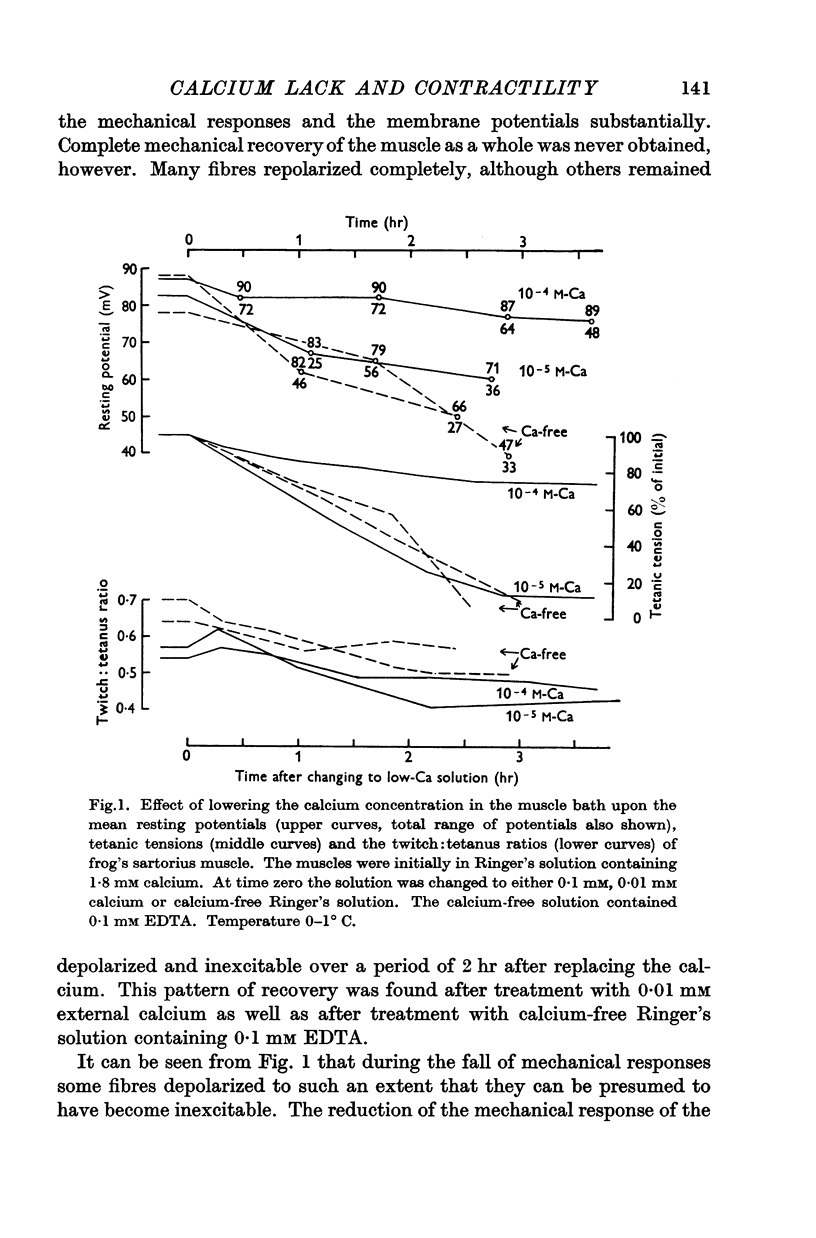
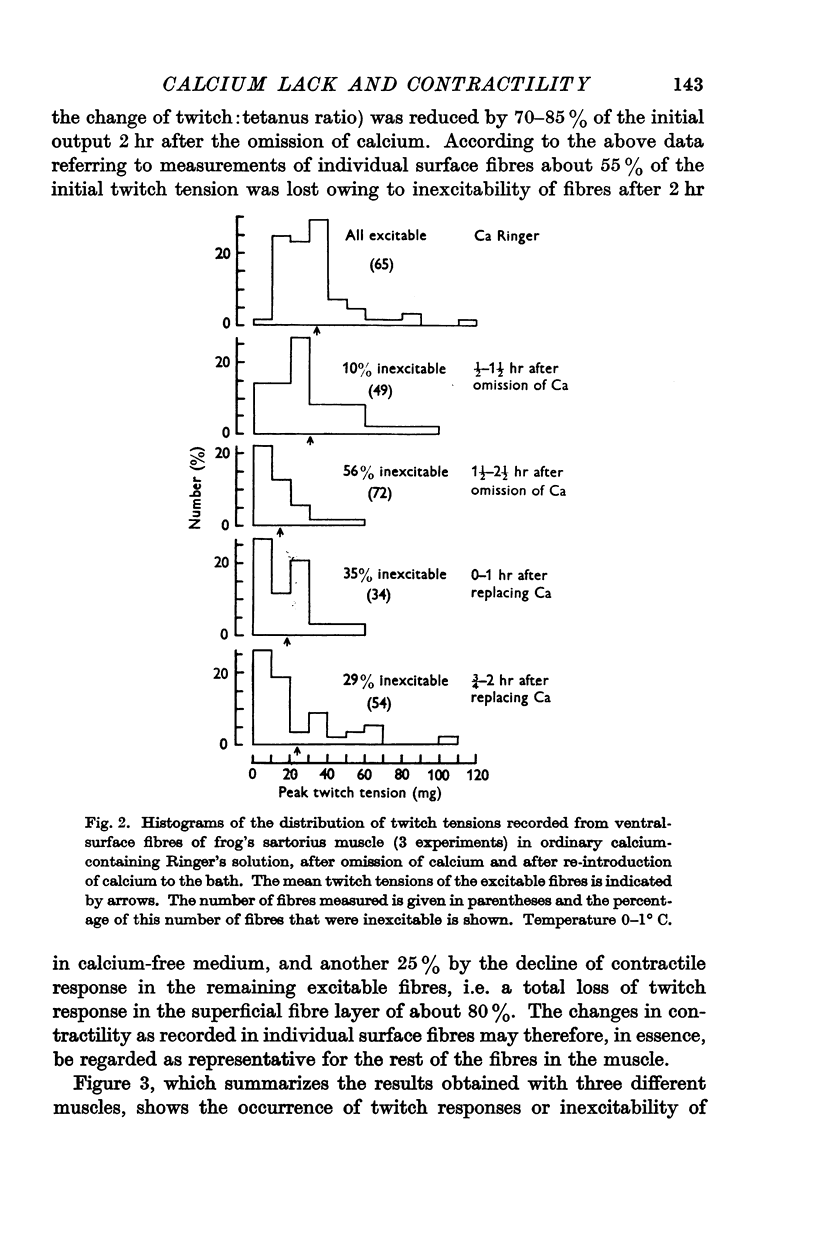
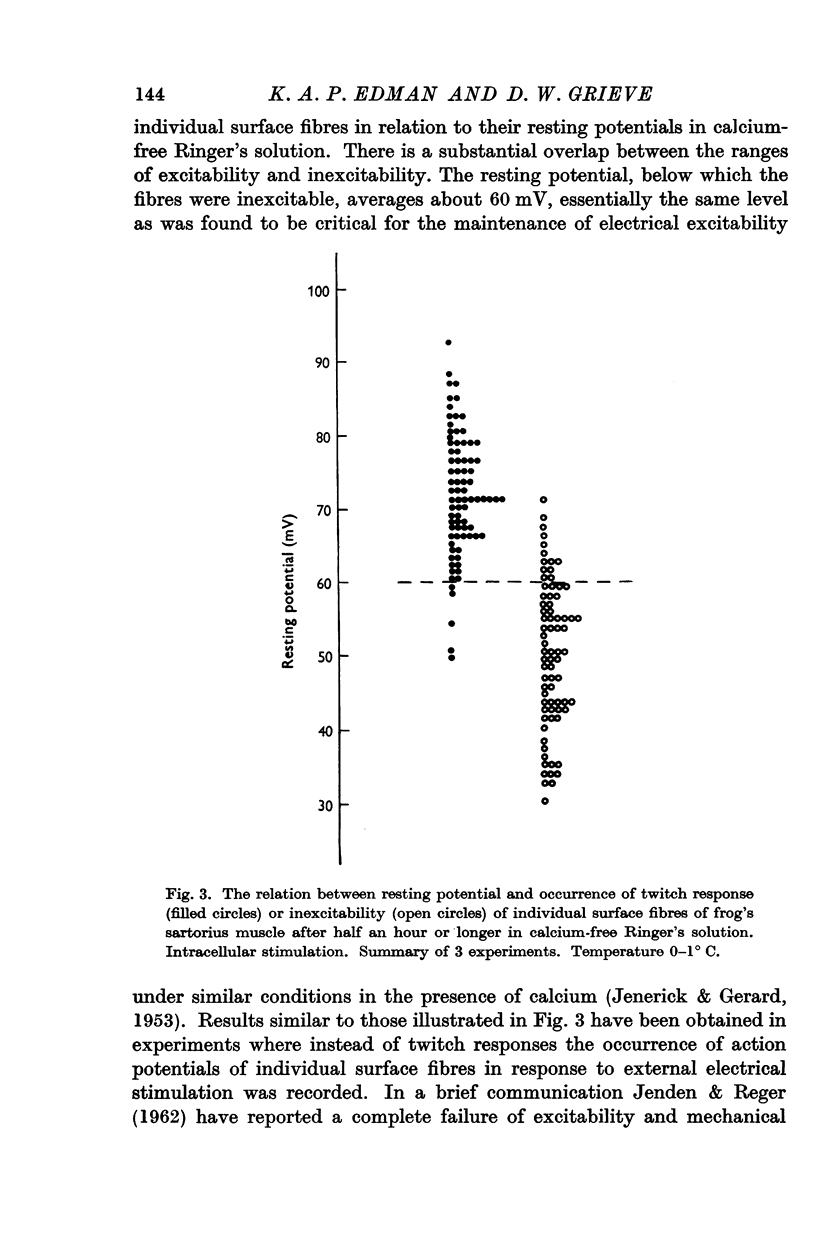
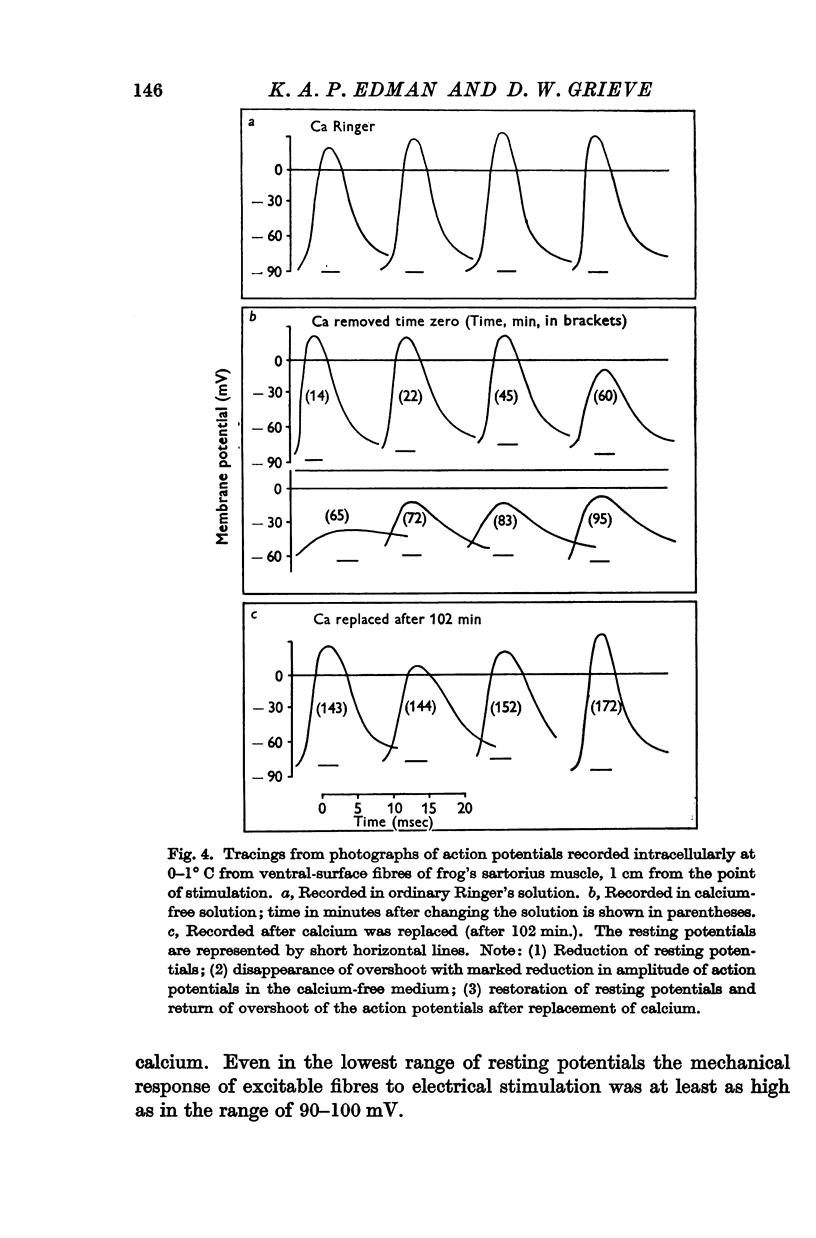
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELMAN W. J., Jr, ADAMS J. Effects of calcium lack on action potential of motor axons of the lobster limb. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Jan 20;42(3):655–664. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.3.655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIANCHI C. P., SHANES A. M. Calcium influx in skeletal muscle at rest, during activity, and during potassium contracture. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Mar 20;42(4):803–815. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle P. J., Conway E. J. Potassium accumulation in muscle and associated changes. J Physiol. 1941 Aug 11;100(1):1–63. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1941.sp003922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS B. A. Some effects of Ca-free choline-Ringer solution on frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1963 Apr;166:75–86. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURBIN R. P., JENKINSON D. H. The calcium dependence of tension development in depolarized smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1961 Jun;157:90–96. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMAN K. A., GRIEVE D. W. The role of calcium and zinc in the electrical and mechanical responses of frog sartorius muscle. Experientia. 1961 Dec 15;17:557–558. doi: 10.1007/BF02156422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMAN K. A., SCHILD H. O. Interaction of acetylcholine, calcium and depolarization in the contraction of smooth muscle. Nature. 1961 Apr 22;190:350–352. doi: 10.1038/190350b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDMAN K. A., SCHILD H. O. The need for calcium in the contractile responses induced by acetylcholine and potassium in the rat uterus. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:424–441. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., MEVES H. The effect of magnesium and calcium on the frog myelinated nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1958 Jul 14;142(2):360–365. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B. The effect of calcium on the myelinated nerve fibre. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):245–260. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK G. B. Effects of changes in extracellular calcium concentration on the potassium-induced contracture of frog's skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1960 Jun;151:518–538. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANK G. B. Utilization of bound calcium in the action of caffeine and certain multivalent cations on skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1962 Sep;163:254–268. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HOROWICZ P. Potassium contractures in single muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Sep;153:386–403. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISHIKO N., SATO M. The effect of calcium ions on electrical properties of striated muscle fibres. Jpn J Physiol. 1957 Mar 15;7(1):51–63. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.7.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENERICK H. P., GERARD R. W. Membrane potential and threshold of single muscle fibers. J Cell Physiol. 1953 Aug;42(1):79–102. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030420106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKETSU K., NODA K. Membrane responses of frog skeletal muscle fibers in calcium-free media. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1962 Jun;59:323–332. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030590312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIEDERGERKE R. The potassium chloride contracture of the heart and its modification by calcium. J Physiol. 1956 Dec 28;134(3):584–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTSON P. A. Calcium and contractility in depolarized smooth muscle. Nature. 1960 Apr 23;186:316–317. doi: 10.1038/186316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDOW A. Contracture responses of skeletal muscle. Am J Phys Med. 1955 Feb;34(1):145–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDOW A. Excitation-contraction coupling in muscular response. Yale J Biol Med. 1952 Dec;25(3):176–201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDOW A., KAHN A. J. The immediate effects of potassium on responses of skeletal muscle. J Cell Physiol. 1952 Aug;40(1):89–114. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030400107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEN-KNUDSEN O. The ineffectiveness of the `window field' in the initiation of muscle contraction. J Physiol. 1954 Aug 27;125(2):396–404. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDMANN S. Effects of calcium ions and local anesthetics on electrical properties of Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1955 Sep 28;129(3):568–582. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINEGRAD S., SHANES A. M. Calcium flux and contractility in guinea pig atria. J Gen Physiol. 1962 Jan;45:371–394. doi: 10.1085/jgp.45.3.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINEGRAD S. The possible role of calcium in excitation-contraction coupling of heart muscle. Circulation. 1961;24:523–529. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.24.2.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


