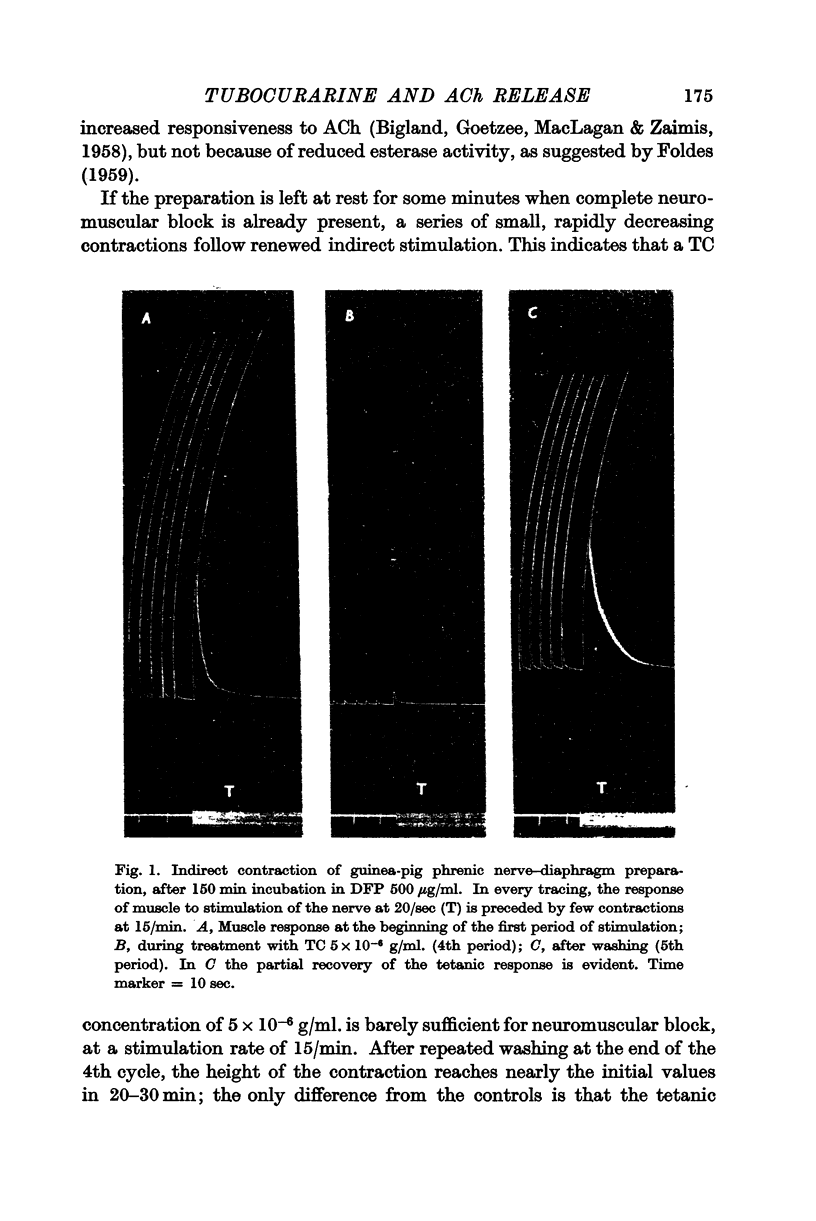
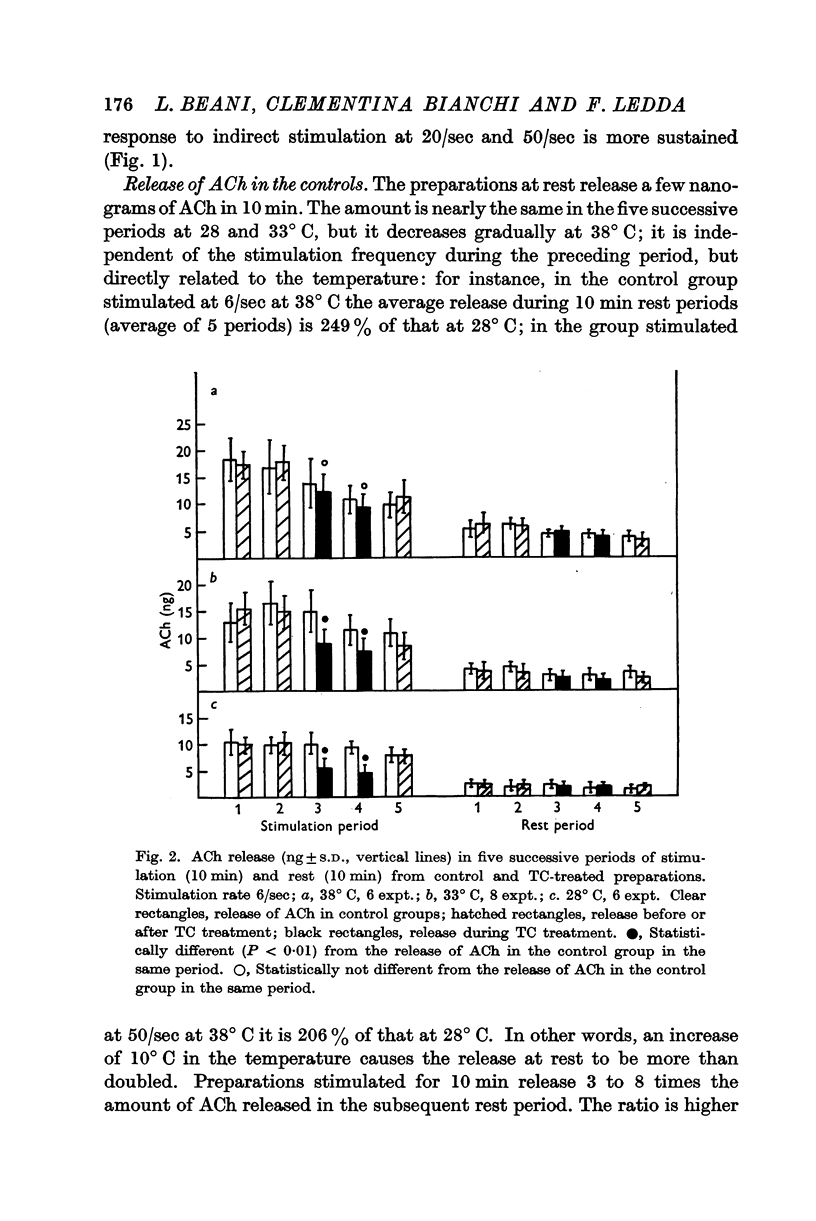
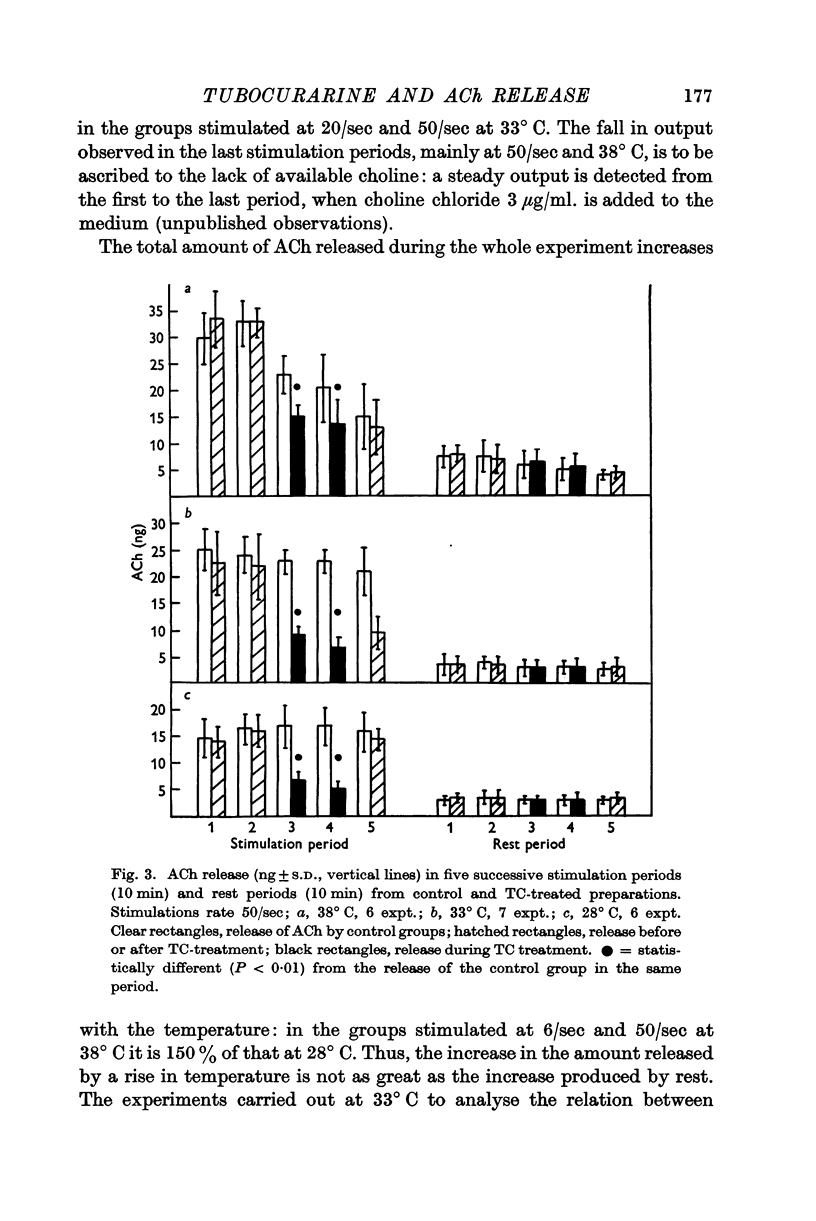
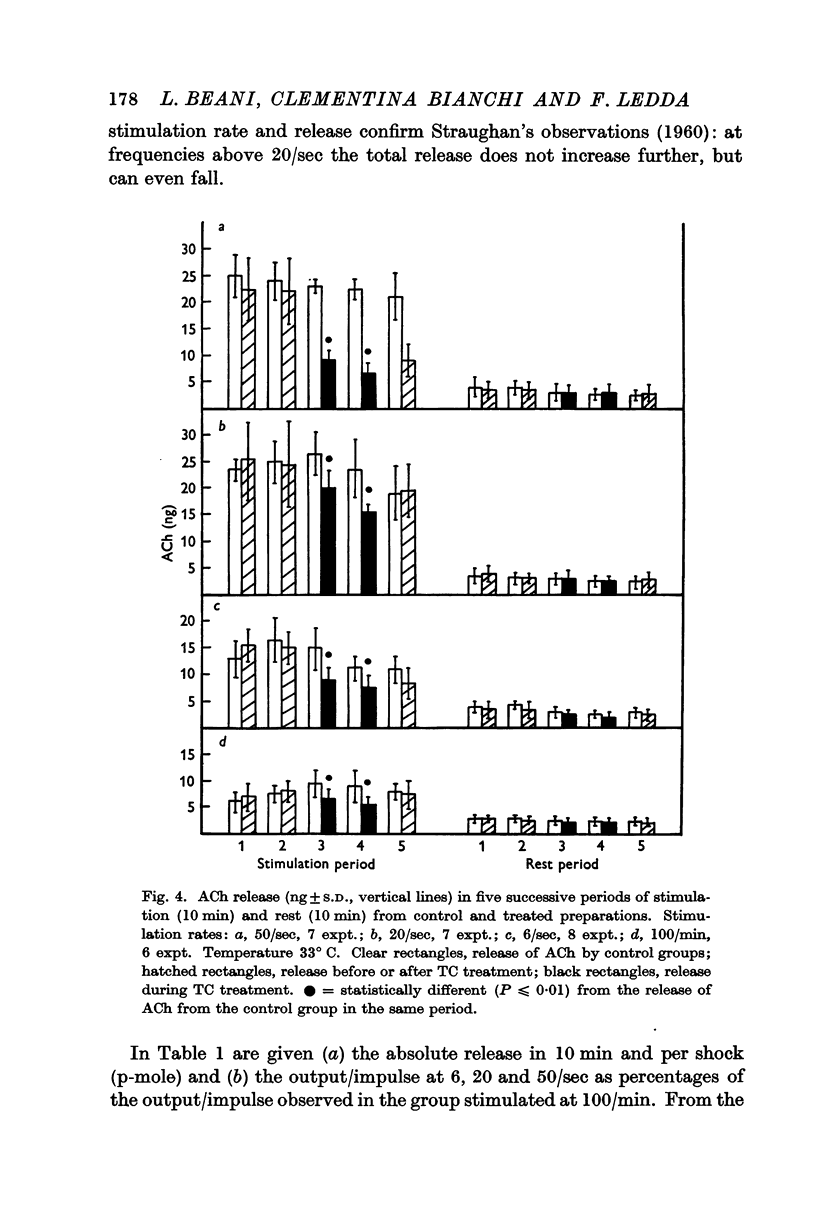
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEANI L., BIANCHI C., LEDDA F. [The relation between body weight and total acetylcholine in the diaphragm muscle of the guinea pig]. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1962 Apr 15;38:320–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEANI L., BIANCHI C. [The interference of D-tubocurarine with acetylcholine release from the guinea pig phrenic nerve-diaphragm preparation]. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1961 Jun 15;37:504–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENTLEY G. A., SHAW F. H. The separation and assay of acethylcholine in tissue extracts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Oct;106(2):193–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIGLAND B., GOETZEE B., MACLAGAN J., ZAIMIS E. The effect of lowered muscle temperature on the action of neuromuscular blocking drugs. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):425–434. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKS V. B., THIES R. E. Reduction of quantum content during neuromuscular transmission. J Physiol. 