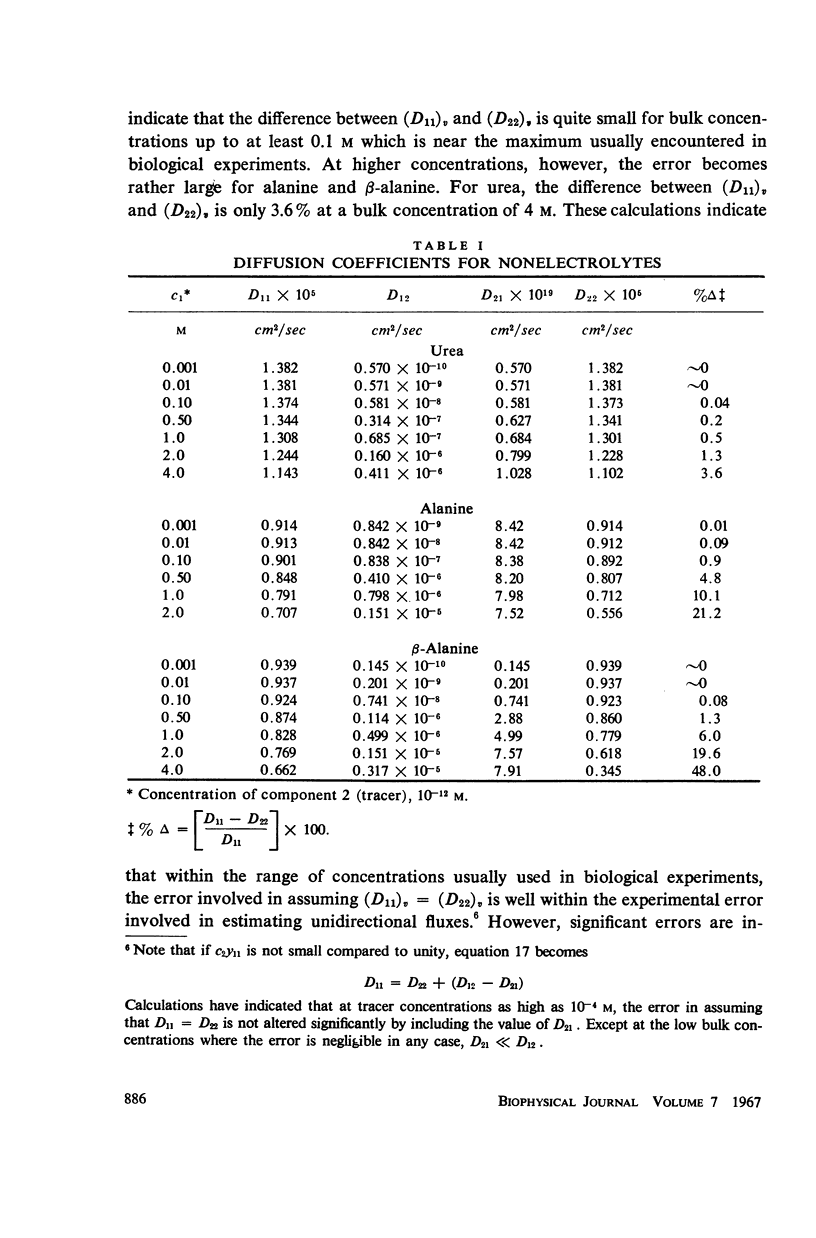
Abstract
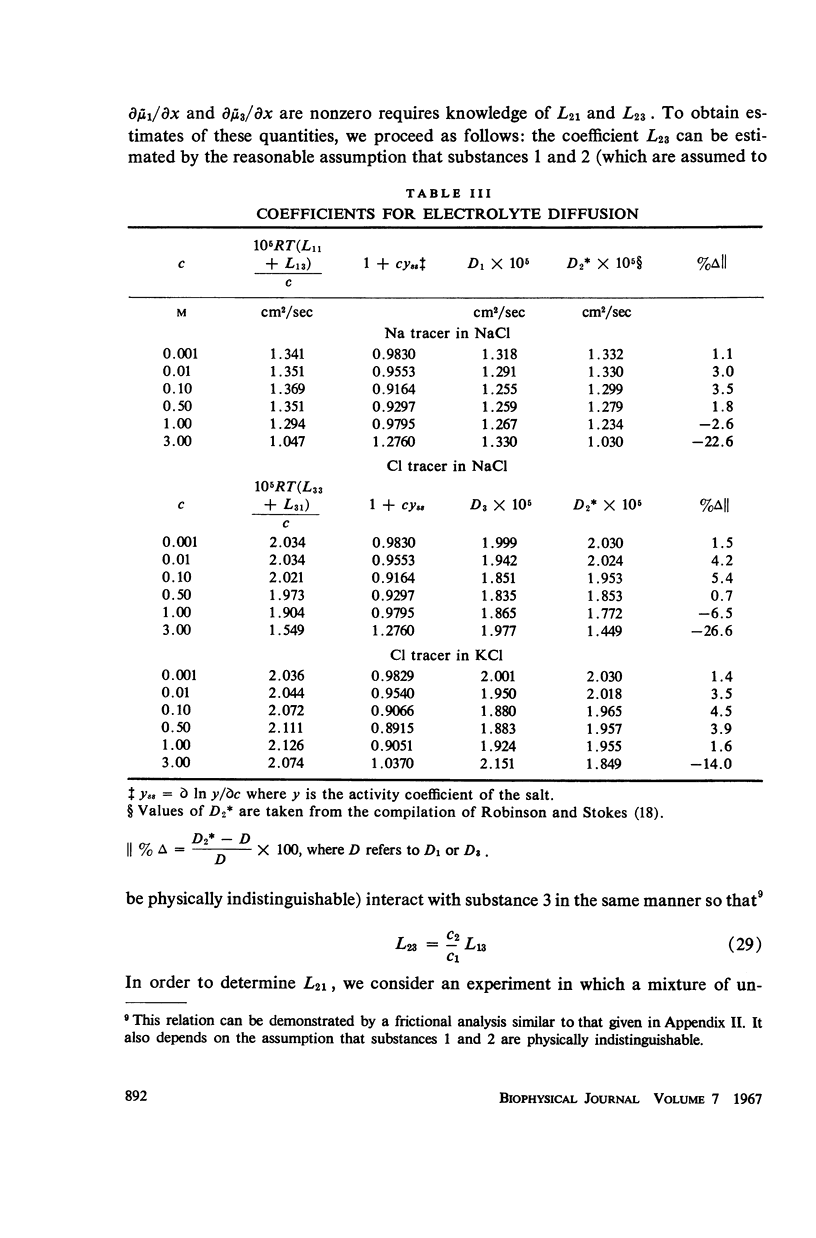
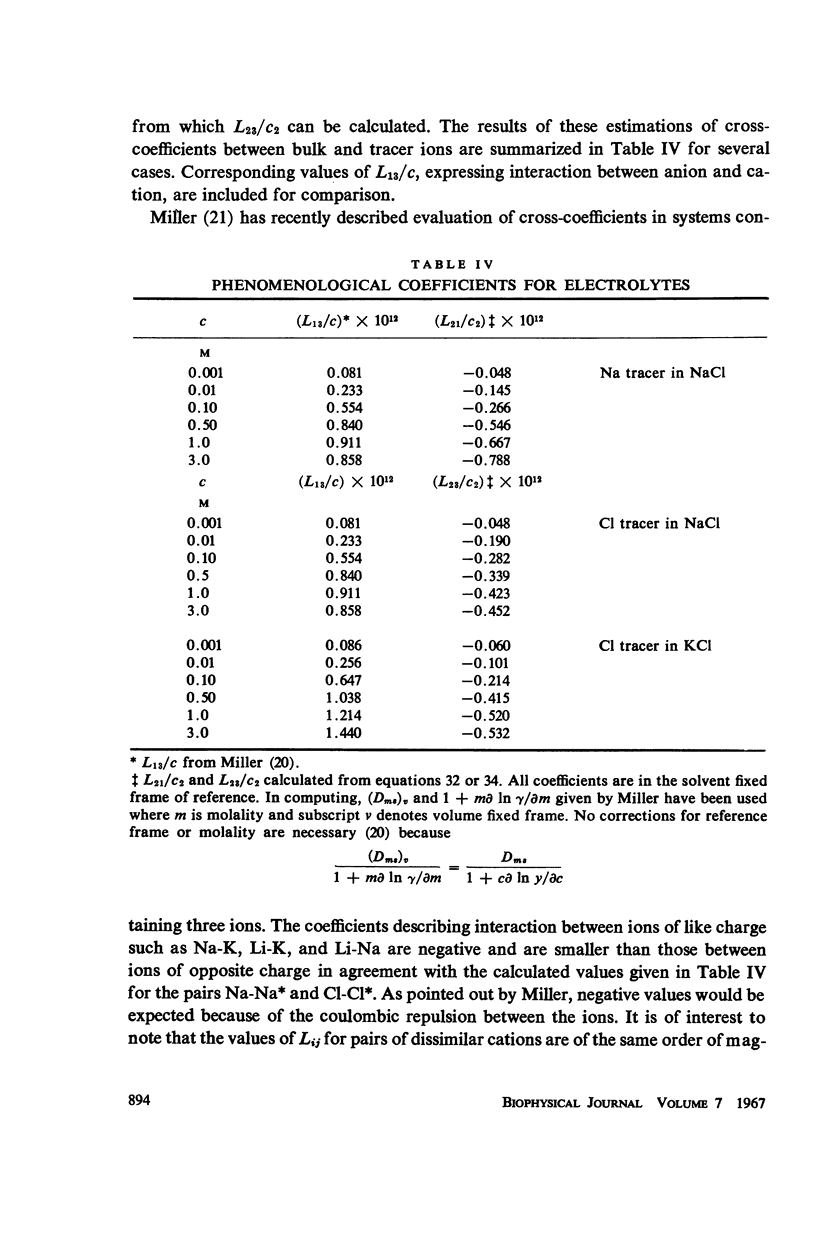
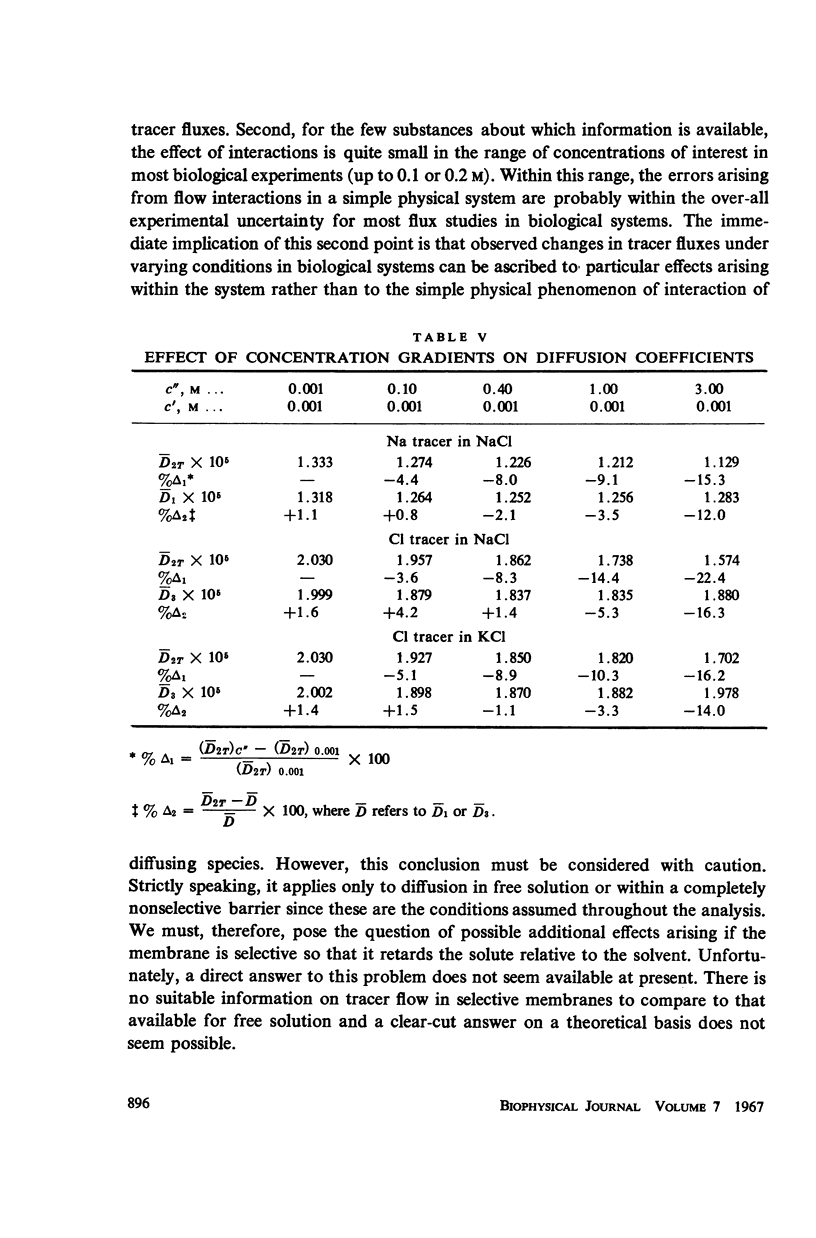
Available experimental data have been utilized to examine the effects of cross-coefficients on tracer diffusion and on the estimation of unidirectional fluxes from observations on tracer flow. In free solution or in a nonselective membrane, the interaction between the flows of tracer and the unlabelled substance are small at concentrations of biological interest for the nonelectrolytes urea, alanine, and β-alanine, and for sodium and chloride ions. Under these conditions, measurement of tracer flow can be used to predict flow of the bulk substance to an accuracy of a few per cent.
Full text
PDF


















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GINZBURG B. Z., KATCHALSKY A. THE FRICTIONAL COEFFICIENTS OF THE FLOWS OF NON-ELECTROLYTES THROUGH ARTIFICIAL MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1963 Nov;47:403–418. doi: 10.1085/jgp.47.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEDEM O., KATCHALSKY A. A physical interpretation of the phenomenological coefficients of membrane permeability. J Gen Physiol. 1961 Sep;45:143–179. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedem O., Essig A. Isotope flows and flux ratios in biological membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1965 Jul;48(6):1047–1070. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.6.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitahara S., Heinz E., Stahlmann C. Effect of trans-solutes on the fluxes of chloride ions across artificial membranes. Nature. 1965 Oct 9;208(5006):187–189. doi: 10.1038/208187a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIMS L. F. Membranes, tagged components, and membrane transfer coefficient. Yale J Biol Med. 1959 Jun;31:373–386. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nims L. F. Tracers, Transfer through Membranes, and Coefficients of Transfer. Science. 1962 Jul 13;137(3524):130–132. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3524.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


