Abstract
1. ICI 169,369 (2-(2-dimethylamino ethylthio)-3-phenyl quinoline) is a potent selective competitive antagonist of the 5-HT2 receptor in animal models. Effects of ICI 169,369 as single oral doses (80 and 120 mg) separated by 1 week, on the power spectrum of waking EEG, dark adapted pupil responses and sedation score, were studied in a double-blind, placebo controlled, randomised cross over within subject comparison, in six healthy male volunteers. 2. Pupillary responses were measured using a portable infrared pupillometer following 15 min dark adaptation, assessing resting vertical pupil diameter (RPD), light constricted diameter (MPD) and recovered final diameter (FPD) at the end of a 3 s measurement cycle. 3. Both doses of ICI 169,369 produced a mean 36% (range 10-54%) decrease in log 10 power of the waking EEG alpha activity with eyes closed (P less than 0.02), and mean 38% (range 2-86%) increase in theta activity at 2 h compared with placebo. 4. Both 80 and 120 mg doses of ICI 169,369 reduced RPD by approximately 30% from a predose value of 6.25 mm (+/- 0.87; 95% CI) and from placebo values 6.41 mm (+/- 1.06) and 7.48 mm (+/- 1.49) at 3 and 5 h after dosing. MPD was reduced by 50% with the 120 mg dose at 5 h after dosing (placebo 5.2 mm; ICI 169,369 2.7 mm; P less than 0.05). FPD was significantly reduced (P less than 0.01) by both doses at 3 h after dosing.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
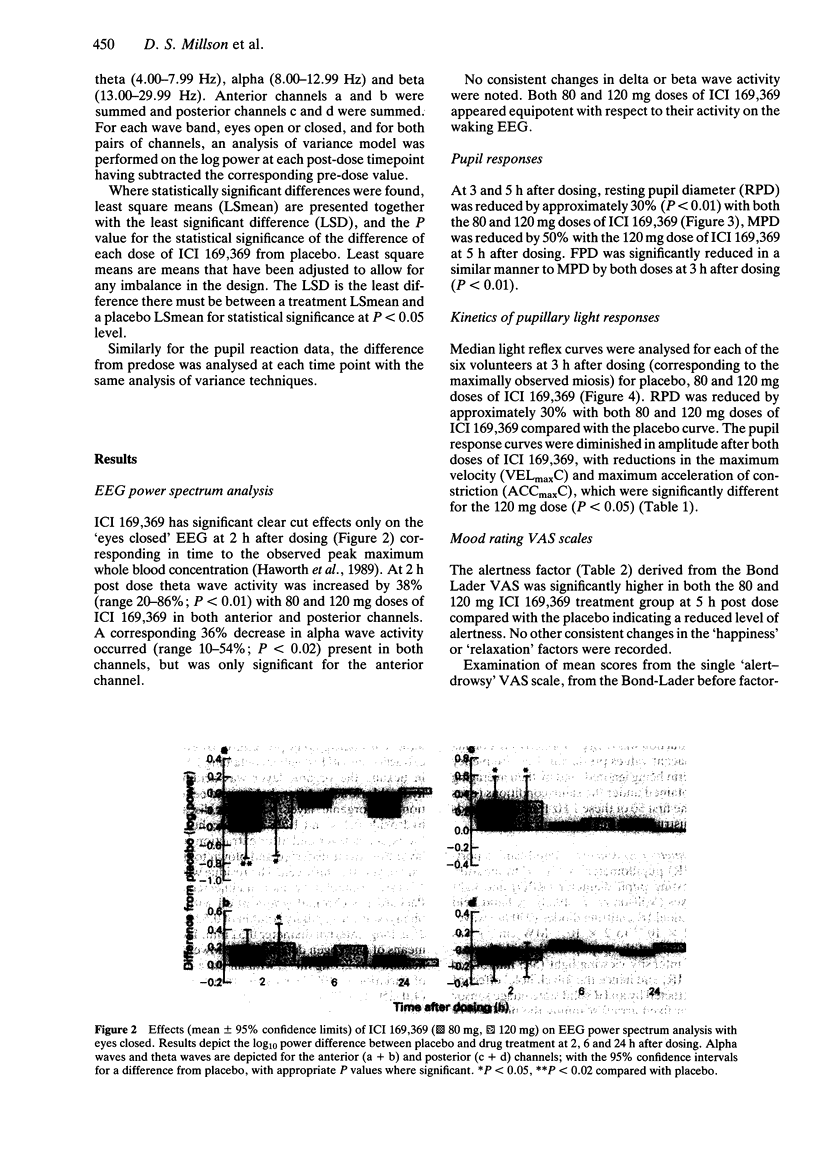
PDF


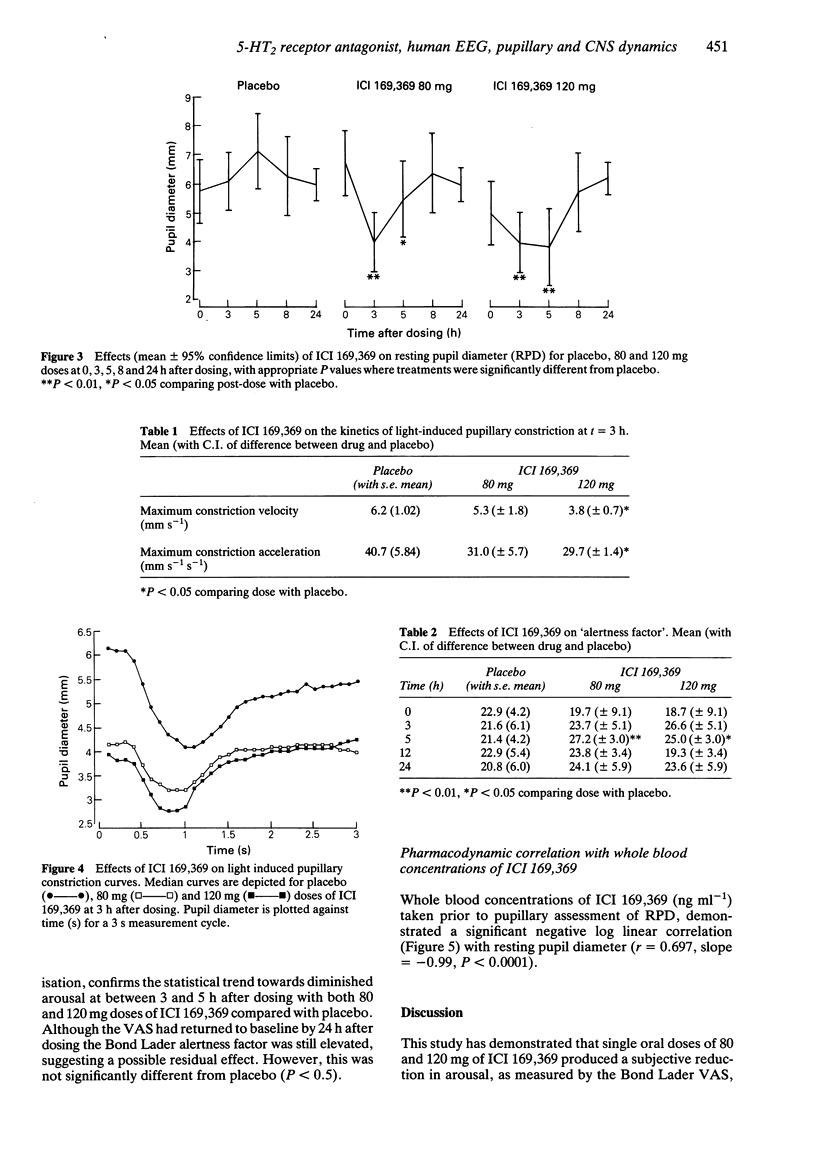
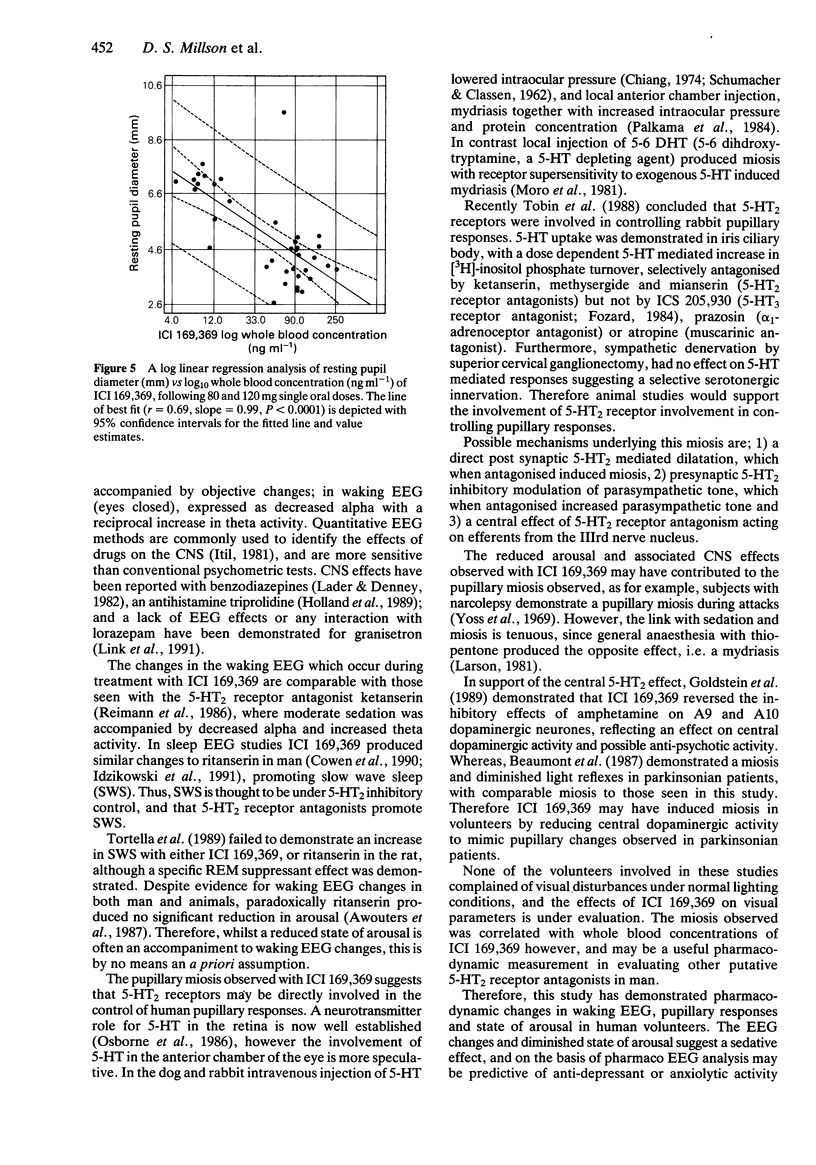


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn T. P., Thornber C. W., Pearce R. J., Cox B. In vitro studies with ICI 169,369, a chemically novel 5-HT antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun 10;150(3):247–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blauw G. J., van Brummelen P., Chang P. C., Vermeij P., van Zwieten P. A. Regional vascular effects of serotonin and ketanserin in young, healthy subjects. Hypertension. 1988 Mar;11(3):256–263. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.11.3.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron H. A., Waller P. C., Ramsay L. E. Ketanserin in essential hypertension: use as monotherapy and in combination with a diuretic or beta-adrenoceptor antagonist. