Abstract
1. Flupirtine is a novel and, in all probability, centrally acting, analgesic. The present investigation was conducted in order to investigate dose-related effects of perorally administered flupirtine in man, with special regard to specifically analgesic actions, employing a model based on pain-related chemosomatosensory evoked potentials and subjective intensity estimates of painful stimuli. 2. Plasma concentrations of flupirtine measured 2 h after dosing linearly increased as a function of the administered dose. 3. It was possible to reproduce our own previously obtained results, which established the analgesic action of 200 mg flupirtine administered perorally. 4. Intensity estimates linearly decreased as a function of the administered dose, whereas chemosomatosensory evoked potential amplitudes non-linearly changed in relation to the administered dose. 5. In the spontaneous EEG, a dose-dependent increment in the power-spectra was observed, and this mainly in the alpha- and beta-range.
Full text
PDF


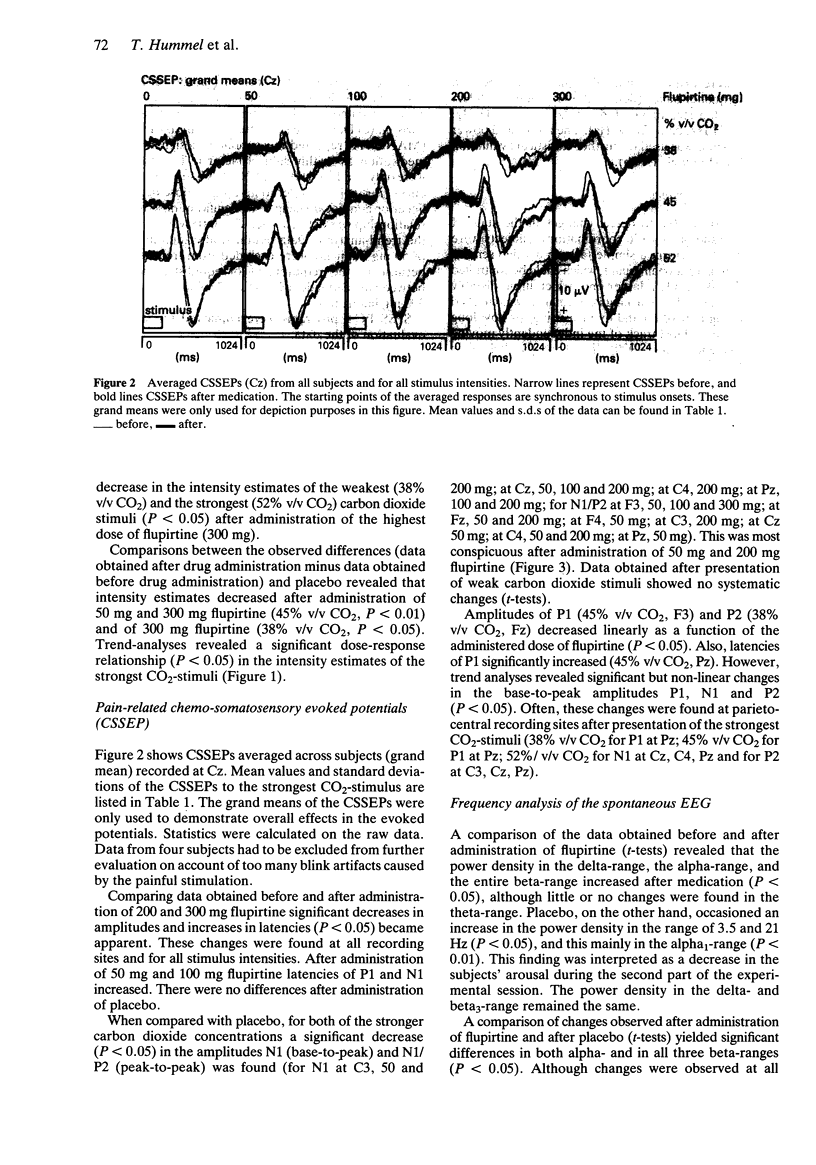
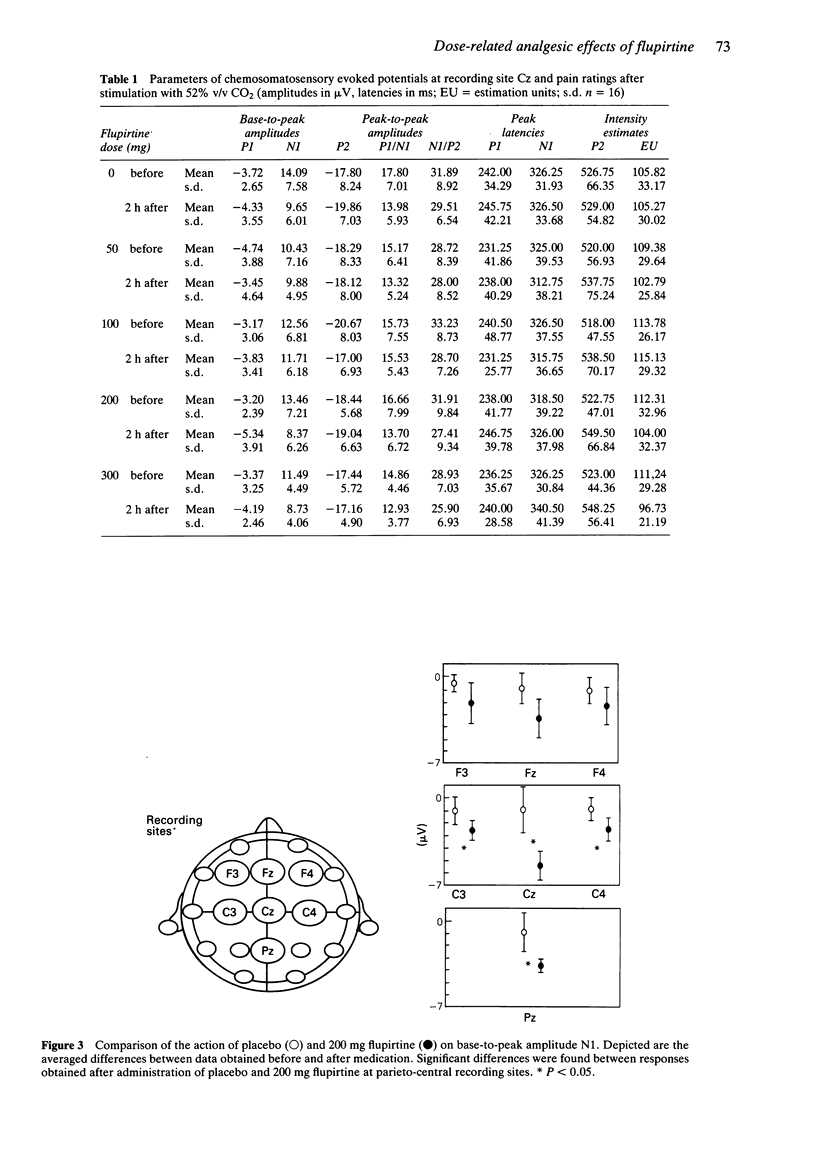
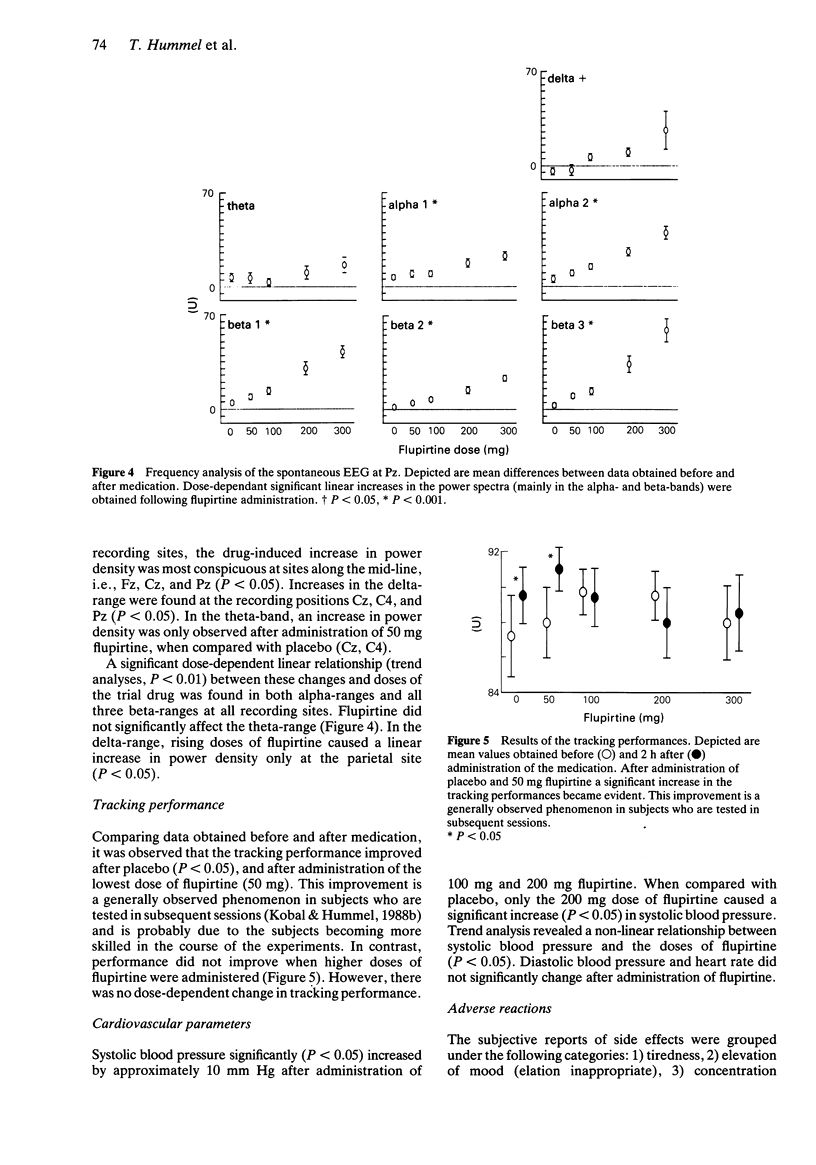


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bleyer H., Carlsson K. H., Erkel H. J., Jurna I. Flupirtine depresses nociceptive activity evoked in rat thalamus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 7;151(2):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90806-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromm B., Ganzel R., Herrmann W. M., Meier W., Scharein E. The analgesic efficacy of flupirtine in comparison to pentazocine and placebo assessed by EEG and subjective pain ratings. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 3):109–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson K. H., Jurna I. Depression by flupirtine, a novel analgesic agent, of motor and sensory responses of the nociceptive system in the rat spinal cord. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Nov 3;143(1):89–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90738-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A. C., Chapman C. R., Harkins S. W. Brain evoked potentials are functional correlates of induced pain in man. Pain. 1979 Jun;6(3):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(79)90054-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chudler E. H., Dong W. K., Kawakami Y. Tooth pulp-evoked potentials in the monkey: cortical surface and