Abstract
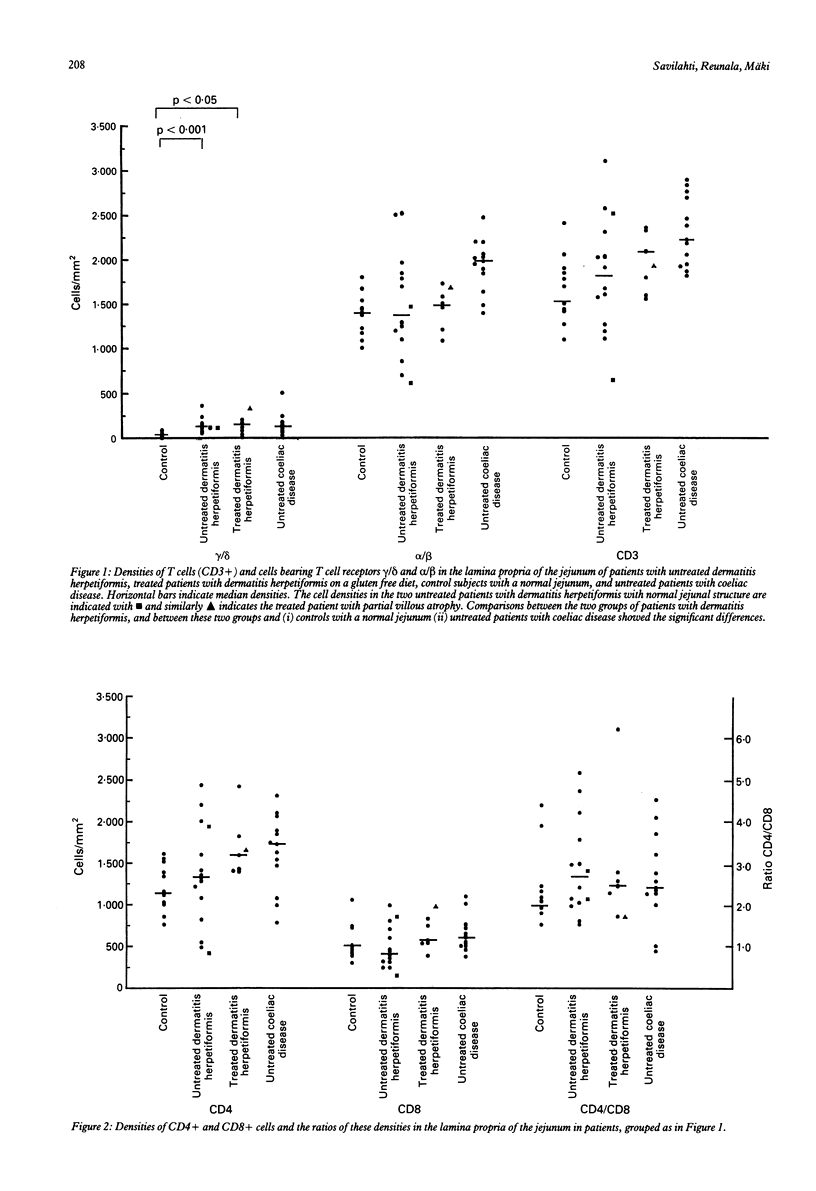
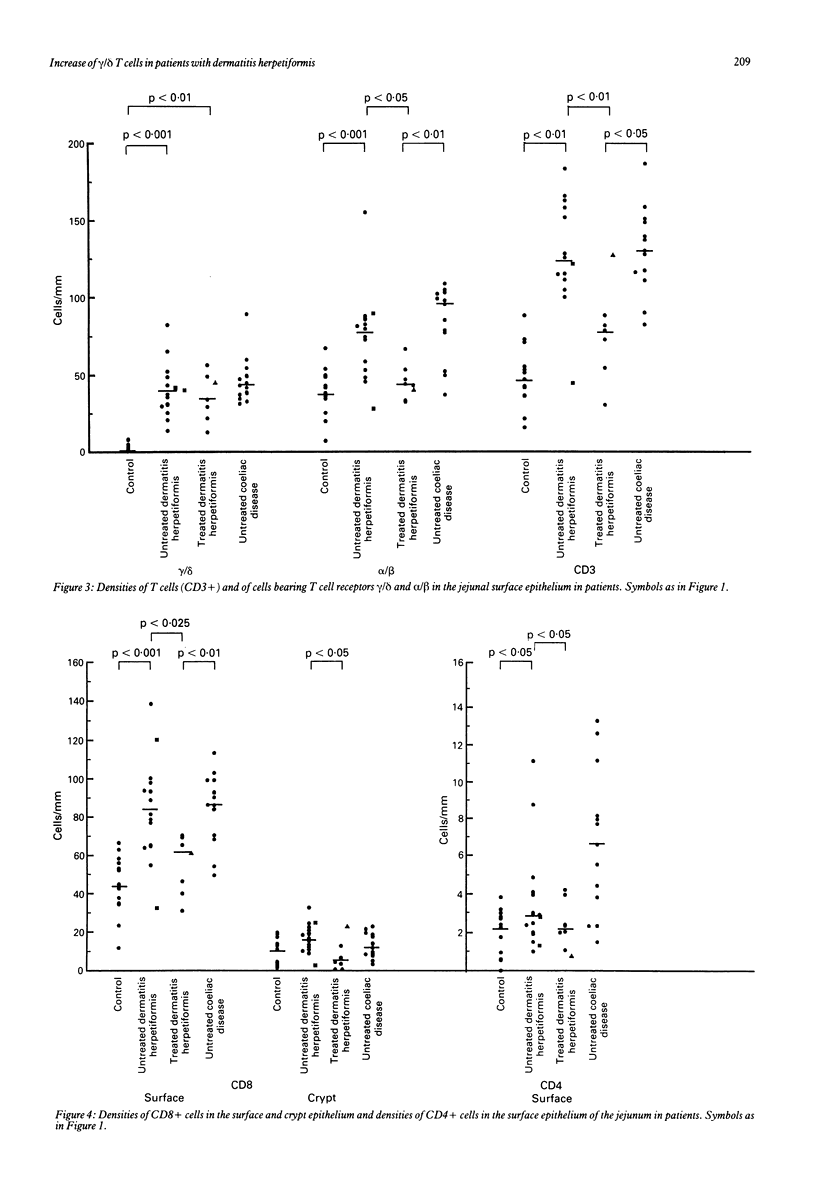
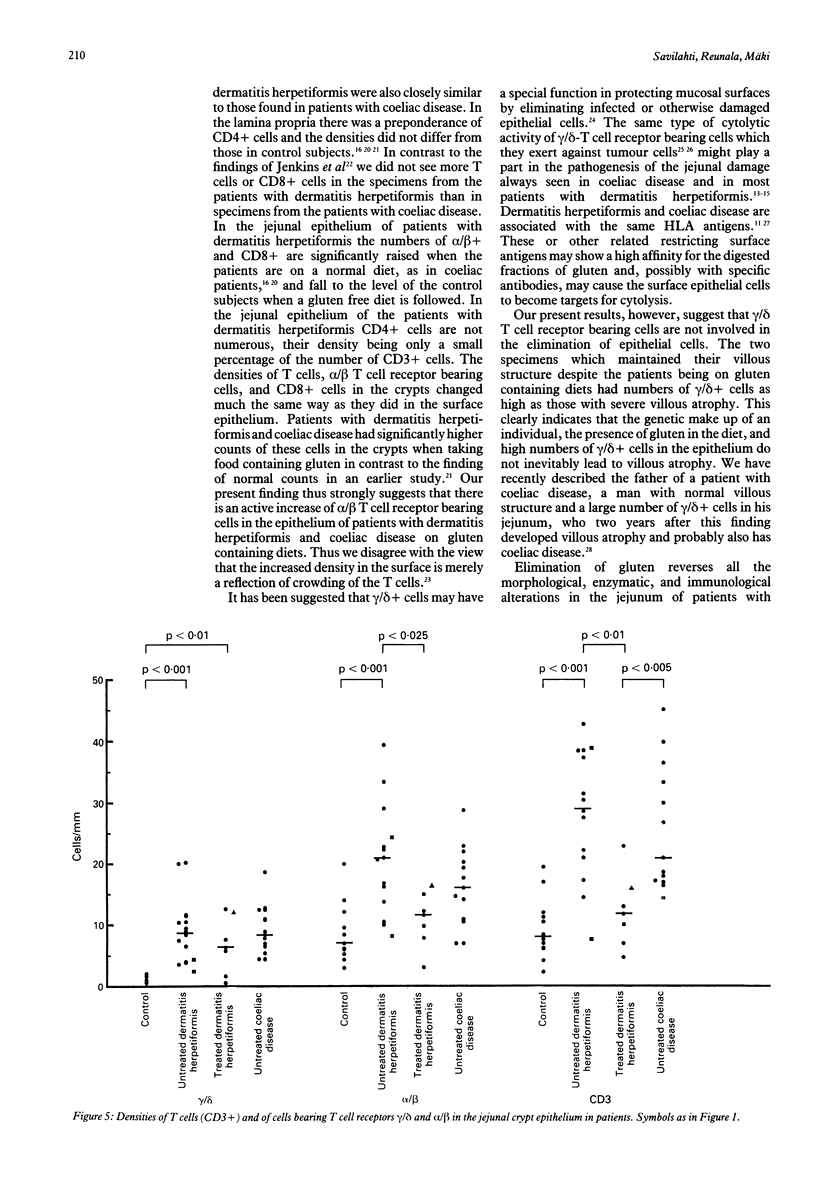
The densities of T cells and of cells bearing the T cell receptors gamma/delta and alpha/delta and the surface antigens CD4 and CD8 in jejunal specimens from 21 patients with dermatitis herpetiformis were compared with those in specimens from 13 untreated adults with coeliac disease and 13 control subjects. In the lamina propria of the jejunum the median density of gamma/delta+ cells was significantly (p less than 0.001) greater in untreated patients with dermatitis herpetiformis than in control subjects (114 v 36 cells/mm2) and similar to that found in the patients with coeliac disease (115 cells/mm2). The difference in gamma/delta+ cell density between patients with dermatitis herpetiformis and control subjects was much greater in the surface epithelium of the jejunum: the median density for 14 untreated patients with dermatitis herpetiformis was 39 cells/mm, for seven patients with dermatitis herpetiformis on a gluten free diet 34 cells/mm, and for control subjects 2 cells/mm; the coeliac patients had the same density as the patients with dermatitis herpetiformis (45 cells/mm). The higher density of cells bearing the alpha/delta T cell receptor in the epithelium (median 77 cells/mm) of untreated patients with dermatitis herpetiformis was associated with a gluten containing diet; in specimens taken from patients with dermatitis herpetiformis on a gluten free diet the median density was similar to that in the control subjects (44 v 39 cells/mm). The increase in the number of lymphocytes bearing the T cell receptor gamma/delta, particularly in the epithelium of the jejunum, seems to be a constant marker for these closely related diseases, whereas the density of alpha/delta+ T cells is dependent on the diet.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Band H., Hochstenbach F., McLean J., Hata S., Krangel M. S., Brenner M. B. Immunochemical proof that a novel rearranging gene encodes the T cell receptor delta subunit. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):682–684. doi: 10.1126/science.3672118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bank I., DePinho R. A., Brenner M. B., Cassimeris J., Alt F. W., Chess L. A functional T3 molecule associated with a novel heterodimer on the surface of immature human thymocytes. