Abstract
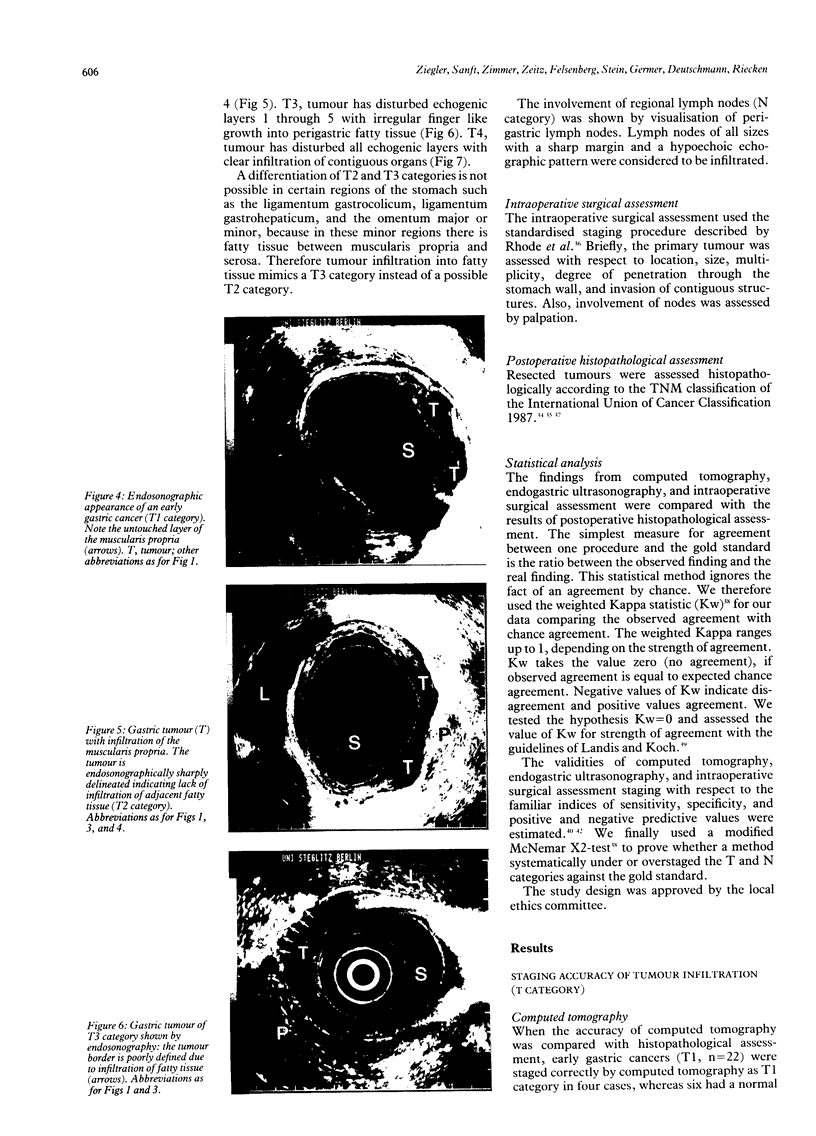
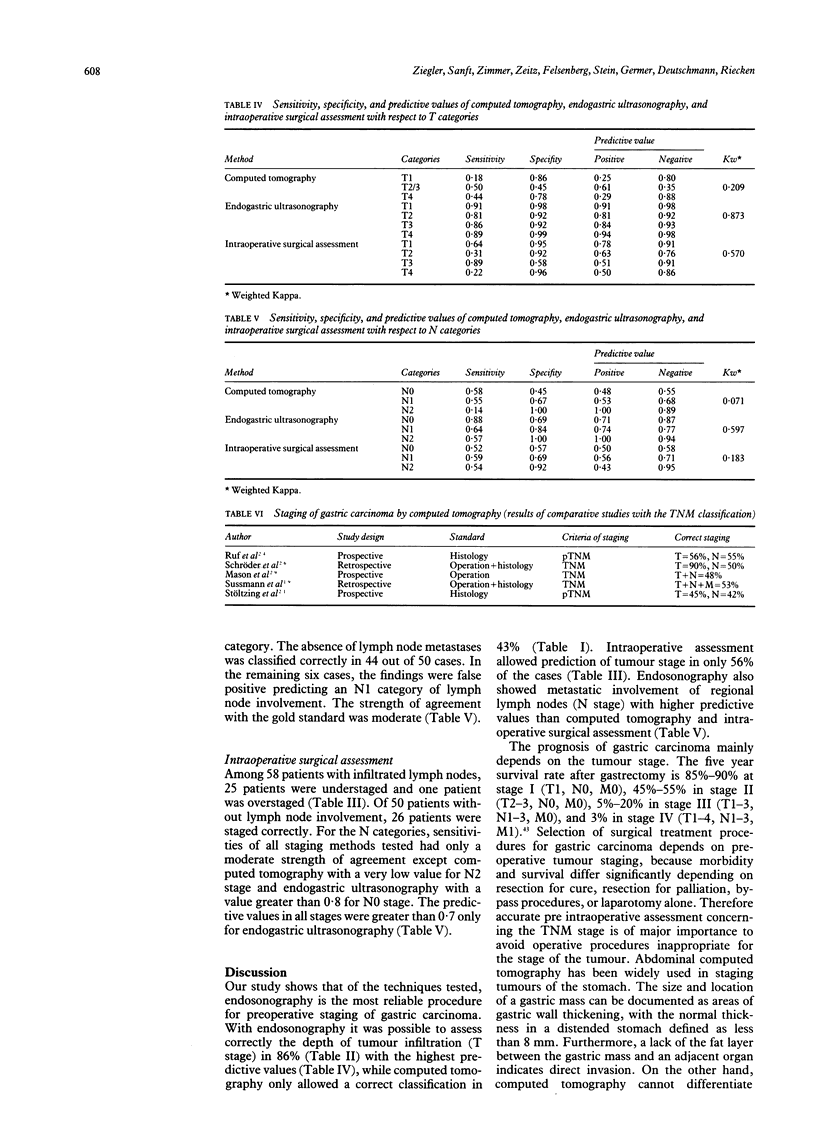
From 1986 to 1990 a prospective comparative study was undertaken to compare the relative accuracy of computed tomography, endogastric ultrasonography, and intraoperative surgical assessment in evaluating the depth of invasion (T category) and involvement of lymph nodes (N category) of patients with gastric carcinoma. One hundred and eight consecutive patients, who were treated by total gastrectomy and previously evaluated with computed tomography, endogastric ultrasonography, and intraoperative surgical assessment, entered the study. Results (T and N category) were compared with those of histopathological staging (pT and pN category). T categories were correctly staged in 43% of cases with computed tomography, 86% with endogastric ultrasonography, and 56% with intraoperative surgical assessment. Computed tomography scanning correctly staged 51% of all N1 and N2 lymph nodes compared with 74% for endogastric ultrasonography and 54% for intraoperative surgical assessment. In general, computed tomography was more accurate for advanced stages of cancer and showed a tendency to overstage the T category and understage N category of gastric tumours. By contrast, endogastric ultrasonography was equally accurate for all T categories and showed an understaging for N categories. Intraoperative surgical assessment overstaged early T stages, understaged T4 tumours, and was equally accurate for all grades of N categories. Computed tomography scanning and intraoperative surgical assessment of T and N categories were of little value in staging of gastric carcinoma. Endogastric ultrasonography is more accurate than computed tomography scanning and intraoperative surgical assessment. Therefore endogastric ultrasonography should be introduced in the preoperative assessment of patients with gastric carcinoma.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cook A. O., Levine B. A., Sirinek K. R., Gaskill H. V., 3rd Evaluation of gastric adenocarcinoma. Abdominal computed tomography does not replace celiotomy. Arch Surg. 1986 May;121(5):603–606. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1986.01400050121016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehn T. C., Reznek R. H., Nockler I. B., White F. E. The pre-operative assessment of advanced gastric cancer by computed tomography. Br J Surg. 1984 Jun;71(6):413–417. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efsen F., Fischerman K. Angiography in gastric tumours. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1974 Mar;15(2):193–197. doi: 10.1177/028418517401500210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeny P. C., Marks W. M. Adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction: barium and CT examination. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1982 Jun;138(6):1077–1084. doi: 10.2214/ajr.138.6.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosser G., Wimmer B., Ruf G. Diagnostischer Wert der Computertomographie beim Magenkarzinom. Rofo. 1985 May;142(5):514–519. