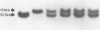Abstract
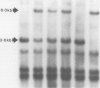
The familial adenomatous polyposis gene has recently been assigned to the long arm of chromosome five through linkage to several 5q DNA probes. These probes can now be used to trace inheritance of the disease gene in affected families. In this study, DNA samples from 152 members of 10 Australian familial adenomatous polyposis families have been examined for restriction fragment length polymorphisms detected by DNA probes C11P11, ECB27, and YN5.48. Linkage analysis confirmed linkage between the familial adenomatous polyposis gene and each probe with a maximum combined LOD score of 2.82 for C11P11, 2.90 for ECB27 and 5.49 for YN5.48 all at a recombination fraction of zero. Risk estimates were determined for the 51 at risk individuals in these families based on their restriction fragment length polymorphism data alone or in addition by including the effect of age dependent penetrance. Thirty two of those at risk (63%) could be assigned specific high (greater than or equal to 95%) or low (less than or equal to 5%) risks of developing familial adenomatous polyposis on the basis of their probe results. When the effect of age dependent penetrance was included, 26 (51%) fell at the extremes of risk (greater than or equal to 99% or less than or equal to 1%). Such estimates provide a sound basis for planning sigmoidoscopic screening of at risk family members and will thus facilitate surveillance in familial adenomatous polyposis families.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk T., Bülow S., Cohen Z., DeCosse J. J., Hawley P. R., Jagelman D. G., Järvinen H. J., Macrae F. A. Surgical aspects of familial adenomatous polyposis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 1988 Mar;3(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/BF01649676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F., Bailey C. J., Bodmer J., Bussey H. J., Ellis A., Gorman P., Lucibello F. C., Murday V. A., Rider S. H., Scambler P. Localization of the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis on chromosome 5. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):614–616. doi: 10.1038/328614a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. G., Wyllie A. H., Nakamura Y., Steel C. M., Evans H. J., White R. L., Bird C. C. Genetic linkage map of six polymorphic DNA markers around the gene for familial adenomatous polyposis on chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Dec;47(6):982–987. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop M. G., Wyllie A. H., Steel C. M., Piris J., Evans H. J. Linked DNA markers for presymptomatic diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis. Lancet. 1991 Feb 9;337(8737):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90940-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera L., Kakati S., Gibas L., Pietrzak E., Sandberg A. A. Gardner syndrome in a man with an interstitial deletion of 5q. Am J Med Genet. 1986 Nov;25(3):473–476. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320250309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyen F., Jagelman D. G., Romania A., Zakov Z. N., Lavery I. C., Fazio V. W., McGannon E. Predictive value of congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium as a clinical marker for familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990 Dec;33(12):1003–1008. doi: 10.1007/BF02139213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodge S. E., Spence M. A., Crandall B. F., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C., Crist M., Tideman S. Huntington disease: linkage analysis with age-of-onset corrections. Am J Med Genet. 1980;5(3):247–254. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320050305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlston R., Slack J., Murday V. Risk estimates for screening adenomatous polyposis coli. Lancet. 1990 Feb 24;335(8687):484–484. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90724-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Nilbert M. C., Vogelstein B., Bryan T. M., Levy D. B., Smith K. J., Preisinger A. C., Hamilton S. R., Hedge P., Markham A. Identification of a gene located at chromosome 5q21 that is mutated in colorectal cancers. Science. 1991 Mar 15;251(4999):1366–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.1848370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop G. M., Lalouel J. M. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Mar;36(2):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leppert M., Dobbs M., Scambler P., O'Connell P., Nakamura Y., Stauffer D., Woodward S., Burt R., Hughes J., Gardner E. The gene for familial polyposis coli maps to the long arm of chromosome 5. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.3479843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P., Tops C. M., vd Broek M., Breukel C., Wijnen J. T., Oldenburg M., vd Bos J., van Leeuwen-Cornelisse I. S., Vasen H. F., Griffioen G. Close linkage of a highly polymorphic marker (D5S37) to familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) and confirmation of FAP localization on chromosome 5q21-q22. Hum Genet. 1988 Jun;79(2):183–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00280563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Lathrop M., Leppert M., Dobbs M., Wasmuth J., Wolff E., Carlson M., Fujimoto E., Krapcho K., Sears T. Localization of the genetic defect in familial adenomatous polyposis within a small region of chromosome 5. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;43(5):638–644. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet. 1974 Sep;26(5):588–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustin R. B., Jagelman D. G., McGannon E., Fazio V. W., Lavery I. C., Weakley F. L. Spontaneous mutation in familial adenomatous polyposis. Dis Colon Rectum. 1990 Jan;33(1):52–55. doi: 10.1007/BF02053203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tops C. M., Wijnen J. T., Griffioen G., von Leeuwen I. S., Vasen H. F., den Hartog Jager F. C., Breukel C., Nagengast F. M., van der Klift H. M., Lamers C. B. Presymptomatic diagnosis of familial adenomatous polyposis by bridging DNA markers. Lancet. 1989 Dec 9;2(8676):1361–1363. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91968-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varesco L., Thomas H. J., Cottrell S., Murday V., Fennell S. J., Williams S., Searle S., Sheer D., Bodmer W. F., Frischauf A. M. CpG island clones from a deletion encompassing the gene for adenomatous polyposis coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10118–10122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]