Abstract
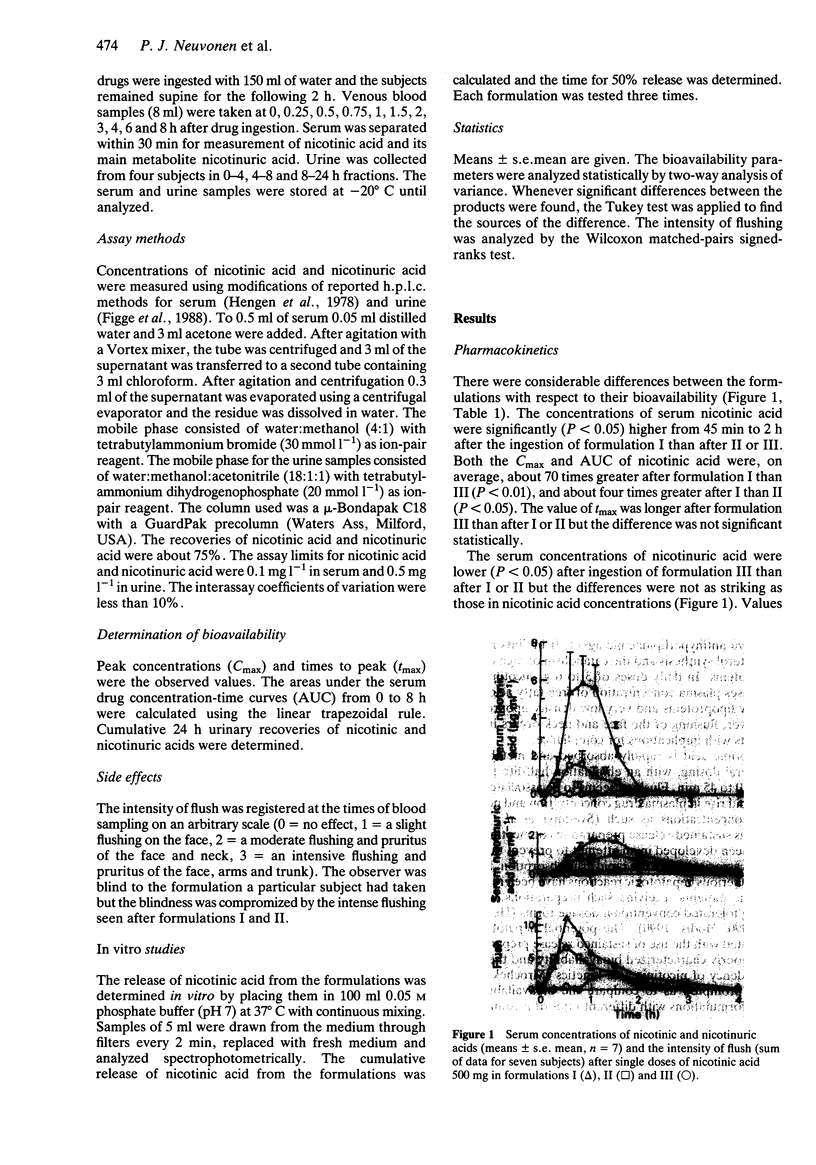
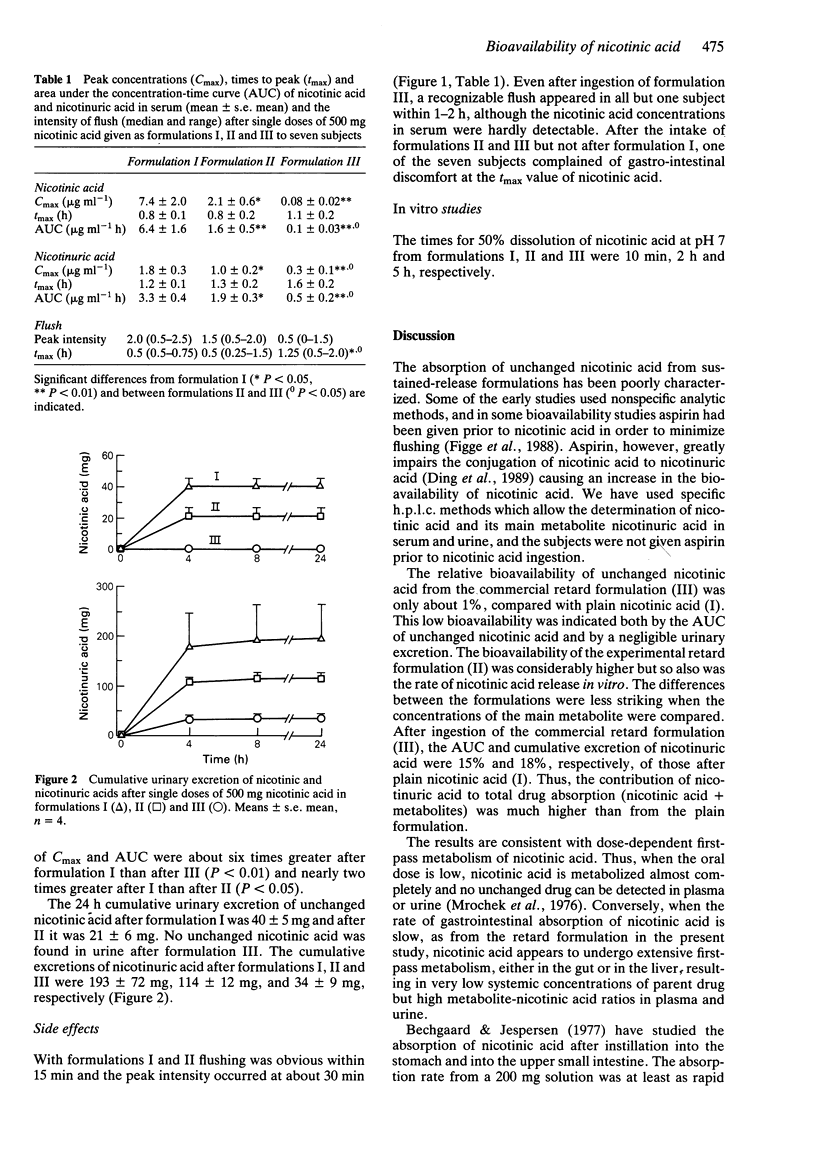
1. The bioavailability of three nicotinic acid formulations was investigated in a randomized cross-over study. 2. Single doses of nicotinic acid (500 mg) were given to seven healthy volunteers. The concentrations of nicotinic acid and its main metabolite nicotinuric acid were measured in serum up to 8 h and in urine up to 24 h. 3. The relative bioavailability of unchanged nicotinic acid from two slow release formulations compared with a rapid-release form was only 1% and 25%, respectively. Relative values of AUC (0.8 h) for nicotinuric acid were 15% and 58%, and relative urinary recoveries were 18% and 59%, respectively. Facial flushing was less when slow release formulations were used. 4. The bioavailability of unchanged nicotinic acid is low and the ratio of nicotinuric acid to nicotinic acid in serum and urine is high when slow release formulations are used.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bechgaard H., Jespersen S. GI absorption of niacin in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1977 Jun;66(6):871–872. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600660635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTENSEN N. A., ACHOR R. W., BERGE K. G., MASON H. L. Nicotinic acid treatment of hypercholesteremia. Comparison of plain and sustained-action preparations and report of two cases of jaundice. JAMA. 1961 Aug 26;177:546–550. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040340010003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson L. A., Orö L., Ostman J. Effect of a single dose of nicotinic acid on plasma lipids in patients with hyperlipoproteinemia. Acta Med Scand. 1968 May;183(5):457–465. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1968.tb10508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayen M. N. Disposition, metabolism and pharmacokinetics of antihyperlipidemic agents in laboratory animals and man. Pharmacol Ther. 1985;29(2):157–204. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(85)90028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding R. W., Kolbe K., Merz B., de Vries J., Weber E., Benet L. Z. Pharmacokinetics of nicotinic acid-salicylic acid interaction. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1989 Dec;46(6):642–647. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1989.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge H. L., Figge J., Souney P. F., Sacks F. M., Shargel L., Janosik J. E., Kaul A. F. Comparison of excretion of nicotinuric acid after ingestion of two controlled release nicotinic acid preparations in man. J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;28(12):1136–1140. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1988.tb05731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengen N., Seiberth V., Hengen M. High-performance liquid-chromatographic determination of free nicotinic acid and its metabolite, nicotinuric acid, in plasma and urine. Clin Chem. 1978 Oct;24(10):1740–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkin Y., Johnson K. C., Segrest J. P. Rechallenge with crystalline niacin after drug-induced hepatitis from sustained-release niacin. JAMA. 1990 Jul 11;264(2):241–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodis H. N. Acute hepatic failure associated with the use of low-dose sustained-release niacin. JAMA. 1990 Jul 11;264(2):181–181. doi: 10.1001/jama.1990.03450020033012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopp R. H., Ginsberg J., Albers J. J., Hoff C., Ogilvie J. T., Warnick G. R., Burrows E., Retzlaff B., Poole M. Contrasting effects of unmodified and time-release forms of niacin on lipoproteins in hyperlipidemic subjects: clues to mechanism of action of niacin. Metabolism. 1985 Jul;34(7):642–650. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse W., Kruse W., Raetzer H., Heuck C. C., Oster P., Schellenberg B., Schlierf G. Nocturnal inhibition of lipolysis in man by nicotinic acid and derivatives. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;16(1):11–15. doi: 10.1007/BF00644960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrochek J. E., Jolley R. L., Young D. S., Turner W. J. Metabolic response of humans to ingestion of nicotinic acid and nicotinamide. Clin Chem. 1976 Nov;22(11):1821–1827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr N., Harthon L., Lundholm L. The relationship between the plasma concentration of free nicotinic acid and some of its pharmacologic effects in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Jul-Aug;10(4):559–570. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969104559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


