Abstract
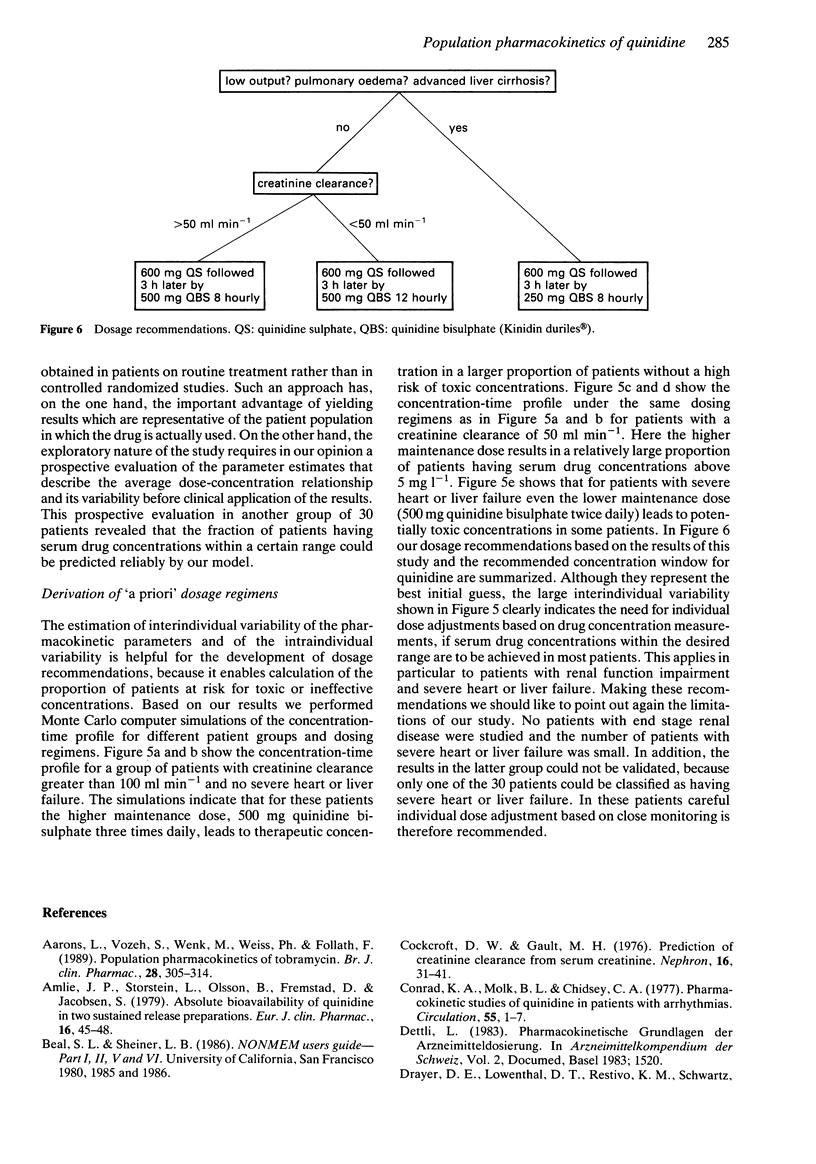
1. Population pharmacokinetic parameters of quinidine were determined based on 260 serum drug concentration measurements in 60 patients treated for arrhythmias with quinidine sulphate or quinidine bisulphate (Kinidin duriles) orally. 2. Quinidine kinetics were best described by a two compartment model with zero order absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. The pharmacokinetics are influenced by severe heart or liver failure and renal function impairment. No effect was found for mild or moderate heart failure, for age, for body weight or for coadministration of nifedipine. 3. Population pharmacokinetic parameters of quinidine (assuming 100% bioavailability of oral quinidine sulphate) were: nonrenal clearance for patients without severe heart and liver failure 12.6 l h-1, reduction in patients with severe heart or liver failure to 6.8 l h-1, renal clearance (l h-1) related to creatinine clearance (ml min-1), proportionality constant 0.0566, volume of distribution of the central compartment 161 l, maximum serum drug concentration 1.4 h after administration of quinidine sulphate and 6.0 h after administration of quinidine bisulphate. 4. The results were validated by predicting the serum drug concentration in a separate group of 30 patients. The model reliably predicted both the population average and the variability of the serum concentration of quinidine. 5. Using Monte Carlo computer simulations, an a priori dosing regimen was derived that should maximize the proportion of patients having quinidine serum concentrations within the recommended range (2-5 mg l-1): initial dose of 600 mg quinidine sulphate in all patients, 3 h later first maintenance dose of quinidine bisulphate.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aarons L., Vozeh S., Wenk M., Weiss P., Follath F. Population pharmacokinetics of tobramycin. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;28(3):305–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb05431.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amlie J. P., Storstein L., Olsson B., Fremstad D., Jacobsen S. Absolute bioavailability of quinidine in two sustained release preparations. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;16(1):45–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00644965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft D. W., Gault M. H. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron. 1976;16(1):31–41. doi: 10.1159/000180580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad K. A., Molk B. L., Chidsey C. A. Pharmacokinetic studies of quinidine in patients with arrhythmias. Circulation. 1977 Jan;55(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer D. E., Lowenthal D. T., Restivo K. M., Schwartz A., Cook C. E., Reidenberg M. M. Steady-state serum levels of quinidine and active metabolites in cardiac patients with varying degrees of renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Jul;24(1):31–39. doi: 10.1002/cpt197824131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farringer J. A., Green J. A., O'Rourke R. A., Linn W. A., Clementi W. A. Nifedipine-induced alterations in serum quinidine concentrations. Am Heart J. 1984 Dec;108(6):1570–1572. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90717-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follath F., Ganzinger U., Schuetz E. Reliability of antiarrhythmic drug plasma concentration monitoring. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1983 Jan-Feb;8(1):63–82. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198308010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P., Müller-Enoch D., Blair I. A. Oxidation of quinidine by human liver cytochrome P-450. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Sep;30(3):287–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guentert T. W., Holford N. H., Coates P. E., Upton R. A., Riegelman S. Quinidine pharmacokinetics in man: choice of a disposition model and absolute bioavailability studies. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1979 Aug;7(4):315–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01062532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroyer R., Jarreau C., Pays M. Specific determination of quinidine and metabolites in biological fluids by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1982 Mar 12;228:366–371. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitre P. O., Vozeh S., Heykants J., Thomson D. A., Stanski D. R. Population pharmacokinetics of alfentanil: the average dose-plasma concentration relationship and interindividual variability in patients. Anesthesiology. 1987 Jan;66(1):3–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munger M. A., Jarvis R. C., Nair R., Kasmer R. J., Nara A. R., Urbancic A., Green J. A. Elucidation of the nifedipine-quinidine interaction. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Apr;45(4):411–416. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs H. R., Greenblatt D. J., Woo E., Smith T. W. Reduced quinidine clearance in elderly persons. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Sep;42(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90944-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakhit A., Holford N. H., Guentert T. W., Maloney K., Riegelman S. Pharmacokinetics of quinidine and three of its metabolites in man. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1984 Feb;12(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF01063608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiner L. B., Rosenberg B., Marathe V. V. Estimation of population characteristics of pharmacokinetic parameters from routine clinical data. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1977 Oct;5(5):445–479. doi: 10.1007/BF01061728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vozeh S., Uematsu T., Aarons L., Maitre P., Landolt H., Gratzl O. Intravenous phenytoin loading in patients after neurosurgery and in status epilepticus. A population pharmacokinetic study. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Feb;14(2):122–128. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198814020-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