1962 Jul;162:298–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN J. A., POSTHUMUS C. H. The mechanism of action of anti-cholinesterases. III. The action of anti-cholinesterases on the phrenic nerve-diaphragm preparation of the rat. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Neerl. 1957 Oct;5(4):385–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Biophysical aspects of neuro-muscular transmission. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1956;6:121–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUGLAS W. W., GRAY J. A. B. The excitant action of acetylcholine and other substances on cutaneous sensory pathways and its prevention by hexamethonium and D-tubocurarine. J Physiol. 1953 Jan;119(1):118–128. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale H. H., Feldberg W., Vogt M. Release of acetylcholine at voluntary motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1936 May 4;86(4):353–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1936.sp003371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLDES F. F. Factors which alter the effects of muscle relaxants. Anesthesiology. 1959 Jul-Aug;20(4):464–504. doi: 10.1097/00000542-195907000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYES A. H., Jr, RIKER W. F., Jr ACETYLCHOLINE RELEASE AT THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Nov;142:200–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Presynaptic failure of neuromuscular propagation in rats. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:1–22. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MITCHELL J. F. Diffusion of acetylcholine in agar gels and in the isolated rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1960 Oct;153:562–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MITCHELL J. F. The release of acetylcholine in the isolated rat diaphragm. J Physiol. 1961 Feb;155:246–262. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDGREN S., LILJESTRAND G., ZOTTERMAN Y. Chemical transmission in taste fibre endings. Acta Physiol Scand. 1954;30(2-3):105–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1954.tb01079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. F., Silver A. The spontaneous release of acetylcholine from the denervated hemidiaphragm of the rat. J Physiol. 1963 Jan;165(1):117–129. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAESS K. The specificity of diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP). Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1956;12(2):154–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1956.tb01371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RITCHIE J. M., ARMETT C. J. The role of acetylcholine in conduction in mammalian nonmyelinated nerve fibers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Feb;139:201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANES A. M. Electrochemical aspects of physiological and pharmacological action in excitable cells. I. The resting cell and its alteration by extrinsic factors. Pharmacol Rev. 1958 Mar;10(1):59–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THESLEFF S. Motor end-plate 'desensitization' by repetitive nerve stimuli. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:659–664. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAN DER MEER C., MEETER E. The mechanism of action of anticholinesterases. II. The effect of diisopropylfluorophosphonate (DPF) in the isolated rat phrenic nervediaphragm preparation. B. Reversible effects. Acta Physiol Pharmacol Neerl. 1956 Mar;4(4):472–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]