intracortical distribution. Pain. 1985 Jul;22(3):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(85)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann W. M., Kern U., Aigner M. On the adverse reactions and efficacy of long-term treatment with flupirtine: preliminary results of an ongoing twelve-month study with 200 patients suffering from chronic pain states in arthrosis or arthritis. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 3):87–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusinger J. H. Efficacy and tolerance of flupirtine and pentazocine in two multicentre trials. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 3):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hlavica P., Niebch G. Untersuchungen zur Pharmakokinetik und Biotransformation des Analgetikums Flupirtin beim Menschen. Arzneimittelforschung. 1985;35(1):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttunen J., Kobal G., Kaukoranta E., Hari R. Cortical responses to painful CO2 stimulation of nasal mucosa; a magnetoencephalographic study in man. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1986 Oct;64(4):347–349. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(86)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobal G., Hummel C. Cerebral chemosensory evoked potentials elicited by chemical stimulation of the human olfactory and respiratory nasal mucosa. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1988 Jul-Aug;71(4):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0168-5597(88)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobal G., Hummel C., Nuernberg B., Brune K. Effects of pentazocine and acetylsalicylic acid on pain-rating, pain-related evoked potentials and vigilance in relationship to pharmacokinetic parameters. Agents Actions. 1990 Mar;29(3-4):342–359. doi: 10.1007/BF01966467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobal G., Hummel T. Effects of flupirtine on the pain-related evoked potential and the spontaneous EEG. Agents Actions. 1988 Feb;23(1-2):117–119. doi: 10.1007/BF01967210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobal G. Pain-related electrical potentials of the human nasal mucosa elicited by chemical stimulation. Pain. 1985 Jun;22(2):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(85)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon F. G., Arndt W. F., Jr, Newton J. J., Montgomery P. A., Perhach J. L. Clinical experience with flupirtine in the U.S. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 3):81–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel B., Herz A., Jakovlev V., Tibes U. Untersuchungen zum Wirkmechanismus des Analgetikums Flupirtin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1985;35(9):1402–1409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel B., Jakovlev V., Szelenyi I. Einfluss von Flupirtin, verschiedener Analgetika und Muskelrelaxantien auf den Skelettmuskeltonus wacher Ratten. Arzneimittelforschung. 1990 Aug;40(8):909–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel B. The antinociceptive activity of flupirtine: a structurally new analgesic. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 3):19–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickel B., Zerrahn H. Pharmaco-electroencephalography in the rat as a method for characterization of different types of analgesics. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 3):45–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield R. C. The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory. Neuropsychologia. 1971 Mar;9(1):97–113. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(71)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell-Jackson P., Williams R. Use of flupirtine maleate as an analgesic in patients with liver disease. Br J Clin Pract. 1985 Feb;39(2):63–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riethmüller-Winzen H. Flupirtine in the treatment of post-operative pain. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 3):61–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheef W. Analgesic efficacy and safety of oral flupirtine in the treatment of cancer pain. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 3):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szelenyi I., Nickel B., Borbe H. O., Brune K. Mode of antinociceptive action of flupirtine in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):835–842. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szelenyi I., Nickel B. Putative site(s) and mechanism(s) of action of flupirtine, a novel analgesic compound. Postgrad Med J. 1987;63 (Suppl 3):57–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel D. B., Nickel B., Becketts K. Flupirtine antinociception in the dog is primarily mediated by nonopioid supraspinal mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 29;162(3):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


