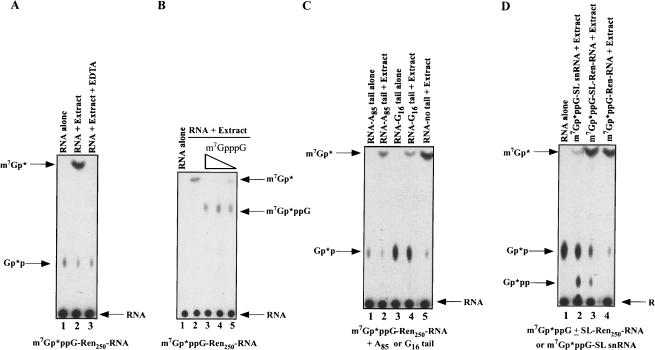
FIGURE 1.
RNA decay and decapping activity in Ascaris embryo extracts illustrates contribution of 3′ to 5′ exoribonuclease and scavenger activities. (A) m7Gp*ppG 32P-cap-labeled RNA undergoes decay and decapping in Ascaris extracts producing m7Gp*. A 250 nucleotide cap-labeled RNA substrate (the * follows the 32P-labeled phosphate) derived from the 5′ end of pRLnull was incubated in Ascaris embryo extract for 50 min at 30°C, aliquots of the reactions were then applied to PEI-cellulose thin layer chromatography (TLC) plates, the plates developed in 0.45 M ammonium sulfate, and labeled substrate and products detected by autoradiography. Comigration of appropriate markers followed by UV shadowing, enzymatic conversion assays, and inhibition studies were used to identify and confirm reaction products. Note that the Gp*p spot is derived from the cap-labeling reaction and is not present in gel-purified RNA substrates that were used in other experiments with similar results. (B) Inhibition of scavenger activity during RNA decay leads to accumulation of m7GpppG in Ascaris extracts. Reactions were carried out with or without cap analogs. Concentrations of competitive cap inhibitors are 200, 50, and 20 μM. (C) Addition of a 3′ poly(A)-tail or G16 to the RNA substrate leads to reduction in m7Gp* product. (D) Inherent SL snRNA structure and SL RNP formation in Ascaris extracts leads to a reduction in decay and scavenger product. Note that the SL snRNA undergoes reduced decay and cap hydrolysis (cf. lane 2 and lanes 3,4), while an mRNA with only the m7Gp*ppG-capped 22 nucleotide SL sequence added to its 5′ end is degraded and hydrolyzed normally (cf. lanes 3 and 4). RNA alone = m7Gp*ppG-SL snRNA. Reactions in (B)–(D) were carried out and analyzed as described in (A).