Abstract
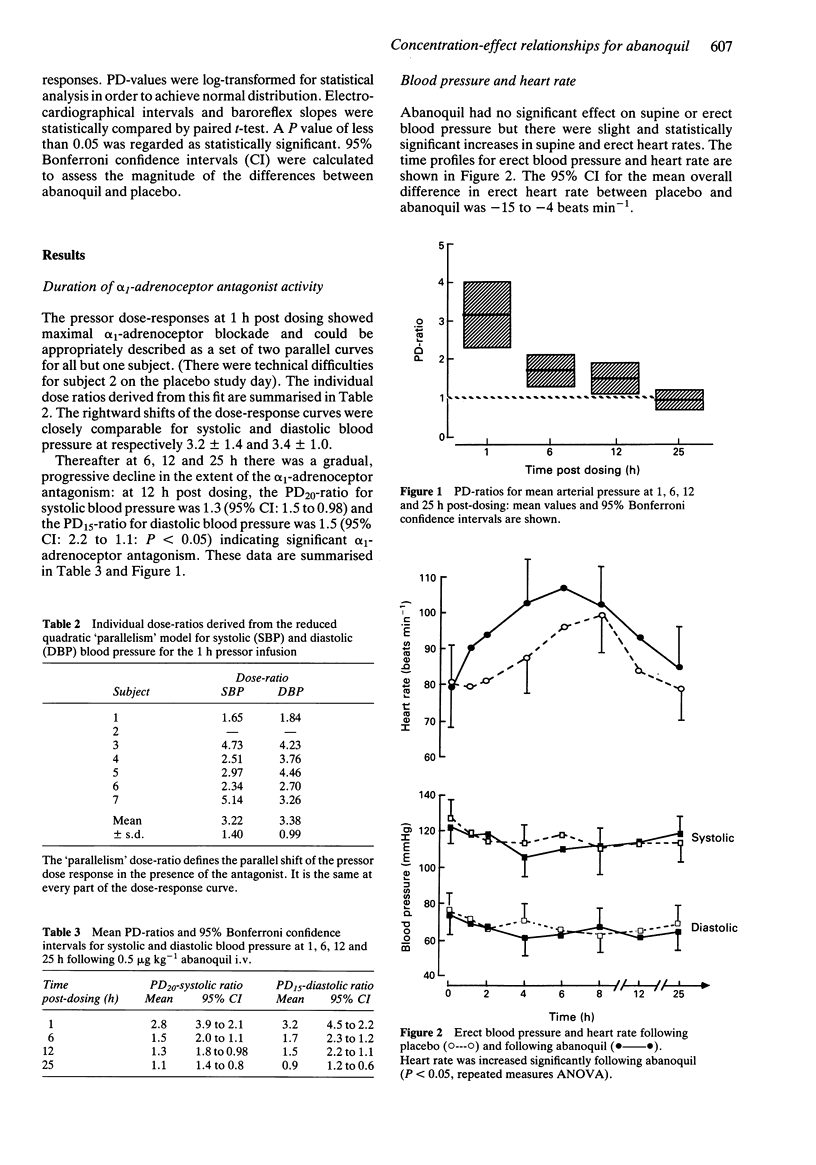
1. This study further examines the quinoline-derivative abanoquil with particular respect to the duration of its alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist activity and its concentration-effect relationship following a single intravenous bolus dose of 0.5 micrograms kg-1 in young, normotensive males. 2. alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonism (as assessed by phenylephrine pressor responses) was detectable for up to 12 h post dosing: at 12 h there was a significant 1.5-fold rightward shift (95% CI: 2.2 to 1.1) of the pressor dose-response curve for diastolic blood pressure. 3. Despite evidence of substantial alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonism abanoquil had no significant effect on blood pressure, supine and erect, but there were small and statistically significant increments in heart rate. 4. The degree of alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonism was related to whole blood concentrations abanoquil: the PD-ratios of phenylephrine pressor responses performed at 1, 6, and 12 h post dosing were significantly correlated with log drug concentrations (r = 0.57 for systolic (P less than 0.05) and r = 0.78 for diastolic blood pressure (P less than 0.005). 5. In conclusion, abanoquil produced significant alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonism which was related to circulating drug concentrations. The absence of other significant cardiovascular effects suggests that abanoquil warrants further clinical study as an antiarrhythmic agent.
