Abstract
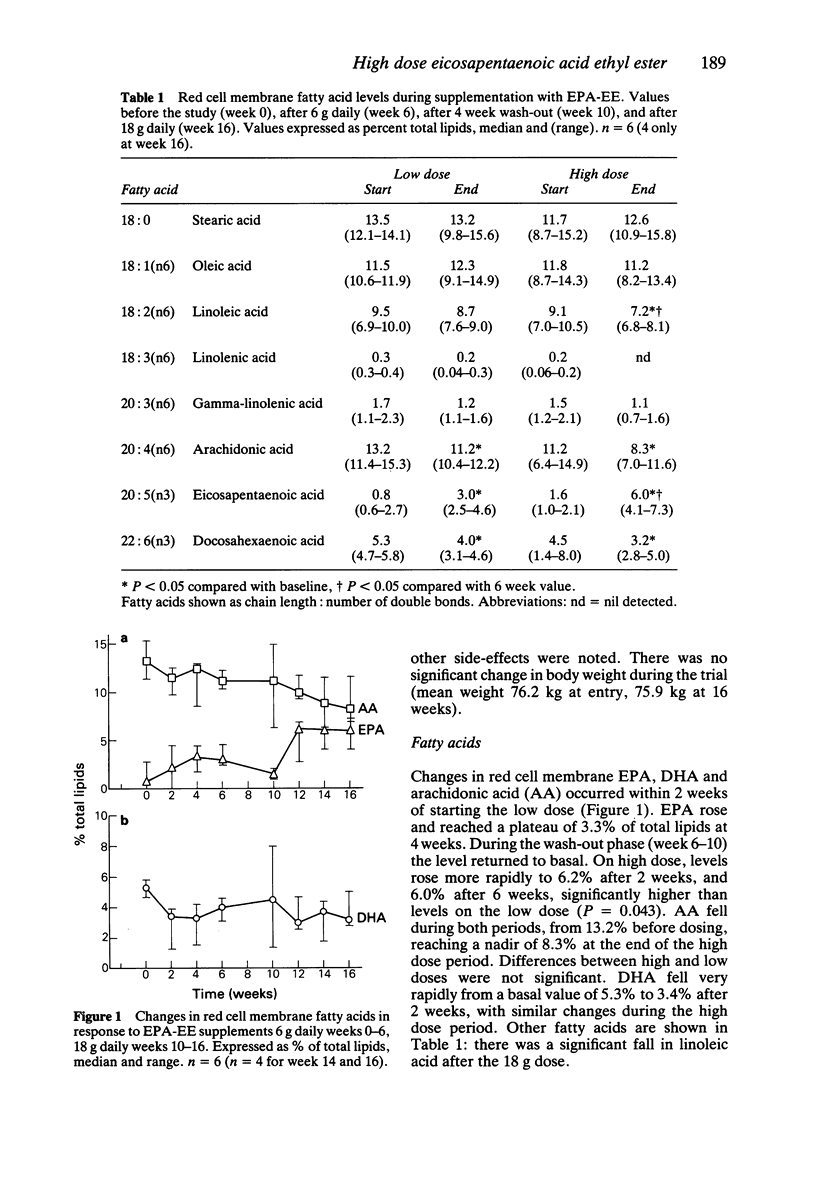
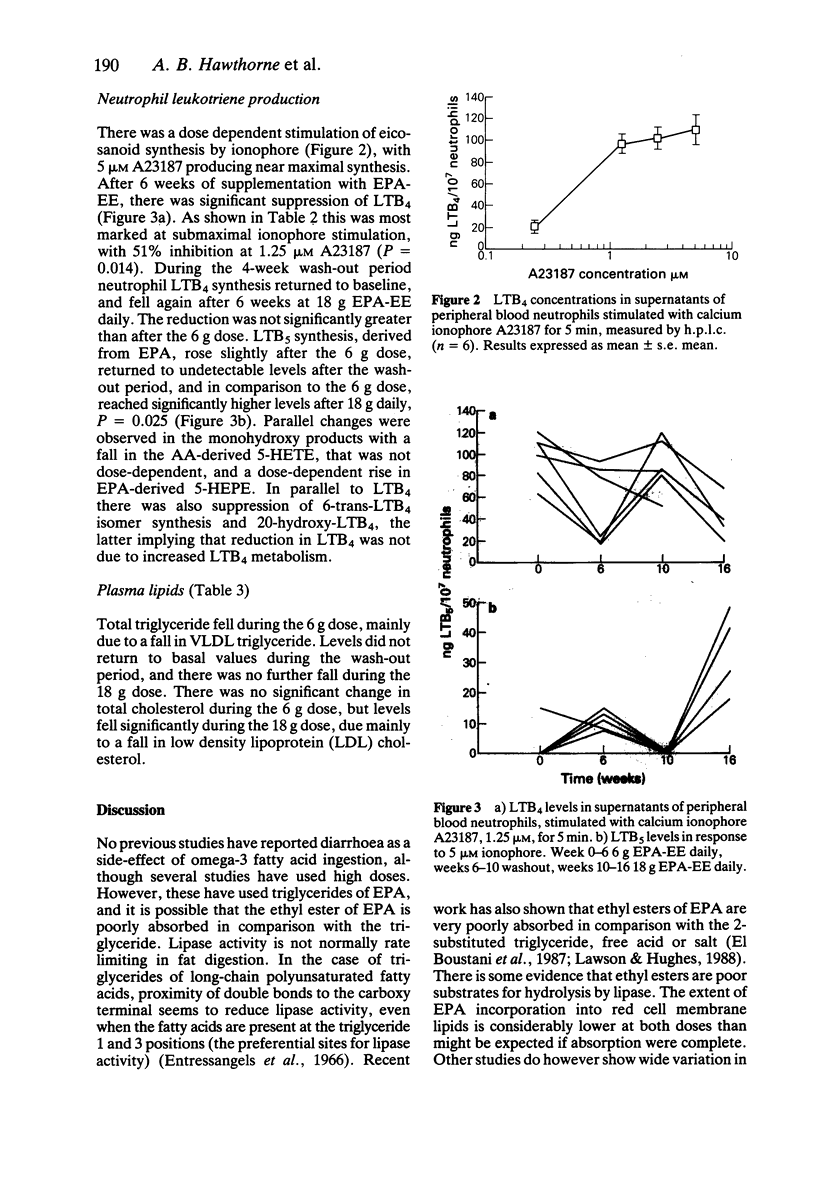
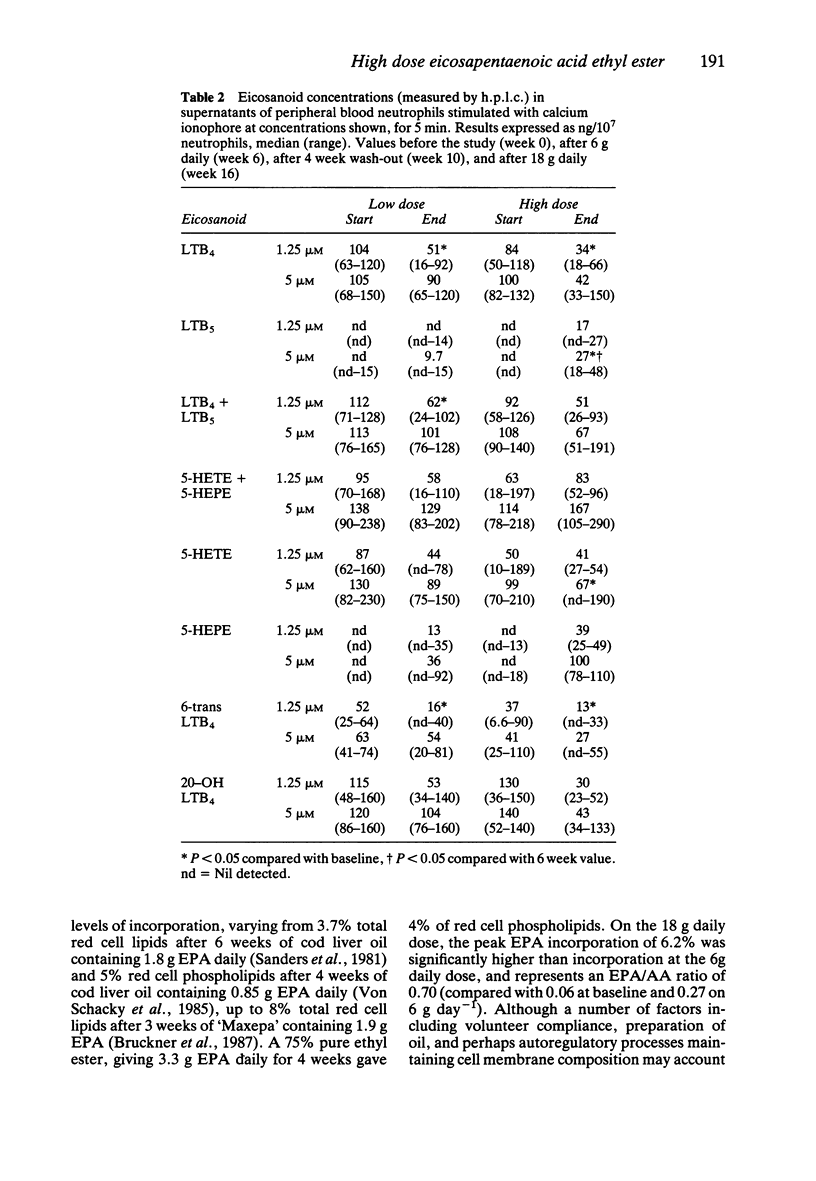
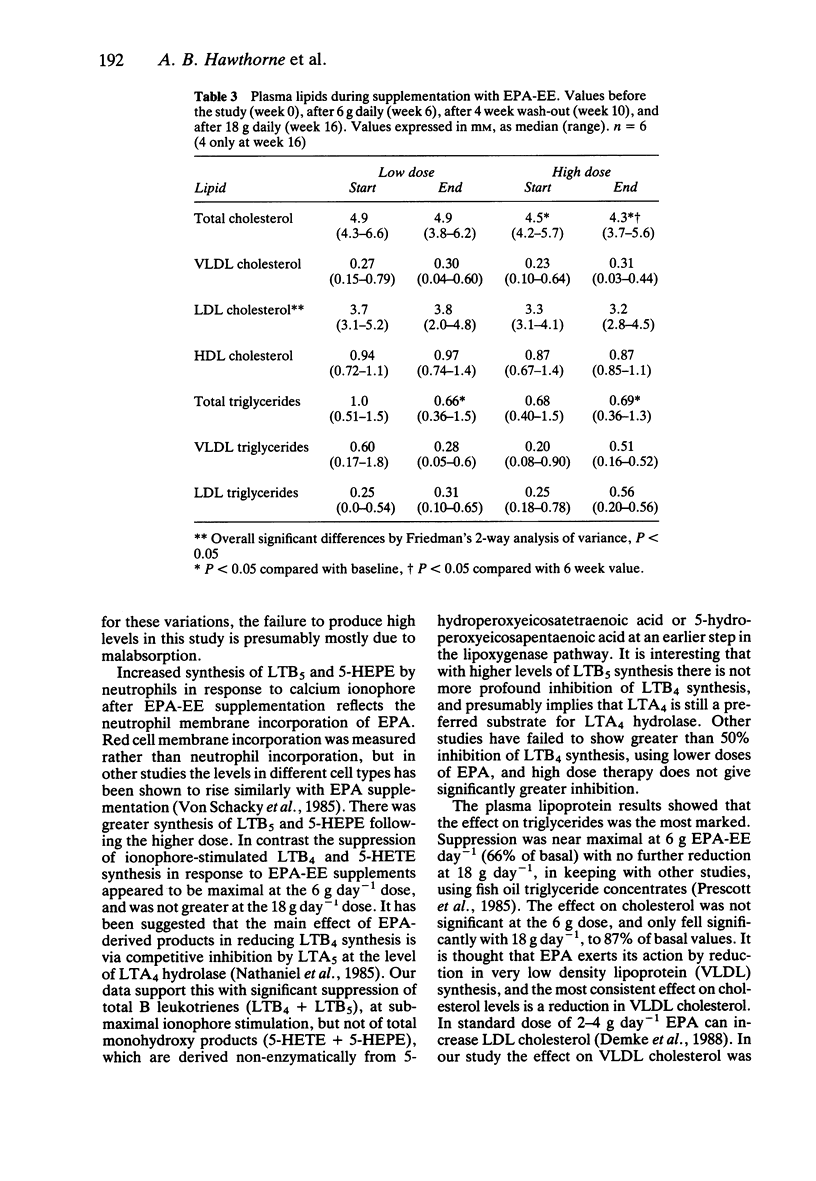
1. A 93% pure ethyl ester of eicosapentaenoic acid was investigated for tolerability and biochemical effects on neutrophil leukotriene synthesis and plasma lipoproteins when given in high dose. Six healthy volunteers received 6 g eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester daily for 6 weeks, followed by a 4 week wash-out and then 18 g daily for 6 weeks. 2. There was inhibition of neutrophil leukotriene B4 and 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid synthesis, with no significant differences between low and high dose. 3. There was a dose dependent increase in leukotriene B5 and 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid acid synthesis. 4. Plasma triglycerides were reduced maximally on 6 g daily, with no greater suppression at 18 g daily. 5. Plasma cholesterol was only suppressed significantly at 18 g daily. 6. The 6 g daily dose was well tolerated but the 18 g daily dose produced diarrhoea and steatorrhoea.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bang H. O., Dyerberg J., Hjøorne N. The composition of food consumed by Greenland Eskimos. Acta Med Scand. 1976;200(1-2):69–73. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb08198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjørneboe A., Søyland E., Bjørneboe G. E., Rajka G., Drevon C. A. Effect of dietary supplementation with eicosapentaenoic acid in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 1987 Oct;117(4):463–469. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1987.tb04926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner G., Webb P., Greenwell L., Chow C., Richardson D. Fish oil increases peripheral capillary blood cell velocity in humans. Atherosclerosis. 