 Apr;37(4):589–596. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfit H. K. Pharmacologic evidence for the modulation of nociception by noradrenergic neurons. Prog Brain Res. 1988;77:357–370. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62802-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisby N., Gram L. F., Bech P., Nagy A., Petersen G. O., Ortmann J., Ibsen I., Dencker S. J., Jacobsen O., Krautwald O. Imipramine: clinical effects and pharmacokinetic variability. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1977 Nov 15;54(3):263–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00426574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindrup S. H., Ejlertsen B., Frøland A., Sindrup E. H., Brøsen K., Gram L. F. Imipramine treatment in diabetic neuropathy: relief of subjective symptoms without changes in peripheral and autonomic nerve function. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;37(2):151–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00558223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindrup S. H., Gram L. F., Skjold T., Frøland A., Beck-Nielsen H. Concentration-response relationship in imipramine treatment of diabetic neuropathy symptoms. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1990 Apr;47(4):509–515. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1990.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W. Depression masquerading as diabetic neuropathy. JAMA. 1980 Mar 21;243(11):1147–1150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. J., Clarke B. F. Pain relief in diabetic neuropathy: the effectiveness of imipramine and related drugs. Diabet Med. 1985 Sep;2(5):363–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1985.tb00652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