Full text
PDF

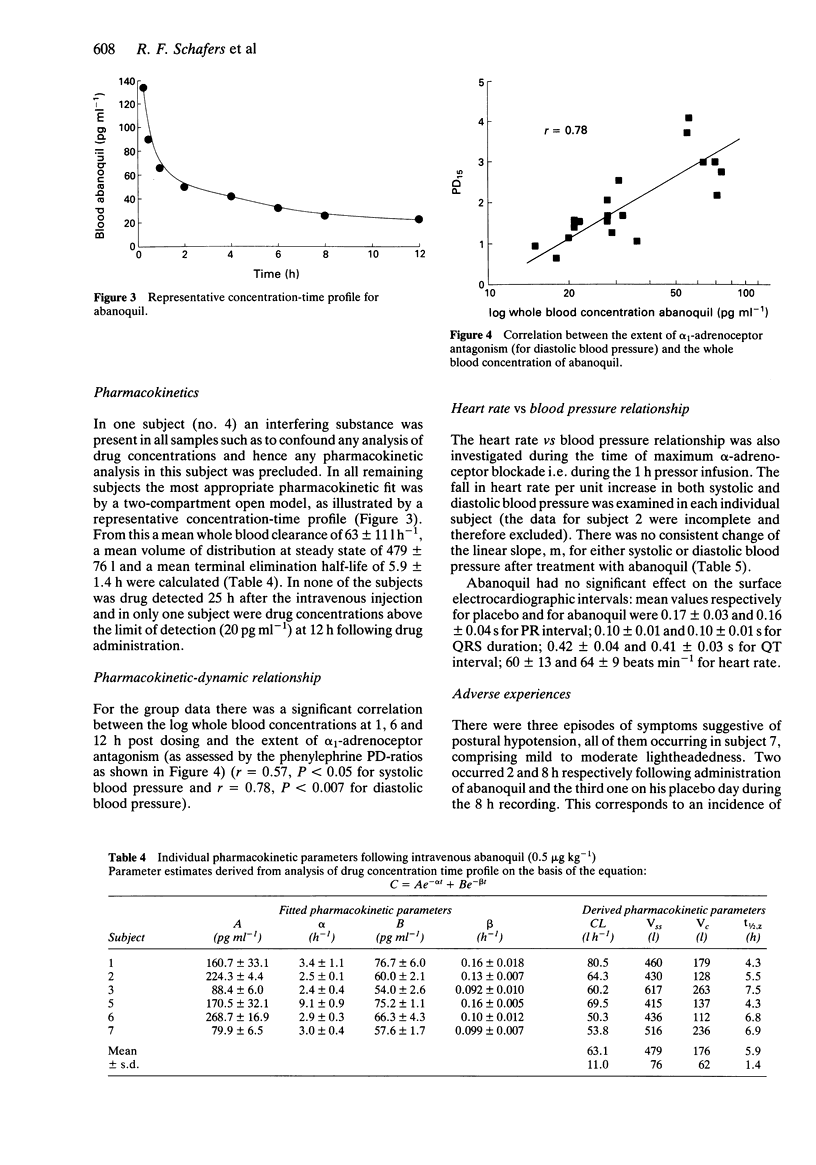


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alabaster V. A., Davey M. J. The alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist profile of doxazosin: preclinical pharmacology. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986;21 (Suppl 1):9S–17S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barin E. S., Wong C. K., Elstob J. E., Davies D. W., Nathan A. W. An acute study of the electrophysiological and haemodynamic effects of intravenous UK-52,046, a novel alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;29(3):359–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman D. N., Hobbs D. C., Twomey T. M., Stevens E. A., Rawlins M. D. Prazosin, pharmacokinetics and concentration effect. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Sep;16(3):177–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00562058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D., Davey M. J., Massingham R. Prazosin, a selective antagonist of post-synaptic alpha-adrenoceptors [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1977 Mar;59(3):514P–515P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott H. L., McLean K., Sumner D. J., Meredith P. A., Reid J. L. Immediate cardiovascular responses to oral prazosin--effects of concurrent beta-blockers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Mar;29(3):303–309. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott H. L., Meredith P. A., Sumner D. J., McLean K., Reid J. L. A pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic assessment of a new alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist, doxazosin (UK33274) in normotensive subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 May;13(5):699–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb01439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott H. L., Vincent J., Meredith P. A., Reid J. L. Relationship between plasma prazosin concentration and alpha-antagonism in humans: comparison of conventional and rate-controlled (Oros) formulations. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1988 May;43(5):582–587. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1988.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jauernig R. A., Moulds R. F., Shaw J. The action of prazosin in human vascular preparations. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1978 Jan;231(1):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khatri I. M., Levinson P., Notargiacomo A., Freis E. D. Initial and long-term effects of prazosin on sympathetic vasopressor responses in essential hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 1985 Apr 1;55(8):1015–1018. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(85)90737-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKaigue J. P., Harron D. W. Effect of UK-52,046, an alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist, on baroreflex function in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;30(4):579–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb03816.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith P. A., Elliott H. L., Kelman A. W., Reid J. L. Application of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modelling for the comparison of quinazoline alpha-adrenoceptor agonists in normotensive volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985 May-Jun;7(3):532–537. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198505000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morley C. A., Dehn T. C., Perrins E. J., Chan S. L., Sutton R. Baroreflex sensitivity measured by the phenylephrine pressor test in patients with carotid sinus and sick sinus syndromes. Cardiovasc Res. 1984 Dec;18(12):752–761. doi: 10.1093/cvr/18.12.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafers R. F., Elliott H. L., Howie C. A., Reid J. L. Studies with abanoquil (UK-52,046) a novel quinoline alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist: I. Effects on blood pressure, heart rate and pressor responsiveness in normotensive subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;32(5):599–604. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1991.tb03958.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner D. J., Elliott H. L., Reid J. L. Analysis of the pressor dose response. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Oct;32(4):450–458. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uprichard A. G., Harron D. W., Wilson R., Shanks R. G. Effects of the myocardial-selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist UK-52046 and atenolol, alone and in combination, on experimental cardiac arrhythmias in dogs. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1241–1254. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J., Elliott H. L., Meredith P. A., Reid J. L. Doxazosin, an alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist: pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationships in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;15(6):719–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J., Elliott H. L., Meredith P. A., Reid J. L. Doxazosin, an alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist: pharmacokinetics and concentration-effect relationships in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;15(6):719–725. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01556.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Bahr C., Lindström B., Seideman P. Alpha-receptor function changes after the first dose of prazosin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1982 Jul;32(1):41–47. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1982.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