1987 Aug;66(3):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(87)90067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demke D. M., Peters G. R., Linet O. I., Metzler C. M., Klott K. A. Effects of a fish oil concentrate in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 1988 Mar;70(1-2):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(88)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Entressangles B., Sari H., Desnuelle P. On the positional specificity of pancreatic lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 7;125(3):597–600. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(66)90048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehily A. M., Yarnell J. W., Bolton C. H., Butland B. K. Dietary determinants of plasma lipids and lipoproteins: the Caerphilly Study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1988 May;42(5):405–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illingworth D. R., Harris W. S., Connor W. E. Inhibition of low density lipoprotein synthesis by dietary omega-3 fatty acids in humans. Arteriosclerosis. 1984 May-Jun;4(3):270–275. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.4.3.270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp H. R., FitzGerald G. A. The antihypertensive effects of fish oil. A controlled study of polyunsaturated fatty acid supplements in essential hypertension. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 20;320(16):1037–1043. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904203201603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaf A., Weber P. C. Cardiovascular effects of n-3 fatty acids. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 3;318(9):549–557. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803033180905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. H., Hoover R. L., Williams J. D., Sperling R. I., Ravalese J., 3rd, Spur B. W., Robinson D. R., Corey E. J., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Effect of dietary enrichment with eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids on in vitro neutrophil and monocyte leukotriene generation and neutrophil function. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 9;312(19):1217–1224. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505093121903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathaniel D. J., Evans J. F., Leblanc Y., Léveillé C., Fitzsimmons B. J., Ford-Hutchinson A. W. Leukotriene A5 is a substrate and an inhibitor of rat and human neutrophil LTA4 hydrolase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Sep 16;131(2):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91314-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payan D. G., Wong M. Y., Chernov-Rogan T., Valone F. H., Pickett W. C., Blake V. A., Gold W. M., Goetzl E. J. Alterations in human leukocyte function induced by ingestion of eicosapentaenoic acid. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Sep;6(5):402–410. doi: 10.1007/BF00915380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillipson B. E., Rothrock D. W., Connor W. E., Harris W. S., Illingworth D. R. Reduction of plasma lipids, lipoproteins, and apoproteins by dietary fish oils in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 9;312(19):1210–1216. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505093121902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., Morrison A. R. The effects of a diet rich in fish oil on human neutrophils: identification of leukotriene B5 as a metabolite. Prostaglandins. 