Abstract
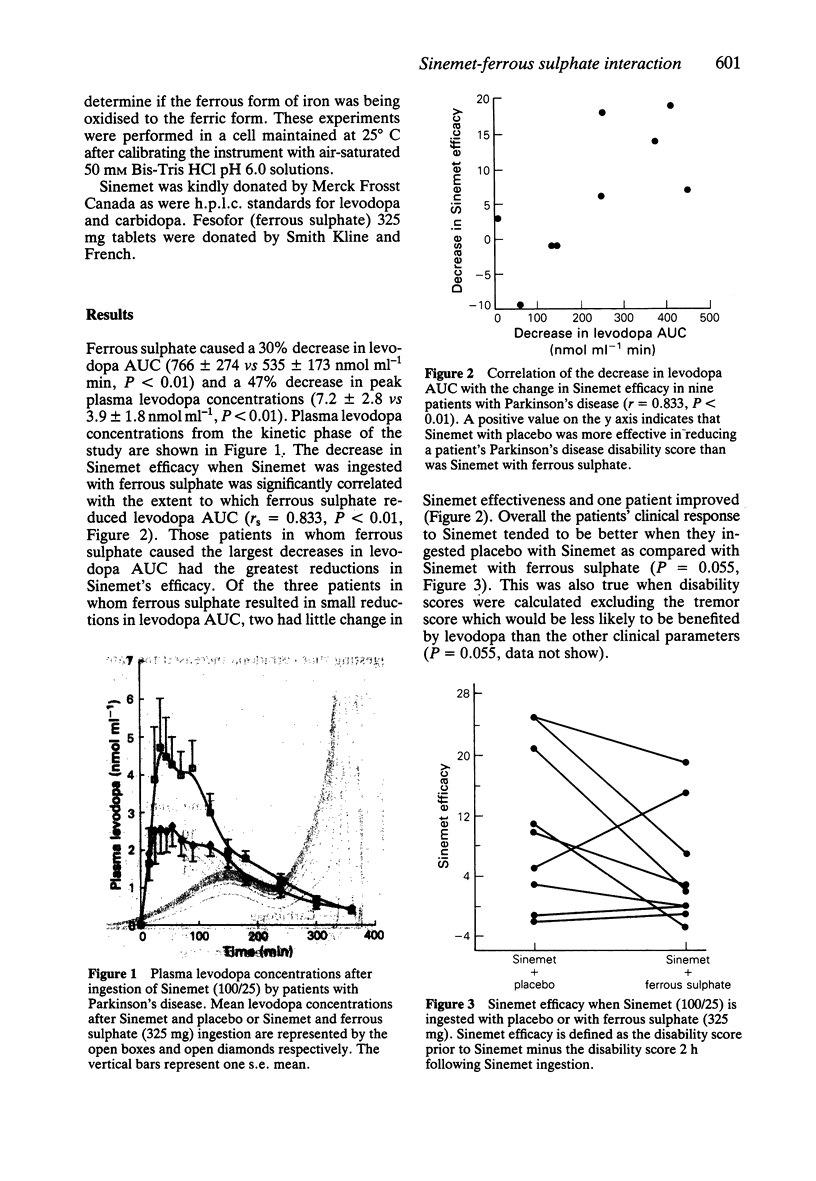
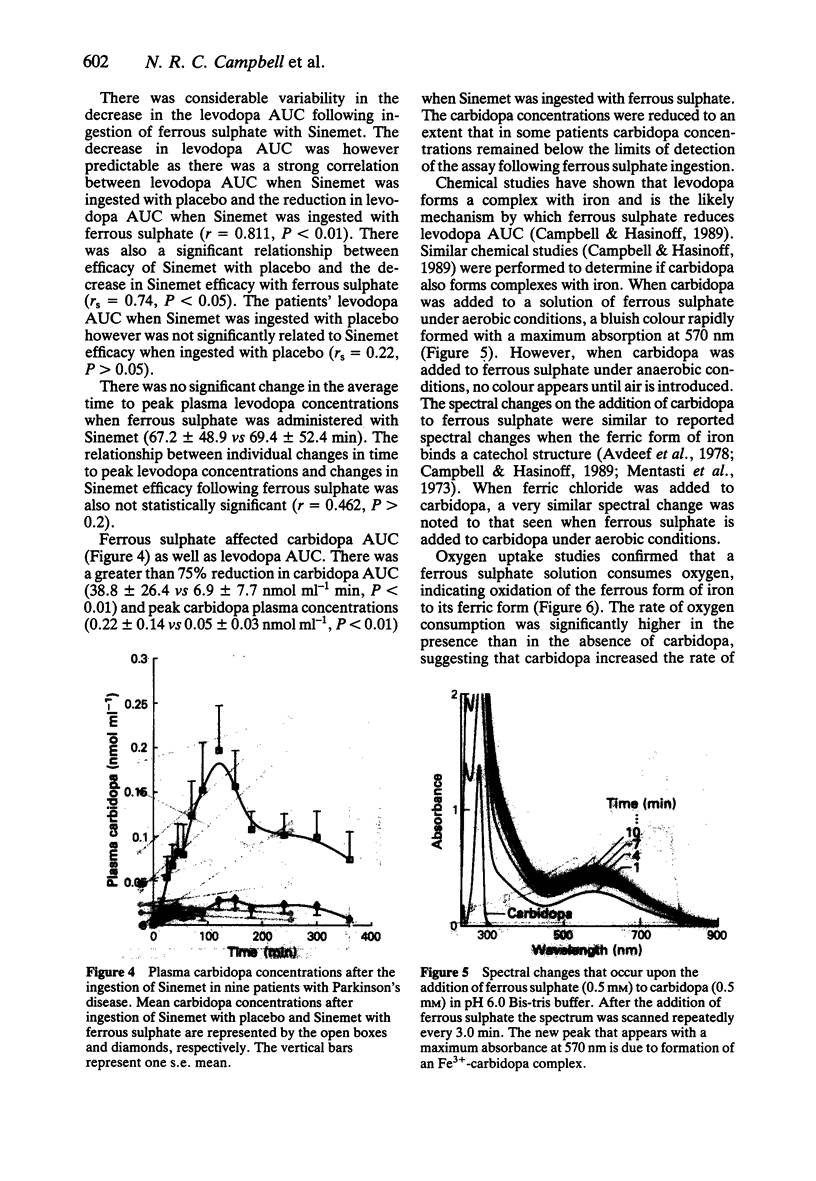
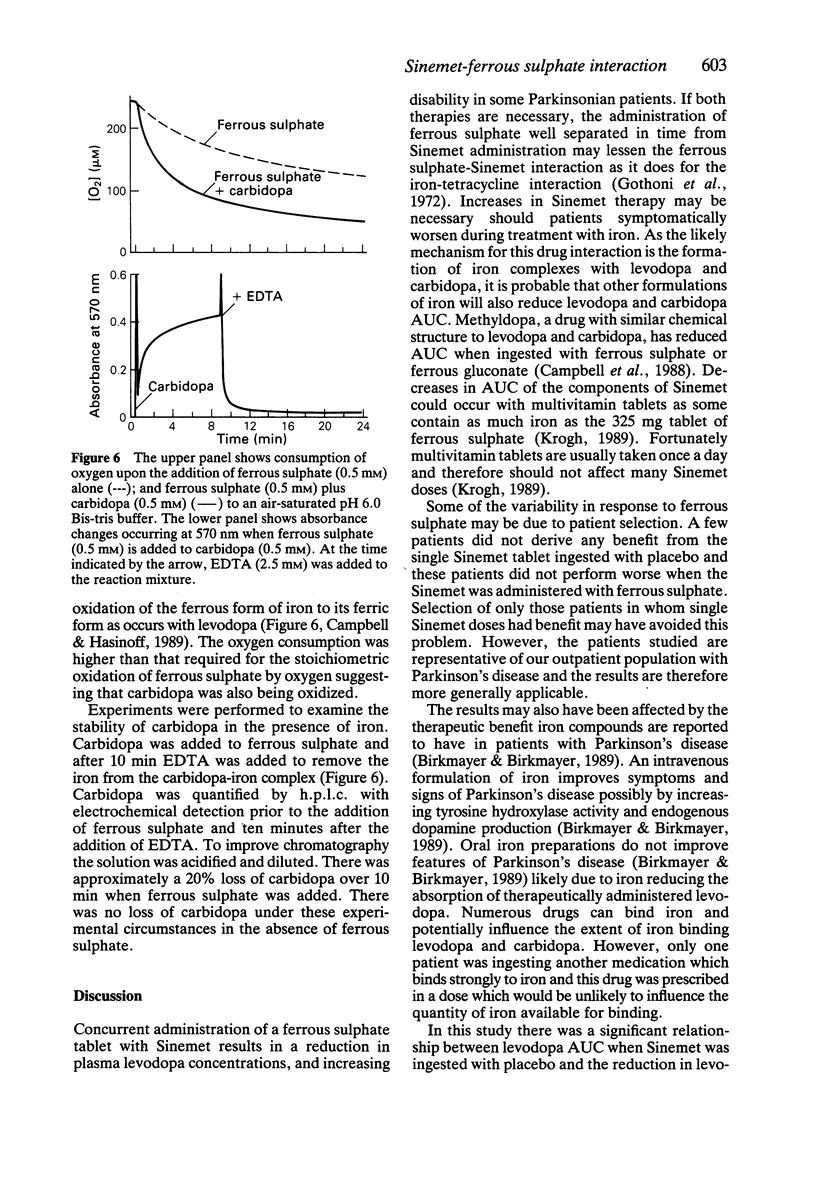
1. This study examined the effects of administering ferrous sulphate 325 mg with Sinemet (100/25 tablet) on levodopa and carbidopa bioavailability and on signs of Parkinson's disease in nine patients. 2. Ferrous sulphate ingestion with Sinemet resulted in a decrease in levodopa area under the curve (AUC) of 30% (P less than 0.01) and a greater than 75% decrease in carbidopa AUC. Despite a strong relationship between reductions in levodopa AUC and reductions in Sinemet efficacy (r = 0.83, P less than 0.01), the average reduction in Sinemet's efficacy associated with ferrous sulphate did not achieve statistical significance (P = 0.055). 3. Chemical studies indicate that iron forms chemical complexes with carbidopa in a similar manner to levodopa and is a likely mechanism for the drug interactions. 4. AUC when a Sinemet tablet is taken concurrently with a ferrous sulphate tablet appears to be clinically significant in some but not all patients. The clinical significance of repeated ingestion of ferrous sulphate with Sinemet requires further studies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borri-Voltattorni C., Minelli A., Borri P. Interaction of L-alpha-methyl-alpha-hydrazino-3,4 dihydroxyphenylpropionic acid with dopa-decarboxylase from pig kidney. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):277–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell N. R., Hasinoff B. Ferrous sulfate reduces levodopa bioavailability: chelation as a possible mechanism. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Mar;45(3):220–225. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell N., Paddock V., Sundaram R. Alteration of methyldopa absorption, metabolism, and blood pressure control caused by ferrous sulfate and ferrous gluconate. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988 Apr;43(4):381–386. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1988.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. R., Hasinoff B., Chernenko G., Barrowman J., Campbell N. R. The effect of ferrous sulfate and pH on L-dopa absorption. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1990 May;68(5):603–607. doi: 10.1139/y90-087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. S., Stull R., Zimlichman R., Levinson P. D., Smith H., Keiser H. R. Simultaneous measurement of DOPA, DOPAC, and catecholamines in plasma by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Clin Chem. 1984 May;30(5):815–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gothoni G., Neuvonen P. J., Mattila M., Hackman R. Iron-tetracycline interaction: effect of time interval between the drugs. Acta Med Scand. 1972 May;191(5):409–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert P. S., Cortese M., Fix J. A. The effects of carbidopa dose and time and route of administration on systemic L-dopa levels in rats. Pharm Res. 1988 Sep;5(9):587–591. doi: 10.1023/a:1015946114321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenter M. D. Double-blind, placebo-controlled study of levodopa therapy in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 1970 Dec;20(12):6–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muenter M. D., Tyce G. M. L-dopa therapy of Parkinson's disease: plasma L-dopa concentration, therapeutic response, and side effects. Mayo Clin Proc. 1971 Apr;46(4):231–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissinen E., Taskinen J. Simultaneous determination of carbidopa, levodopa and 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-acetic acid using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr. 1982 Sep 10;231(2):459–462. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81872-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osiecka I., Cortese M., Porter P. A., Borchardt R. T., Fix J. A., Gardner C. R. Intestinal absorption of alpha-methyldopa: in vitro mechanistic studies in rat small intestinal segments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Aug;242(2):443–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