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):179–181. doi: 10.1038/322179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Bosnes V., Halstensen T. S., Scott H., Sollid L. M., Valnes K. N. T lymphocytes in human gut epithelium preferentially express the alpha/beta antigen receptor and are often CD45/UCHL1-positive. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jul;30(1):123–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., McLean J., Dialynas D. P., Strominger J. L., Smith J. A., Owen F. L., Seidman J. G., Ip S., Rosen F., Krangel M. S. Identification of a putative second T-cell receptor. Nature. 1986 Jul 10;322(6075):145–149. doi: 10.1038/322145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner M. B., Strominger J. L., Krangel M. S. The gamma delta T cell receptor. Adv Immunol. 1988;43:133–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucy R. P., Chen C. L., Cooper M. D. Tissue localization and CD8 accessory molecule expression of T gamma delta cells in humans. J Immunol. 1989 May 1;142(9):3045–3049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciccone E., Ferrini S., Bottino C., Viale O., Prigione I., Pantaleo G., Tambussi G., Moretta A., Moretta L. A monoclonal antibody specific for a common determinant of the human T cell receptor gamma/delta directly activates CD3+WT31- lymphocytes to express their functional program(s). J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):1–11. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciclitira P. J., Hall M. A. Coeliac disease. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1990 Mar;4(1):43–59. doi: 10.1016/0950-3528(90)90038-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuenod B., Brousse N., Goulet O., De Potter S., Mougenot J. F., Ricour C., Guy-Grand D., Cerf-Bensussan N. Classification of intractable diarrhea in infancy using clinical and immunohistological criteria. Gastroenterology. 1990 Oct;99(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90624-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure F., Jitsukawa S., Triebel F., Hercend T. Characterization of human peripheral lymphocytes expressing the CD3-gamma/delta complex with anti-receptor monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3357–3360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisch P., Malkovsky M., Braakman E., Sturm E., Bolhuis R. L., Prieve A., Sosman J. A., Lam V. A., Sondel P. M. Gamma/delta T cell clones and natural killer cell clones mediate distinct patterns of non-major histocompatibility complex-restricted cytolysis. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1567–1579. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groh V., Porcelli S., Fabbi M., Lanier L. L., Picker L. J., Anderson T., Warnke R. A., Bhan A. K., Strominger J. L., Brenner M. B. Human lymphocytes bearing T cell receptor gamma/delta are phenotypically diverse and evenly distributed throughout the lymphoid system. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1277–1294. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. P. The pathogenesis of dermatitis herpetiformis: recent advances. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1987 Jun;16(6):1129–1144. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70148-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall R. P., Ward F. E., Wenstrup R. J. An HLA class II region restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) in patients with dermatitis herpetiformis: association with HLA-DP phenotype. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Aug;95(2):172–177. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12477943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstensen T. S., Scott H., Brandtzaeg P. Intraepithelial T cells of the TcR gamma/delta+ CD8- and V delta 1/J delta 1+ phenotypes are increased in coeliac disease. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Dec;30(6):665–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb02474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D., Goodall A., Scott B. B. T-lymphocyte populations in normal and coeliac small intestinal mucosa defined by monoclonal antibodies. Gut. 1986 Nov;27(11):1330–1337. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.11.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins D., Goodall A., Scott B. T-cell and plasma cell populations in coeliac small intestinal mucosa in relation to dermatitis herpetiformis. Gut. 1989 Jul;30(7):955–958. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.7.955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M. N. Studies of intestinal lymphoid tissue. III. Quantitative analyses of epithelial lymphocytes in the small intestine of human control subjects and of patients with celiac sprue. Gastroenterology. 1980 Sep;79(3):481–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäki M., Holm K., Collin P., Savilahti E. Increase in gamma/delta T cell receptor bearing lymphocytes in normal small bowel mucosa in latent coeliac disease. Gut. 1991 Nov;32(11):1412–1414. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.11.1412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reunala T. Gluten-free diet in dermatitis herpetiformis. II. Morphological and immunological findings in the skin and small intestine of 12 patients and matched controls. Br J Dermatol. 