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Dec;24(6):705–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03235.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang T. S. Effects of intravenous infusions of histamine 5-hydroxytryptamine, bradykinin and prostaglandins on intraocular pressure. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1974 Jan;207(1):131–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn P. J., Sanders-Bush E. Regulation of serotonin-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis: relation to the serotonin 5-HT-2 binding site. J Neurosci. 1986 Dec;6(12):3669–3675. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-12-03669.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. J., Abbott A. Clinical psychopharmacology may benefit from new advances in 5-HT pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):269–271. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. T., Steiner T. J. Serotonin S2 receptors and migraine: a study with the selective antagonist ICI 169,369. Headache. 1990 May;30(6):340–343. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.1990.hed3006340.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clerck F., Van Nueten J. M. Platelet-mediated vascular contractions: inhibition of the serotonergic component by ketanserin. Thromb Res. 1982 Sep 15;27(6):713–727. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M. Pharmacoelectroencephalography: a note on its history. Neuropsychobiology. 1984;12(2-3):173–178. doi: 10.1159/000118132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fozard J. R. MDL 72222: a potent and highly selective antagonist at neuronal 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1984 May;326(1):36–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00518776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. M., Litwin L. C., Sutton E. B., Malick J. B. Effects of ICI 169,369, a selective serotonin2 antagonist, in electrophysiological tests predictive of antipsychotic activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jun;249(3):673–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idzikowski C., Cowen P. J., Nutt D., Mills F. J. The effects of chronic ritanserin treatment on sleep and the neuroendocrine response to L-tryptophan. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1987;93(4):416–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00207228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idzikowski C., Mills F. J., James R. J. A dose-response study examining the effects of ritanserin on human slow wave sleep. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;31(2):193–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb05514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. A., Roberts H. C., Sillito A. M. Further studies on the action of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Brain Res. 1982 Aug 26;246(2):334–337. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91187-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R., Rubicek M., Turner P. The role of norfenfluramine in fenfluramine-induced mydriasis. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;25(7):575–576. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb09161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lader M., Denney S. C. A double-blind study to establish the residual effects of zopiclone on performance in healthy volunteers. Int Pharmacopsychiatry. 1982;17 (Suppl 2):98–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson M. D. Dilation of the pupil in human subjects after intravenous thiopental. Anesthesiology. 1981 Mar;54(3):246–249. doi: 10.1097/00000542-198103000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link C. G., Leigh T. J., Fell G. L. Effects of granisetron and lorazepam, alone and in combination, on the EEG of human volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;31(1):93–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb03863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longmore J., Banjar W., Bradshaw C. M., Szabadi E. Effects of a controlled-release formulation of trazodone on psychomotor and autonomic functions in healthy volunteers: comparison with trazodone (conventional formulation), amitriptyline and placebo. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1988;34(1):97–99. doi: 10.1007/BF01061427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moro F., Scapagnini U., Scaletta S., Drago F. Serotonin nerve endings and regulation of pupillary diameter. Ann Ophthalmol. 1981 Apr;13(4):487–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne N. N., Beaton D. W. Direct histochemical localisation of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine and the uptake of serotonin by a subpopulation of GABA neurones in the rabbit retina. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 10;382(1):158–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazos A., Probst A., Palacios J. M. Serotonin receptors in the human brain--IV. Autoradiographic mapping of serotonin-2 receptors. Neuroscience. 1987 Apr;21(1):123–139. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90327-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann I. W., Ziegler G., Ludwig L., Frölich J. C. Central and autonomic nervous system side effects of ketanserin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1986 Nov;36(11):1681–1684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUMACHER H., CLASSEN H. G. [Neuropharmacological studies on the analysis of pupillar motor activity]. Albrecht Von Graefes Arch Ophthalmol. 1962;164:533–537. doi: 10.1007/BF00682800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpley A. L., Solomon R. A., Fernando A. I., da Roza Davis J. M., Cowen P. J. Dose-related effects of selective 5-HT2 receptor antagonists on slow wave sleep in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1990;101(4):568–569. doi: 10.1007/BF02244239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shur E., Checkley S., Delgado I. Failure of mianserin to affect autonomic function in the pupils of depressed patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1983 Jan;67(1):50–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb00330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin A. B., Unger W., Osborne N. N. Evidence for the presence of serotonergic nerves and receptors in the iris-ciliary body complex of the rabbit. J Neurosci. 1988 Oct;8(10):3713–3721. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-10-03713.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tortella F. C., Echevarria E., Pastel R. H., Cox B., Blackburn T. P. Suppressant effects of selective 5-HT2 antagonists on rapid eye movement sleep in rats. Brain Res. 1989 Apr 24;485(2):294–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoss R. E., Moyer N. J., Ogle K. N. The pupillogram and narcolepsy. A method to measure decreased levels of wakefulness. Neurology. 1969 Oct;19(10):921–928. doi: 10.1212/wnl.19.10.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



