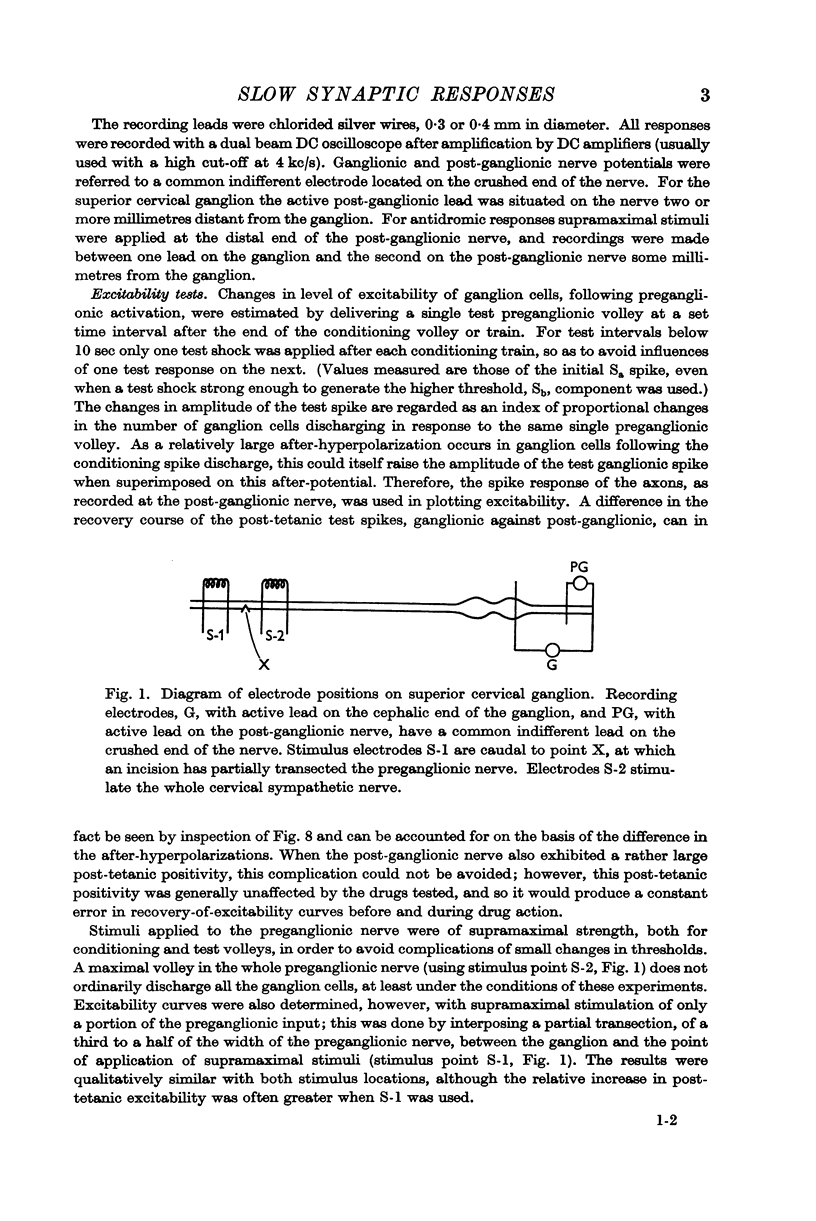
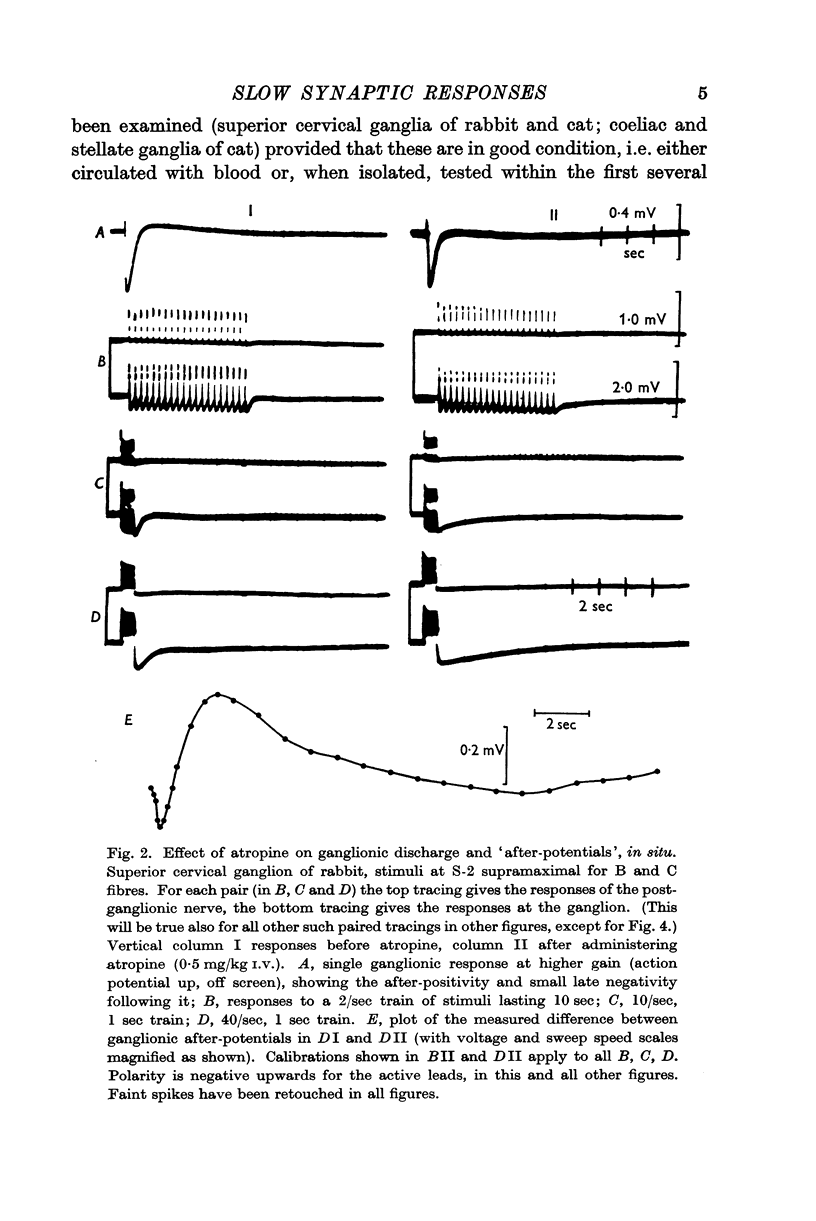
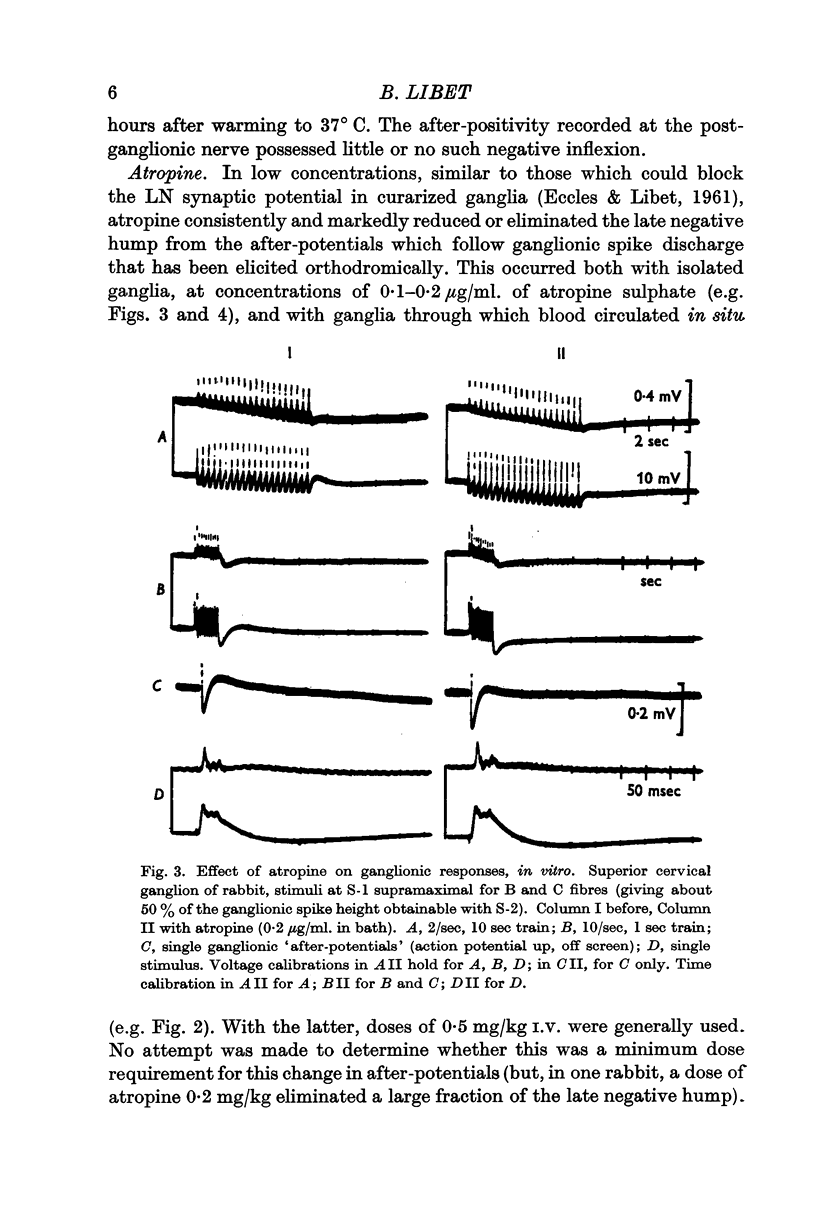
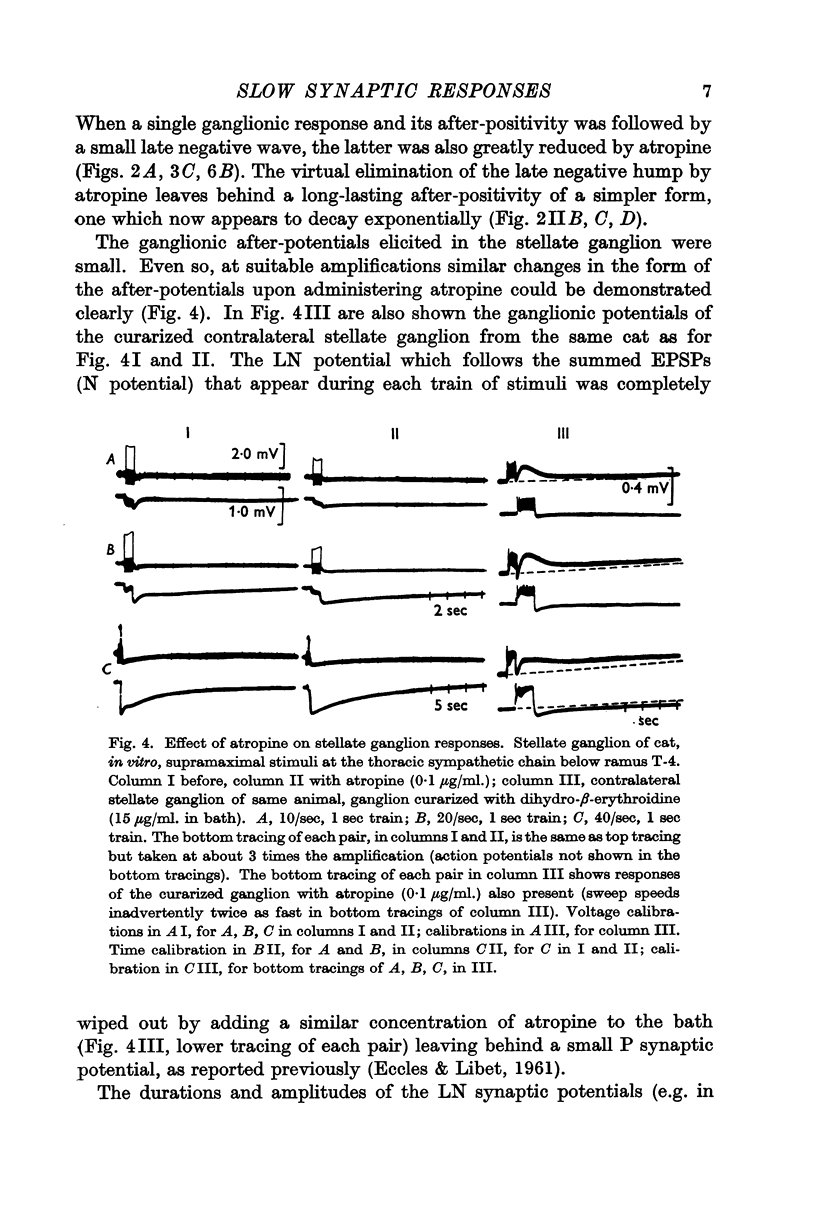
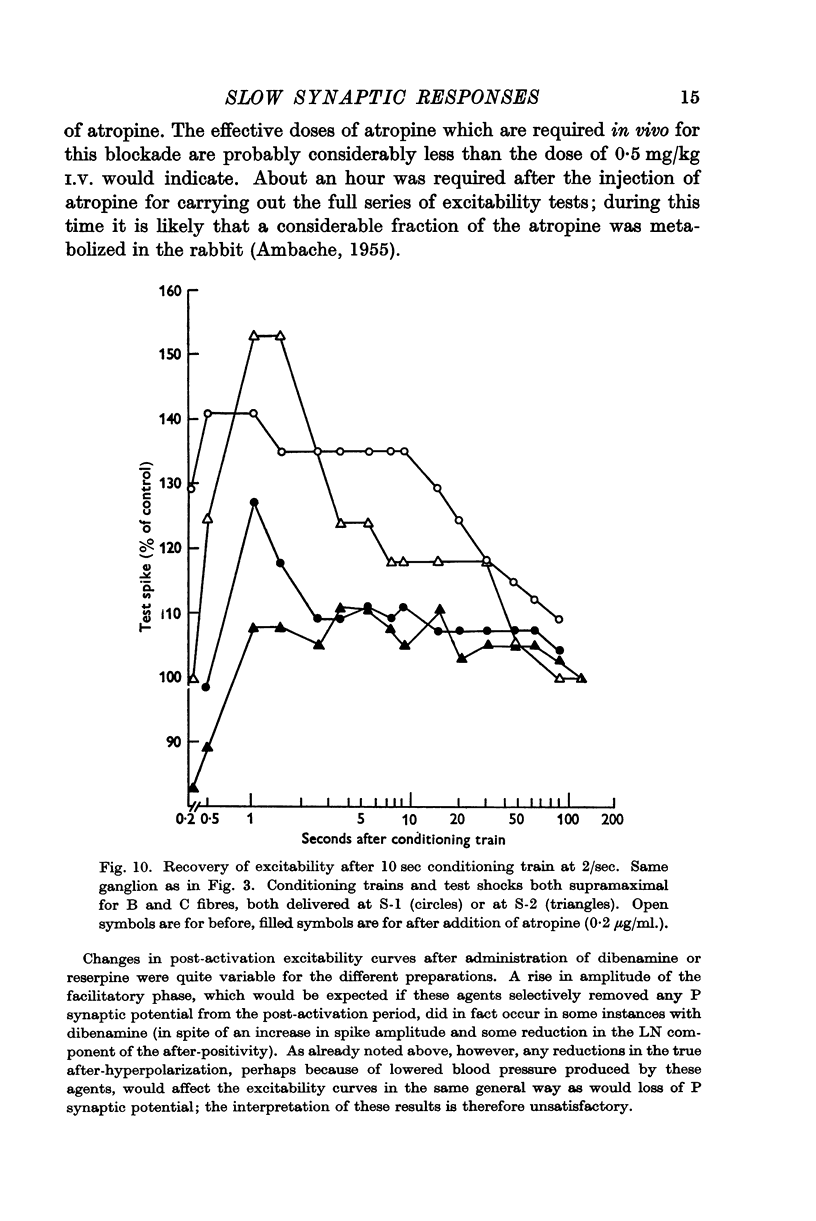
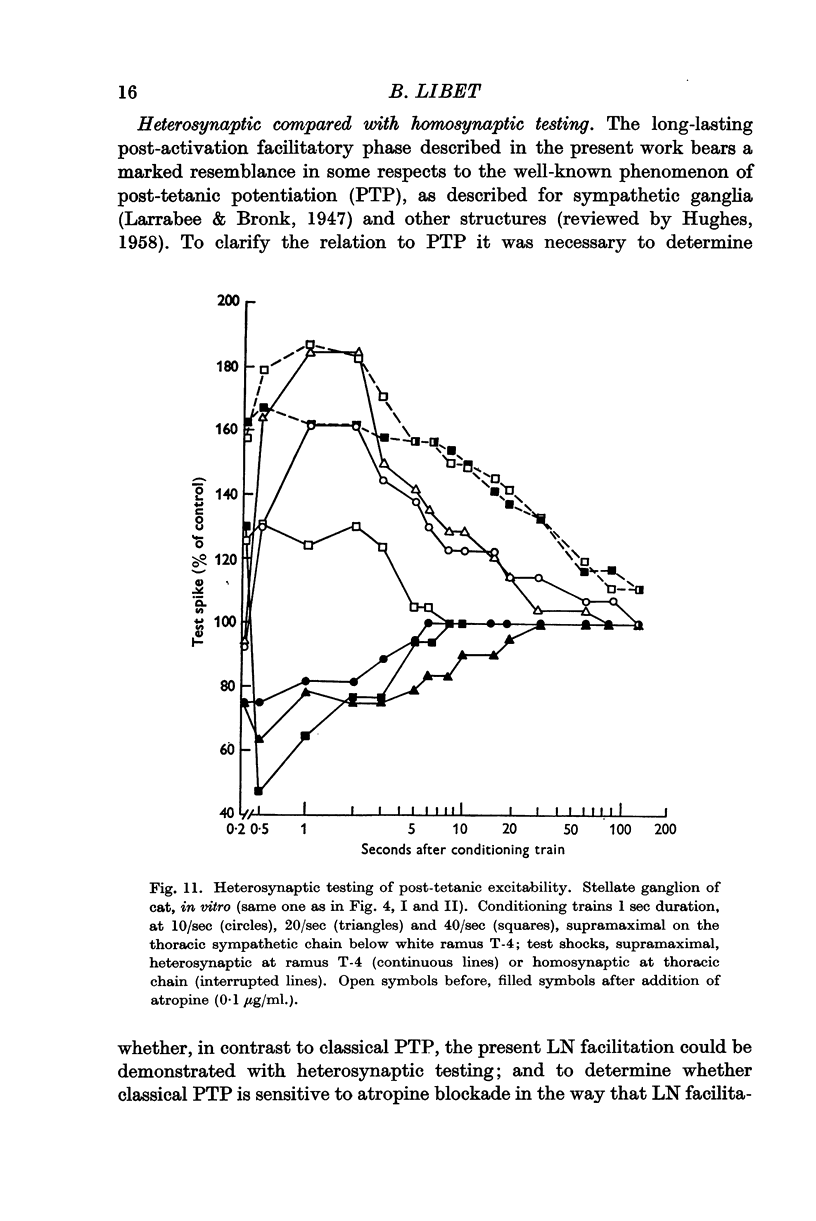
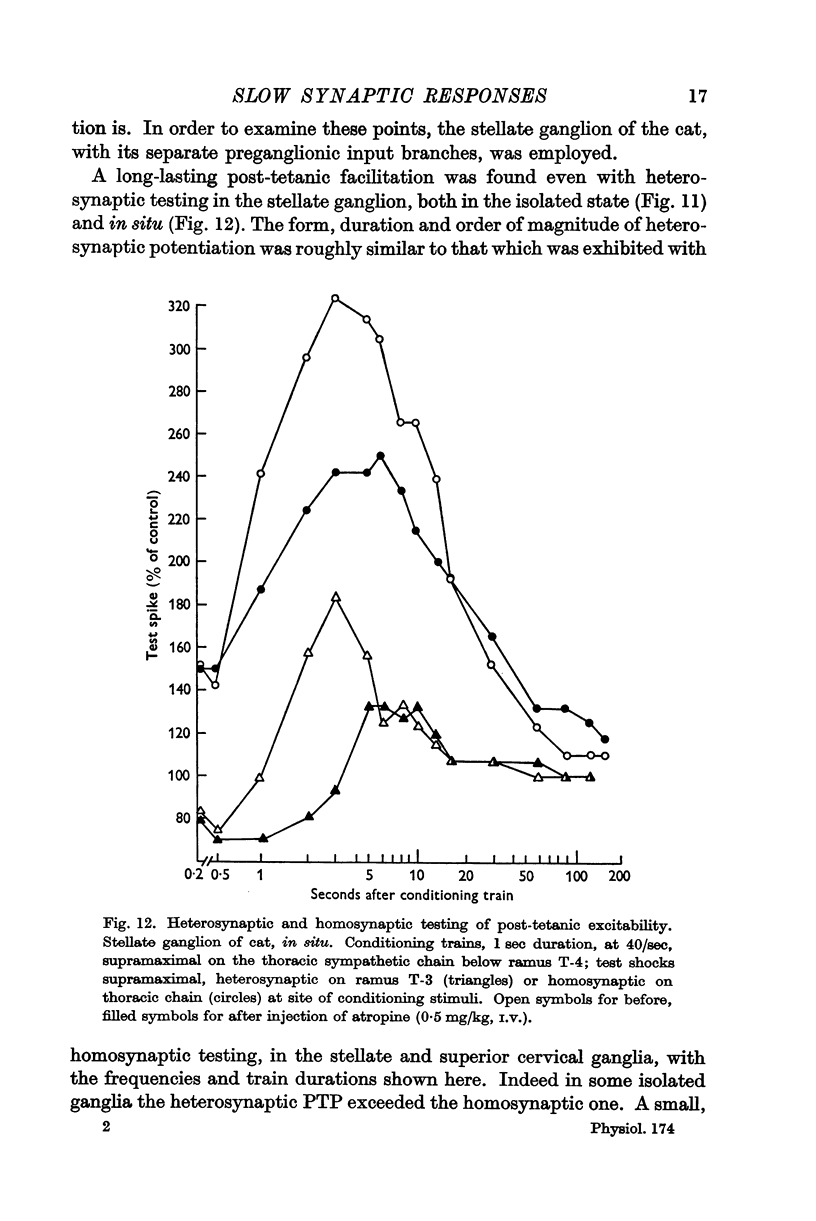
Full text
PDF


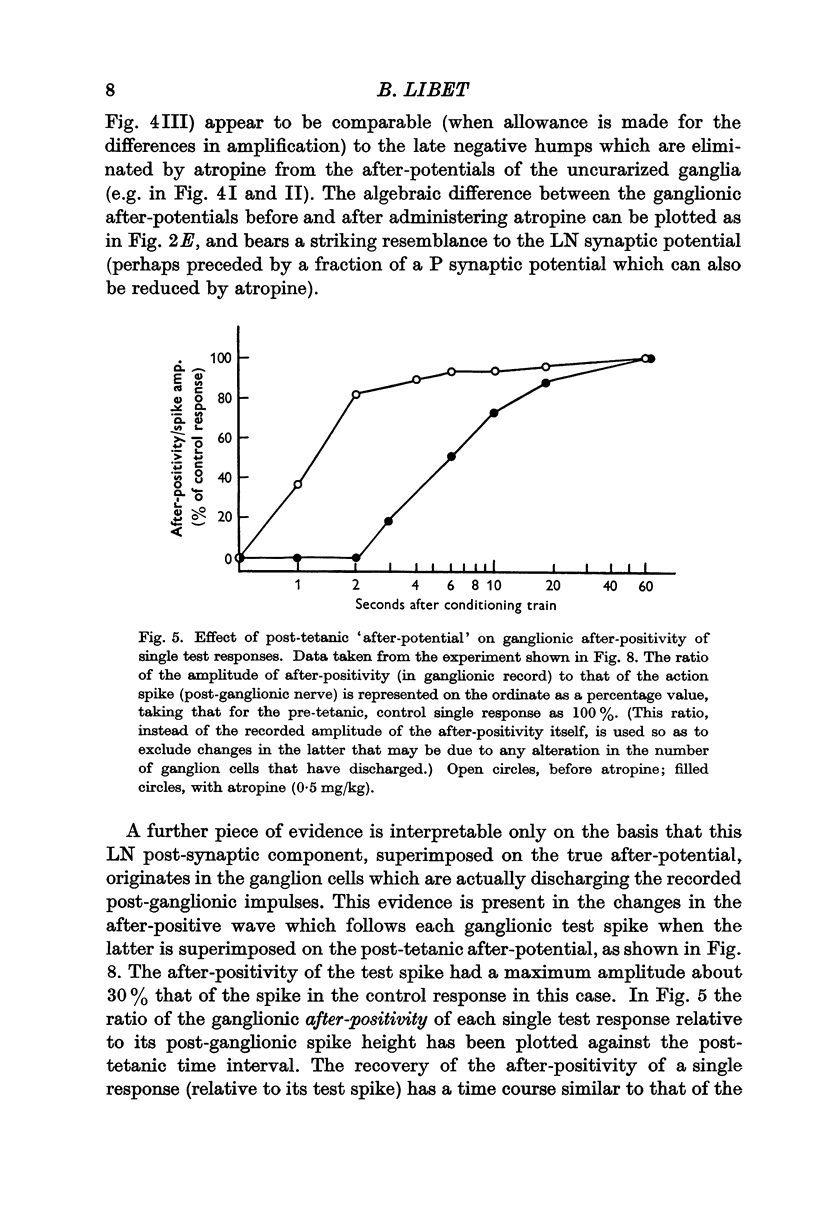


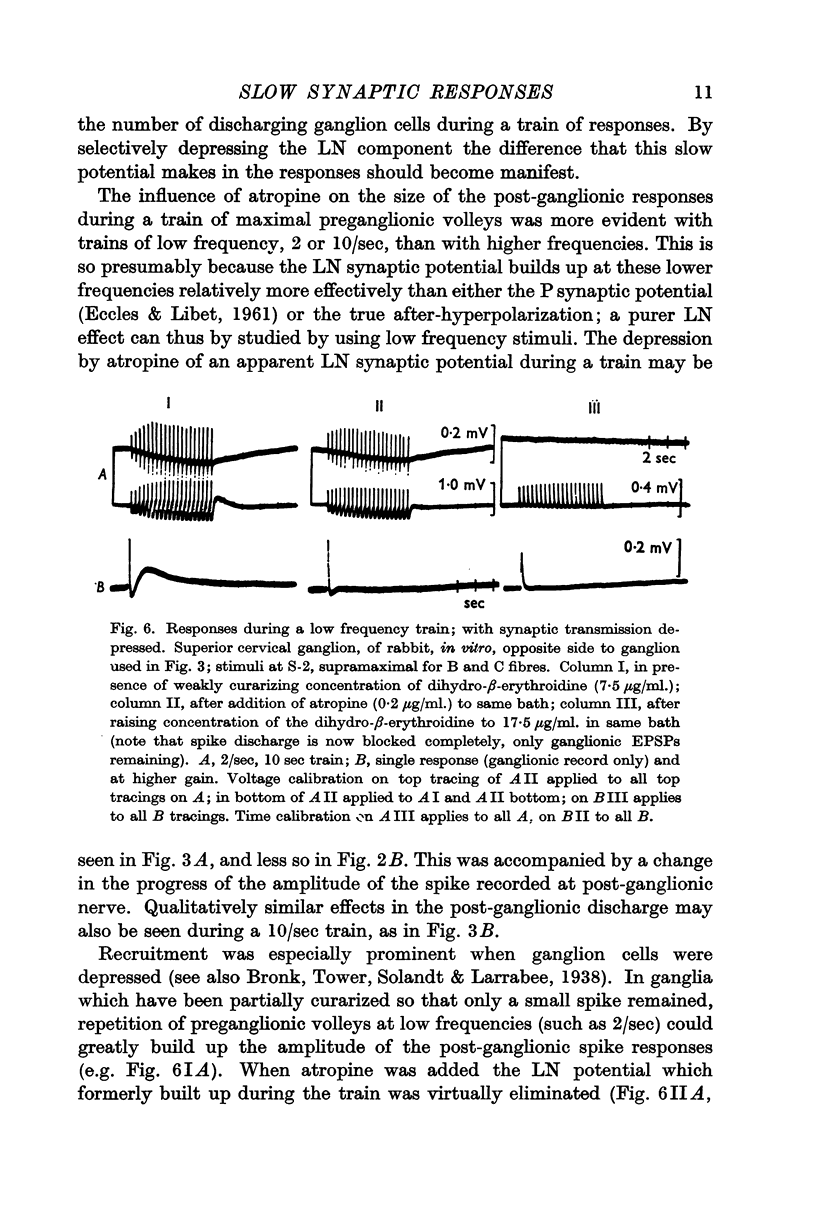

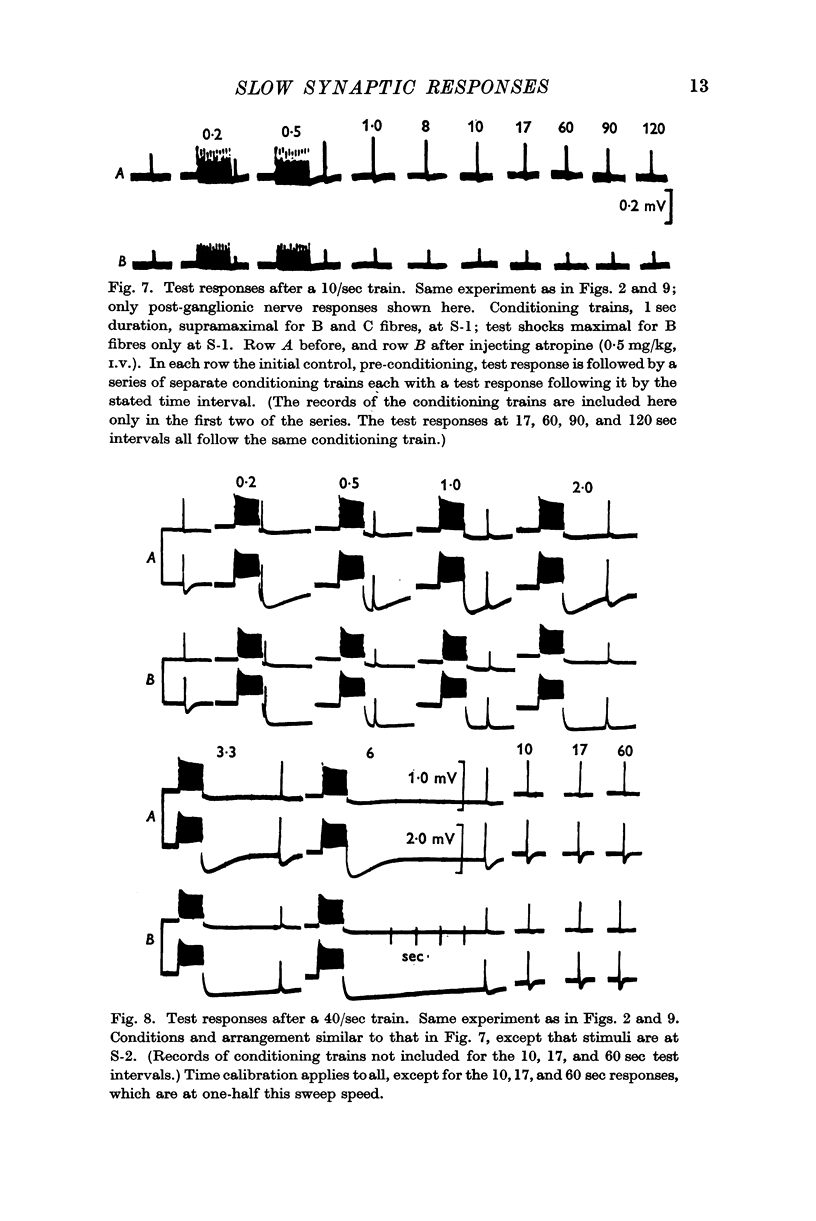
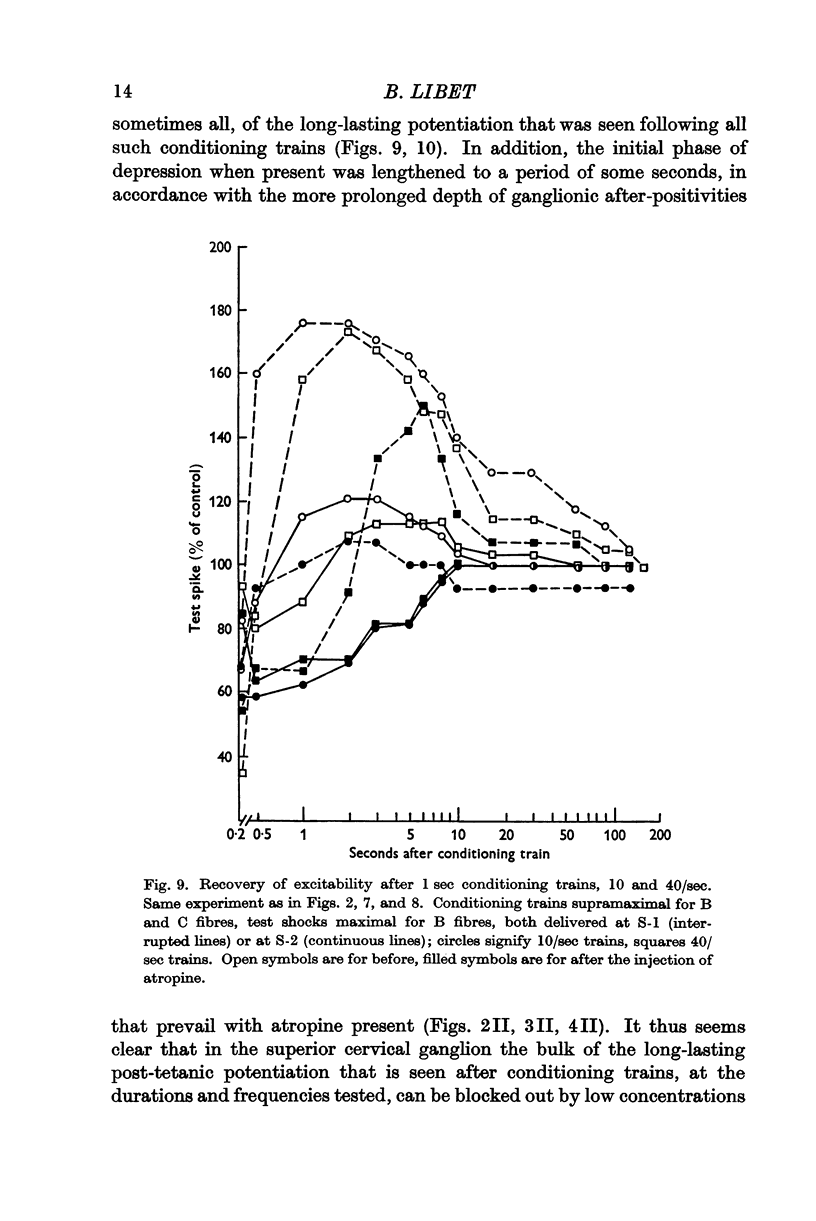








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COSTA E., REVZIN A. M., KUNTZMAN R., SPECTOR S., BRODIE B. B. Role for ganglionic norepinephrine in sympathetic synaptic transmission. Science. 1961 Jun 9;133(3467):1822–1823. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3467.1822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., RITCHIE J. M. A technique for recording functional activity in specific groups of medullated and non-medullated fibres in whole nerve trunks. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):19–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M. Intracellular potentials recorded from a mammalian sympathetic ganglion. J Physiol. 1955 Dec 29;130(3):572–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. M., LIBET B. Origin and blockade of the synaptic responses of curarized sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1961 Aug;157:484–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES R. Responses of isolated curarized sympathetic ganglia. J Physiol. 1952 Jun;117(2):196–217. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C. Facilitation and inhibition in the superior cervical ganglion. J Physiol. 1935 Oct 26;85(2):207–238.3. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1935.sp003314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles J. C. Slow potential waves in the superior cervical ganglion. J Physiol. 1935 Dec 16;85(4):464–501. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1935.sp003333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles R. M. Orthodromic activation of single ganglion cells. J Physiol. 1963 Mar;165(3):387–391. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B. Impulse frequency in sympathetic vasomotor fibres correlated to the release and elimination of the transmitter. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952;25(1):49–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1952.tb00858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENGARD P., STRAUB R. W. Metabolic studies on the hyperpolarization following activity in mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1962 May;161:414–423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES J. R. Post-tetanic potentiation. Physiol Rev. 1958 Jan;38(1):91–113. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.1.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOB C., LUNDBERG A. On the significance of post- and pre-synaptic events