Abstract
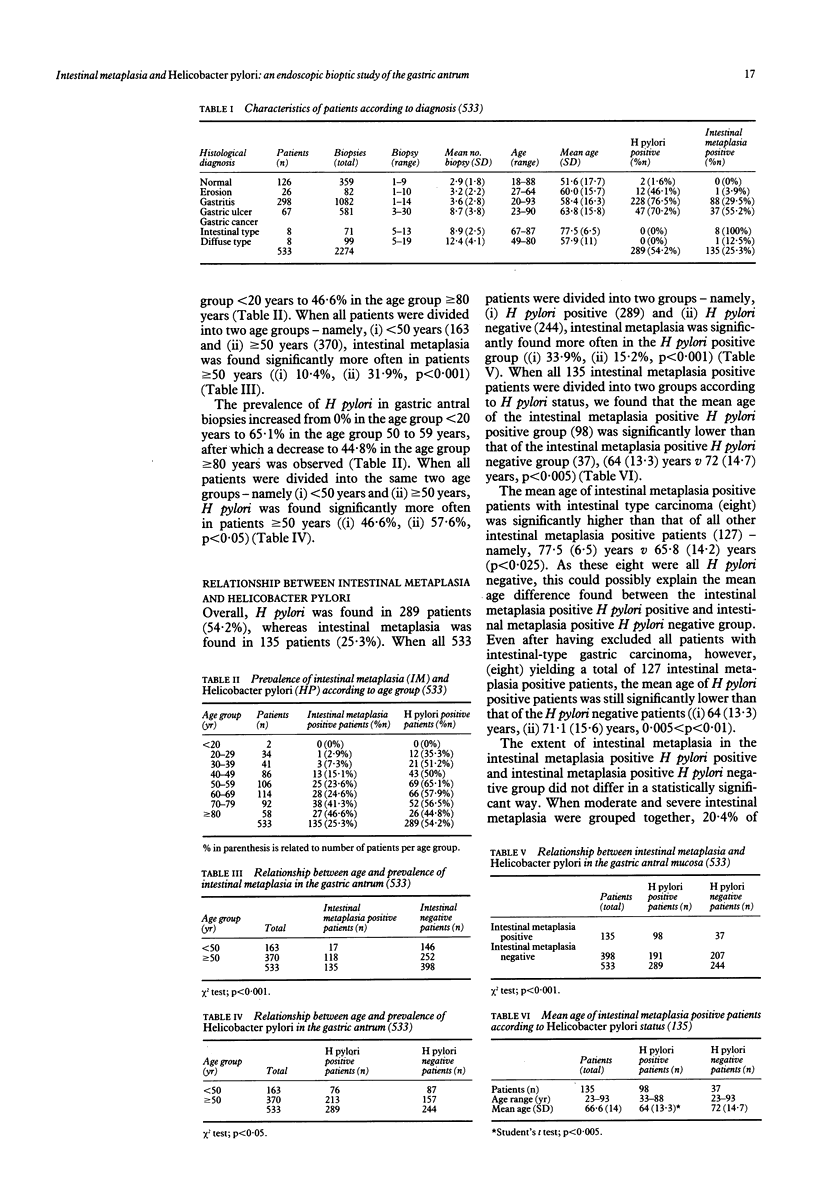
To study the relationship between intestinal metaplasia and Helicobacter pylori infection, 2274 gastroscopic antral biopsies taken from 533 patients were examined. Overall, intestinal metaplasia was found in 135 patients (25.3%) and H pylori in 289 patients (54.2%). The prevalence of intestinal metaplasia and H pylori was age related, being more common in patients greater than or equal to 50 years compared with patients less than 50 years (intestinal metaplasia, p less than 0.001 and H pylori, p less than 0.05). Intestinal metaplasia was found more often in H pylori positive patients compared with H pylori negative patients (33.9% v 15.2%, p less than 0.001). The mean age of intestinal metaplasia positive patients who were also H pylori positive was 64 (13.3) years, whereas the mean age of intestinal metaplasia positive patients who were H pylori negative was 72 (14.7) years (p less than 0.005). The extent of intestinal metaplasia was not statistically different in the latter two groups. Although our data do not prove a causal relationship between H pylori infection and the histogenesis of intestinal metaplasia it is suggested that H pylori infection is an important factor in the development of intestinal metaplasia, which is generally recognised as a precursor lesion of intestinal type gastric carcinoma.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J. Gastric Campylobacter-like organisms, gastritis, and peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Aug;93(2):371–383. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)91028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth L., Holdstock G., MacBride H., Hawtin P., Gibson J. R., Ireland A., Bamforth J., DuBoulay C. E., Lloyd R. S., Pearson A. D. Clinical importance of Campylobacter pyloridis and associated serum IgG and IgA antibody responses in patients undergoing upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. J Clin Pathol. 1986 Feb;39(2):215–219. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheli R., Giacosa A. Chronic atrophic gastritis and gastric mucosal atrophy--one and the same. Gastrointest Endosc. 1983 Feb;29(1):23–25. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(83)72493-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. Chronic gastritis: a clinico-pathological classification. Am J Gastroenterol. 1988 May;83(5):504–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P., Cuello C., Duque E., Burbano L. C., Garcia F. T., Bolanos O., Brown C., Haenszel W. Gastric cancer in Colombia. III. Natural history of precursor lesions. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Nov;57(5):1027–1035. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.5.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correa P. The epidemiology and pathogenesis of chronic gastritis: three etiologic entites. Front Gastrointest Res. 1980;6:98–108. doi: 10.1159/000403325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontham E., Zavala D., Correa P., Rodriguez E., Hunter F., Haenszel W., Tannenbaum S. R. Diet and chronic atrophic gastritis: a case-control study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Apr;76(4):621–627. doi: 10.1093/jnci/76.4.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. Y. Campylobacter pylori and peptic ulcer disease. Gastroenterology. 1989 Feb;96(2 Pt 2 Suppl):615–625. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(89)80057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai T., Murayama H. Time trend in the prevalence of intestinal metaplasia in Japan. Cancer. 1983 Jul 15;52(2):353–361. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830715)52:2<353::aid-cncr2820520229>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerzy Glass G. B., Pitchumoni C. S. Structural and ultrastructural alterations, exfoliative cytology and enzyme cytochemistry and histochemistry, proliferation kinetics, immunological derangements and other causes, and clinical associations and sequallae. Hum Pathol. 1975 Mar;6(2):219–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. M., Eldridge J., Fox A. J., Sethi P., Whorwell P. J. Antibody to the gastric campylobacter-like organism ("Campylobacter pyloridis")--clinical correlations and distribution in the normal population. J Med Microbiol. 1986 Aug;22(1):57–62. doi: 10.1099/00222615-22-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekki M., Siurala M., Varis K., Sipponen P., Sistonen P., Nevanlinna H. R. Classification principles and genetics of chronic gastritis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1987;141:1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUREN P. THE TWO HISTOLOGICAL MAIN TYPES OF GASTRIC CARCINOMA: DIFFUSE AND SO-CALLED INTESTINAL-TYPE CARCINOMA. AN ATTEMPT AT A HISTO-CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:31–49. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingwood C. A., Law H., Pellizzari A., Sherman P., Drumm B. Gastric glycerolipid as a receptor for Campylobacter pylori. Lancet. 1989 Jul 29;2(8657):238–241. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90428-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSON B. C. Carcinoma arising from areas of intestinal metaplasia in the gastric mucosa. Br J Cancer. 1955 Sep;9(3):377–385. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1955.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Armstrong J. A., McGechie D. B., Glancy R. J. Attempt to fulfil Koch's postulates for pyloric Campylobacter. Med J Aust. 1985 Apr 15;142(8):436–439. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1985.tb113443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall B. J., Goodwin C. S., Warren J. R., Murray R., Blincow E. D., Blackbourn S. J., Phillips M., Waters T. E., Sanderson C. R. Prospective double-blind trial of duodenal ulcer relapse after eradication of Campylobacter pylori. Lancet. 1988 Dec 24;2(8626-8627):1437–1442. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90929-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNulty C. A., Watson D. M. Spiral bacteria of the gastric antrum. Lancet. 1984 May 12;1(8385):1068–1069. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91469-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Nicholson G. Ingestion of Campylobacter pyloridis causes gastritis and raised fasting gastric pH. Am J Gastroenterol. 1987 Mar;82(3):192–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura A., Yamakawa H., Ishidate T., Kamiyama S., Masuda H., Stemmermann G. N., Heilburn L. K., Hankin J. H. Intestinal metaplasia in Japan: association with diet. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Mar;68(3):401–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Perez G. I., Dworkin B. M., Chodos J. E., Blaser M. J. Campylobacter pylori antibodies in humans. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Jul 1;109(1):11–17. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-1-11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B., Levi J., Dolby J. M., Dunscombe P. L., Smith A., Clark J., Stephenson M. L. Campylobacter pyloridis in peptic ulcer disease: microbiology, pathology, and scanning electron microscopy. Gut. 1985 Nov;26(11):1183–1188. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.11.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauws E. A., Langenberg W., Houthoff H. J., Zanen H. C., Tytgat G. N. Campylobacter pyloridis-associated chronic active antral gastritis. A prospective study of its prevalence and the effects of antibacterial and antiulcer treatment. Gastroenterology. 1988 Jan;94(1):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauws E. A., Tytgat G. N. Cure of duodenal ulcer associated with eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1990 May 26;335(8700):1233–1235. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91301-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N., Lansdown M., Diament R., Rathbone B., Murday V., Wyatt J. I., McMahon M., Dixon M. F., Quirke P. Helicobacter gastritis and intestinal metaplasia in a gastric cancer family. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):728–728. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90845-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siurala M., Isokoski M., Varis K., Kekki M. Prevalence of gastritis in a rural population. Bioptic study of subjects selected at random. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1968;3(2):211–223. doi: 10.3109/00365526809180125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemmermann G. N., Hayashi T. Intestinal metaplasia of the gastric mucosa: a gross and microscopic study of its distribution in various disease states. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Sep;41(3):627–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Suzuki K., Arii M., Shikata T., Fukuda R., Tao Y. X. Geographical pathology of duck livers infected with duck hepatitis B virus from Chiba and Shimane in Japan and Shanghai in China. Cancer Res. 1988 Mar 1;48(5):1319–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead R., Truelove S. C., Gear M. W. The histological diagnosis of chronic gastritis in fibreoptic gastroscope biopsy specimens. J Clin Pathol. 1972 Jan;25(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/jcp.25.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt J. I., Dixon M. F. Chronic gastritis--a pathogenetic approach. J Pathol. 1988 Feb;154(2):113–124. doi: 10.1002/path.1711540203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


