Abstract
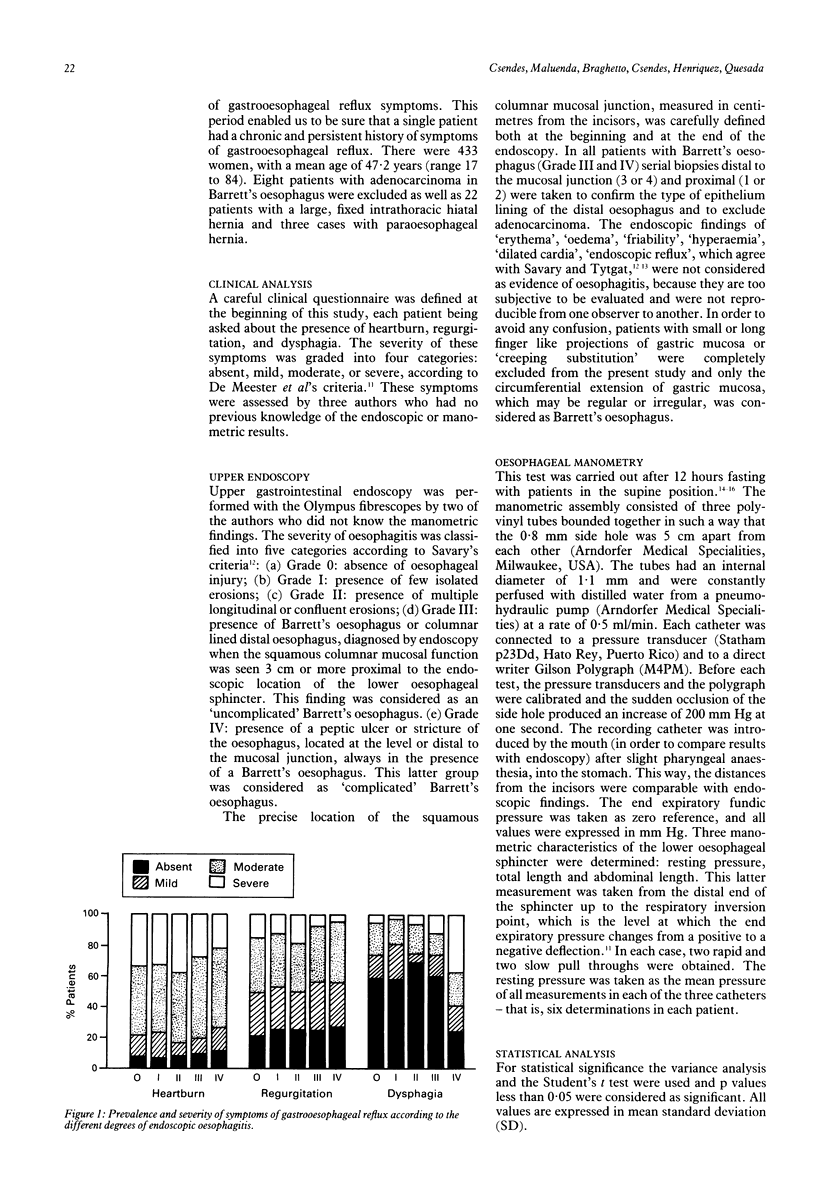
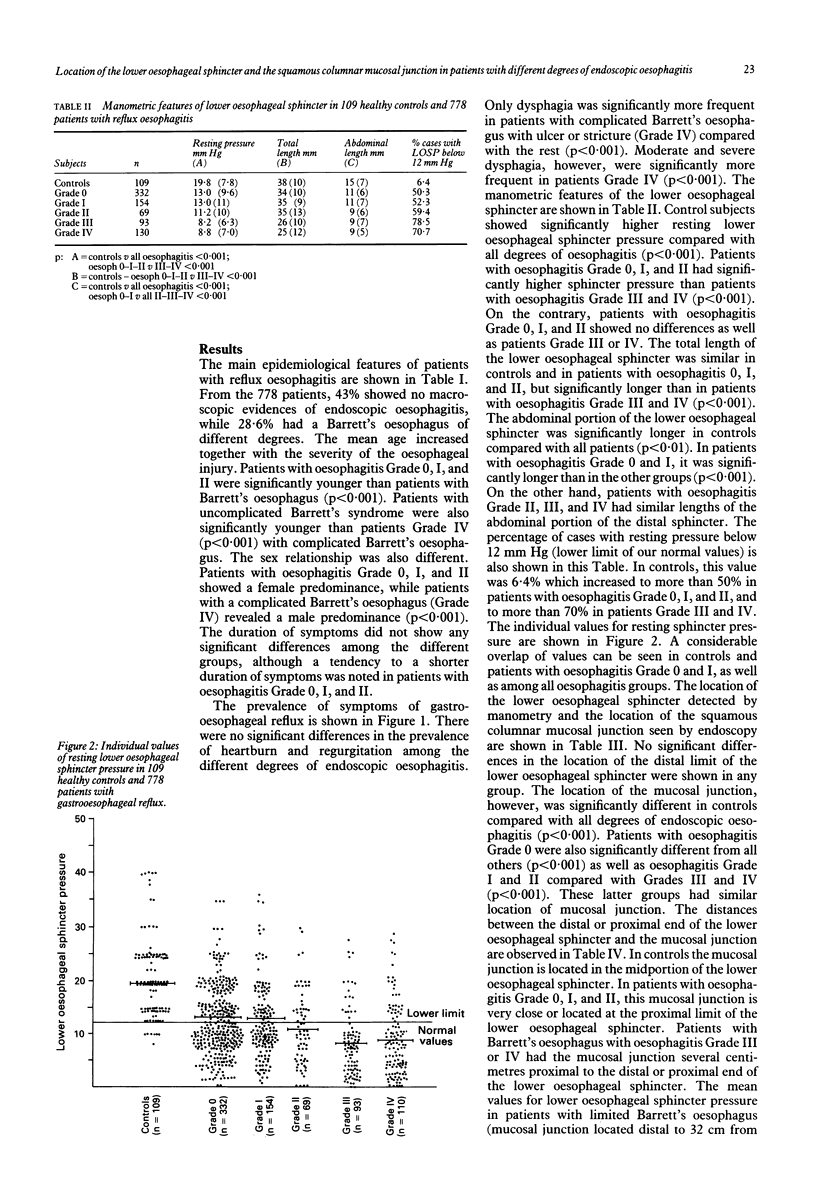
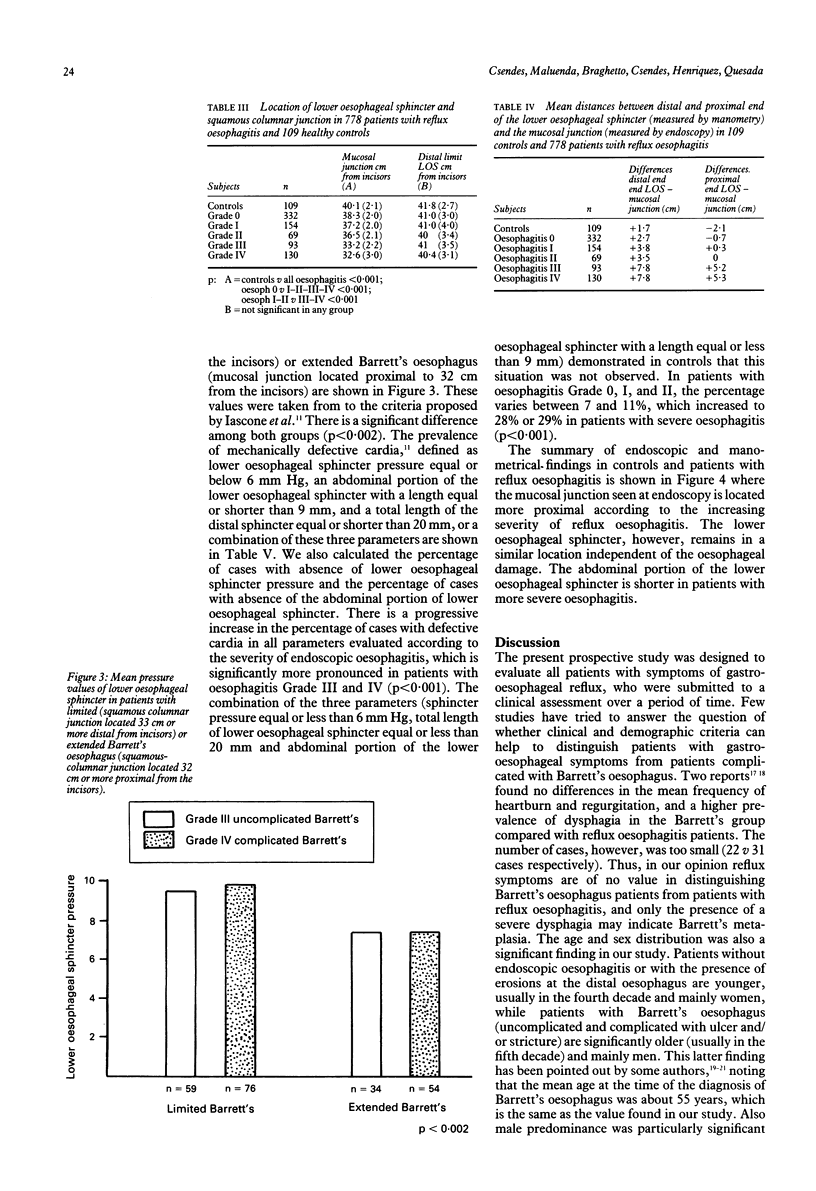
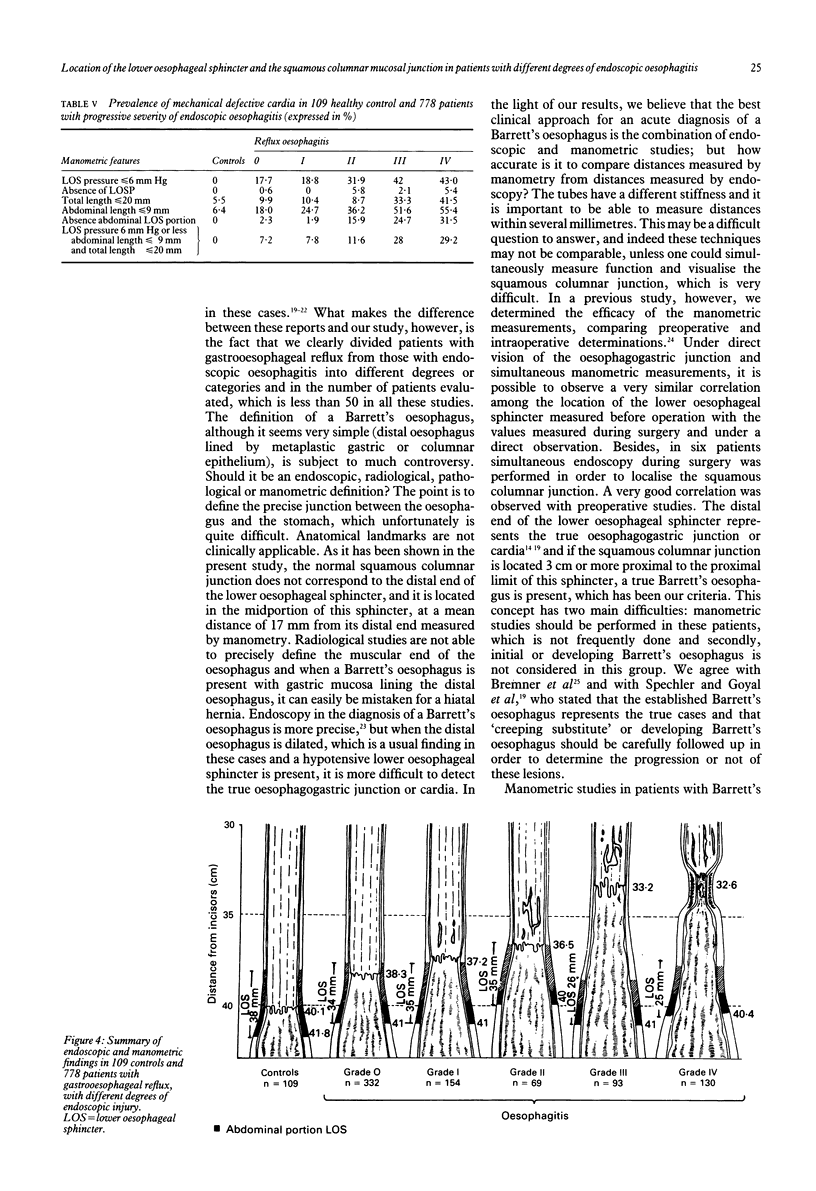
In this study the location of the lower oesophageal sphincter measured by manometry and the location of the squamous columnar junction measured by endoscopy were determined in 109 healthy controls and 778 patients with different degrees of endoscopic oesophagitis. No significant differences in the prevalence and severity of the heartburn and regurgitation were observed when different degrees of oesophagitis were compared but dysphagia was more common and severe in patients with complicated Barrett's oesophagus (p < 0.001). This group also showed a male predominance and older age compared with other groups. The total length of the oesophagus, measured by the location of the distal end of the lower oesophageal sphincter was similar in all patients; however, the location of the squamous columnar junction extended more proximally and was related to the increasing severity of endoscopic oesophagitis. The manometric defects at the cardia were more frequent in severe oesophagitis (p < 0.001). These results suggest that, during the course of oesophagitis, the squamous columnar junction is displaced proximally. This displacement is limited to the mucosa, however, and does not involve the muscular layer, because the lower oesophageal sphincter undergoes no dislocation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck I. T., Hernandez N. A. Transmural potential difference in patients with hiatus hernia and oesophageal ulcer. Gut. 1969 Jun;10(6):469–476. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.6.