Abstract
1. Atrial fibrillation is an inefficient cardiac rhythm associated with impaired exercise tolerance, exertional dyspnoea, palpitation and a substantial risk of thromboembolism. 2. The first decision in management is to consider cardioversion which can be achieved in suitable cases electrically, or pharmacologically with a class Ic antiarrhythmic drug like flecainide or propafenone. 3. Prophylaxis in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation is best achieved with a class Ic drug or a class III drug such as sotalol or amiodarone. 4. Control of ventricular rate in chronic atrial fibrillation can be achieved by pharmacological manipulation of the atrioventricular node by digoxin alone, or in combination with the calcium channel blockers verapamil or diltiazem, or beta-adrenoceptor blockers with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity like pindolol or xamoterol. 5. In view of the considerable risk of thromboembolism in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation anticoagulation or at least treatment with aspirin should be considered.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. L., Gilbert E. M., Alpert B. L., Henthorn R. W., Waldo A. L., Bhandari A. K., Hawkinson R. W., Pritchett E. L. Prevention of symptomatic recurrences of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in patients initially tolerating antiarrhythmic therapy. A multicenter, double-blind, crossover study of flecainide and placebo with transtelephonic monitoring. Flecainide Supraventricular Tachycardia Study Group. Circulation. 1989 Dec;80(6):1557–1570. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.6.1557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ang E. L., Chan W. L., Cleland J. G., Moore D., Krikler S. J., Alexander N. D., Oakley C. M. Placebo controlled trial of xamoterol versus digoxin in chronic atrial fibrillation. Br Heart J. 1990 Oct;64(4):256–260. doi: 10.1136/hrt.64.4.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antman E. M., Beamer A. D., Cantillon C., McGowan N., Friedman P. L. Therapy of refractory symptomatic atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter: a staged care approach with new antiarrhythmic drugs. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1990 Mar 1;15(3):698–707. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(90)90649-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwood J. E., Sullivan M., Forbes S., Myers J., Pewen W., Olson H. G., Froelicher V. F. Effect of beta-adrenergic blockade on exercise performance in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Aug;10(2):314–320. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R., Smith D. A., McHaffie D. J. Exercise heart rates at different serum digoxin concentrations in patients with atrial fibrillation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jan 5;290(6461):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6461.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertini G., Conti A., Fradella G., Francardelli L., Giglioli C., Mangialavori G., Margheri M., Moschi G. Propafenone versus amiodarone in field treatment of primary atrial tachydysrhythmias. J Emerg Med. 1990 Jan-Feb;8(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0736-4679(90)90380-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianconi L., Boccadamo R., Pappalardo A., Gentili C., Pistolese M. Effectiveness of intravenous propafenone for conversion of atrial fibrillation and flutter of recent onset. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Aug 1;64(5):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90530-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blevins R. D., Kerin N. Z., Benaderet D., Frumin H., Faitel K., Jarandilla R., Rubenfire M. Amiodarone in the management of refractory atrial fibrillation. Arch Intern Med. 1987 Aug;147(8):1401–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brembilla-Perrot B., Amor M., Auque F., Isaaz K., Terrier de la Chaise A., Bertrand A., Cherrier F., Pernot C. Effect of flecainide on left ventricular ejection fraction. Eur Heart J. 1987 Jul;8(7):754–761. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/8.7.754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky M. A., Allen B. J., Capparelli E. V., Luckett C. R., Morton R., Henry W. L. Factors determining maintenance of sinus rhythm after chronic atrial fibrillation with left atrial dilatation. Am J Cardiol. 1989 May 1;63(15):1065–1068. