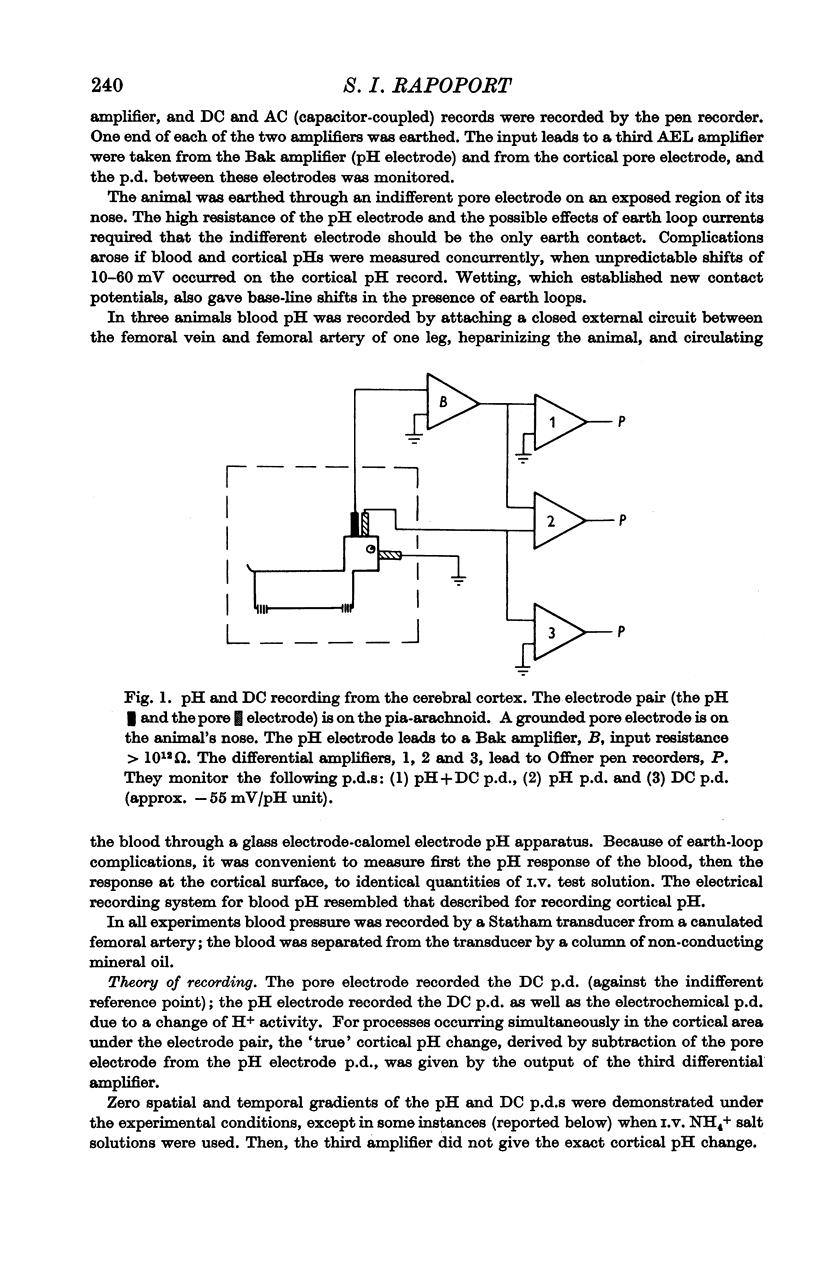
Full text
PDF










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAK A. F. A unity gain cathode follower. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1958 Nov;10(4):745–748. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(58)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALDWIN M., GALINDO A., FARRIER R. Cerebral reaction to sodium fluorescein during profound hypothermia. Neurology. 1962 Mar;12:193–201. doi: 10.1212/wnl.12.3.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARLOW C. F., DOMEK N. S., GOLDBERG M. A., ROTH L. J. Extracellular brain space measured by S35 sulfate. Arch Neurol. 1961 Jul;5:102–110. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1961.00450130104012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODIE B. B., KURZ H., SCHANKER L. S. The importance of dissociaton constant and lipid-solubility in influencing the passage of drugs into the cerebrospinal fluid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Sep;130:20–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLEMEDSON C. J., HARTELIUS H., HOLMBERG G. The influence of carbon dioxide inhalation on the cerebral vascular permeability to trypan blue (the blood-brain barrier). Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1958;42(2):137–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1958.tb03178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDSTROM R. An explanation of the blood-brain barrier phenomenon. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand. 1958;33(4):403–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERNSTER L., HERLIN L. The fate of intracisternally injected tracer phosphate in the rabbit, normally and as influenced by sulphydryl reagents. A kinetic approach to the mechanism of the blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem. 1961 Mar;6:267–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN R. A. Factors influencing the exchange of sodium between plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Invest. 1959 Oct;38:1698–1708. doi: 10.1172/JCI103948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIACOBINI E. Localization of carbonic anhydrase in the nervous system. Science. 1961 Nov 10;134(3489):1524–1525. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3489.1524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY W. D., MAREN T. H., SISSON G. M., SMITH F. H. Carbonic anhydrase inhibition. VII. Carbonic anhydrase inhibition and anticonvulsant effect. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Oct;121(2):160–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAZER F. M., CLEMENTE C. D. Developing blood brain barrier to trypan blue. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Apr;94(4):758–760. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-23077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMDAHL M. H., NAHAS G. G., HASSAM D., VEROSKY M. Acidbase changes in the cerebrospinal fluid following rapid changes in the bicarbonate/carbonic acid ratio in the blood. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1961 Jun 17;92:520–527. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1961.tb45002.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENDING M., SLOBODY L. B., MESTERN J. Effect of hyperoxia, hypercapnia, and hypoxia on blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Am J Physiol. 1961 May;200:959–962. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.5.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSHALL W. H. Spreading cortical depression of Leao. Physiol Rev. 1959 Apr;39(2):239–279. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1959.39.2.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER J. S., GOTOH F. Interaction of cerebral hemodynamics and metabolism. Neurology. 1961 Apr;11(4):46–65. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.4_part_2.46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLICHAP J. G., WOODBURY D. M., GOODMAN L. S. Mechanism of the anticonvulsant action of acetazoleamide, a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1955 Nov;115(3):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R. Passage of molecules through capillary wals. Physiol Rev. 1953 Jul;33(3):387–423. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1953.33.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBIN E. D., WHALEY R. D., CRUMP C. H., TRAVIS D. M., BICKELMANN A. G. Acid-base relations between spinal fluid and arterial blood with special reference to control of ventilation. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Nov;13(3):385–392. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.13.3.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHIPLEY R. A., BAKER N., INCEFY G. E., CLARK R. E. C14 studies in carbohydrate metabolism. IV. Characteristics of bicarbonate pool system in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Jul;197(1):41–46. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWANSON A. G., STAVNEY L. S., PLUM F. Effects of blood pH and carbon dioxide on cerebral electrical activity. Neurology. 1958 Oct;8(10):787–792. doi: 10.1212/wnl.8.10.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWEET W. H., SELVERSTONE B., SOLOWAY S., STETTEN D., Jr Studies of formation, flow and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. II. Studies with heavy water in the normal man. Surg Forum. 1950:376–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSCHIRGI R. D., TAYLOR J. L. Slowly changing bioelectric potentials associated with the blood-brain barrier. Am J Physiol. 1958 Oct;195(1):7–22. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1958.195.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER C., SODERBERG U. Medullary chemosensitive receptors. J Physiol. 1952 Dec;118(4):545–554. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINTERSTEIN H., GOKHAN N. Ammoniumchlorid-Acidose und Reactionstheorie der Atmungsregulation. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1953 Mar;93(2):212–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