1985 Aug;30(2):209–227. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(85)90186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders T. A., Vickers M., Haines A. P. Effect on blood lipids and haemostasis of a supplement of cod-liver oil, rich in eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids, in healthy young men. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Sep;61(3):317–324. doi: 10.1042/cs0610317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling R. I., Weinblatt M., Robin J. L., Ravalese J., 3rd, Hoover R. L., House F., Coblyn J. S., Fraser P. A., Spur B. W., Robinson D. R. Effects of dietary supplementation with marine fish oil on leukocyte lipid mediator generation and function in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Sep;30(9):988–997. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziboh V. A., Cohen K. A., Ellis C. N., Miller C., Hamilton T. A., Kragballe K., Hydrick C. R., Voorhees J. J. Effects of dietary supplementation of fish oil on neutrophil and epidermal fatty acids. Modulation of clinical course of psoriatic subjects. Arch Dermatol. 1986 Nov;122(11):1277–1282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Boustani S., Colette C., Monnier L., Descomps B., Crastes de Paulet A., Mendy F. Enteral absorption in man of eicosapentaenoic acid in different chemical forms. Lipids. 1987 Oct;22(10):711–714. doi: 10.1007/BF02533970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Schacky C., Fischer S., Weber P. C. Long-term effects of dietary marine omega-3 fatty acids upon plasma and cellular lipids, platelet function, and eicosanoid formation in humans. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1626–1631. doi: 10.1172/JCI112147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


