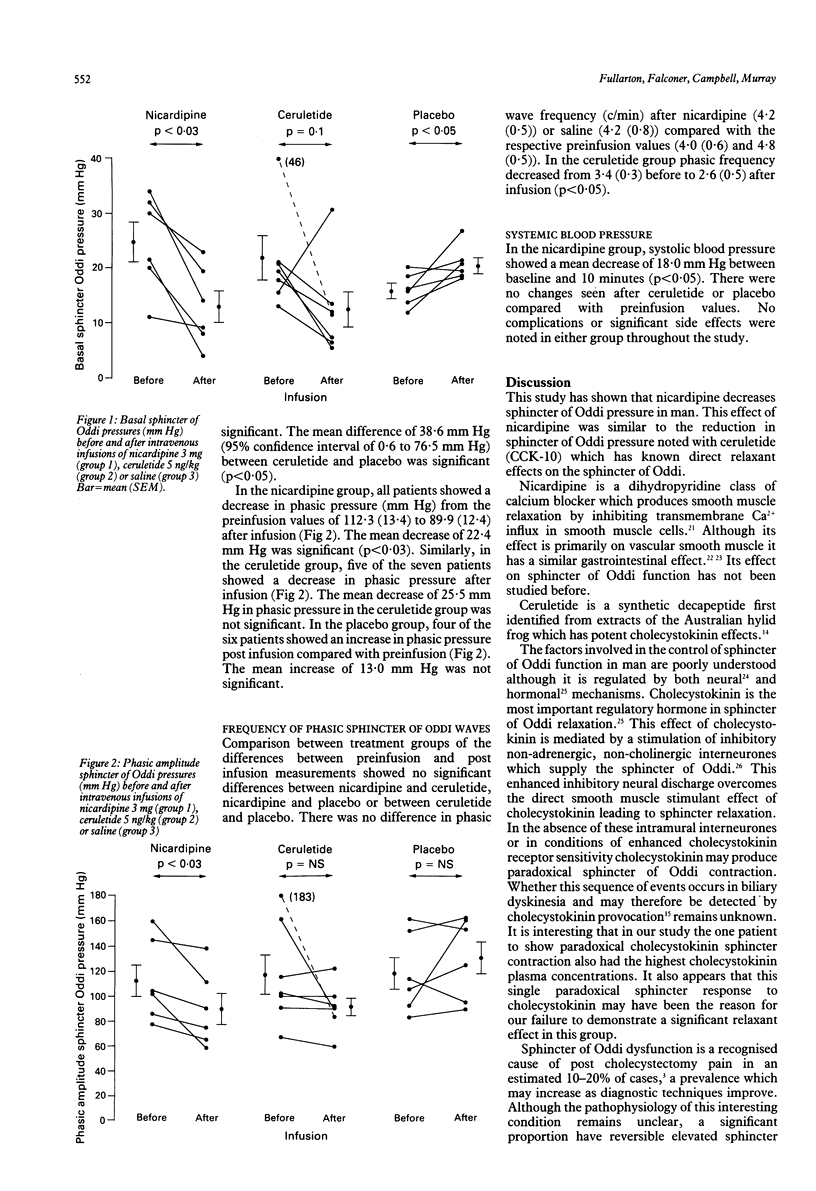
Abstract
Although sphincter of Oddi dysfunction is a recognised cause of post cholecystectomy pain, the control mechanisms involved in sphincter of Oddi function are poorly understood. Pharmacological relaxation of the sphincter of Oddi may have a beneficial effect particularly in sphincter of Oddi dysfunction where basal sphincter pressure is high. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of calcium channel blockade (nicardipine) and synthetic cholecystokinin (ceruletide) on sphincter of Oddi pressures. Nineteen patients (median age 49 years; range 21-75) attending for routine endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic (ERCP) examination were studied. No patients with evidence of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction were included in the study. Each patient was randomly allocated to receive a three minute intravenous infusion of nicardipine 3 mg (six) ceruletide 5 ng/kg (seven) or placebo (six). Endoscopic biliary manometry was done with recording of basal sphincter of Oddi pressures, sphincter of Oddi phasic wave amplitude and frequency before and after intravenous infusions. In the nicardipine group patients showed a decrease in both basal and phasic amplitude sphincter of Oddi pressure (mm Hg) from the preinfusion values (mean (SEM)) of 24.7 (3.6) and 112.3 (13.4) to 12.9 (2.9) (p less than 0.01) and 89.9 (12.4) (p less than 0.03) after infusion respectively. Ceruletide produced a decrease in sphincter of Oddi phasic wave frequency (c/min) from 3.4 (0.3) before infusion to 2.6 (0.5) after infusion (p less than 0.05). We conclude that nicardipine effectively decreases sphincter of Oddi pressure. This drug may therefore be of value in the treatment of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction where raised sphincter pressures are thought to be the primary pathogenic feature.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allescher H. D., Neuhaus H., Hagenmüller F., Classen M. Effect of N-butylscopolamine on sphincter of Oddi motility in patients during routine ERCP--a manometric study. Endoscopy. 1990 Jul;22(4):160–163. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1012829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Meir S., Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Stewart E. T., Arndorfer R. C. Biliary and pancreatic duct pressures measured by ERCP manometry in patients with suspected papillary stenosis. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Mar;24(3):209–213. doi: 10.1007/BF01308431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Meir S., Halpern Z., Bardan E., Gilat T. Frequency of papillary dysfunction among cholecystectomized patients. Hepatology. 1984 Mar-Apr;4(2):328–330. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Biancani P. Effect of cholecystokinin and the octapeptide of cholecystokinin on the feline sphincter of Oddi and gallbladder. Mechanisms of action. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1231–1239. doi: 10.1172/JCI109974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behar J., Biancani P. Neural control of the sphincter of Oddi. A physiological role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in the regulation of basal sphincter of Oddi motor activity in the cat. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):551–559. doi: 10.1172/JCI111003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertaccini G., De Caro G., Endean R., Erspamer V., Impicciatore M. The actions of caerulein on the smooth muscle of the gastrointestinal tract and the gall bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1968 Oct;34(2):291–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb07052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coelho J. C., Senninger N., Runkel N., Herfarth C., Messmer K. Effect of nifedipine on the motility of the sphincter of Oddi and small bowel of the opossum. Res Exp Med (Berl) 1987;187(1):19–24. doi: 10.1007/BF01854964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Masi E., Corazziari E., Habib F. I., Fontana B., Gatti V., Fegiz G. F., Torsoli A. Manometric study of the sphincter of Oddi in patients with and without common bile duct stones. Gut. 1984 Mar;25(3):275–278. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.3.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodds W. J. Instrumentation and methods for intraluminal esophageal manometry. Arch Intern Med. 1976 May;136(5):515–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullarton G. M., Allan A., Hilditch T., Murray W. R. Quantitative 99mTc-DISIDA scanning and endoscopic biliary manometry in sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gut. 1988 Oct;29(10):1397–1401. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.10.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fullarton G. M., Hilditch T., Campbell A., Murray W. R. Clinical and scintigraphic assessment of the role of endoscopic sphincterotomy in the treatment of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gut. 1990 Feb;31(2):231–235. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.2.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funch-Jensen P., Kruse A., Csendes A., Oster M. J., Amdrup E. Biliary manometry in patients with post-cholecystectomy syndrome. Acta Chir Scand. 1982;148(3):267–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Toouli J., Venu R. P. The efficacy of endoscopic sphincterotomy after cholecystectomy in patients with sphincter-of-Oddi dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 12;320(2):82–87. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901123200203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guelrud M., Mendoza S., Rossiter G., Ramirez L., Barkin J. Effect of nifedipine on sphincter of Oddi motor activity: studies in healthy volunteers and patients with biliary dyskinesia. Gastroenterology. 1988 Oct;95(4):1050–1055. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan W. J., Geenen J. E. Biliary dyskinesia. Endoscopy. 1988 Aug;20 (Suppl 1):179–183. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplita P. V., Triggle D. J. Actions of Ca2+ antagonists on the guinea-pig ileal myenteric plexus preparation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 1;32(1):65–68. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(83)90653-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshkinpour H., Mollot M., Eckerling G. B., Bookman L. Bile duct dyskinesia. Clinical and manometric study. Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):759–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody F. G., Becker J. M., Potts J. R. Transduodenal sphincteroplasty and transampullary septectomy for postcholecystectomy pain. Ann Surg. 1983 May;197(5):627–636. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198305000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior A., Harris S. R., Whorwell P. J. Reduction of colonic motility by intravenous nicardipine in irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 1987 Dec;28(12):1609–1612. doi: 10.1136/gut.28.12.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolny P., Anderberg B., Ihse I., Lindström E., Olaison G., Arvill A. Pancreatitis after sphincter of Oddi manometry. Gut. 1990 Jul;31(7):821–824. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.7.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolny P., Arlebäck A., Funch-Jensen P., Kruse A., Ravnsbaeck J., Järnerot G. Paradoxical response of sphincter of Oddi to intravenous injection of cholecystokinin or ceruletide. Manometric findings and results of treatment in biliary dyskinesia. Gut. 1986 Dec;27(12):1507–1511. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.12.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarles J. C. Hormonal control of sphincter of Oddi. Dig Dis Sci. 1986 Feb;31(2):208–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01300710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staritz M., Poralla T., Ewe K., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Effect of glyceryl trinitrate on the sphincter of Oddi motility and baseline pressure. Gut. 1985 Feb;26(2):194–197. doi: 10.1136/gut.26.2.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Ikeda S., Matsumoto S., Yoshimoto H., Nakayama F. Manometric diagnosis of sphincter of Oddi spasm as a cause of postcholecystectomy pain and the treatment by endoscopic sphincterotomy. Ann Surg. 1985 Dec;202(6):712–719. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198512000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Geenen J. E., Hogan W. J., Dodds W. J., Arndorfer R. C. Sphincter of Oddi motor activity: a comparison between patients with common bile duct stones and controls. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jan;82(1):111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Hogan W. J., Geenen J. E., Dodds W. J., Arndorfer R. C. Action of cholecystokinin-octapeptide on sphincter of Oddi basal pressure and phasic wave activity in humans. Surgery. 1982 Sep;92(3):497–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Roberts-Thomson I. C., Dent J., Lee J. Manometric disorders in patients with suspected sphincter of Oddi dysfunction. Gastroenterology. 1985 May;88(5 Pt 1):1243–1250. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(85)80086-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J., Roberts-Thomson I. C., Dent J., Lee J. Sphincter of Oddi motility disorders in patients with idiopathic recurrent pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 1985 Nov;72(11):859–863. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800721104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toouli J. What is sphincter of Oddi dysfunction? Gut. 1989 Jun;30(6):753–761. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.6.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