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biancani P., Goyal R. K., Phillips A., Spiro H. M. Mechanics of sphincter action. Studies on the lower esophageal sphincter. J Clin Invest. 1973 Dec;52(12):2973–2978. doi: 10.1172/JCI107494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bombeck C. T., Dillard D. H., Nyhus L. M. Muscular anatomy of the gastroesophageal junction and role of phrenoesophageal ligament; autopsy study of sphincter mechanism. Ann Surg. 1966 Oct;164(4):643–654. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196610000-00011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauthorne R. T., Vanhoutte J. J., Donner M. W., Hendrix T. R. Study of patients with lower esophageal ring by simultaneous cineradiography and manometry. Gastroenterology. 1965 Dec;49(6):632–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csendes A., Braghetto I., Henríquez A., Cortés C. Late results of a prospective randomised study comparing forceful dilatation and oesophagomyotomy in patients with achalasia. Gut. 1989 Mar;30(3):299–304. doi: 10.1136/gut.30.3.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csendes A., Miranda M., Espinoza M., Velasco N., Henríquez A. Perimeter and location of the muscular gastroesophageal junction or 'cardia' in control subjects and in patients with reflux esophagitis or achalasia. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1981;16(7):951–956. doi: 10.3109/00365528109181829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csendes A., Oster M., Møller J., Brandsborg O., Brandsborg M., Amdrup E. The effect of extrinsic denervation of the lower part of the esophagus on resting and cholinergic stimulated gastroesophageal sphincter in man. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 Mar;148(3):375–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Attwood S. E., Smyrk T. C., Therkildsen D. H., Hinder R. A. Surgical therapy in Barrett's esophagus. Ann Surg. 1990 Oct;212(4):528–542. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199010000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland G. W., Melcher D. H., Berridge F. R., Gresham G. A. Debatable points in the anatomy of the lower oesophagus. Thorax. 1966 Nov;21(6):487–498. doi: 10.1136/thx.21.6.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillen P., Keeling P., Byrne P. J., Hennessy T. P. Barrett's oesophagus: pH profile. Br J Surg. 1987 Sep;74(9):774–776. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iascone C., DeMeester T. R., Little A. G., Skinner D. B. Barrett's esophagus. Functional assessment, proposed pathogenesis, and surgical therapy. Arch Surg. 1983 May;118(5):543–549. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1983.01390050027005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebermann-Meffert D., Allgöwer M., Schmid P., Blum A. L. Muscular equivalent of the lower esophageal sphincter. Gastroenterology. 1979 Jan;76(1):31–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann N. S., Tsai M. F., Nair P. K. Barrett's esophagus in patients with symptomatic reflux esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 1989 Dec;84(12):1494–1496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meckeler K. J., Ingelfinger F. J. Correlation of electric surface potentials, intraluminal pressures, and nature of tissue in the gastroesophageal junction of man. Gastroenterology. 