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grote R., Döhring W., Meyer H. J., Schmied W., Löhlein D. Computertomographie bei malignen Tumoren des Magens. Rofo. 1984 Dec;141(6):654–660. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1053209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthaner D. F., Miller D. C., Silverman J. F., Stinson E. B., Wexler L. Fate of the false lumen following surgical repair of aortic dissections: an angiographic study. Radiology. 1979 Oct;133(1):1–8. doi: 10.1148/133.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther B. Magencarcinom--Spätprognose nach radikalen Eingriffen. Langenbecks Arch Chir. 1987;372:593–597. doi: 10.1007/BF01297888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inberg M. V., Heinonen R., Rantakokko V., Viikari S. J. Surgical treatment of gastric carcinoma: a regional study of 2,590 patients over a 27-year period. Arch Surg. 1975 Jun;110(6):703–707. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1975.01360120021003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinhaus U., Militianu D. Computed tomography in the preoperative evaluation of gastric carcinoma. Gastrointest Radiol. 1988;13(2):97–101. doi: 10.1007/BF01889034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komaki S., Toyoshima S. CT's capability in detecting advanced gastric cancer. Gastrointest Radiol. 1983;8(4):307–313. doi: 10.1007/BF01948140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. S., Feinstein A. R. Clinical biostatistics. LIV. The biostatistics of concordance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Jan;29(1):111–123. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAUREN P. THE TWO HISTOLOGICAL MAIN TYPES OF GASTRIC CARCINOMA: DIFFUSE AND SO-CALLED INTESTINAL-TYPE CARCINOMA. AN ATTEMPT AT A HISTO-CLINICAL CLASSIFICATION. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;64:31–49. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.64.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis J. R., Koch G. G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics. 1977 Mar;33(1):159–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundh G., Burn J. I., Kolig G., Richard C. A., Thomson J. W., van Elk P. J., Oszacki J. A co-operative international study of gastric cancer (under the auspices of the International Federation of Surgical Colleges). Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1974 May;54(5):219–228. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden M. V., Price S. K., Learmonth G. M., Dent D. M. Surgical staging of gastric carcinoma: sources and consequences of error. Br J Surg. 1987 Feb;74(2):119–121. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800740217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason R. C., Rankin S., Taylor P. R., Rowe P. H., Linsell J., Owen W. J., Jourdan M. H., McColl I. Computerised tomographic scanning and staging of gastric carcinoma. Lancet. 1987 Jan 10;1(8524):108–108. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91950-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss A. A., Schnyder P., Marks W., Margulis A. R. Gastric adenocarcinoma: a comparison of the accuracy and economics of staging by computed tomography and surgery. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jan;80(1):45–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picus D., Balfe D. M., Koehler R. E., Roper C. L., Owen J. W. Computed tomography in the staging of esophageal carcinoma. Radiology. 1983 Feb;146(2):433–438. doi: 10.1148/radiology.146.2.6849089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint L. E., Glazer G. M., Orringer M. B., Gross B. H. Esophageal carcinoma: CT findings. Radiology. 1985 Apr;155(1):171–175. doi: 10.1148/radiology.155.1.3975398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder R., Triller J., Roder R. Wert der Computertomographie beim fortgeschrittenen Magenkarzinom. Ist die Probelaparotomie vermeidbar? Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1986 Jul 19;116(29):956–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott H. W., Jr, Adkins R. B., Jr, Sawyers J. L. Results of an aggressive surgical approach to gastric carcinoma during a twenty-three-year period. Surgery. 1985 Jan;97(1):55–59. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg E. Cancer statistics, 1980. CA Cancer J Clin. 1980 Jan-Feb;30(1):23–38. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.30.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipponen P., Järvi O., Kekki M., Siurala M. Decreased incidences of intestinal and diffuse types of gastric carcinoma in Finland during a 20-year period. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1987 Sep;22(7):865–871. doi: 10.3109/00365528708991927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stöltzing H., Thon K., Pohl C., Mariss G., Röher H. D. Stellenwert des Computertomogramms für das präoperative Staging beim Magenkarzinom. Z Gastroenterol. 1989 Oct;27(10):601–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman S. K., Halvorsen R. A., Jr, Illescas F. F., Cohan R. H., Saeed M., Silverman P. M., Thompson W. M., Meyers W. C. Gastric adenocarcinoma: CT versus surgical staging. Radiology. 1988 May;167(2):335–340. doi: 10.1148/radiology.167.2.3357941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tio T. L., Coene P. P., Schouwink M. H., Tytgat G. N. Esophagogastric carcinoma: preoperative TNM classification with endosonography. Radiology. 1989 Nov;173(2):411–417. doi: 10.1148/radiology.173.2.2678255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallgren S., Hedenbro J., Götberg S., Walther B. Preoperative computed tomography for evaluation of tumour growth in patients with gastric cancer. Acta Chir Scand. 1985;151(6):571–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls W. J. The evaluation of malignant gastric neoplasms by ultrasonic B-scanning. Radiology. 1976 Jan;118(1):159–163. doi: 10.1148/118.1.159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler K., Sanft C., Zeitz M., Friedrich M., Stein H., Häring R., Riecken E. O. Evaluation of endosonography in TN staging of oesophageal cancer. Gut. 1991 Jan;32(1):16–20. doi: 10.1136/gut.32.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler K., Sanft C., Zeitz M., Riecken E. O. Preoperative staging of gastrointestinal tumors by endosonography. Surg Endosc. 1990;4(3):154–160. doi: 10.1007/BF02336595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]