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky M. A., Allen B. J., Walker C. J., 3rd, Casey T. P., Luckett C. R., Henry W. L. Amiodarone for maintenance of sinus rhythm after conversion of atrial fibrillation in the setting of a dilated left atrium. Am J Cardiol. 1987 Sep 1;60(7):572–575. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(87)90307-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. W., Goble A. J. Effect of propranolol on exercise tolerance of patients with atrial fibrillation. Br Med J. 1969 May 3;2(5652):279–280. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5652.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain D. A. Digitalis: where are we now? Br Heart J. 1985 Sep;54(3):227–233. doi: 10.1136/hrt.54.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channer K. S., Jones J. V. Atrial systole: its role in normal and diseased hearts. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Jul;75(1):1–4. doi: 10.1042/cs0750001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channer K. S., Jones J. V. The contribution of atrial systole to mitral diastolic blood flow increases during exercise in humans. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:53–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Channer K. S., Papouchado M., James M. A., Pitcher D. W., Rees J. R. Towards improved control of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 1987 Feb;8(2):141–147. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David D., Segni E. D., Klein H. O., Kaplinsky E. Inefficacy of digitalis in the control of heart rate in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation: beneficial effect of an added beta adrenergic blocking agent. Am J Cardiol. 1979 Dec;44(7):1378–1382. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(79)90456-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean J. W., Lab M. J. Arrhythmia in heart failure: role of mechanically induced changes in electrophysiology. Lancet. 1989 Jun 10;1(8650):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92697-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBianco R., Morganroth J., Freitag J. A., Ronan J. A., Jr, Lindgren K. M., Donohue D. J., Larca L. J., Chadda K. D., Olukotun A. Y. Effects of nadolol on the spontaneous and exercise-provoked heart rate of patients with chronic atrial fibrillation receiving stable dosages of digoxin. Am Heart J. 1984 Oct;108(4 Pt 2):1121–1127. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90592-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmertsen K., Bjerregaard P., Andreasen F. Amiodarone for refractory supraventricular tachycardias. Acta Med Scand. 1987;221(5):435–439. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1987.tb01277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evered D. C., Chapman C. Plasma digoxin concentrations and digoxin toxicity in hospital patients. Br Heart J. 1971 Jul;33(4):540–545. doi: 10.1136/hrt.33.4.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forfar J. C., Toft A. D. Thyrotoxic atrial fibrillation: an underdiagnosed condition? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Oct 2;285(6346):909–910. doi: 10.1136/bmj.285.6346.909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold R. L., Haffajee C. I., Charos G., Sloan K., Baker S., Alpert J. S. Amiodarone for refractory atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1986 Jan 1;57(1):124–127. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(86)90964-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goy J. J., Kaufmann U., Kappenberger L., Sigwart U. Restoration of sinus rhythm with flecainide in patients with atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1988 Aug 25;62(6):38D–40D. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(88)90503-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON D. C., GRIFFIN J. R., FIENE T. J. EFFECTS OF BETA-ADRENERGIC BLOCKADE WITH PROPRANOLOL IN PATIENTS WITH ATRIAL ARRHYTHMIAS. N Engl J Med. 1965 Aug 19;273:410–415. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196508192730802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammill S. C., Wood D. L., Gersh B. J., Osborn M. J., Holmes D. R., Jr Propafenone for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1988 Feb 15;61(6):473–474. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(88)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillestad L., Bjerkelund C., Dale J., Maltau J., Storstein O. Quinidine in maintenance of sinus rhythm after electroconversion of chronic atrial fibrillation. A controlled clinical study. Br Heart J. 1971 Jul;33(4):518–521. doi: 10.1136/hrt.33.4.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton R. C., Kistler J. P., Fallon J. T., Friedlich A. L., Fisher C. M. Influence of etiology of atrial fibrillation on incidence of systemic embolism. Am J Cardiol. 1977 Oct;40(4):509–513. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(77)90064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