1967 Jun;52(6):966–971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messian R. A., Hermos J. A., Robbins A. H., Friedlander D. M., Schimmel E. M. Barrett's esophagus. Clinical review of 26 cases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1978 Apr;69(4):458–466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr W. C., Lackey C., Robinson M. G., Johnson L. F., Welsh J. D. Esophageal acid clearance during sleep in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 1988 Jun;33(6):654–659. doi: 10.1007/BF01540426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott D. J., Wu W. C., Gelfand D. W. Reflux esophagitis revisited: prospective analysis of radiologic accuracy. Gastrointest Radiol. 1981 Jan 15;6(1):1–7. doi: 10.1007/BF01890213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafoth R. J., Freeland G., Pailey P., Anderson D. S., Fornes M. F. Comparison of endoscopy and manometry in assessment of lower esophageal sphincter pressure. Gastrointest Endosc. 1978 May;24(4):152–153. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(78)73491-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo J. A., Jr, Gahagan T. The narrow lower esophageal ring: pathogenesis and physiology. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Apr;11(4):257–265. doi: 10.1007/BF02233972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg J. C., Budev H., Edwards R. C., Singal S., Steiger Z., Sundareson A. S. Analysis of adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus utilizing a staging system. Cancer. 1985 Mar 15;55(6):1353–1360. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850315)55:6<1353::aid-cncr2820550632>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarr M. G., Hamilton S. R., Marrone G. C., Cameron J. L. Barrett's esophagus: its prevalence and association with adenocarcinoma in patients with symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Surg. 1985 Jan;149(1):187–193. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(85)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. B., Walther B. C., Riddell R. H., Schmidt H., Iascone C., DeMeester T. R. Barrett's esophagus. Comparison of benign and malignant cases. Ann Surg. 1983 Oct;198(4):554–565. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198310000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Goyal R. K. Barrett's esophagus. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 7;315(6):362–371. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608073150605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spechler S. J., Robbins A. H., Rubins H. B., Vincent M. E., Heeren T., Doos W. G., Colton T., Schimmel E. M. Adenocarcinoma and Barrett's esophagus. An overrated risk? Gastroenterology. 1984 Oct;87(4):927–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strawn T., Knutson C. O., Max M. H. The role of endoscopy in patients with suspected esophageal reflux. Am Surg. 1980 Feb;46(2):95–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winters C., Jr, Spurling T. J., Chobanian S. J., Curtis D. J., Esposito R. L., Hacker J. F., 3rd, Johnson D. A., Cruess D. F., Cotelingam J. D., Gurney M. S. Barrett's esophagus. A prevalent, occult complication of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Jan;92(1):118–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