1978 Jan;98(1):69–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1978.tb07335.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reunala T., Kosnai I., Karpati S., Kuitunen P., Török E., Savilahti E. Dermatitis herpetiformis: jejunal findings and skin response to gluten free diet. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Jun;59(6):517–522. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.6.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savilahti E., Arato A., Verkasalo M. Intestinal gamma/delta receptor-bearing T lymphocytes in celiac disease and inflammatory bowel diseases in children. Constant increase in celiac disease. Pediatr Res. 1990 Dec;28(6):579–581. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199012000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Bofill M., Jewell D. P. Lymphocyte subpopulations in the human small intestine. The findings in normal mucosa and in the mucosa of patients with adult coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Apr;52(1):219–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sollid L. M., Markussen G., Ek J., Gjerde H., Vartdal F., Thorsby E. Evidence for a primary association of celiac disease to a particular HLA-DQ alpha/beta heterodimer. J Exp Med. 1989 Jan 1;169(1):345–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J., Isaacson P. G., Diss T. C., MacDonald T. T. Expression of disulfide-linked and non-disulfide-linked forms of the T cell receptor gamma/delta heterodimer in human intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1335–1338. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triebel F., Hercend T. Subpopulations of human peripheral T gamma delta lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1989 Jun;10(6):186–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90321-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkasalo M. A., Arató A., Savilahti E., Tainio V. M. Effect of diet and age on jejunal and circulating lymphocyte subsets in children with coeliac disease: persistence of CD4-8-intraepithelial T cells through treatment. Gut. 1990 Apr;31(4):422–425. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.4.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viney J., MacDonald T. T., Spencer J. Gamma/delta T cells in the gut epithelium. Gut. 1990 Aug;31(8):841–844. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.8.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