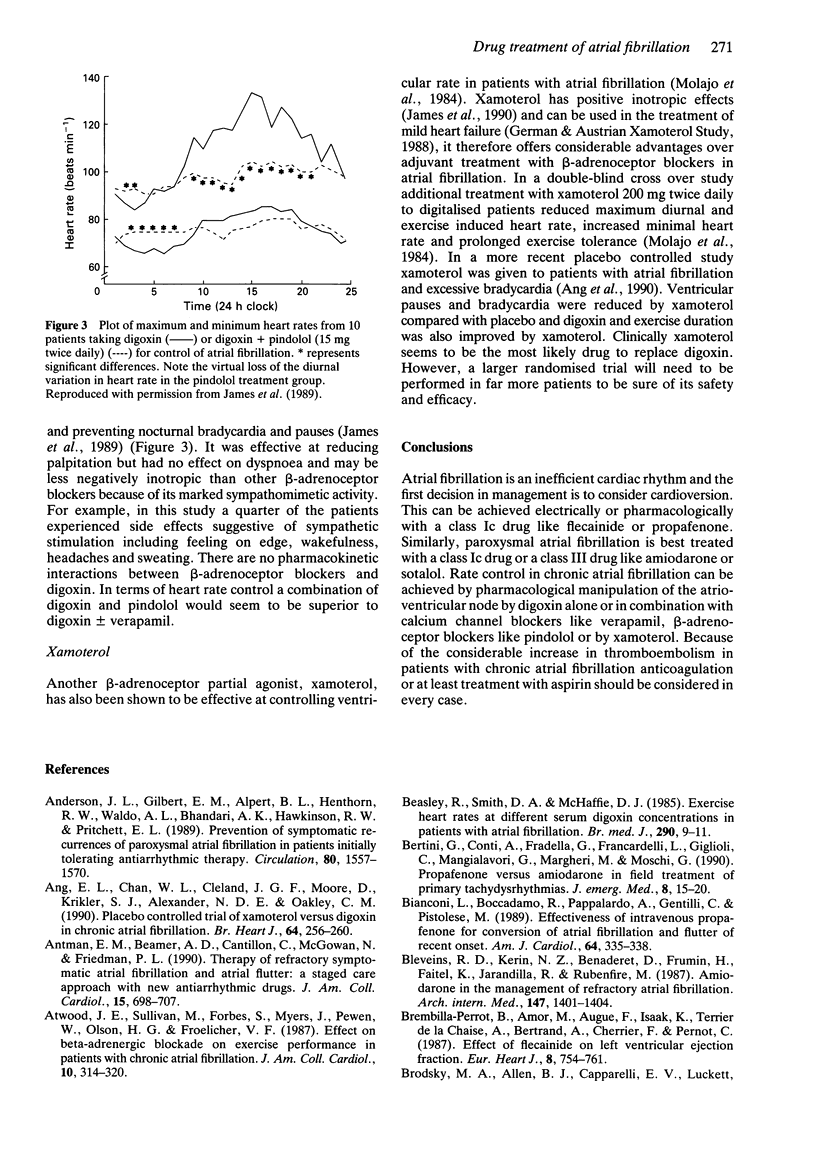
- James M. A., Channer K. S., Papouchado M., Rees J. R. Improved control of atrial fibrillation with combined pindolol and digoxin therapy. Eur Heart J. 1989 Jan;10(1):83–90. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. A., Papouchado M., Channer K. S., Jones J. V., Marlow H. F., Bastain W., Barker N. P., Harry J. D., Wardleworth A. G. The effect of oral dosing of xamoterol on systolic time intervals in man and xamoterol plasma concentrations in heart failure patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;29(4):447–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03663.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr C. R., Klein G. J., Axelson J. E., Cooper J. C. Propafenone for prevention of recurrent atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1988 Apr 15;61(11):914–916. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(88)90373-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. O., Lang R., Weiss E., Di Segni E., Libhaber C., Guerrero J., Kaplinsky E. The influence of verapamil on serum digoxin concentration. Circulation. 1982 May;65(5):998–1003. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.5.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R., Klein H. O., Weiss E., David D., Sareli P., Levy A., Guerrero J., Di Segni E., Kaplinsky E. Superiority of oral verapamil therapy to digoxin in treatment of chronic atrial fibrillation. Chest. 1983 Mar;83(3):491–499. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Irvine N., McDevitt D. G. Relationships between heart rate, exercise tolerance and cardiac output in atrial fibrillation: the effects of treatment with digoxin, verapamil and diltiazem. Eur Heart J. 1988 Jul;9(7):777–781. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/9.7.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R., Lakhani M., Moreland T. A., McDevitt D. G. A comparison of verapamil and digoxin in the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 1987 Feb;8(2):148–153. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malcolm A., Coltart J. Relation between concentrations of digoxin in the myocardium and in the plasma. Br Heart J. 1977 Sep;39(9):935–938. doi: 10.1136/hrt.39.9.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maragno I., Santostasi G., Gaion R. M., Trento M., Grion A. M., Miraglia G., Dalla Volta S. Low- and medium-dose diltiazem in chronic atrial fibrillation: comparison with digoxin and correlation with drug plasma levels. Am Heart J. 1988 Aug;116(2 Pt 1):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(88)90610-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAlister H. F., Luke R. A., Whitlock R. M., Smith W. M. Intravenous amiodarone bolus versus oral quinidine for atrial flutter and fibrillation after cardiac operations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1990 May;99(5):911–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molajo A. O., Coupe M. O., Bennett D. H. Effect of Corwin (ICI 118587) on resting and exercise heart rate and exercise tolerance in digitalised patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Br Heart J. 1984 Oct;52(4):392–395. doi: 10.1136/hrt.52.4.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher D., Papouchado M., James M. A., Rees J. R. Twenty four hour ambulatory electrocardiography in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1986 Mar 1;292(6520):594–594. doi: 10.1136/bmj.292.6520.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomfret S. M., Beasley C. R., Challenor V., Holgate S. T. Relative efficacy of oral verapamil and digoxin alone and in combination for the treatment of patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Apr;74(4):351–357. doi: 10.1042/cs0740351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porterfield J. G., Porterfield L. M. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of oral propafenone for atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Jan 1;63(1):114–116. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)91091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen V., Jensen G., Schnohr P., Hansen J. F. Premature ventricular beats in healthy adult subjects 20 to 79 years of age. Eur Heart J. 1985 Apr;6(4):335–341. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a061860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawles J. M., Metcalfe M. J., Jennings K. Time of occurrence, duration, and ventricular rate of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: the effect of digoxin. Br Heart J. 1990 Apr;63(4):225–227. doi: 10.1136/hrt.63.4.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawles J. M. What is meant by a "controlled" ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation? Br Heart J. 1990 Mar;63(3):157–161. doi: 10.1136/hrt.63.3.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth A., Harrison E., Mitani G., Cohen J., Rahimtoola S. H., Elkayam U. Efficacy and safety of medium- and high-dose diltiazem alone and in combination with digoxin for control of heart rate at rest and during exercise in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1986 Feb;73(2):316–324. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.2.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schamroth L. Immediate effects of intravenous verapamil on atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 1971 Oct;5(4):419–424. doi: 10.1093/cvr/5.4.419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. B., Keefe D., Kates R. E., Kirsten E., Harrison D. C. Acute and chronic pharmacodynamic interaction of verapamil and digoxin in atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1982 Jun;65(6):1163–1170. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.65.6.1163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sihm I., Hansen F. A., Rasmussen J., Pedersen A. K., Thygesen K. Flecainide acetate in atrial flutter and fibrillation. The arrhythmogenic effects. Eur Heart J. 1990 Feb;11(2):145–148. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a059670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloman G., Spokes J., Ramshaw J., Vohra J. Haemodynamic effect of intravenous verapamil in controlled atrial fibrillation. Aust N Z J Med. 1975 Oct;5(5):420–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.1975.tb03049.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg J. S., Katz R. J., Bren G. B., Buff L. A., Varghese P. J. Efficacy of oral diltiazem to control ventricular response in chronic atrial fibrillation at rest and during exercise. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Feb;9(2):405–411. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80396-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttorp M. J., Kingma J. H., Lie-A-Huen L., Mast E. G. Intravenous flecainide versus verapamil for acute conversion of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation or flutter to sinus rhythm. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Mar 15;63(11):693–696. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90253-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Södermark T., Jonsson B., Olsson A., Orö L., Wallin H., Edhag O., Sjögren A., Danielsson M., Rosenhamer G. Effect of quinidine on maintaining sinus rhythm after conversion of atrial fibrillation or flutter. A multicentre study from Stockholm. Br Heart J. 1975 May;37(5):486–492. doi: 10.1136/hrt.37.5.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Gelder I. C., Crijns H. J., Van Gilst W. H., Van Wijk L. M., Hamer H. P., Lie K. I. Efficacy and safety of flecainide acetate in the maintenance of sinus rhythm after electrical cardioversion of chronic atrial fibrillation or atrial flutter. Am J Cardiol. 1989 Dec 1;64(19):1317–1321. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90574-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafa S. S., Ward D. E., Parker D. J., Camm A. J. Efficacy of flecainide acetate for atrial arrhythmias following coronary artery bypass grafting. Am J Cardiol. 1989 May 1;63(15):1058–1064. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(89)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf P. A., Kannel W. B., McGee D. L., Meeks S. L., Bharucha N. E., McNamara P. M. Duration of atrial fibrillation and imminence of stroke: the Framingham study. Stroke. 1983 Sep-Oct;14(5):664–667. doi: 10.1161/01.str.14.5.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahalom J., Klein H. O., Kaplinsky E. Beta-adrenergic blockade as adjunctive oral therapy in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Chest. 1977 May;71(5):592–596. doi: 10.1378/chest.71.5.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


