Abstract
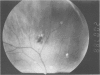
The rarity of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) means that many clinicians may be unaware of the major advances that have taken place in screening for the condition over the past five years. This review is not only to document the current scene but also to give details of those involved in establishing registries throughout the country. FAP is a hereditary disorder which carries with it almost a 100% risk of colorectal cancer. The aim of screening is to detect gene carriers before they present with symptoms attributable to colonic polyps. In this way the incidence of colorectal cancer can be greatly reduced. The use of gene probes to identify patients with FAP is in its infancy but in selected pedigrees gene carriers can be identified using a venous blood sample. The recognition that congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium is an extracolonic manifestation of FAP in most pedigrees allows non-invasive ophthalmological screening of relatives at risk. The combination of these new screening methods with an effective regional registry for FAP can increase the number of patients detected by screening rather than by symptoms. This facilitates appropriate prophylactic surgery and reduces mortality related to colorectal cancer.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken R. J., Elliot M. S., Torrington M., Louw J. H. Twenty year experience with familial polyposis coli in Cape Town. Br J Surg. 1986 Mar;73(3):210–213. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800730319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alm T. Surgical treatment of hereditary adenomatosis of the colon and rectum in Sweden during the last 20 years. Part I. Introduction. Surgical procedures used. Pre-and postoperative measures. Arrangement of follow-up. Propositi group, primary and late results. Acta Chir Scand. 1975;141(3):218–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beart R. W., Jr Familial polyposis. Br J Surg. 1985 Sep;72 (Suppl):S31–S32. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800721319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk T., Cohen Z., McLeod R. S., Parker J. A. Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium as a marker for familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1988 Apr;31(4):253–257. doi: 10.1007/BF02554355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bess M. A., Adson M. A., Elveback L. R., Moertel C. G. Rectal cancer following colectomy for polyposis. Arch Surg. 1980 Apr;115(4):460–467. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1980.01380040084015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair N. P., Trempe C. L. Hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium associated with Gardner's syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1980 Nov;90(5):661–667. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75133-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn J., Chapman P., Delhanty J., Wood C., Lalloo F., Cachon-Gonzalez M. B., Tsioupra K., Church W., Rhodes M., Gunn A. The UK Northern region genetic register for familial adenomatous polyposis coli: use of age of onset, congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium, and DNA markers in risk calculations. J Med Genet. 1991 May;28(5):289–296. doi: 10.1136/jmg.28.5.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H. J. The familial polyposis coli register. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 1987 Jul;16(3):532–534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S. Familial polyposis coli. Dan Med Bull. 1987 Mar;34(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S. Familial polyposis coli. Dan Med Bull. 1987 Mar;34(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S., Holm N. V., Hauge M. The incidence and prevalence of familial polyposis coli in Denmark. Scand J Soc Med. 1986;14(2):67–74. doi: 10.1177/140349488601400205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bülow S. The Danish Polyposis Register. Description of the methods of detection and evaluation of completeness. Dis Colon Rectum. 1984 Jun;27(6):351–355. doi: 10.1007/BF02552996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. D., Church W., Burn J., Gunn A. Congenital hypertrophy of retinal pigment epithelium: a sign of familial adenomatous polyposis. BMJ. 1989 Feb 11;298(6670):353–354. doi: 10.1136/bmj.298.6670.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHN I., JONSSON N., LUNDH G. DESMOID TUMOURS. A SERIES OF 33 CASES. Acta Chir Scand. 1963 Oct;126:305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz Llopis M., Menezo J. L. Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium and familial polyposis of the colon. Am J Ophthalmol. 1987 Feb 15;103(2):235–236. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)74236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dozois R. R., Kelly K. A., Welling D. R., Gordon H., Beart R. W., Jr, Wolff B. G., Pemberton J. H., Ilstrup D. M. Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis: comparison of results in familial adenomatous polyposis and chronic ulcerative colitis. Ann Surg. 1989 Sep;210(3):268–273. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198909000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARDNER E. J., RICHARDS R. C. Multiple cutaneous and subcutaneous lesions occurring simultaneously with hereditary polyposis and osteomatosis. Am J Hum Genet. 1953 Jun;5(2):139–147. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galandiuk S., Hermann R. E., Jagelman D. G., Fazio V. W., Sivak M. V. Villous tumors of the duodenum. Ann Surg. 1988 Mar;207(3):234–239. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198803000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera-Ornelas L., Elsiah S., Petrelli N., Mittelman A. Causes of death in patients with familial polyposis coli (FPC). Semin Surg Oncol. 1987;3(2):109–117. doi: 10.1002/ssu.2980030212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlston R., Slack J., Murday V. Risk estimates for screening adenomatous polyposis coli. Lancet. 1990 Feb 24;335(8687):484–484. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90724-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isbister W. H. Colorectal polyps: an endoscopic experience. Aust N Z J Surg. 1986 Sep;56(9):717–722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagelman D. G., DeCosse J. J., Bussey H. J. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet. 1988 May 21;1(8595):1149–1151. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91962-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagelman D. G. Extracolonic manifestations of familial polyposis coli. Semin Surg Oncol. 1987;3(2):88–91. doi: 10.1002/ssu.2980030208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagelman D. G. Familial polyposis coli. Surg Clin North Am. 1983 Feb;63(1):117–128. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42933-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen H. J., Husa A., Aukee S., Laitinen S., Matikainen M., Havia T. Finnish registry for familial adenomatosis coli. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 Oct;19(7):941–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen H. J., Husa A., Aukee S., Laitinen S., Matikainen M., Havia T. Finnish registry for familial adenomatosis coli. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1984 Oct;19(7):941–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen H. J., Peltokallio P., Landtman M., Wolf J. Gardner's stigmas in patients with familial adenomatosis coli. Br J Surg. 1982 Dec;69(12):718–721. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800691211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen H. J. Time and type of prophylactic surgery for familial adenomatosis coli. Ann Surg. 1985 Jul;202(1):93–97. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198507000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Järvinen H., Nyberg M., Peltokallio P. Upper gastrointestinal tract polyps in familial adenomatosis coli. Gut. 1983 Apr;24(4):333–339. doi: 10.1136/gut.24.4.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemmer S., Pascoe L., DeCosse J. Occurrence of desmoids in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis of the colon. Am J Med Genet. 1987 Oct;28(2):385–392. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320280217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKHART-MUMMERY H. E., DUKES C. E., BUSSEY H. J. The surgical treatment of familial polyposis of the colon. Br J Surg. 1956 Mar;43(181):476–481. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004318105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart-Mummery J. P. THE CAUSATION AND TREATMENT OF MULTIPLE ADENOMATOSIS OF THE COLON. Ann Surg. 1934 Jan;99(1):178–184. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193401000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotfi A. M., Dozois R. R., Gordon H., Hruska L. S., Weiland L. H., Carryer P. W., Hurt R. D. Mesenteric fibromatosis complicating familial adenomatous polyposis: predisposing factors and results of treatment. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1989;4(1):30–36. doi: 10.1007/BF01648547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. H., Sweet R. H. MULTIPLE POLYPOSIS OF THE COLON: A FAMILIAL DISEASE. Ann Surg. 1937 Apr;105(4):511–515. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193704000-00004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moertel C. G., Hill J. R., Adson M. A. Surgical management of multiple polyposis. The problem of cancer in the retained bowel segment. Arch Surg. 1970 Apr;100(4):521–526. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1970.01340220197033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murday V., Slack J. Inherited disorders associated with colorectal cancer. Cancer Surv. 1989;8(1):139–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., Leppert M., Dobbs M., Wasmuth J., Wolff E., Carlson M., Fujimoto E., Krapcho K., Sears T. Localization of the genetic defect in familial adenomatous polyposis within a small region of chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):638–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. J., Moskowitz R. L., Shepherd N. A. Restorative proctocolectomy with ileal reservoir. Br J Surg. 1985 Sep;72 (Suppl):S76–S79. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800721341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishisho I., Nakamura Y., Miyoshi Y., Miki Y., Ando H., Horii A., Koyama K., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Hedge P. Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer patients. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):665–669. doi: 10.1126/science.1651563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nivatvongs S. Complications in colonoscopic polypectomy: lessons to learn from an experience with 1576 polyps. Am Surg. 1988 Feb;54(2):61–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks A. G., Nicholls R. J. Proctocolectomy without ileostomy for ulcerative colitis. Br Med J. 1978 Jul 8;2(6130):85–88. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6130.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks T. G. Extracolonic manifestations associated with familial adenomatous polyposis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1990 May;72(3):181–184. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plail R. O., Bussey H. J., Glazer G., Thomson J. P. Adenomatous polyposis: an association with carcinoma of the thyroid. Br J Surg. 1987 May;74(5):377–380. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranzi T., Castagnone D., Velio P., Bianchi P., Polli E. E. Gastric and duodenal polyps in familial polyposis coli. Gut. 1981 May;22(5):363–367. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.5.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitamo J. J., Häyry P., Nykyri E., Saxén E. The desmoid tumor. I. Incidence, sex-, age- and anatomical distribution in the Finnish population. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Jun;77(6):665–673. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/77.6.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes M., Chapman P. D., Burn J., Gunn A. Role of a regional register for familial adenomatous polyposis: experience in the northern region. Br J Surg. 1991 Apr;78(4):451–452. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R. C., Rogers S. W., Gardner E. J. Spontaneous mesenteric fibromatosis in Gardner's syndrome. Cancer. 1981 Feb 1;47(3):597–601. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810201)47:3<597::aid-cncr2820470329>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan D. P., Schapiro R. H., Warshaw A. L. Villous tumors of the duodenum. Ann Surg. 1986 Mar;203(3):301–306. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198603000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarre R. G., Frost A. G., Jagelman D. G., Petras R. E., Sivak M. V., McGannon E. Gastric and duodenal polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis: a prospective study of the nature and prevalence of upper gastrointestinal polyps. Gut. 1987 Mar;28(3):306–314. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.3.306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarre R. G., Jagelman D. G., Beck G. J., McGannon E., Fazio V. W., Weakley F. L., Lavery I. C. Colectomy with ileorectal anastomosis for familial adenomatous polyposis: the risk of rectal cancer. Surgery. 1987 Jan;101(1):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spigelman A. D., Williams C. B., Talbot I. C., Domizio P., Phillips R. K. Upper gastrointestinal cancer in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet. 1989 Sep 30;2(8666):783–785. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90840-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURCOT J., DESPRES J. P., ST PIERRE F. Malignant tumors of the central nervous system associated with familial polyposis of the colon: report of two cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1959 Sep-Oct;2:465–468. doi: 10.1007/BF02616938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. A., Wolff B. G., Dozois R. R., Kelly K. A., Pemberton J. H., Beart R. W., Jr Ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for chronic ulcerative colitis and familial polyposis coli complicated by adenocarcinoma. Dis Colon Rectum. 1988 May;31(5):358–362. doi: 10.1007/BF02564884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboulsi E. I., Maumenee I. H., Krush A. J., Giardiello F. M., Levin L. S., Hamilton S. R. Pigmented ocular fundus lesions in the inherited gastrointestinal polyposis syndromes and in hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Ophthalmology. 1988 Jul;95(7):964–969. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(88)33093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utsunomiya J., Nakamura T. The occult osteomatous changes in the mandible in patients with familial polyposis coli. Br J Surg. 1975 Jan;62(1):45–51. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800620111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watne A. L., Carrier J. M., Durham J. P., Hrabovsky E. E., Chang W. The occurrence of carcinoma of the rectum following ileoproctostomy for familial polyposis. Ann Surg. 1983 May;197(5):550–554. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198305000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welling D. R., Beart R. W., Jr Surgical alternatives in the treatment of polyposis coli. Semin Surg Oncol. 1987;3(2):99–104. doi: 10.1002/ssu.2980030210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]