for facilitation and inhibition in the sympathetic ganglion of the cat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Mar 31;28(1):14–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALSER M. H., FRYE C. W., GORDON A. S. Postural hypotension induced by atropine sulfate. Circulation. 1954 Sep;10(3):413–422. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.10.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAPORTE Y., LORENTE de NO R. Potential changes evoked in a curarized sympathetic ganglion by presynaptic volleys of impulses. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1950 Jul;35(Suppl 2):61–106. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030350505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARRABEE M. G., HOLADAY D. A. Depression of transmission through sympathetic ganglia during general anesthesia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Aug;105(4):400–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. C. Influence of asphyxia upon the responses of spinal motoneurons. J Gen Physiol. 1953 May;36(5):673–702. doi: 10.1085/jgp.36.5.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. C. Post-tetanic potentiation of response in monosynaptic reflex pathways of the spinal cord. J Gen Physiol. 1949 Nov;33(2):147–170. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER R. D., KALSER M. H., FRYE C. W., GORDON A. S. Measurement of atropine-induced vascular pooling. Circulation. 1954 Sep;10(3):423–429. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.10.3.423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHOLL E., VOGT M. The action of reserpine on the peripheral sympathetic system. J Physiol. 1958 Apr 3;141(1):132–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISHI S., KOKETSU K. Electrical properties and activities of single sympathetic neurons in frogs. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1960 Feb;55:15–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030550104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REINERT H. Role and origin of noradrenaline in the superior cervical ganglion. J Physiol. 1963 Jun;167:18–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANGHVI I., MURAYAMA S., SMITH C. M., UNNA K. R. ACTION OF MUSCARINE ON THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANGLION OF THE CAT. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Nov;142:192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKESHIGE C., VOLLE R. L. Bimodal response of sympathetic ganglia to acetylcholine following eserine or repetitive preganglionic stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962 Oct;138:66–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON V. J. Post-tetanic potentiation of polysynaptic reflexes of the spinal cord. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Nov 20;39(2):197–206. doi: 10.1085/jgp.39.2.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


