Abstract
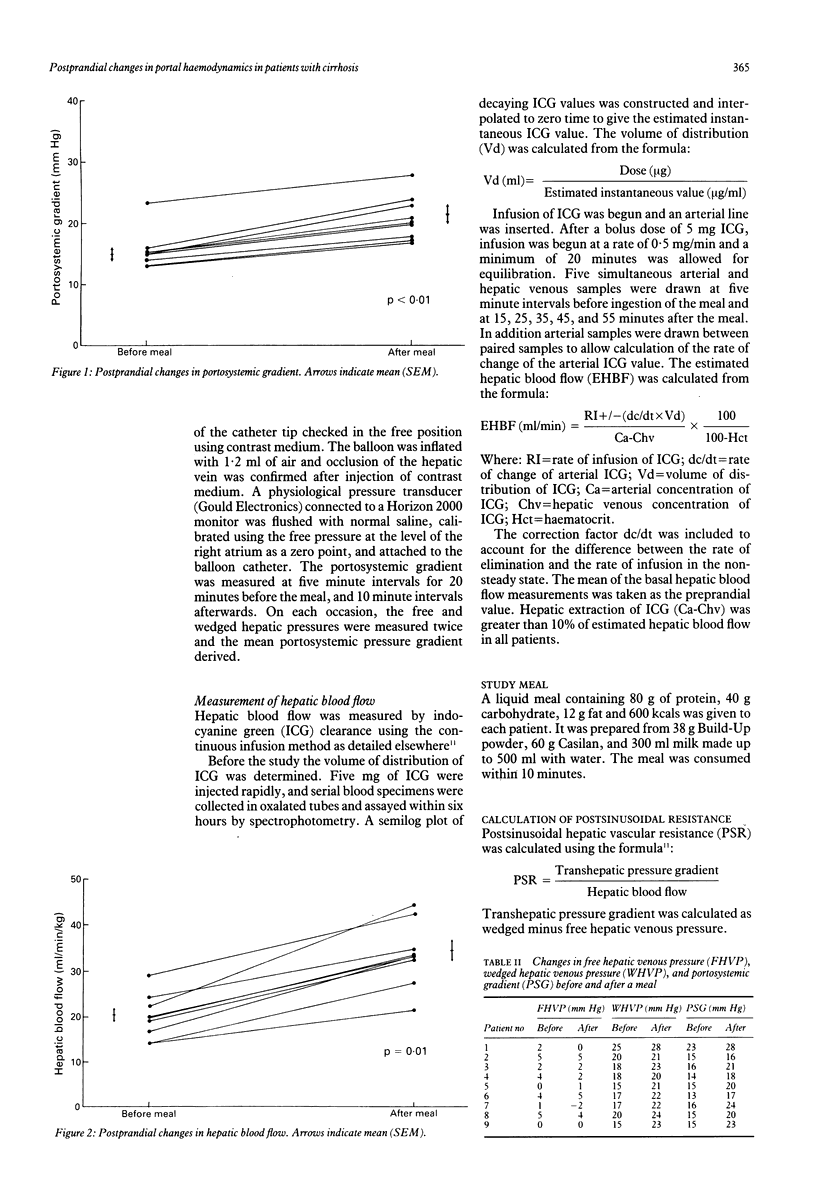
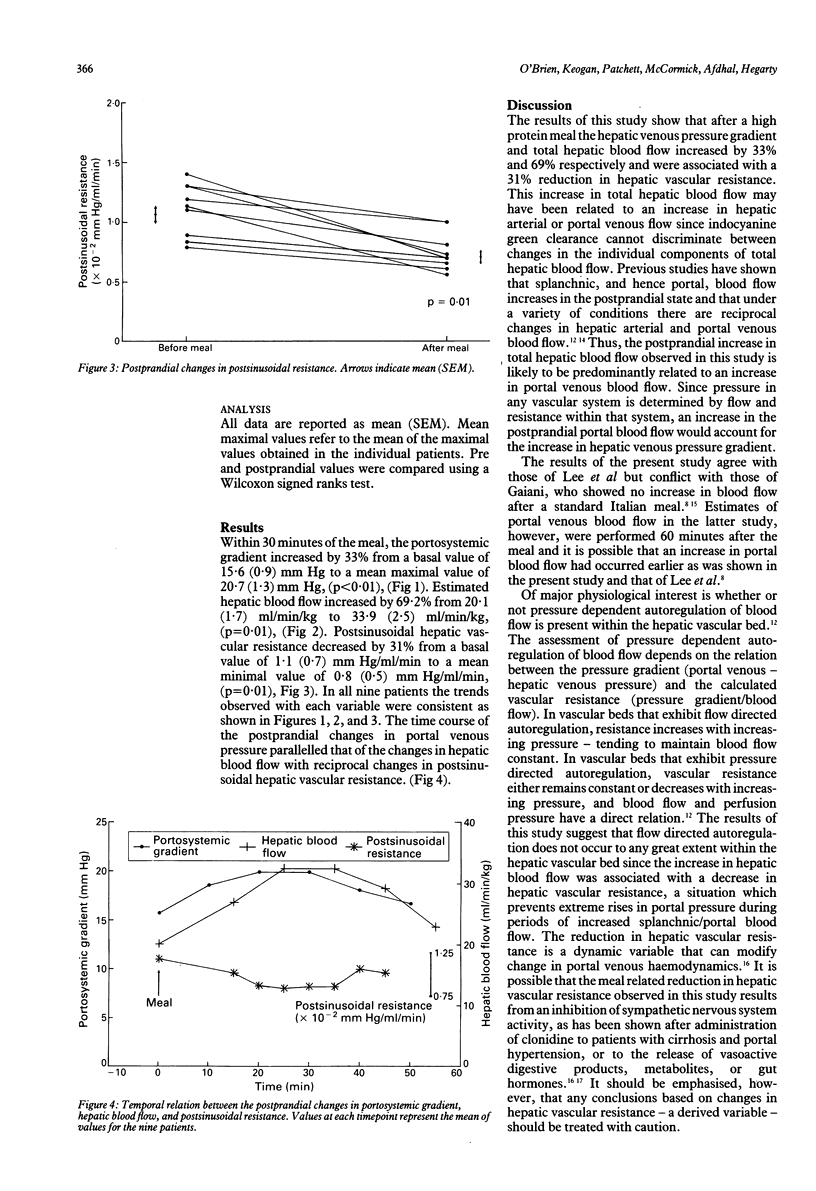
Previous studies have shown that portal venous pressure increases in patients with cirrhosis after a protein meal. Since this increase may be mediated by an increase in hepatic blood flow or postsinusoidal hepatic vascular resistance, the present study was designed to examine the precise relation between the postprandial changes in these three variables in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Estimated hepatic blood flow (EHBF; indocyanine green clearance), portosystemic gradient (PSG; wedged free hepatic venous pressure), and postsinusoidal hepatic vascular resistance (PSR = PSG/EHBF) were measured simultaneously before and at 10 minute intervals after a high protein meal, containing 80 g protein, 40 g carbohydrate and 12 g fat (600 kcal) in nine patients (seven alcoholic, two non-alcoholic) with cirrhosis and portal hypertension. After the meal, the portosystemic gradient increased by 33% from mean (SEM) 15.6 (0.9) mm Hg to 20.7 (1.3) mm Hg, (p less than 0.01; Wilcoxon signed ranks test) within 30 minutes. Coincident with this increase in portosystemic gradient, estimated hepatic blood flow increased by 69.2% from 20.1 (1.7) ml/min/kg to 33.9 (2.5) ml/min/kg (p = 0.01), peak values occurring at 25 minutes, at which time the postsinusoidal hepatic vascular resistance had decreased by 31% from 1.10 (0.1) 10(-2) mm Hg/ml/min to 0.8 (0.5) 10(-2) mm Hg/ml/min (p = 0.01). These results suggest that the postprandial increase in portal venous pressure in patients with cirrhosis is mediated by an increase in hepatic blood flow and modified by a simultaneous decrease in postsinusoidal resistance.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRANDT J. L., CASTLEMAN L., RUSKIN H. D., GREENWALD J., KELLY J. J., Jr The effect of oral protein and glucose feeding of splanchnic blood flow and oxygen utilization in normal and cirrhotic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jul;34(7 Pt 1):1017–1025. doi: 10.1172/JCI103151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoit J. N., Barrowman J. A., Harper S. L., Kvietys P. R., Granger D. N. Role of humoral factors in the intestinal hyperemia associated with chronic portal hypertension. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 1):G486–G493. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.5.G486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoit J. N., Womack W. A., Hernandez L., Granger D. N. "Forward" and "backward" flow mechanisms of portal hypertension. Relative contributions in the rat model of portal vein stenosis. Gastroenterology. 1985 Nov;89(5):1092–1096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burroughs A. K., Jenkins W. J., Sherlock S., Dunk A., Walt R. P., Osuafor T. O., Mackie S., Dick R. Controlled trial of propranolol for the prevention of recurrent variceal hemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Dec 22;309(25):1539–1542. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198312223092502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTLEMAN L., BRANDT J. L., RUSKIN H. The effect of oral feedings of meat and glucose on hepatic vein wedge pressure in normal and cirrhotic subjects. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Jun;51(6):897–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombo M., de Franchis R., Tommasini M., Sangiovanni A., Dioguardi N. Beta-blockade prevents recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding in well-compensated patients with alcoholic cirrhosis: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Hepatology. 1989 Mar;9(3):433–438. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaiani S., Bolondi L., Li Bassi S., Santi V., Zironi G., Barbara L. Effect of meal on portal hemodynamics in healthy humans and in patients with chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 1989 Jun;9(6):815–819. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840090604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groszmann R. J., Glickman M., Blei A. T., Storer E., Conn H. O. Wedged and free hepatic venous pressure measured with a balloon catheter. Gastroenterology. 1979 Feb;76(2):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida T., Chou J., Lewis R. M., Hartley C. J., Entman M., Field J. B. The effect of ingestion of meat on hepatic extraction of insulin and glucagon and hepatic glucose output in conscious dogs. Metabolism. 1983 Jun;32(6):558–567. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautt W. W. Control of hepatic arterial blood flow: independence from liver metabolic activity. Am J Physiol. 1980 Oct;239(4):H559–H564. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1980.239.4.H559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lautt W. W. Relationship between hepatic blood flow and overall metabolism: the hepatic arterial buffer response. Fed Proc. 1983 Apr;42(6):1662–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrec D., Poynard T., Hillon P., Benhamou J. P. Propranolol for prevention of recurrent gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis: a controlled study. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 3;305(23):1371–1374. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112033052302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. S., Hadengue A., Girod C., Braillon A., Lebrec D. Reduction of intrahepatic vascular space in the pathogenesis of portal hypertension. In vitro and in vivo studies in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jul;93(1):157–161. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90328-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. S., Hadengue A., Moreau R., Sayegh R., Hillon P., Lebrec D. Postprandial hemodynamic responses in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988 May-Jun;8(3):647–651. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. S., Moreau R., Hadengue A., Cerini R., Koshy A., Lebrec D. Glucagon selectively increases splanchnic blood flow in patients with well-compensated cirrhosis. Hepatology. 1988 Nov-Dec;8(6):1501–1505. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840080606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. A., Faloona G. R., Aguilar-Parada E., Unger R. H. Abnormal alpha-cell function in diabetes. Response to carbohydrate and protein ingestion. N Engl J Med. 1970 Jul 16;283(3):109–115. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197007162830301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORREGO H., MENA I., BARAONA E., PALMA R. MODIFICATIONS IN HEPATIC BLOOD FLOW AND PORTAL PRESSURE PRODUCED BY DIFFERENT DIETS. Am J Dig Dis. 1965 Mar;10:239–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02233754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. A., Jacobson E. D. Physiology of the splanchnic circulation. Arch Intern Med. 1985 Jul;145(7):1278–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premen A. J., Hall J. E., Smith M. J., Jr Postprandial regulation of renal hemodynamics: role of pancreatic glucagon. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 2):F656–F662. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.5.F656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. D., Withrington P. G. Liver blood flow. I. Intrinsic and nervous control of liver blood flow. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jul;81(1):159–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikuler E., Groszmann R. J. Interaction of flow and resistance in maintenance of portal hypertension in a rat model. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 1):G205–G212. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.2.G205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva G., Navasa M., Bosch J., Chesta J., Pilar Pizcueta M., Casamitjana R., Rivera F., Rodés J. Hemodynamic effects of glucagon in portal hypertension. Hepatology. 1990 Apr;11(4):668–673. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840110421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve J. P., Huot R., Marleau D., Huet P. M. The estimation of hepatic blood flow with indocyanine green: comparison between the continuous infusion and single injection methods. Am J Gastroenterol. 1982 Apr;77(4):233–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeneuve J. P., Pomier-Layrargues G., Infante-Rivard C., Willems B., Huet P. M., Marleau D., Viallet A. Propranolol for the prevention of recurrent variceal hemorrhage: a controlled trial. Hepatology. 1986 Nov-Dec;6(6):1239–1243. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840060602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett I. R., Esler M., Jennings G., Dudley F. J. Sympathetic tone modulates portal venous pressure in alcoholic cirrhosis. Lancet. 1986 Oct 25;2(8513):939–943. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90599-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


